Over the years, certain parameters have been formed in obstetric practice by which one can determine the norm or abnormalities in the development of a baby in the womb. Thus, using the well-known method of ultrasound diagnostics, doctors can monitor the dynamics of the baby’s development, measure the size of individual parts of his body and compare the obtained parameters with those that are considered normal for a specific period of pregnancy.
One of the main parameters that the ultrasound doctor almost primarily pays attention to is the biparietal size of the fetal head (BFS). What does this indicator mean, what is it, and what value of BPD in the fetus is considered normal? We will talk about this with you further.
The concept of BPR
During the ultrasound procedure, doctors pay special attention to the baby’s head. And this is not surprising, since the brain is one of the most important organs of the body, and its (brain) development has a direct impact on the state of the embryo. And the BDP just determines the size of the head and, consequently, the degree of brain development.
This index denotes the “width” of the skull, so to speak, which is measured between the temples, i.e. along the minor axis.
Scheme for measuring biparietal and fronto-occipital size
Note! Together with the BPR, the LZR is usually measured - the distance between the forehead and the back of the head, i.e. the measurement is performed along the major axis. Note that the values of both indices can be obtained with maximum accuracy only between the 12th and 28th weeks of pregnancy.
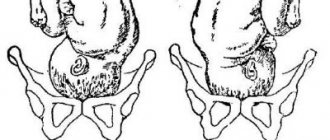
The BDP index is important in determining the possibility of natural childbirth. If the circumference of the birth canal is smaller than the circumference of the baby's head, then doctors decide to resort to a caesarean section.
BDP sizes by week of pregnancy
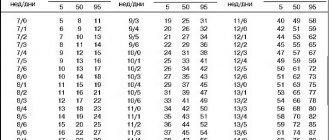
Data obtained during ultrasound are compared with average values. As the child grows, his parameters also change. Changes in BDP by week of pregnancy can be tracked using special tables. They indicate fetometry indices, including average norms for the biparietal distance, as well as permissible fluctuations of this index. The average value characterizes the so-called. The 50th percentile, upper and lower bounds define the 95th and 5th percentile, respectively. Each baby is individual, so identifying intervals of reference indicators makes it possible to distinguish pathology from the child’s developmental characteristics.
BPD at 12 weeks of pregnancy
If the pregnancy proceeds without complications, the first ultrasound is recommended to be performed between 11 and 13 weeks. Very often, expectant mothers choose the “golden mean” and go for examination at 12 full weeks of gestation. At this stage, it is already possible to accurately discern the baby, the presence and location of its main organs, as well as the symmetry of the cerebral hemispheres. Among the main characteristics of the baby, which are monitored during this period, it is worth highlighting fetometric parameters (the length of the child - its coccygeal-parietal size (CPR), biparietal width (BPD), the size of the fronto-occipital distance (FZ), abdominal circumference), thickness its nuchal space (TN), the size of the nasal bone and heart rate.
BPD at 20 weeks of pregnancy
The woman undergoes the next planned ultrasound in the second trimester - from 18 to 22 weeks of gestation. During this examination, the specialist checks not only the presence of the child’s organs, but also their structure. The rate of development of the baby is still assessed on the basis of fetometric indicators - abdominal and head circumference, biparietal and fronto-occipital dimensions, length of the humerus, femur, forearm and tibia bones. Information on such an index as the BDP should not be underestimated - deviations, especially downward, may indicate a child’s developmental delay.
BDP at 32 weeks of pregnancy
Even if the pregnancy develops absolutely normally and there is no reason to worry, the woman is recommended to undergo an ultrasound in the third trimester. The optimal period for conducting this examination is the period from 30 to 34 weeks of gestation. The functional development of the baby at this stage is not studied particularly closely.
During the examination, the specialist pays attention to the size of the baby - measures the circumference of his head and abdomen, the size of his femur and humerus, assesses the degree of maturity and position of the placenta, the condition and amount of amniotic fluid. Measuring the biparietal width of the head at this stage is carried out not only to assess the rate of development of the child, but also to make a forecast regarding the method of delivery
What is the BPR norm?
To evaluate this index week by week, a special table was created, which indicates the norms of the embryo’s BDP, as well as permissible deviations.
Biparietal head size of fetal BPD by week
During pregnancy, a woman has to undergo ultrasound examinations more than once to show how correctly the fetus is developing in the womb. To assess the condition of the baby, a number of indicators are used, one of which is the biparental size of the fetal head. In other words, the distance between the temples of the baby's head is measured, and the results are compared week by week.
BDP parameters change over the course of pregnancy; each week has its own norm of indicators. Active growth of the head is observed in the first two trimesters of pregnancy; the indicator is most informative in the period from 12 to 28 weeks and allows you to determine the approximate date of birth.
A discrepancy between the biparental size of the fetal head and the gestational age may indicate intrauterine growth retardation, hydrocephalus, microcephaly and other developmental anomalies of the child.
But deviations of the BPD from the norm are not always caused by pathological conditions. If the size of the head is comparable to the size of the arms/legs and abdominal circumference, then it is likely that the baby will simply be born large. Conclusions about the baby’s condition and deviations in its development can only be made by a gynecologist after assessing all fetal fetometry parameters.
The value of measuring the size of the fetal head on ultrasound
The main parameters measured during the study are the size of the skull, the length of the humerus, the length of the femur and the volume of the child’s abdomen.
When determining the parameters of the skull, two values are important: BPR (biparietal size of the fetal head) and LZR (fronto-occipital size). BPR means the transverse size of the head, the distance between the temporal bones.
LZR is measured from the occipital to the frontal bone and means the longitudinal size of the skull.
These indicators are developed for each week of pregnancy, starting from the eleventh.
All values measured by ultrasound are indicated as a whole, since during normal fetal development they must be balanced among themselves and proportional to a certain week of gestation.
The size of the child’s skull, the BPD in particular, is a very important indicator. Significant deviations may indicate a serious pathology of the fetus and become the basis for a decision on the possibility of continuing gestation or on the method of delivery. Other fetal fetometry values can be found here.
Bpr - transcript
During an ultrasound examination, special attention is paid to examining the baby's head. This is not surprising: the brain is the most important organ, the growth and development of which directly affects the condition of the fetus
BDP will help determine the size of the head, and therefore the level of brain development. Biparietal size is a kind of “width” of the head, measured along the minor axis, from temple to temple.
In addition to the BPR, the fronto-occipital size (FOR) is also determined - along the major axis, from the forehead to the back of the head. However, the main parameter remains the biparietal size: it is this that is used to determine the duration of pregnancy. With particular accuracy, this can be established in the period of 12-28 weeks.
In the BDP tables, fetal head size values are presented as percentiles. In order to use such a table and determine the norm of fetal BPD by week, it is necessary to find the value of the 50th percentile, the remaining values determine the boundaries of normal readings.
More than normal
When the biparietal size (BSD) of the fetal head is larger than normal, this may indicate the following phenomena:
- heredity. If someone in the family also has a large head volume, then in this case treatment is not required;
- large fruit;
- brachycephaly (short head) - the skull is smaller than usual;
- macrocephaly;
- hydrocephalus;
- disorders in the development of bone and cartilage tissue;
- tumor of the skull bones;
- brain tumor or brain hernia;
- diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman.
Less than normal
The main reasons for which insufficient indicators of BPR of the fetal head may be recorded are:
- heredity. In this case, if at least one of the parents has a small head volume, then there is no reason for concern and no treatment is required;
- small embryo size;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- genetic diseases;
- dolichocephaly (long-headed);
- disruption of the development of the spine, bone and cartilage tissues
- pathology of brain development or complete absence of some of its parts;
- intrauterine infection.
Conclusion
Only a doctor can evaluate the full picture of an ultrasound. In turn, the doctor leading the pregnancy compares the data from the study of the fetal head with other studies, tests and complaints of the pregnant woman, which allows him to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The fetal BDP exceeds the norm - what does this mean?
In some cases, the index exceeds the permissible norms. In this case, the attending physician is obliged to determine other parameters of the embryo (such as abdominal circumference, thigh length, etc.) in order to make sure that there are no pathologies. And if other parameters exceed the norm by at least one or two weeks, it means that the expectant mother has a large fetus. But if these indicators are within acceptable limits, then it is likely that the child is simply developing in leaps and bounds, and all parameters will soon level out.
As for significant deviations of the BPD from the norm, they often indicate serious problems in development. For example, an increased index may occur with a tumor of the cranial bones or the brain itself, as well as with hydrocephalus and cerebral hernia. In each of the listed cases (the exception is hydrocephalus), women are advised to immediately terminate the pregnancy, since such pathologies are, unfortunately, incompatible with life. But hydrocephalus is treated with antibiotics or (if treatment does not produce any results) an abortion is performed.
Note! If the BPD in the embryo is too low, nothing good should be expected either - this often indicates underdevelopment of the brain or the absence of certain of its components (right, left hemispheres, or both at once, the cerebellum, etc.). In such cases, the fetus is aborted regardless of the gestational age.
In the last trimester of pregnancy, low biparietal size indicates delayed fetal development. This syndrome is treated with special drugs (such as Actovegin, Chimes, etc.), which stimulate blood flow in the uterine cavity and placenta.
Average fetal fetometry values
| Week of pregnancy | Height, mm (KTR - coccygeal-parietal size) | Weight, g | Chest diameter, mm |
| 11 | 6,8 | 11 | 20 |
| 12 | 8,2 | 19 | 24 |
| 13 | 10 | 31 | 24 |
| 14 | 12,3 | 52 | 26 |
| 15 | 14,2 | 77 | 28 |
| 16 | 16,4 | 118 | 34 |
| 17 | 18 | 160 | 38 |
| 18 | 20,3 | 217 | 41 |
| 19 | 22,1 | 270 | 44 |
| 20 | 24,1 | 345 | 48 |
| 21 | 25,9 | 416 | 50 |
| 22 | 27,8 | 506 | 53 |
| 23 | 29,7 | 607 | 56 |
| 24 | 31,2 | 733 | 59 |
| 25 | 32,4 | 844 | 62 |
| 26 | 33,9 | 969 | 64 |
| 27 | 35,5 | 1135 | 69 |
| 28 | 37,2 | 1319 | 73 |
| 29 | 38,6 | 1482 | 76 |
| 30 | 39,9 | 1636 | 79 |
| 31 | 41,1 | 1779 | 81 |
| 32 | 42,3 | 1930 | 83 |
| 33 | 43,6 | 2088 | 85 |
| 34 | 44,5 | 2248 | 88 |
| 35 | 45,4 | 2414 | 91 |
| 36 | 46,6 | 2612 | 94 |
| 37 | 47,9 | 2820 | 97 |
| 38 | 49 | 2992 | 99 |
| 39 | 50,2 | 3170 | 101 |
| 40 | 51,3 | 3373 | 103 |
Video - Fetal Anatomy Screening
BPD does not correspond to gestational age
Deviation of the obtained data of the BPD index beyond the reference intervals is always a reason for a more careful examination of the baby, but does not at all indicate pathologies of the child’s functional systems. Assessment of the biparietal width is carried out in conjunction with the data on the abdominal circumference and the size of the child’s limbs. Excess or lag in size by 1-2 weeks in all parameters often indicates a large or, on the contrary, small toddler. You should also not panic if all fetometry characteristics are normal, and only the BPR slightly (!) deviates from it. The child grows in leaps and bounds, so perhaps within a week or two all indices will “even out.” Significant deviations from acceptable limits often indicate serious problems with the child’s health.
BDP - which means increased value during pregnancy
A significant increase in biparietal size is possible with:
- neoplasms (tumors) of the bones of the skull or brain;
- hydrocephalus - dropsy of the brain;
- cerebral hernia.
These pathologies are very severe and are considered incompatible with life. The only exception is hydrocephalus, in which the damage is caused by an infection that has entered the mother's body. In this case, antibiotic therapy is carried out. If it is ineffective, the woman, as with other pathologies, is recommended to stop the development of pregnancy.
BDP lower than expected for gestational age
A significant reduction in the baby's head is also not a very good sign.
A low BDP index may indicate:
- insufficient functional development of the brain;
- partial or complete absence of its individual structures (cerebellum, hemispheres);
- intrauterine growth retardation.
It is strongly recommended to stop pregnancy if there is structural damage to the brain. In this case, the child has virtually no chance of life. If low numbers of biparietal distance are detected only in the third trimester, there may be a delay in the development of the baby (if the necessary brain structures are present). This condition is corrected with the help of medications (including Curantil, Actovegin, etc.) that improve uteroplacental blood circulation. In this case, an additional Doppler examination of the vessels of the toddler and the umbilical cord is carried out, and the child’s heartbeat is checked.
Developmental delays in the prenatal period can be caused by:
- Infection of a child while in the womb of a woman.
- Chronic hypoxia (oxygen starvation).
- Violations of the structure and functions of the placenta.
After receiving the ultrasound results, do not interpret the indicators yourself. The doctor evaluates the BDP index (as well as other development indicators) not selectively, but in conjunction with other fetometric and biochemical data. If necessary, the woman is recommended to repeat the ultrasound in 1-2 weeks and undergo additional examinations. Only an integrated approach will help you correctly assess the situation and make the right decision.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=H9nrBuBViJg
Features of scanning
Ultrasound can be performed in two ways: transvaginal and abdominal . The first type of study is used mainly in the first trimester of pregnancy. A special sensor is inserted into the vagina of the expectant mother.
Transvaginal ultrasound allows early detection of normal or disturbed intrauterine pregnancy and diagnosis of embryo developmental defects.
Abdominal ultrasound examination begins, as a rule, from the second trimester of pregnancy . To perform an ultrasound, the patient lies on her back, and her stomach is treated with a special gel. The doctor, using an abdominal probe, makes longitudinal, oblique and transverse scans to obtain a detailed image of the fetus.
What do deviations from the norm mean?
A slight exceeding of the BPR limits is quite acceptable. If there are some deviations from the norm, the doctor takes additional measurements of the embryo, including checking the fronto-occipital size (FOR). If all other indicators are also higher than accepted, this indicates that the child is simply larger than the average size and is developing normally. It is possible that a large head is a hereditary phenomenon.
Even if there are small deviations only in the BDP index, this may indicate somewhat uneven development and over time all values may return to normal.
To unambiguously identify abnormalities, they need to be identified many times; therefore, if at some point the examination shows a number outside the normal range, the doctor prescribes a repeat ultrasound after a short period of time. And only if the violation is repeated does it draw conclusions and take the necessary measures.
A serious deviation in BPR values on ultrasound during pregnancy indicates dangerous birth defects in development, which, unfortunately, are often incompatible with life.
Biparietal size of the fetal head table by week
During an ultrasound examination, which is carried out repeatedly during pregnancy, a parameter such as the biparietal size of the fetal head is established.
What is meant by the definition of “biparietal size”?
The biparietal size (BDS) of the baby's head is one of the most accurate indices that determine possible deviations in the development of the baby during pregnancy. It is calculated by measuring the distance between the inner and outer contours of the parietal bones of the fetal skull. Simply put, this is the “width” of the head, measured from temple to temple along the smallest axis.
The maximum information content of this indicator is observed at 12-28 weeks of pregnancy. That is why it is set within these deadlines.
BDP changes with the duration of pregnancy. That is why a table was created that shows the biparietal size of the fetal head on a weekly basis. The indicators obtained as a result of ultrasound are compared with the table ones, which suggests possible disorders and developmental delays.
How to use the fetal birth control chart?
In order to assess the value of the BPR, the doctor refers to a table that shows the BPR norms by week. In it, the values of this parameter are given in the form of percentiles (a special way of presenting medical statistics). In this case, as a rule, the average value of the indicator taken for evaluation is established, in this case the BPR. The 50th percentile is taken as the norm, the lower limit is the 5th percentile, the upper limit of the norm is the 95th percentile.
So, in order to estimate the obtained value of the biparietal size, it is enough to find in the table the column in which the gestational age is indicated and draw a horizontal line from it to the intersection with the column in which “50” (50th percentile) is written. It is this value that is the norm for BDP for a specific period of pregnancy. For example, when performing an ultrasound at 12 weeks, the normal BPR should be 21 mm, and the permissible deviations should be 18-24 mm. Therefore, if it has been established that the BPD is 20 mm, this does not indicate any violation, but is simply an individual feature of the baby’s development.
Despite the fact that using this table is not at all difficult, the expectant mother should not do this on her own. The thing is that this indicator must be used only in conjunction with others, which are also determined during ultrasound. Therefore, only the doctor is responsible for interpreting the results.
What is biparietal size
An ultrasound machine allows you to see the size of the developing fetus by visualizing the waves on the monitor screen. The most important of them is the biparietal size of the baby’s head or BPR. This is the maximum distance between the parietal bones located opposite each other.
- Doctors believe that the most informative indicator will be that shown by ultrasound from 12 to 28 weeks of pregnancy. BDP data are quite important for determining the actual gestational age; biparietal size helps gynecologists determine the date of expected birth. It is these data that characterize the degree of development of the fetal nervous system.
- Determining the biparietal size of the fetal head before birth allows you to determine the safest method of delivery for the woman and child. If the last weeks of pregnancy show a large discrepancy between the woman’s birth canal and the size of the fetal head, then, most likely, doctors will prefer to perform a cesarean section so as not to risk the health of mom and baby.
- Both the initial weeks of fetal development and the last ones have their own normative indicators for the biparietal size of the baby’s head. They are always recorded in the study protocol and give a clear picture of the child’s development and growth.