What kind of pathology is this
The main function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen to all tissues of the body. When the cell size is small, the function cannot be performed fully, for this reason anemia begins to develop. Moreover, this condition does not arise independently, but manifests itself as a result of serious diseases.
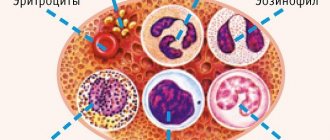
There are 3 types of red blood cells in the blood:
- Normocytes, their size is 7.5 micrometers.
- Microcytes are small cells.
- Macrocytes are large.
Normally, a person has a few small red cells in his blood. If their number exceeds 30%, then microcytosis of erythrocytes occurs.
Medical description of the pathology
Medicine clearly defines what anisocytosis is and what it is not. Anisocytosis is not an independent nosology, since it is a phenomenon, a process of changing the size of the diameter of blood cells, indicating the presence of trouble in the body.
Anisocytosis is detected by a general blood test during microscopic examination. Modern equipment in hematology laboratories allows for quantitative assessment of anisocytosis. The blood cells listed above must have certain sizes. The normal diameter of a red blood cell is 7.1-9.1 µm (micrometers), the diameter of a white blood cell is 15-16 µm and the diameter of a platelet is 3-4 µm. It is acceptable if 30% of blood cells have other parameters: 15% more than normal and 15% less. In other words, in a healthy person, at least 70% of blood cells have standard sizes.
The specificity of the clinical manifestation and the degree of severity directly depend on the type and type of anisocytosis. Pathologically altered cells have received their own names in medicine.
Using the example of red blood cells, whose normal diameter is 7.1-9.1 microns, we can distinguish:
- normocytes - cells that correspond in size to the norm;
- microcytes - cells with a diameter less than 7.1 microns;
- macrocytes - cells exceeding a diameter of 9 microns;
- megalocytes are cells significantly larger than normal (their diameter starts from 12 microns).
The predominance of microcytes, macrocytes, and even more so megalocytes in the blood is a clear indicator of anisocytosis of one or another type of cell, which is divided into:
- microanisocytosis (microcytosis) - the predominance of microcytes in the blood, i.e. cells with a diameter less than normal;
- macroanisocytosis (macrocytosis) - the predominance of macrocytes in the blood - cells with an increased diameter.
The process of anisocytosis is divided into stages:
- at stage I, the number of pathological cells in the blood does not exceed 50% of the total number;
- at stage II this figure is between 50% and 70%;
- at stage III, the number of pathological cells exceeds 70%.
Thus, if a microscopic analysis of a blood smear reveals approximately 60% of red blood cells with a diameter of 6.5 microns, then the doctor will record in the outpatient card that the patient has stage II erythrocyte microcytosis.
Symptoms
Any pathological changes in red blood cells adversely affect the human condition. You should consult a doctor and get tested if you experience the following symptoms:
- Fatigue, general malaise.
- Deterioration of breathing, shortness of breath with slight physical exertion.
- Heart rhythm disturbances. Appears quickly and disappears on its own.
- Pale skin.
- Brittle hair and nails.
- Regular bumps on the corners of the lips.
- Dry mucous membranes.
- Difficulty swallowing, feeling of a foreign body in the throat.
- Deterioration in taste.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Burning, itching on the labia minora and majora in women.
- Headache.
- Dizziness. Fainting conditions.
- During pregnancy - swelling, fetal hypoxia.
Carrying out diagnostics
How is anisocytosis detected? The norm was indicated earlier.
The main method of diagnosis is a blood test for all indicators. It indicates the characteristics of the blood composition, the indicators of red blood cells and platelets necessary to detect anisocytosis. The erythrocyte index can be recognized by the line called the coefficient of variation of erythrocyte volume and the mean deviation of erythrocyte volume. A characteristic line for the study of platelets is the average platelet volume and the rate of platelet anisocytosis.
Anisocytosis and poikilocytosis are the main indicators of the development of any disorders in the body. If the shape of a cell is changed, its size or color is increased, this indicates the development of a pathological condition in the internal organs of the patient. Diagnosis of blood composition disorders is carried out exclusively through laboratory testing. To do this, a person is prescribed a general blood test. Additional research is rarely required.
To correctly pass the test, the patient must adhere to the following recommendations:
- in the morning before taking the test, you should not eat or drink; dinner the night before should be light and not contain spicy, fatty, salty, or smoked foods;
- one day before blood sampling, you cannot exercise, drink alcohol, or go to the pool or sauna;
- Before donating blood, all medications are discontinued;
- It is advisable to carry out repeated analysis at the same time of day. Immediately before the procedure you need to catch your breath and calm down.
If these recommendations are ignored, the analysis will be inaccurate, which will cause difficulty in making a diagnosis.
Causes of pathology
The main reason for the formation of a high level of small red blood cells is considered to be a failure of hemoglobin synthesis. The second reason is diseases of the plasma membranes. A number of diseases also contribute to pathology:
- Iron deficiency anemia - development causes starvation of the body due to an insufficient amount of incoming oxygen. Failures in hemoglobin synthesis occur.
- Microspherocytosis. In most cases (75%), it manifests itself hereditarily, provoked by a gene mutation, a failure in the production of substances responsible for the condition of the membrane - it can be significantly damaged. In such cases, the size of red blood cells decreases, they become round, entering the spleen. In children, the skull becomes deformed, a high palate develops, it is possible that they have extra fingers on the limbs, and the spleen and liver become enlarged.
- Thalassemia. Passed along a hereditary line, otherwise called “Cooley's syndrome,” it is characterized by low production of adult hemoglobin. In a child, the skull may resemble a cube; there is a violation of the shape of the nose and bite. If the pathology was formed in the early stages of life, then a lag in mental and physical development is possible.
- Inflammation, chronic infections.
- Cancer pathologies, which often manifests itself in neoplasms in the lungs, thyroid gland, mammary gland, bone marrow. A child has neuroblastoma.
If microspherocytosis is detected in a general blood test, additional tests are prescribed, thanks to which the presence of hepatitis is accurately determined.
In addition to diseases, the following factors can provoke microcytosis:
- Significant blood loss.
- Lack of iron in food.
- Breastfeeding period during pregnancy.
Causes of anisocytosis
Viral infections can lead to anisocytosis
There are many reasons for the appearance of blood picture disorders. Doctors highlight the following as the main ones:
- cancerous lesions of the bone marrow;
- anemia;
- blood transfusion;
- Niemann-Pick disease;
- spinal cord pathologies;
- exposure to radiation;
- severe viral infections;
- poor nutrition.
The prognosis for a patient with a disorder depends on what caused the change in the size of blood cells. Also of great importance is how quickly the pathology was identified.
Pathology in children
In the first months of life, an increased level of microcytes is observed, and this is normal. This is explained by the fact that the child’s organs are not fully formed.
This process is completed by about three months. If significant deviations are diagnosed, the child is hospitalized to exclude the development of congenital diseases.
In 1 year, the indicator should be completely normalized, otherwise a thorough examination is required. The primary degree of development indicates a violation of the immune system and requires adjustments in nutrition and the prescription of a vitamin complex.
In severe situations, indicates the development of leukemia.
Minor violations are normally allowed in adolescence, this is associated with hormonal levels and goes away on its own.
Anisocytosis in a child
Different types of anisocytosis can occur in newborns, infants, and older children. An increased content of microcytes in the blood of a child can be observed after any infectious disease.
Macrocytosis is normal and can be observed as a physiological process in infants, especially during the first 14 days of life. By the second month of life, macrocytosis in infants goes away on its own.
Diagnosis of various forms of anisocytosis in a child may also indicate the unfavorable development of such pathologies:
- neuroblastoma;
- hypochromic anemia;
- chlorosis.
Diagnostics
Microcytosis is detected during a blood test. If the presence of anemia is determined, a smear of peripheral material is additionally prescribed.
Thanks to this measure, the initial symptoms of micro- and macrocytosis (the diameter of red blood cells exceeds the norm) or a mixed type of anisocytosis, combining signs of the first and second types, are revealed. Normo-, hyper- or hypochromia are detected in the same way.
A hematologist deals with the disease; it is he who prescribes further diagnostics, determines the cause, and the necessary treatment.
As additional diagnostic measures, tests are prescribed to determine celiac disease, blood and stool tests for the presence of the microorganism Helicobacter pylori.
The specialist clarifies in detail all the signs and symptoms present in the patient; it often becomes necessary to consult a gastroenterologist (if pain appears in the abdominal area). Sometimes the following diagnostic methods are needed:
- Transabdominal ultrasound examination.
- Endoscopy of the stomach and intestines.
- Computed tomography of the abdomen.
If adult women experience heavy periods with pain, it is necessary to exclude the presence of uterine fibrosis and other factors that cause heavy bleeding.
Mixed type of anisocytosis
There is also mixed type anisocytosis, when micro- and macrocytes are found in the blood simultaneously. This phenomenon occurs less frequently when there are 2 or more diseases at the same time or simply when there is a lack of folic acid in the body.
The mixed type of anisocytosis is usually divided into 4 degrees of severity, each designated by the number of pluses, which more clearly defines the degree of the pathological process compared to dividing by stages:
- 1 plus sign (+) - anisocytosis is insignificant in degree, in which altered cells are present in the blood in an amount of up to 25%;
- (++) - moderate anisocytosis, when the number of cells with sizes beyond the normal range already reaches half of all available;
- designation +++ - pronounced degree, when the diameter of 75% of all cells differs from the permissible values;
- 4 pluses (++++) - severe degree of mixed anisocytosis, i.e. more than 75% of blood cells have diameters that are unacceptable for normal.
Treatment
Therapy is initially aimed at eliminating the causes of the pathology. For example, a lack of iron requires taking medications with a high iron content, which eliminates anemia. At the same time, it is recommended to use vitamin C, as it promotes better absorption of iron.
When diagnosing serious blood loss (acute or chronic), the clinical picture worsens. Women with heavy periods and iron deficiency are prescribed hormonal treatment.
The development of complications such as heart failure requires a blood transfusion or restoration of the number of red blood cells from a donor.
If nutrient deficiencies are detected, the diet must be reviewed. Such situations are best treated.
In advanced situations, lack of treatment can cause serious complications.
Consequences
If, with severe microcytosis, the patient does not receive the necessary treatment, the consequences can be serious. This primarily concerns cancer diseases, since their development leads to death.
Microcytic anemia can cause starvation of organs and tissues of the body due to low oxygen supply. This often results from heart failure and lung diseases.
In children, this leads to a decrease in the immune system, disruption of all organs and systems in the body.
Over time, clinical analysis shows that the number of normocytes decreases, this reduces the area of red cell membranes, and as a result, a number of disorders are observed:
- Deterioration of nutrition, protection, and gas transportation by cells.
- Disorders of metabolic processes.
- Decreased vascular tone.
- Low blood pressure.
- Coronary vascular disorders.
- Pulmonary pathologies.
- Shock.
Why does anisocytosis occur?
When talking about the reasons for changes in the distribution of blood cell volume, it is necessary to distinguish between different types of anisocytosis. For example, microcytosis occurs more often with iron deficiency anemia, because. Due to insufficient iron content in the body, the red bone marrow is not able to produce red blood cells of sufficient size. In addition, a decrease in red blood cell volume can occur with thalassemia, sideroblastic anemia, cancer, and lead poisoning.
In turn, macrocytosis may not be a pathological condition at all. As mentioned earlier, anisocytosis in infants in the first days of life is a completely normal phenomenon, and it most often occurs as a macrocytosis. In the athological variant, such a change in the volume of blood cells can occur with a deficiency of certain microelements, myelodysplasia, or taking certain medications. In addition, the health of the liver and spleen, which also take part in the synthesis of blood cells, plays an important role in maintaining normal blood composition.
Anisocytosis generally accompanies many diseases. In addition to various types of anemia, such diseases include liver diseases (including metastases of cancerous tumors and the consequences of alcoholism), Alzheimer's disease, microspherocytosis, bone marrow metaplasia, as well as a number of cardiovascular diseases. In particular, the detection of changes in the diameter of red blood cells is considered a diagnostic sign of ischemia.
Prevention
There are the following measures to prevent microcytosis:
- Healthy eating. The diet should include fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs, and lean meat. Avoid eating processed foods and fast food.
- Exercise, walks in the fresh air. Due to them, the supply of oxygen to tissues and organs is improved.
- Refusal of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products.
- Establish a daily routine with eight hours of sleep and sufficient time for rest.
- Regular tests. Timely treatment starts speeds up recovery and avoids any complications.
- Avoid close contact with poisons and chemicals.
Self-medication is extremely unwise, since such measures can aggravate the situation . The specialist will make an accurate diagnosis as soon as possible, find out the cause that provoked the pathology, and prescribe the necessary therapy.
Macrocytosis, or the presence of abnormally large red blood cells in the blood
Macrocytosis
is the presence in the blood of abnormally large red blood cells (or red blood cells), which in this case are called macrocytes.
Macrocytosis is determined in the laboratory by microscopy of a blood sample.
Most often, macrocytosis does not manifest itself with any symptoms, but is discovered by chance during a regular blood test.
Macrocytosis is not an independent disease, but it can be a manifestation of certain blood diseases or intoxication.
The most common causes of macrocytosis are:
1. Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) deficiency. 2. Vitamin B9 (folic acid) deficiency. 3. Posthemorrhagic anemia (anemia associated with blood loss). 4. Hemolytic anemia (anemia associated with the destruction of red blood cells). 5. Myelodysplastic diseases (bone marrow diseases). 6. Leukemia (blood cancer). 7. Hypothyroidism (low thyroid function). 8. Severe alcoholism. 9. Liver diseases. 10. Taking certain medications. 11. Pregnancy period.
It should be borne in mind that a deficiency of vitamins B9 and B12 can be caused either by simple starvation or by diseases of the digestive system that impair the absorption of these vitamins. In addition, there are a number of rare genetic diseases of the hematopoietic system that are accompanied by macrocytosis.
If you have macrocytosis, you need to undergo an in-depth examination to determine the cause. The examination may take some time. This will likely require taking a bone marrow sample, a painful but necessary procedure.
Treatment for macrocytosis is aimed at the underlying cause. If macrocytosis is caused by severe anemia, a blood transfusion may be needed.
Anisocytosis of platelets in the blood
The protective function that prevents acute bleeding, performed by blood elements - platelets, is one of the most important in the circulatory system. This is a fairly important component of the human body, responsible for coagulation.
During the analysis process, the standard for the number of parts with dimensional deformation is 14.1 to 18.2%. When platelet anisocytosis is detected, this indicator changes.
This pathology has its own prerequisites, which are explained by various diseases, therefore, in a general analysis, such a modification is defined as a symptom.
Among the possible prerequisites for pathology:
- myeloneoplastic process;
- blood cancer;
- kidney and liver problems, hepatitis;
- infection by virus;
- radiation sickness;
- initial stage of aplastic anemia;
- deficiency in biologically active substances;
- DIC pathology.
Microcytosis of erythrocytes in a general blood test: what is it?
Each of us, having been to the laboratory and donated blood for a general analysis, is looking forward to the results. Often, having received them in our hands, we begin to panic when we see terrible words and do not understand their meaning. These include microcytosis. What it is and whether it’s scary to live with, your attending physician will explain at your appointment and, if necessary, prescribe corrective therapy.
It is important to understand that changes in red blood cells in shape and size can be either a sign of a minor malfunction in the body or evidence of a serious illness. However, in both cases, put off panic - the phenomenon of microcytosis is reversible, and with timely diagnosis, even complex cases can be cured.
The phenomenon of microcytosis
The human blood contains the most red blood cells. By nature, they have a characteristic biconvex shape and precise dimensional characteristics. If red blood cells are not changed, then in medicine they are usually called normocytes.
In various diseases, which are easily determined by a clinical blood test, the shape and size of red blood cells may change, which indicates a pathological process. The modified cells will indicate which one:
- small bodies - microcytes,
- increased size bodies - macrocytes.
The danger of such cells is that they stop performing their job efficiently: transporting hemoglobin in the required quantities.
Doctors talk about three types of microcytes:
Microcytosis is one of the forms of anisocytosis, microanisocytosis.
Microcytosis is a condition when more than 30% of red blood cells have changed in a smaller direction. There were a lot of them, but their size became several times smaller than normal. Such an erythrocyte is not able to transport oxygen to tissues and organs in the same way as a healthy and full-fledged normocyte would do.
If a blood test reveals microcytosis, you may be dealing with iron deficiency anemia.
Causes of microcytosis
In human serum biomaterial, the presence of all types of erythrocytes - normal and altered - is quite acceptable. Only there should be a certain percentage of modified cells and no more.
The norm is considered acceptable when there are no more than 15% of microcytes in the blood of the total number of cells.
A general blood test can detect microcytosis in three stages:
- moderate - no more than 40% of modified cells,
- average - no more than 70% modified bodies
- pronounced - more than 70% of red blood cells have changed their size.
The main cause of microcytosis is considered to be a violation of protein synthesis, which leads to a number of diseases and pathologies.
Microchanges in red blood cells often occur for other reasons. These include diseases of the thyroid gland, deficiency of iron, vitamins A and vitamin B12, viral diseases that cause complications, and liver diseases.
When is microcytosis not a pathology?
There are often cases when modification of red blood cells is considered normal:
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding,
- in the blood of a child up to 3 months. This is due to the composition of the blood not yet fully formed. By 5-6 months, the baby’s blood will be approximately the same as that of an adult, and the quantitative and qualitative composition of red blood cells will return to normal.
- microcytosis of a teenager. An age-related change that, with proper and nutritious nutrition, will disappear over time.
Microcytosis, which is most often caused by iron deficiency anemia, is considered a separate type of hypochromia. Hypochromia is a disorder of the functioning of red cells, in which the level of hemoglobin sharply decreases.
Hypochromia in clinical analysis
The indicator of hypochromia is determined initially by a general blood test. To identify pathology, the doctor very carefully evaluates the color characteristics of the red blood cell. Normally it should be completely red. Color standard - 0.85 - 1.05.
When hemoglobin in the blood decreases, this is immediately indicated by the color of the red body - red with a white center. Such a cell visually resembles a target. This is hypochromia.
It can occur for various reasons: a lack of foods containing iron in the diet, or it can occur due to frequent but slight blood loss.
For this pathology, special therapy is prescribed, which involves adjusting the diet and taking special iron-containing drugs.
Symptoms of microcytosis
Any disturbance of red blood cells affects the general well-being of a person. Under no circumstances should obvious signs of illness be ignored. The signs of microcytosis and macrocytosis are almost the same. Even without going to the laboratory, you can understand that your body needs help.
- fatigue, lethargy, fatigue,
- shortness of breath, difficulty breathing even with the slightest exertion,
- abnormal heart rhythm: arrhythmia, tachycardia, may occur unexpectedly and also disappear unexpectedly.
- pale skin, painful pallor,
- hair and nails become brittle and lifeless,
- dry mucous membranes,
- frequent seizures along the edges of the lips,
- difficulty swallowing with a feeling of constant presence of a foreign body in the throat,
Prevention and treatment of microcytosis
Having understood what microcytosis is, it is important to know how to live with it if the analysis shows modified cells.
Fortunately, in most cases microcytosis is reversible.
The doctor does not treat microcytosis, but the cause that caused it. We found out the diagnosis, prescribed appropriate treatment, and the condition of the red blood cells returned to normal. This chain is a natural way out of an unpleasant situation.
Most often, microcytosis is caused by iron deficiency. In this case, the doctor prescribes appropriate nutrition to raise hemoglobin, and in parallel the patient must take iron supplements.
Among the products that normalize hemoglobin are:
- liver
- buckwheat
- apples (controversial, but useful)
- pomegranate
- beef
If after therapy and diet, hemoglobin remains at a low level, then the issue is not iron deficiency. Microcytoses caused by cancerous tumors persist until the tumor is excised or "disarmed" by other means.
Remember, only a doctor can prescribe treatment for you. Do-it-yourself treatment of microcytosis can play a cruel joke on you.
Classification
Blood cells affected by the process:
- anisocytosis of erythrocytes;
- platelet anisocytosis.
Predominant pathological size:
- microcytosis (more typical for various types of anemia);
- macrocytosis;
- mixed type is the most common.
The presence of microcytes in the field of view under a microscope
By degree:
- the first (also insignificant) - the number of non-standard cells in diameter is no more than 25% of the total number. When such a degree is detected, an entry is made in the medical documents about anisocytosis and one “+” is put;
- the second (also moderate) - the number of non-standard cells in diameter ranges from 25 to 50% of the total number. Denoted by two pluses “++”;
- third (or pronounced) - non-standard shaped elements exceed 50% of the total volume;
- fourth (also pronounced) - almost all the formed elements in the blood smear have atypical sizes.
We also recommend that you pay attention to the article: “Hypersplenism: how to increase the concentration of ETL in the blood?”
Important! The only case not associated with any disease when the rate of erythrocyte anisocytosis is higher than normal is pregnancy. Therefore, there is no need to panic - after childbirth, your blood counts will return to normal.
Macrocytosis
1. Small medical encyclopedia. — M.: Medical encyclopedia. 1991–96 2. First aid. - M.: Great Russian Encyclopedia. 1994 3. Encyclopedic Dictionary of Medical Terms. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia. — 1982—1984
See what “Macrocytosis” is in other dictionaries:
macrocytosis - macrocytosis ... Spelling dictionary-reference book
MACROCYTOSIS - (macrocytosis) the presence in the blood of abnormally large red blood cells (macrocytes). Macrocytosis is one of the symptoms of certain types of anemia (macrocytic anemias), including those caused by... ... Explanatory Dictionary of Medicine
macrocytosis - (macrocytosis, macrocyt + oz) the predominance of macrocytes among peripheral blood erythrocytes ... Big Medical Dictionary
macrocytosis - macrocytosis, and ... Russian spelling dictionary
macrocytosis - u, h. Reimportance of macrocytes in the middle of erythrocytes of peripheral blood ... Ukrainian Tlumachny Dictionary
macrocytosis is the name of the human family... Spelling dictionary of Ukrainian language
macrocytosis - macro/cyt/oz/ ... Morphemic-spelling dictionary
Macrocytosis is the presence of abnormally large red blood cells (macrocytes) in the blood. Macrocytosis is one of the symptoms of certain types of anemia (macrocytic anemias), including those caused by insufficient... ... Medical terms
Anemia - (anaemiae, Greek negative prefix an + haima blood, synonym anemia) a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood, usually accompanied by erythrocytopenia. A. a common pathological condition that occurs more often as a syndrome... ... Medical encyclopedia
Anemia - Histological picture of blood, with iron deficiency ... Wikipedia
Anemia - Anemia Histological picture of the blood, with iron deficiency anemia ICD 10 D50 D89 ICD 9 xxx ... Wikipedia
Analysis on RDW
We recommend reading the article: Why is there an increased number of red blood cells in the blood?
Blood is examined for anisocytosis during a general analysis. The fence is made from a finger. You need to take it on an empty stomach in the morning. The degree of anisocytosis can be determined manually by laboratory assistants. Today, the RDW index is increasingly calculated using modern hematology analyzers, which provide faster and more accurate results. This parameter is determined automatically using a special formula, taking into account other erythrocyte indices.
The analysis is deciphered by the attending physician, and the values of other indicators are taken into account. Thus, in parallel with the assessment of RDW, the erythrocyte index MCV (average erythrocyte volume) is assessed. This is due to the fact that the anidocytosis index may remain normal, but the presence of micro- and macrocytes is a pathology.
The value of the anisocytosis index is necessary for the doctor to interpret the test result and diagnose anemia, including differential diagnosis. Determining the number of red blood cells in the blood and the level of hemoglobin does not give a complete picture, but only indicates the presence of anemia.
Let's understand what macrocytosis is and is it dangerous?
Blood is the most important component of any living organism, which is represented by liquid tissue and consists of plasma and formed bodies (leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets). The function of the circulatory system is to connect and nourish absolutely all organs of the body , so it is very important to monitor the condition of the blood by conducting regular clinical tests.
Based on the results of a laboratory blood test, a specialist can judge the functional disorders of the body.
Red blood cells with abnormalities
In some cases, red blood cells may be found in human blood, the size of which deviates from the norm (68 microns) up or down. Large red blood cells are called macrocytes, and the process of changing cell size is called macrocytosis.
Abnormal platelets
- fatigue, lack of energy, increased fatigue,
- shortness of breath, respiratory dysfunction,
- increased heart rate (in any condition),
- pallor of the skin, mucous membranes, nails (sometimes the skin may acquire a blue tint).
The presence in the blood of both abnormally large and unnaturally small red blood cells (macrocytes and microcytes) is a condition called anisocytosis. A condition such as anisocytosis has 3 degrees:
- anisocytosis of the first degree - deviation from the norm in the size of the erythrocyte (in one direction or another) is observed in 30-50% of the total number of cells,
- anisocytosis II degree - deviation in 50-70% of cells,
- Anisocytosis III degree - more than 70% of macro- and/or microcytes.
As a rule, such macrocytosis as red blood cells does not manifest itself in any way and is detected only during a clinical blood test, when other diseases are treated.
Causes of macrocytosis of erythrocytes and platelets
Macrocytosis (both red blood cells and platelets) is not a disease, but only a sign of pathological processes occurring in the human body. This condition can be caused by a number of reasons, which can only be determined by a doctor based on test data and a more detailed examination.
The causes of this condition in the case of red blood cells:
- deficiency of vitamin B9 and/or B12,
- anemia caused by blood loss (posthemorrhagic),
- anemia that develops due to the destruction of red blood cells (hemolytic),
- bone marrow pathologies,
- oncological diseases (usually blood cancer),
- functional disorders of the thyroid gland,
- chronic alcoholism,
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs,
- pregnancy,
- use of certain medications.
Each of us, having been to the laboratory and donated blood for a general analysis, is looking forward to the results. Often, having received them in our hands, we begin to panic when we see terrible words and do not understand their meaning. These include microcytosis. What it is and whether it’s scary to live with, your attending physician will explain at your appointment and, if necessary, prescribe corrective therapy.
It is important to understand that changes in red blood cells in shape and size can be either a sign of a minor malfunction in the body or evidence of a serious illness. However, in both cases, put off panic - the phenomenon of microcytosis is reversible, and with timely diagnosis, even complex cases can be cured.
Anisocytosis: forms and types
Changes in the size and shape of blood components do not always indicate pathological processes in the body. It is considered normal if the deviation does not exceed 30% of the total number of red and white blood cells, and their percentage ratio in relation to each other must also be taken into account - it should be approximately the same. In the vast majority of cases, anisocytosis occurs simultaneously with poikilocytosis, a condition in which the structure of red blood cells is deformed and their work is disrupted.
Poikilocytosis in blood test
The standard size of red blood cells (blood cells that contain hemoglobin and provide gas exchange in the body) can range from 7 to 9 micrometers. If these numbers are less or more than the normal value, the person is diagnosed with anisocytosis, which can occur in several forms, which are classified according to the size of the predominant red blood cells.
| Type of anisocytosis | The size of the deformed cells that make up the red blood cell mass (in micrometers). |
Microcytosis | ≤ 6,9 |
Macrocytosis | 8-12 |
Megalocytosis | ≥ 12 |
Combined anisocytosis | All three types of modified red blood cells can be detected in the blood in different percentages. |
Normal red blood cells under an electron microscope
When we talk about anisocytosis, in most cases we mean an excess of the number of red blood cells of non-standard size by more than 30% of the total number of red blood cells, but sometimes the changes also affect small spherical plates of red color - platelets. Platelets are responsible for blood clotting, and changes in their size are almost always caused by pathological processes in the body, which can have a sluggish course and are detected by chance during a general blood test.
Platelets
If a patient is diagnosed with platelet anisocytosis, the doctor will definitely prescribe an additional examination to exclude diseases of the hematopoietic system (including oncological processes), severe viral pathologies and diseases accompanied by latent forms of inflammation. When diagnosing, the doctor also necessarily takes into account the degree of pathology, which depends on how much the deviations exceed the permissible norm.
| Deviation degree | Minimum volume of modified blood components (as a percentage of the total mass) | Maximum volume of modified blood components (in percent) | How is it indicated in the transcript of the analysis? |
| First (minor deviations) | 15 | 25 | + |
| Second (the change in the size of blood cells does not significantly exceed the permissible norm) | 25 | 50 | ++ |
| Third (anisocytosis exceeds the norm by more than 50%) | 50 | 75 | +++ |
| Fourth (sharply expressed, requires immediate examination and correction/treatment) | 75 | 100 | ++++ |
You should know it! In deciphering the results of a complete blood count, erythrocyte anisocytosis and platelet anisocytosis are designated as RDW and PDW, respectively.
RDW indicators in blood tests
Capillary blood for general analysis
The phenomenon of microcytosis
The human blood contains the most red blood cells. By nature, they have a characteristic biconvex shape and precise dimensional characteristics. If red blood cells are not changed, then in medicine they are usually called normocytes.
In various diseases, which are easily determined by a clinical blood test, the shape and size of red blood cells may change, which indicates a pathological process. The modified cells will indicate which one:
- bodies of reduced size - microcytes;
- increased size bodies - macrocytes.
The danger of such cells is that they stop performing their job efficiently: transporting hemoglobin in the required quantities.
Doctors talk about three types of microcytes:
| Microcyte type | Characteristic |
| The microcytes themselves | |
| Schizocytes | Fragments of red blood components measuring 2-3 microns |
| Microspherocytes | These red blood cells have changed not only their size, but also their shape: biconvex, they turn into red balls with a diameter of 4-6 microns in diameter |
Microcytosis is one of the forms of anisocytosis, microanisocytosis.
Microcytosis is a condition when more than 30% of red blood cells have changed in a smaller direction. There were a lot of them, but their size became several times smaller than normal. Such an erythrocyte is not able to transport oxygen to tissues and organs in the same way as a healthy and full-fledged normocyte would do.
If a blood test reveals microcytosis, you may be dealing with iron deficiency anemia.
Factors in the development of the disease
Formal components can distort their shape and size under the influence of various kinds of prerequisites. When performing a complete blood test, anisocytosis is detected immediately. A more in-depth analysis is required to detect poikilocytosis.
The main factors causing anisocytosis include a number of reasons:
- Poor nutrition.
- Blood transfusion.
- Myelodysplastic syndrome.
- Oncological diseases.
- Lack of iron, vitamins A, B12.
- Liver diseases.
- Various types of anemia.
- Thyroid gland dysfunction.
In addition, physiological disturbances in the diameter of red blood cells can be detected in an infant from the first days of life, which is not a symptom of any illness.
Factors causing an increase in anisocytosis are:
- microcytosis – iron deficiency anemia;
- megakaryocytes – lack of vitamin B12.
When a complete blood count reveals anisocytosis, nutrition should be reconsidered. The body requires elements involved in the construction of blood cells.
Causes of microcytosis
In human serum biomaterial, the presence of all types of erythrocytes - normal and altered - is quite acceptable. Only there should be a certain percentage of modified cells and no more.
The norm is considered acceptable when there are no more than 15% of microcytes in the blood of the total number of cells.
A general blood test can detect microcytosis in three stages:
- moderate - no more than 40% of modified cells;
- average - no more than 70% modified bodies
- pronounced - more than 70% of red blood cells have changed their size.
The main cause of microcytosis is considered to be a violation of protein synthesis, which leads to a number of diseases and pathologies.
| Cause of microcytosis | Characteristics of the disease |
| Iron-deficiency anemia | This disease is characterized by oxygen starvation of all tissues and organs due to dysfunction of carrier cells |
| Microspherocytosis | Hereditary pathology associated with gene mutation and disruption of the production of a special substance responsible for the normal state of the membrane film of red blood cells. The consequences are catastrophic. So in children with a similar pathology, external deformities are observed in the form of extra fingers, deformation of the skull. It is impossible to make such a serious diagnosis using a general clinical blood test alone, so an additional examination is prescribed for the presence of specific antibodies. |
| Cooley's syndrome or thalassemia | A disorder in hemoglobin synthesis is exclusively hereditary. The norms for the formation of adult hemoglobin are violated. Signs of a thalassemia patient are a square skull, malocclusion combined with mental and physical developmental delay. |
| Inflammatory processes that have become chronic | Active hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, peptic ulcer |
| Oncology | Because red blood cells are produced by the bone marrow, microcytosis may be a sign of bone marrow cancer or other cancers that have metastasized to the bone marrow. In a child it could be neuroblastoma. |
Microchanges in red blood cells often occur for other reasons. These include diseases of the thyroid gland, deficiency of iron, vitamins A and vitamin B12, viral diseases that cause complications, and liver diseases.
When is microcytosis not a pathology?
There are often cases when modification of red blood cells is considered normal:
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- in the blood of a child up to 3 months. This is due to the composition of the blood not yet fully formed. By 5-6 months, the baby’s blood will be approximately the same as that of an adult, and the quantitative and qualitative composition of red blood cells will return to normal.
- microcytosis of a teenager. An age-related change that, with proper and nutritious nutrition, will disappear over time.
Microcytosis, which is most often caused by iron deficiency anemia, is considered a separate type of hypochromia. Hypochromia is a disorder of the functioning of red cells, in which the level of hemoglobin sharply decreases.
How is the treatment carried out?
Nutrition during anisocytosis occupies one of the leading places
Treatment is chosen depending on what caused the pathology. In most cases, nutritional adjustments are made to enrich the diet with iron and vitamin B12.
Drug therapy is prescribed only after the cause of the changes has been established. This may require hospitalization of the patient and treatment not only with medications, but also with surgical intervention.
Hypochromia in clinical analysis
The indicator of hypochromia is determined initially by a general blood test. To identify pathology, the doctor very carefully evaluates the color characteristics of the red blood cell. Normally it should be completely red. Color standard - 0.85 - 1.05.
When hemoglobin in the blood decreases, this is immediately indicated by the color of the red body - red with a white center. Such a cell visually resembles a target. This is hypochromia.
It can occur for various reasons: a lack of foods containing iron in the diet, or it can occur due to frequent but slight blood loss.
For this pathology, special therapy is prescribed, which involves adjusting the diet and taking special iron-containing drugs.
Treatment and prevention
There is no specific treatment for anisocytosis. Correction of disorders is aimed at treating the underlying disease and preventing its relapses. If the cause of the deviation is anemia, the patient is prescribed iron supplements and a diet rich in iron-containing foods. It is useful to include red meats (lamb, beef, pork, veal), apple and pomegranate juice, sunflower and pumpkin seeds, and liver in the menu.
Natural pomegranate juice
To eliminate or prevent vitamin deficiency, you can take mineral supplements or vitamin-mineral complexes, for example:
- "Pikovit";
- "Alphabet";
- "Complivit";
- "Vitrum".
Vitamins
Women suffering from menorrhagia – heavy and prolonged menstruation – need to be especially attentive to their own health. Large blood losses lead to increased loss of iron and the development of anemia, so during this period it is important to maximally enrich the diet with foods with a high iron content.
Products containing iron
In case of uterine bleeding (for example, against the background of discontinuation of oral contraceptives), it is necessary to monitor the level of hemoglobin and the chemical composition of the blood in order to notice any deviations in time and take action.
Hemoglobin norm
After stopping the attack, the woman is prescribed a special diet and medications that replenish the lack of iron in the body, and a gentle regimen.
Fenyuls
Anisocytosis is not a disease, but may indicate serious problems in the functioning of the body. To avoid pathology, it is important to eat right, move more and walk in the fresh air. Movement helps cells better absorb and transport oxygen molecules involved in the process of iron absorption.
Walking is very beneficial
For viral infections, even if it is a common acute respiratory infection, you should not self-medicate, since improper treatment can cause complications and cause disruption of the structure and appearance of blood components.
Symptoms of microcytosis
Any disturbance of red blood cells affects the general well-being of a person. Under no circumstances should obvious signs of illness be ignored. The signs of microcytosis and macrocytosis are almost the same. Even without going to the laboratory, you can understand that your body needs help.
- fatigue, lethargy, fatigue;
- shortness of breath, heaviness of breathing even with the slightest exertion;
- abnormal heart rhythm: arrhythmia, tachycardia; It can appear unexpectedly and also go away unexpectedly.
- pale skin, painful pallor;
- hair and nails become brittle and lifeless;
- dry mucous membranes;
- frequent jamming along the edges of the lips;
- difficulty swallowing with a feeling of the constant presence of a foreign body in the throat;