By platelets, modern medicine means colorless spherical cell bodies ranging in size from two to four micrometers with an absent nucleus, which constantly circulate in the blood.
The five main forms of platelets in the blood are divided into young, mature, old, irritated and degenerative objects, the vast majority of which are classified as mature cells (up to 95 percent): their lifespan is about ten days. They are considered the basis of the platelet system, which closes damaged vessels like a “plug”. The second function of platelets in the blood is to catalyze plasma coagulation.
As recent studies show, the above structures also play a leading role in the regeneration of tissue structures of the body, acting as a stimulator of cell growth and division.
What does it mean
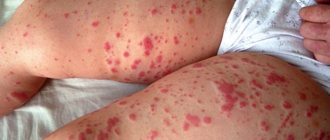
Platelets are called red blood cells, the main task of which is to ensure normal blood clotting. When the number of platelets in the blood drops significantly, the cells are unable to perform their function properly. This pathological condition is called thrombocytopenia. Its symptoms: an increase in the time required to stop bleeding, regular releases of blood from the mucous membranes of the nose and mouth, and the appearance of bruises of unknown origin on the body.
Throughout the day, the level of platelets in the blood may fluctuate slightly, deviating from the norm by 5-10 percent. In this case, there is no talk of any violations. In addition, a slight decrease in platelets is considered normal during menstruation and pregnancy. These symptoms are temporary and do not require any treatment.
Appearance of records
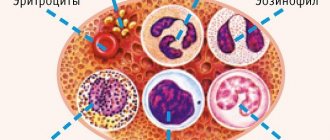
Under a microscope, you can examine the structure of platelets. They look like disks, the diameter of which ranges from 2 to 5 microns. The volume of each of them is about 5-10 µm3.
In terms of their structure, platelets are a complex complex. It is represented by a system of microtubules, membranes, organelles and microfilaments. Modern technologies have made it possible to cut a flattened plate into two parts and select several zones in it. This is how they were able to determine the structural features of platelets. Each plate consists of several layers: peripheral zone, sol-gel, intracellular organelles. Each of them has its own functions and purpose.
Causes
Various diseases and pathological conditions can contribute to a decrease in platelets. These include:
- blood diseases: leukemia, anemia, etc.;
- the use of certain medications: antibiotics, diuretics, analgesics, cytostatics, antihistamines and psychotropic drugs;
- alcohol intoxication;
- hereditary diseases caused by decreased platelet production;
- period of menstruation, childbearing;
- diseases of infectious origin;
- exposure to heavy metals;
- increased platelet consumption;
- bone marrow damage.
Thus, a low level of platelets in the blood can be an independent disease or a symptom indicating the presence of serious problems in the body. To correctly diagnose and determine the cause of thrombocytopenia, it is necessary to carefully examine the patient. A competent diagnosis will allow you to choose the right course of treatment and eliminate all possible health problems.
Intracellular organelles
The third layer contains glycogen granules, mitochondria, α-granules, and dense bodies. This is the so-called organelle zone.
Dense bodies contain ATP, ADP, serotonin, calcium, adrenaline and norepinephrine. All of them are necessary for platelets to work. The structure and functions of these cells ensure adhesion and healing of wounds. Thus, ADP is produced when platelets attach to the walls of blood vessels, and it is also responsible for ensuring that these plates from the bloodstream continue to attach to those that have already stuck. Calcium regulates the intensity of adhesion. Serotonin is produced by the platelet when it releases granules. It is he who ensures the narrowing of their lumen at the site of rupture of blood vessels.
Alpha granules located in the organelle zone promote the formation of platelet aggregates. They are responsible for stimulating the growth of smooth muscles, restoring the walls of blood vessels and smooth muscles.
How to lift
If your platelet level decreases, you need to evaluate your condition. In certain cases, platelet levels drop to a critical level, which requires immediate treatment - on an outpatient or inpatient basis. However, most often the violation is so minor that it can be dealt with at home.
To raise your platelet levels on your own, use the following recommendations:
- Make a proper diet. Include greens, citrus fruits, kiwi, tomatoes and berries. Avoid undiluted coffee, alcohol, excessively fatty and high-calorie foods, and refined sugar.
- Include foods rich in omega-3 acids in your diet. These products include: fatty fish, eggs, flaxseed oil. A worthy alternative could be fish oil capsules.
- Follow a daily routine. Try to get up and go to bed on time, sleep at least 8 hours a day. Do not forget about vacation, which gives the body the opportunity to “reboot”.
- Drink liquid at room temperature. Drinking cold drinks disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and contributes to poorer absorption of nutrients.
- Enrich your diet with minerals and vitamins. You can get them from healthy foods or from special vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Play sports. In physical activity, the emphasis should be placed not on strength training, but on “cardio”. Cardio exercises have the most positive effect on the body: they normalize blood circulation and strengthen the immune system.
Outer layer
The peripheral zone consists of a three-layer membrane. The structure of platelets is such that on its outer side there is a layer that contains plasma factors responsible for blood clotting, special receptors and enzymes. Its thickness does not exceed 50 nm. The receptors of this layer of platelets are responsible for the activation of these cells and their ability to adhesion (attachment to the subendothelium) and aggregation (the ability to connect with each other).
The membrane also contains a special phospholipid factor 3 or the so-called matrix. This part is responsible for the formation of active coagulation complexes together with plasma factors responsible for blood clotting.
In addition, it contains arachidonic acid. Its important component is phospholipase A. It is this that forms the indicated acid necessary for the synthesis of prostaglandins. They, in turn, are designed to form thromboxane A2, which is necessary for powerful platelet aggregation.
The child has
A low level of platelets in a child's blood can be a sign of serious pathologies. Therefore, when the first symptoms of thrombocytopenia are detected, the baby should be shown to a pediatrician as soon as possible.
The following symptoms may indicate the presence of thrombocytopenia in a child: vomiting interspersed with blood, black feces, bruises, pink or red urine, subcutaneous hemorrhages, bleeding disorders, hemorrhages in the retina, headaches, rash.
Treatment of the pathology depends on what caused it. If the low platelet count is a consequence of another disease, then medications are used that target the underlying cause of thrombocytopenia.
In the initial stages of the disease, treatment is possible at home, without placing the child in a hospital. In this case, it is necessary to provide the baby with bed rest and create the right diet for him. Food should be rich in iron and hemoglobin, vitamins, and non-heat-treated fruits and vegetables.
In some cases, treatment is supplemented by the administration of immunoglobulins, the use of hormonal agents, and blood transfusions from a donor. In severe cases, when conservative treatments do not work, surgery is performed to remove the spleen.
Main functions
In order to understand why blood platelets are needed in the body, it is not enough to understand the structural features of human platelets. They are intended primarily to form a primary plug, which should close the damaged vessel. In addition, platelets provide their surface to accelerate plasma coagulation reactions.
In addition, it was found that they are needed for the regeneration and healing of various damaged tissues. Platelets produce growth factors designed to stimulate the development and division of any damaged cells.
It is noteworthy that they can quickly and irreversibly transition to a new state. The stimulus for their activation can be any change in the environment, including simple mechanical stress.
In an adult
The norm of platelets for the male half of the population is from 180 to 320*10^9 units/l. For women, the norm ranges from 150-380*10^9 units/l. In the case of a slight decrease in platelets (up to 10 percent), no action can be taken to increase their level. However, if symptoms of thrombocytopenia are observed, it is necessary to urgently visit a doctor for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
If during diagnosis it turns out that thrombocytopenia is an independent disease, the following methods are used for its treatment: transfusion of a donor mass of platelets, treatment with glucocorticosteroids, anti-Rhesus D serum, immunoglobulin injections into a vein.
If a pregnant woman requires treatment, similar methods are used to increase platelet levels. The only thing is that hormonal therapy and blood transfusions are used in the most severe cases. The entire course of treatment takes place under the close supervision of the attending physician.
In the early stages, thrombocytopenia can be successfully treated. The main thing is to notice the symptoms of the disease in time and seek specialist help.
14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Leave a comment or question
A diagnosis of thrombocytopenia was made based on a complete blood count. No platelet aggregation was detected. Platelets (PLT)96*10^9|l what is aggregation and how to treat thrombopenia and how dangerous it is? A year ago I had surgery to remove my gallbladder.
Thrombocytopenia is dangerous because the body's hemostasis process is disrupted. Thorough research is a must.
Platelet pathology is the cause of bleeding in almost 80% of cases. There are acute and chronic thrombocytopenia. the second is recorded when the decrease in platelets continues for more than six months. But the cause of each case of thrombocytopenia must be clarified.
Algorithm for diagnosing thrombocytopenia:
1. Make sure the analysis data is reliable. The study should definitely be repeated. Be sure to conduct a blood smear examination.
2. Exclude or identify concomitant pathology. You should make the most of your medical history, with special emphasis on heredity, recent infections, taking medications, and identifying bad habits, especially alcohol abuse.
3. The results of the examination provide a lot of information, allowing one to identify the pathology of internal organs and make a diagnosis of the underlying disease of the body.
I have had severe pain in my lower abdomen for two days. I gave blood and urine tests. The surgeon looked at the test results and said that the pain was due to salt leakage. I didn’t add anything more to the tests, although I was alarmed that the platelet count was 96. I’m 66 years old. Please tell me if this could happen and why. Thank you.
The fact is that the task of a specialized specialist is to confirm or exclude pathology. In particular, the surgeon looked and said that the surgeon had no indications for treatment. Pain in the lower abdomen is probably renal colic caused by crystalluria. You should be treated by a urologist. This is a more urgent condition. The platelet count is low, but not dangerous.
There are many causes of thrombocytopenia; one should act by exclusion. For example, some drugs can cause low platelets, some infections, or some types of anemia. The range is quite wide.
I recommend contacting a urologist to treat an attack of urolithiasis, and then looking for the causes of other diseases.
Hello. Please tell me, is it possible to get a free MRI of the abdominal cavity if you have low platelets (woman 61g, platelets 66, for 2 years)?
It is advisable that the patient come to the MRI with a referral from a doctor (any specialist can give this referral). The clinician, having examined the patient, directs him to one or another examination. And in this case, the doctors at the diagnostic center know better what exactly needs to be examined. Instrumental methods differ. If a patient comes from a specialist with a request to examine a specific area with a specific diagnosis, then this particular area will be thoroughly checked.
There are a number of relative and absolute contraindications for MRI. But low platelet levels are not on their list.
Usually, MRI procedures are carried out for a fee and are expensive. But, there are a number of categories of citizens (not many, but they exist) who have the right to a free procedure. It is better to find out about this at the diagnostic center.
In the general blood test, my platelets are 123, how should this be understood?
I believe that the platelet concentration is 123 thousand/µl. This is slightly below the normative values for a healthy person.
The number of platelets can be reduced for many reasons; they can be conditionally divided into 2 groups: congenital thrombocytopenia, acquired thrombocytopenia (including drug-induced thrombocytopenia).
Deviations should always be analyzed in conjunction with other studies. In particular, with indicators of red blood and the number of leukocytes. It will also be useful to evaluate the performance of the coagulation system.
A fairly wide range of drugs can cause a decrease in platelet concentration with a number of side effects, for example, aspirin.
Hello. My son was diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B, liver fibrosis stage 2, and was prescribed a diet of 5 treatments. Additionally, they donated blood for bilirubin - the therapist said that the blood was within normal limits, but recommended going to an infection control doctor, she sent me for a general blood test, the blood showed that there were 113 platelets, and they also did not prescribe any treatment...
A decrease in platelet levels in patients with chronic forms of hepatitis is a common symptom. At the same time, thrombocytopenia can reach a level of 85*10^9 units/l. At the same time, treatment is carried out during an exacerbation and only in a hospital. Bed rest is recommended. Diet No. 5 is prescribed. Among medications, a course of treatment is practiced: vitamin therapy (groups B, C, nicotinic, folic acid). To restore the structure of the liver, the following are used: Anabolic and corticosteroid hormones, immunostimulants, hepatoprotectors. When the patient’s general condition is normalized, the platelet level returns to relative normal (adequate for the disease state).
Hello, my platelet count is 157 and my coagulability is 6;10, how serious is this?
A decrease in platelet levels, disruption of normal hemostasis, there is a risk of bleeding, both internal and external. A decrease in the number of platelets (thrombocytopenia) can occur if there is a lack of cell production in the bone marrow, increased consumption or destruction of platelets (autoimmune processes).
A slight physiological decrease in platelet levels is observed in women during menstruation, in healthy pregnant women, and also, in case of allergies, when taking certain medications. Clinical signs of decreased platelet count are observed when the platelet count decreases below 50 x 103 cells/µl.
It is necessary to determine the cause of thrombocytopenia. This is done by therapists and hematologists.
Hello ! My husband has low platelets after several blood tests
They prescribed a spinal cord puncture, but can platelets drop after pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and is a spinal cord puncture necessary?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is considered conditionally pathogenic, but can cause disease if the patient has a state of immune deficiency. The pathogen is very stable in the external environment and is highly resistant to antibiotics. A decrease in platelets is characteristic of the course of the infection. The disease occurs in stages, one of which involves the entry of bacteria into the systemic bloodstream with subsequent spread to distant organs and tissues. There is a risk of damage to the central nervous system, so it makes sense to examine the cerebrospinal fluid.
Hello! Could frequent headaches, constantly freezing hands in winter, or bruises on the body with minor injuries be a consequence of a low platelet count (up to 120-140 per 10^9)?
Maybe. But the question is not entirely correct.
The symptoms you describe are not specific signs of thrombocytopenia, with the exception of bruises. But there are nuances there too.
If we consider them separately, then headache and freezing extremities are the most common signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia or other diseases not related to thrombocytopenia.
As for hematomas, the reason is a violation of the normal tone of blood vessels, their structure, durability and permeability. There are also a lot of mechanisms here. These include hormonal levels, neuro-endocrine balance, blood pressure, metabolic characteristics, intoxication, diseases of the vascular system and blood, congenital defects of the vascular wall.
A reduced level of platelets is a group of diseases whose main mechanism is both increased cell destruction and insufficient cell synthesis.
Thrombocytopenia is divided into hereditary and acquired forms. Acquired forms are differentiated according to the mechanism of destruction of the process of cell formation. These may be: mechanical damage to platelets, replacement of bone marrow with tumor tissue, inhibition of bone marrow cell division, increased platelet consumption, mutations, deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid.
For diagnosis, blood tests, ultrasound of the liver and spleen are used, and if blood diseases are suspected, bone marrow analysis is used. The doctor who deals with such problems is a hematologist.
Materials: https://medickon.com/analizyi/krov/ponizhenyi-trombotsityi-v-krovi-chto-eto-znachit-kak-podnyat.html
+ — Read more ≫ Click to collapse
Our blood consists of leukocytes, red blood cells and platelets. Each blood cell is responsible for various processes occurring in the body. We have known since childhood that if we cut ourselves, blood will flow, but we understand that this is not so scary and the bleeding will soon stop. For such a useful function of the body, we should be grateful to platelets, which take care of blood clotting. Oval-shaped blood platelets called platelets, about two micrometers in size, are formed in bone marrow cells and support the functioning of the human circulatory system. Platelets belong to blood cells, but it is a stretch to call them a full-fledged cell, due to the absence of a cell nucleus. That is why the word “records” is so often used to refer to them.
- maintain blood in a liquid state;
- protect the walls of blood vessels from damage;
- prevent the formation of blood clots, which can be fatal;
- promote rapid healing of wounds;
- nourishes the vessels of the circulatory system, strengthening them.
The doctor explains what platelets are needed for
The platelet count is examined and measured in thousands per microliter of blood.
General information about platelet counts in a child’s blood is given in the table:
General information about platelet levels in the blood of adult men and women differs from those of a child and is shown in the table:
Visual demonstration of platelet activation
When the number of platelets in the blood is increased, we can talk about the following changes in the body:
- tuberculosis, leukemia, cancer of the liver and kidneys (both in adults and children);
- erythrocytosis, arthritis, enteritis;
- acute poisoning and infections;
- large blood loss, anemia;
- severe stress;
- problems with bone marrow stem cells.
If the platelet count is very small (below 150 thousand units/μl), then we can talk about a disease such as thrombocytopenia. If there is a decrease in the number of platelets below normal by several times (50 thousand units/μl), then we can talk about the clinical form of the disease.
Types of thrombocytopenia
- Congenital or hereditary thrombocytopenia;
- Acquired thrombocytopenia.
There are a great many cases and diseases when thrombocytopenia (indicators below normal) occurs without a hereditary factor:
- immune and autoimmune (occur when damaged by medications or infection, which are haptens);
- symptomatic (occurs with various leukemia, cancer, various infections, anemia, platelet damage, for example, during heart valve surgery or hemangioma).
Causes
Platelet levels drop lower due to the following reasons:
- insufficient formation of platelets in the bone marrow;
- extensive hemorrhage or bleeding;
- consumption thrombocytopenia (when the bone marrow does not compensate for the number of destroyed platelets);
- thrombocytopenia caused by a violation of the distribution of platelets, and as a result, an enlargement of the spleen, since about 90% of all platelets in the body are collected in it;
- due to lack of iron in the body;
- Pregnancy can also be a cause, since the rate of hematopoiesis decreases due to the new blood flow of the child;
- Newborns have congenital thrombocytopenia (Wiscott-Aldrich syndrome, Bernard-Soulier syndrome, Fanconi syndrome).
The specialist talks about the level being below normal
All symptoms of low platelet count in the blood are associated with various types of bleeding, which are very difficult to stop. It often happens that thrombocytopenia is a secondary manifestation of a more serious disease, which may have its own symptoms.
Clinical symptoms of low platelet count in the blood:
- bleeding gums;
- bleeding from the sinuses;
- bleeding in the intestines;
- anemia;
- skin hemorrhages;
- mucous hemorrhages;
- poor blood clotting (when the wound bleeds for a long time);
- skin hemorrhages in a child.
Consequences of prolonged thrombocytopenia
The most dangerous consequences of throbocytopenia:
- Retinal hemorrhage. When the eye vessels burst and fill with blood. It is very important to see a doctor right away to preserve your vision.
- Brain hemorrhage. Occurs when a head injury, blow or deep cut occurs. The disease is very dangerous, with a high risk (25% of cases) of death.
- Posthemorrhagic anemia. Occurs due to bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. This disease is difficult to detect; symptoms may include pale skin and unusual fatigue. If measures are not taken in time, death is possible.
Risk group
Risk groups include:
- school-age children, whose morbidity is more common in winter and spring;
- children whose parents suffer from thrombocytopenia;
- patients who have had cancer.
Diagnosis of the disease is based on the clinical picture and laboratory tests.
A complete examination should be carried out:
- conduct a general blood test to detect deviations from the norm of any indicators (especially indicators below normal);
- bone marrow biopsy (since it is in it that platelets are formed, and if it fails, then there is a high probability of thrombocytopenia as a secondary disease);
- Ultrasound examination of the spleen
Without consulting a doctor, you can increase your platelet level on your own, if it deviates slightly from the norm, follow the recommendations:
- fill your daily diet with healthy and vitamin-rich foods;
- reduce your physical activity so as not to increase the speed of blood flow (with a fast flow, platelets simply will not have time to fill the blood);
- Immune thrombocytopenia is treated with corticosteroids, on the basis of which medications are created. If the situation is critical, only surgery to remove the spleen, in which platelets accumulate, will help;
- if no serious illness is detected, then treatment is carried out by taking medications with vitamin B12;
- if the blood is too thick, which indicates a low level of platelets in the blood, medications that thin the blood are prescribed;
- If the platelet level drops to a critical level, a blood transfusion is prescribed.
Nutrition
There is no special diet for patients with thrombocytopenia, but the following recommendations should be followed:
- your diet should contain only healthy foods;
- foods should be rich in iron;
- It is forbidden to take excessively high-calorie foods containing cholesterol, which contributes to the formation of blood clots;
- Try to eat soft or crushed foods, avoid fish bones, to prevent damage to the walls of the esophagus or oral mucosa;
- eliminate possible allergens from your diet;
- Eat foods rich in folic acid and vitamin K to improve blood clotting.
The influence of a healthy lifestyle on the course of the disease
- Patients with thrombocytopenia should avoid alcoholic beverages. Since alcohol accelerates the flow of blood through the vessels of the body, and contributes to a decrease in platelets in the blood.
- Proper nutrition (no fried or fatty foods), as such foods increase cholesterol levels and increase the risk of blood clots.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment is prescribed only for moderate thrombocytopenia, when hospitalization can be avoided.
Glycoproteins
The structure of platelets is not limited by the presence of an outer membrane. Its lipid bilayer contains glycoproteins. They are designed to bind platelets.
Thus, glycoprotein I is a receptor that is responsible for the attachment of these blood cells to the subendothelial collagen. It ensures the adhesion of the plates, their spreading and their binding to another protein - fibronectin.
Glycoprotein II is intended for all types of platelet aggregation. It ensures that fibrinogen binds to these blood cells. It is thanks to this that the process of aggregation and contraction (retraction) of the clot continues unhindered.
But glycoprotein V is designed to maintain platelet connection. It is hydrolyzed by thrombin.
If the content of various glycoproteins in this layer of the platelet membrane decreases, this becomes the cause of increased bleeding.