What is intrauterine pregnancy?
After fertilization of the egg occurs in the fallopian tube, it moves further to the uterus, while active cell division and growth occurs.
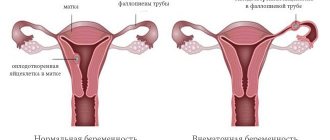
Thus, intrauterine pregnancy is a normal conception with successful attachment of the egg to the wall of the uterus and subsequent development inside the womb for 9 months. The implantation period lasts about 14 days. At this time, the uterine mucosa, under the influence of hormones, becomes looser, which creates favorable conditions for the implantation of the fertilized egg. As it attaches to the egg, blood vessels grow to provide the fetus with nutrition and oxygen. Then cell division begins, the chorion, the future placenta and an embryo with a membrane filled with liquid are formed. Approximately 2 weeks after conception, hormonal changes in the entire female body begin in order to successfully carry intrauterine development.
Diagnosis of intrauterine fertilization
A very important indicator of short-term conception is the diagnosis of the site of attachment of the fertilized egg in order to exclude ectopic fertilization. First of all, already at 5-6 weeks, palpation reveals an increase in the uterine cavity in the anteroposterior direction in the case of normal embryo formation. Also, by 10 weeks, the doctor notices some protrusion characteristic of normal implantation.
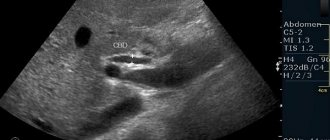
Often, at the conclusion of an ultrasound, you can see a diagnosis of progressive intrauterine pregnancy - this means that the embryo has attached in accordance with normal parameters in the uterus and continues to develop. Additionally, to confirm the diagnosis, the fetal heart rate is listened to, and the size of the fetal egg is assessed in accordance with the term.
In the early stages, in order to exclude ectopic pathology and to confirm normal conception, the vaginal ultrasound method is used, with the insertion of a sensor into the vagina. In this case, the planned first ultrasound is used only at 11-13 weeks of gestation.
Symptoms of intrauterine pregnancy
Despite the presence of clear symptoms, the doctor must make sure that the egg was implanted in the uterus. Because the formation and development of an ectopic pregnancy can lead to rupture of the internal organ in which the zygote was implanted, in the future the situation leads to sepsis and, in the absence of emergency medical care, death is diagnosed.
Distinctive features of a normal pregnancy from an ectopic one
In a woman’s reproductive system, the only place for normal development and gestation of the fetus is the uterine cavity; other organs are not adapted for this purpose. If abnormal implantation of the fertilized egg occurs, an ectopic formation is diagnosed, which can be localized:
- tubal ectopic conception is diagnosed in the fallopian tube, when a fertilized egg, due to pathological reasons, is not able to descend into the uterus.
- in the ovary, implantation occurs due to the fact that the egg is not released from the follicle. This pathology is quite rare in medical practice.
- in the abdominal wall, attachment is observed, both primary and secondary, after tubal fertilization.
- in the cervix, ectopic conception is observed due to impaired functionality of the endometrium of the uterus.
At the beginning of the formation of abnormal fertilization, the symptoms are identical to the normal gestational period, while the hCG level may be significantly lower, which raises suspicion among doctors and becomes the reason for further diagnosis.
Any type of localization of pathological conception is characterized by almost the same symptoms. As the fetus grows and internal organs stretch, bleeding, pain, and subsequent rupture begin. Therefore, an important diagnostic aspect is determining the site of fertilization.
Disturbed intrauterine pregnancy
Disturbed uterine gestation according to ICD-10 is recorded if the pregnancy ended in a miscarriage or the fetus has stopped developing, and therefore medical curettage is prescribed.
To find out the cause of fetal freezing, histology is prescribed - an informative method of studying tissues in order to determine the pathology that caused the impaired conception. At the same time, histological examination does not provide an accurate determination of the factors of frozen pregnancy.
Read more Thrush and infertility
Based on the sent material (pathological tissues after curettage), histologists make, first of all, a micro-description of what was present in the tissues and draw a conclusion. The results may indicate a disrupted intrauterine pregnancy with the detection of chorionic villi, with the presence of blood, mucus or remnants of the fertilized egg.
Subsequently, based on the histological examination, the doctor prescribes additional tests that will more accurately determine the cause of the embryo freezing or miscarriage. The main causes of miscarriage are infectious diseases with sexual transmission, torque infections, hormonal deficiency or other chronic diseases present in the woman.
A progressive pregnancy is a pregnancy that is developing and the baby meets physiological standards. That is, its development occurs according to the established “plan” of nature.
What to do if doctors diagnose a frozen pregnancy?
If, after diagnosis, doctors determine that the pregnancy is regressing, the woman will require treatment. A frozen embryo is a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, which can result in inflammation of the uterus, which will lead to disruption of its contractions. Measures taken after fetal death:
- Scraping. It is done in the early stages of up to 16 weeks in order to prevent infection and the development of the inflammatory process in the female genital organs. During the procedure, the gynecologist also takes chorionic tissue to further investigate the cause of embryo death.
- Introduction of special drugs. At later stages, curettage is not performed, so after 16 weeks, doctors use prostaglandins or antiprogestogens.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy. After removal of the fertilized egg from the uterine cavity, a woman needs to take painkillers and antibacterial drugs.
Signs of advancing pregnancy
The following signs are characteristic of a progressive intrauterine pregnancy.
In the early stages:
- Lack of menstruation;
- Changes in mood due to hormonal changes;
- Changes in taste preferences are observed;
- Irritability;
- Drowsiness;
- Increased sense of smell;
- Temperature rise, but not higher than 37.2;
- Signs of nausea, but no gag reflex;
- Swelling of the mammary glands and pain when touching the nipples;
- Positive pregnancy test or hCG blood test.
Only a gynecologist can confirm or deny a possible pregnancy.
The symptoms of early intrauterine pregnancy are identical to those of pathological ectopic gestation. They can be distinguished in combination with laboratory tests and ultrasound examination.
Ectopic pregnancy is a life-threatening condition for a woman.
Signs of progressive uterine gestation at a later date:
- Active fetal movements.
- Enlargement of the abdomen, according to the gestational period.
The progression of pregnancy is carried out under the supervision of a doctor to prevent the development of adverse consequences.
Symptoms of frozen pregnancy
A regressing pregnancy may not clearly manifest itself for some time and can only be determined by ultrasound performed as planned.
A sign of an undeveloped pregnancy may be the disappearance of such subjective signs of pregnancy as nausea, drowsiness and other early signs of pregnancy. However, these symptoms should not normally accompany a woman throughout her pregnancy. And some people don’t have them at all, so you shouldn’t rely too much on your feelings in this situation. Often the moment of fetal death is elusive.
There may be symptoms of a threatening miscarriage (bloody discharge, nagging pain), but the appearance of these symptoms does not always indicate the death of the embryo, so if you seek medical help in a timely manner, the pregnancy may be able to be saved.
During a gynecological examination, a discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the gestational age is observed.
More valuable are objective indicators such as:
- the level of hCG hormone in the blood - during a frozen pregnancy it decreases sharply. Pregnancy tests after regression may remain positive for several days, and then begin to show a negative result.
- Ultrasound cannot detect fetal heartbeat or movement. An empty fertilized egg (anembryony) may be detected.
If the death of the fertilized egg is detected, the uterine cavity is curetted. Spontaneous miscarriage is usually not expected, since the decay products of the fertilized egg “poison” the mother’s body, cause disruption of blood clotting processes, and can lead to infectious complications.
Even if a miscarriage occurs on its own, it is imperative to do an ultrasound to exclude the retention of parts of the fertilized egg.
Early diagnosis
To confirm the diagnosis of pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo a number of diagnostic procedures, because the initial signs of gestation can be confused:
- with premenstrual syndrome;
- with menopause;
- with an ectopic pregnancy.
Necessary tests
- blood test for hCG - a hormone produced by chorionic tissue after embryonic implantation. Low hCG readings may be an indicator of an abnormal pregnancy. The analysis refers to an enzyme-linked immunosorbent diagnostic method, where the quantitative content of the hormone is determined;
- urine test for hCG, used in an emergency to confirm or deny pregnancy. The method is qualitative, using the necessary reagent.
Medical examination
An examination in a gynecologist's office if pregnancy is suspected is a standard procedure. The doctor conducts a conversation with the patient to collect anamnesis.
Vaginal examination is carried out on a gynecological chair:
- in the speculum: change in color of the cervix (cyanosis is noted), the isthmus is closed;
- palpation of the uterus - superficial and internal. An enlarged uterus indicates a possible pregnancy, which can be confirmed by an ultrasound doctor.
A progressive pregnancy developing in the uterine cavity is confirmed by ultrasound results - transabdominal and vaginal. The vaginal method is used for a period of no more than 10 weeks.
What is visible in the ultrasound machine:
- location of the corpus luteum;
- presence/absence of fertilized egg and its location;
- in addition: the structure and echogenicity of the ovaries, the structure of the uterine cavity, fibroids (if any) and cysts (if any).
Ultrasound diagnostics absolutely confirms whether the pregnancy is progressing and what type it belongs to.
The study also allows us to identify abnormal fetal development in the early stages.
Symptoms
Pregnancy regression can occur at any stage. Up to 85% of all missed miscarriages occur before 12 weeks. In the second trimester of pregnancy, the risk of an unfavorable pregnancy outcome sharply decreases. The shorter the gestational age, the higher the likelihood of genetic damage and the lower the proportion of other causes of regression.
The symptoms of a failed miscarriage have their own distinctive characteristics. First, the woman’s subjective signs of pregnancy disappear. Toxicosis suddenly disappears, the usual nausea and vomiting goes away. The mammary glands become soft and sharply decrease in size. Mood swings, general weakness and increased fatigue persist for a long time.
In the later stages of gestation, regression can be suspected by the cessation of any fetal movements. The baby calms down and does not make itself known for several hours and days. In the period from 16 to 28 weeks, this symptom is quite difficult to interpret. At this stage, fetal movements are not felt clearly enough, so a woman cannot always notice warning signs in time and consult a doctor.
If a dead fetus remains in the uterus for more than 4 weeks, the following symptoms occur:
- fever;
- severe weakness;
- dizziness.
Characteristic changes in the mammary glands are observed 3-4 days after the death of the fetus. In the early stages of pregnancy, only softening and reduction in size of the mammary glands is noted. After 24 weeks, colostrum may be released after fetal death.
2-4 weeks after the death of the fetus, bloody discharge from the genital tract appears, and nagging pain occurs in the lower abdomen. The discharge may be slight or abundant, depending on the stage of the process. Severe bleeding may develop. The longer the pregnancy, the higher the blood loss will be. After the death of the fetus, the woman’s body tries to get rid of its remains, but complete detachment of the fertilized egg does not occur with this pathology. The dead fetus remains in the uterine cavity, which in the future can lead to massive bleeding, infection and sepsis.
Progressive pregnancy after mini-abortion
A mini abortion is the removal of a fetus in the early stages of pregnancy for medical reasons or in case of an unwanted pregnancy. It is carried out using hormonal tablets and using a vacuum device no later than 6 weeks of gestation.
Unfortunately, in some cases, after an abortion, pregnancy progresses.
What does a progressive intrauterine pregnancy mean after a mini-abortion?
This means that termination of pregnancy in the early stages was unsuccessful, and therefore the fetus or its parts continue to grow in the uterine cavity. With such a diagnosis, the termination must be completed.
- lack of qualifications of doctors (especially when performing a vacuum mini-abortion);
- incorrectly selected dosage of the drug;
- non-compliance with the medication regimen or refusal to use them;
- good maternal health;
- the “desire” of the fetus to live.
Read more Bandage a wart with thread
Possible consequences
The development of gestation after an unsuccessful mini-abortion occurs in no more than 5% of the female population, but this condition primarily negatively affects the woman.
- Endometritis;
- Purulent infection of the uterine cavity;
- Sepsis;
- Bacterial shock;
- If you do not seek help in a timely manner, the uterus will be removed due to the development of bleeding and inflammation;
- When deciding to continue the pregnancy, there are severe fetal malformations, often incompatible with life.
Infections
Viral infections pose the greatest danger to the fetus, especially if the mother encountered this infection for the first time during pregnancy. In some cases, when the mother becomes ill, termination of pregnancy is recommended due to the fact that the likelihood of fetal malformations is very high (rubella is best known for its pathogenic effect). For other viral infections (influenza, CMV, herpes), pregnancy is not terminated, but the risk of miscarriage increases sharply.
The risk of miscarriage and sexually transmitted infections, as well as the presence of foci of chronic infection in the body (chronic diseases of the digestive, respiratory, urinary system, carious teeth, etc.) increase the risk of miscarriage.
Progressive pregnancy - ectopic
Progressive ectopic pregnancy is a “doomed” pregnancy, because its development occurs in 95% of cases in the fallopian tube, and the remaining 5% in the abdominal cavity, the development of which stops at 8-9 weeks.
Ectopic pregnancy is a terrible diagnosis for women pursuing the dream of motherhood, but delay in this case costs the life and health of the mother.
Signs of progressive ectopic gestation are similar with the threat of termination, as well as with other pathological changes:
- Bloody discharge after 6 weeks of gestation from the 1st day of the last menstruation;
- Cutting pain in the abdominal cavity and lower abdomen.
- Cramping pain.
It is possible to diagnose an ectopic process after an ultrasound examination.
Possible reasons for failure to get pregnant:
- sexually transmitted infections (STDs);
- infertility (primary);
- pathologies of the pelvic organs;
- hormonal imbalance;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- age;
- incompatibility of partners.
Author: Elena Yuryevna, obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Specially for the site kakrodit.ru
Features of pathology: what does it mean?
Progressive pregnancy can very often develop after a mini-abortion. Statistics show that not all cases end well. With a short pregnancy, the baby has a greater chance of remaining attached. In particular, with a medical abortion, 5% of women can continue to become pregnant. The reasons for this may be:
- Using medications in the wrong order.
- The woman has good immunity and health, the protective function worked, and the fetus remained alive.
- The kid really wanted to live and fought.
Even if the child remains, the abortion is worth completing. Medicines have already greatly affected the development of the fetus. And if you leave him, he can be born with major pathologies and organ defects. When taking this step, you should take the process extremely seriously and follow the instructions of specialists.
Fetal anomalies
This is the most common cause of regression in the early stages. Thus, one might say, “natural selection” takes place. Typically, any harmful factor acting in the early stages causes damage to the fetus of the “all or nothing” type, that is, either the factor does not affect the development of the fetus at all, or causes a pathology incompatible with life, and pregnancy regression occurs. Unfortunately, the number of these harmful factors surrounding us cannot be counted (environmental factors, radiation, unhealthy diet, bad habits, household chemicals, medications, stress), and it is impossible not to encounter them. In the vast majority of cases, nature protects the unborn baby, but sometimes this protection does not work. Most often, it is not possible to specifically determine what caused the harm.
This group also includes a condition called “anembryonia,” when tissue of the fetal egg is determined by ultrasound, but the embryo itself is absent.
The genetic pathology of the fetus can be either accidental, that is, arising only during this pregnancy due to some harmful influence, without which everything would be normal, or programmed, due to genetic disorders in the parents, preventing the birth of healthy offspring (the fetus initially some genetic “damages” are passed on from parents). And if in the first situation the subsequent pregnancy will most likely proceed normally, then in the second, in some cases, the birth of a healthy child may be impossible at all.
The need for ultrasound if such a pathology is suspected
There are cases when a progressive pregnancy is detected in the later stages. When it is no longer possible to have an abortion. There are people who were born with this condition, but they remain disabled for life. Although we are very grateful to be alive. Therefore, during a short period of pregnancy, you should always be examined by a doctor, do an ultrasound, and get tested. You can’t go through your entire pregnancy without going to the hospital, and then just go give birth. This is fraught with consequences.
What is the danger?
A progressive ectopic pregnancy is a great grief for a woman who really wanted a child. But when the fetus begins to develop in the tube, the question arises between the life of the baby and the mother. Doctors have a clear opinion that with a progressive tubal pregnancy it is necessary to terminate the pregnancy. This will save the woman’s life, and it is also not known how the fetus would develop under such conditions.
Still, there are such cases of carrying a child, but they are very few. And in all situations, such courage ended badly for women. Damage to the intestines and other organs, and a caesarean section was always performed before 26 weeks. And this is a very short period for the birth of a child. This may also affect development in the future.
In almost 100% of cases, tubal pregnancy ended before 10 weeks, with tubal rupture and internal bleeding. After this, the tube is removed, and you can’t think about a subsequent pregnancy any time soon. It is worth listening to doctors, they have more experience and practice, it is better to terminate on time than to later lose the opportunity to have a child at all.
Read more Uterine fibroids ICD 10
Signs
What does it mean – pregnancy is progressing? How can you identify this yourself? Let's look at the signs of progressing pregnancy:
- After an unsuccessful termination, you can independently notice that the pregnancy remains. There will be the same nausea, breast swelling and so on. Also, the bleeding will end quickly, and then there may be a delay again. In this case, only an ultrasound can confirm the presence of a developing fetus.
- In the early stages it is very difficult to notice deviations. Contractions and pain in the lower abdomen may appear. With palpation, the doctor may feel a tumor on the side of the uterus. When you press it there will be pain and pulsation. But such a change in the tube may also be old, for example, an inflammatory process of the ovaries.
- If pregnancy hormone levels are low. For an accurate diagnosis, the doctor collects information about menstruation, various diseases, and childbirth. They will definitely do an ultrasound. At 11 weeks, the fetus will be the size of a large egg.
- Bleeding or not heavy, but bloody discharge. In this case, the test will show a positive result. This suggests that the fetus could not attach to the uterus.
- Severe cramping and cutting pain may occur. This is due to compression and stretching of internal organs. Every week the discomfort will get worse.
- Palpable pain in the abdominal cavity. Fainting, which will be a clear sign that a trip to the hospital is required. The pipe becomes severely deformed and may eventually burst. Abdominal bleeding occurs, causing blood pressure to drop and fainting to occur. A pregnant woman becomes very pale, and cyanosis in the form of a hematoma appears in the navel area. This also indicates internal bleeding. After detecting a progressing pregnancy, the woman is immediately admitted to the hospital and undergoes surgery. After an abortion, there is a chance of getting pregnant again. They are not that big, but they are there. Gynecologists also recommend protection with oral contraceptives.
Regressive pregnancy and folk remedies
If there is a threat of a regressing pregnancy, it is recommended to drink Bulgarian, spinach and juices daily, constantly alternating them. It is very useful to eat jam made from green walnuts, which are a source of vitamins C and D.
- To prepare the infusion, take branches that are no thicker than the thickness of the middle finger. Grind the spring bark, take one teaspoon and leave in a glass of water for four hours, boil for five minutes and drink in small portions throughout the day.
- Take equal parts of green pods, lettuce leaves, grains, alfalfa grass and viburnum bark, mix, pour a glass of boiling water over two tablespoons of the resulting mixture. Take half a glass three to four times a day.
- A good anti-inflammatory agent is. To prepare the decoction, pour three tablespoons of chopped inflorescences and leaves into a liter of boiling water and boil for five to ten minutes. Take half a glass three times a day before meals. A 25% tincture is also suitable, which should be taken three times a day, thirty drops.
- Medvedev Yu.M. and Grushko E.A. As a preventive measure for regressing pregnancy, it is suggested to take an infusion prepared from one teaspoon of the root in two glasses of boiling water. Take the prepared infusion an hour before meals, two to three times a day, half a glass. (The authors suggest a higher concentration - one tablespoon of elecampane roots per glass of boiling water).
- Prepare a decoction from the leaves and roots - take three tablespoons of the crushed mass per glass of boiling water. Boil for five to ten minutes, drink half a glass three to four times a day. A 20% dandelion tincture (three to four times a day, twenty-five drops) is also suitable.
To avoid unwanted consequences, you should monitor your health and regularly take decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs, alternating collections.
Collection 1. Infuse one tablespoon of flowers and three tablespoons of crushed dandelion leaves in a glass of boiling water for one hour. Drink the infusion throughout the day.
Collection 2. Take St. John's wort and calendula flowers in equal proportions, pour one tablespoon of the mixture with a glass of boiling water, wrap it and let it brew for an hour. Drink two to three glasses a day a month before giving birth.
Collection 3. Take two parts and one part of peppermint herb. Take half a teaspoon of powder three times a day from the first days of pregnancy.
Collection 4. Take two parts of fruits and one part each of calendula inflorescences, leaves, herbs, St. John's wort, and flowers. Pour one teaspoon of the resulting mixture into a glass of boiling water and drink half a glass of the infusion before bed.
Particular attention should be paid to endangered pregnancies. Causes of regressive pregnancy
- These are primarily diseases of the lungs, kidneys, liver, endocrine glands, as well as diseases of the cardiovascular system. Pregnant women who have a history of premature birth or regressing pregnancy, who have terminated a previous pregnancy, or who have undergone gynecological surgery are also at risk. It should be remembered that these women will require closer attention from the gynecologist observing them.
Vitamin E ensures normal pregnancy. This vitamin is found in yellow, sprouted grains, wheat, rye, liver and chicken yolk.
Folk remedies help increase immunity and physiological stability during the normal course of pregnancy.
- Pour one tablespoon of large seeds into a glass of boiling water and leave for twenty minutes. Take one tablespoon three times a day for a month. After a week's break, you can repeat the course. Seeds can be added a teaspoon to soups or porridges.
- Pour a liter of boiling water over a glass of herbs and use throughout the day as a...
- Leeks have long been considered a symbol of longevity, so you should eat them daily.
- Roast and salt the seeds and eat them.
- For a week, take a decoction of elecampane root three to four times a day. To prepare it, boil one teaspoon of crushed roots in a glass of boiling water for fifteen minutes, and then let it brew for four hours.
- Pour one tablespoon of dried Chinese fruit into a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Take one tablespoon two to four times a day as a tonic and general strengthening agent.
- If an involuntary termination of pregnancy occurs, then dioecious root should be used to regulate the contraction of the smooth muscles of the uterus and blood thickening, as well as as a comprehensive and effective aid. Mixing nettle root and yarrow will help enhance the effectiveness. Drink the decoction three to four times a day, one tablespoon.
- Cardiac is used as a sedative and strengthening agent. To prepare the decoction, take two tablespoons of the herb in a glass of boiling water, boil for ten to fifteen minutes and drink one or two tablespoons three times a day.
- For interrupted pregnancies and various types of childbirth, a decoction of shepherd's purse herb is used. It has a hemostatic and contractile effect. You need to take two tablespoons of the herb per glass of boiling water, drink the decoction three times a day, one tablespoon at a time.
Regressive (frozen) pregnancy: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Women faced with such a misfortune as a frozen pregnancy have a number of questions: what are the causes and consequences of this phenomenon, is it necessary to undergo treatment, will pregnancy be normal after a frozen pregnancy, and does this always happen in the early stages, or does it also happen at a later stage? ? We will try to answer all these questions in this article.
Main symptoms and diagnosis of regression in early pregnancy
Symptoms of a frozen pregnancy may not appear in any way in the early stages. Some women notice that pain in the mammary glands disappears and signs of toxicosis disappear. A little later, about 2-3 weeks after regression, bleeding, cramping pain may appear and a miscarriage may occur.
A gynecologist can diagnose a non-developing pregnancy at the first examination, if its duration is more than 4-5 weeks. The doctor calculates the duration of pregnancy and if, upon examination, the uterus is smaller than it should be at this stage, then he urgently sends you for an ultrasound. If a woman comes to the gynecologist not for the first time during pregnancy, then the doctor may be confused by the lack of uterine growth over a certain period.
In addition to a gynecological examination and ultrasound examination, symptoms of a condition such as a frozen pregnancy can be manifested by a lack of growth of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in the blood. This can be easily noticed by both the woman herself and the doctor if the pregnancy is initially under strict medical control and the dynamics of hCG growth are taken into account.
With an ultrasound examination, the doctor may suspect a non-developing pregnancy if there is no heartbeat at more than 4.5 weeks or the size of the embryo does not correspond to the gestational age. In this case, a control ultrasound is performed after 7-10 days. And if the situation does not change for the better, then such a pregnancy is considered regressive and appropriate treatment is prescribed in order to reduce the likelihood of negative consequences for the body, and so that the next pregnancy (after a frozen one) goes well.
Causes of non-developing pregnancy
The most common cause of regression is anomalies in the development of the fetus, some kind of “breakdown” in the genetic code. Nature itself rejects potentially unviable children. If this is the reason, then you don’t have to worry - there is a very small percentage that history will repeat itself.
Another reason is teratogenic factors, which can not only provoke a non-developing pregnancy, but also all sorts of pathologies in the child (if he is still born). These factors include taking certain medications, dangerous food additives (some preservatives) and even bad habits (smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages).
Another possible reason for regression is hormonal imbalance. If during pregnancy the concentration of male hormones (testosterone) sharply increases, this can cause pregnancy to fail, not only in the early stages, but also in the later stages, in the second trimester.
Often the cause of regression is sexually transmitted infections: chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, herpes type II, mycoplasmosis, etc. It is very dangerous for pregnant women to become infected with toxoplasmosis, chickenpox, and rubella. Because of them, a frozen pregnancy can occur even in the second trimester.
How to carry out treatment and is it necessary?
First, let's talk about tactics for managing a non-developing pregnancy. If regression is confirmed, depending on the duration of pregnancy and some other factors, the doctor may suggest expectant management (if the pregnancy is very short), that is, wait until a spontaneous miscarriage occurs. True, in Russia they rarely do this. But in European countries, on the contrary, “cleansing” is carried out extremely rarely, and during the period of waiting for spontaneous termination of pregnancy, they simply carefully monitor the woman’s health.
If pregnancy is up to 8 weeks, it is possible to terminate it with medication, without surgery. If the period is over 8 weeks, then curettage of the uterine cavity is performed.
In case of late regression (over 16 weeks of pregnancy), labor is artificially induced.
The tactics of further treatment depend on the reasons that caused this pathology. If these are infections, then they must be treated before the next pregnancy. If the problem is with hormonal levels, then you need to undergo a full examination and normalize the situation. If the problem is genetic, then both spouses need to be examined by a geneticist.
Remember that abnormal cessation of intrauterine development of an embryo or fetus is not a death sentence. This happens to thousands of women and most of them go on to have healthy children of their own.
Unfortunately, such a diagnosis as “frozen pregnancy” (regressive pregnancy) is not so rare (up to 15% of all pregnancies that occur). And probably everyone has heard about him. And many women, even with a normal pregnancy, sometimes worry about the question “What if... And how will I know?!”
In fact, the diagnosis of regressing pregnancy indicates that until a certain period the pregnancy developed normally, and then for some reason the fetus died and the pregnancy stopped developing. And although this can happen at any stage, in the vast majority of cases, pregnancy regression occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Causes
Let's look at some more reasons for the occurrence of uterine progressive pregnancy:
- With frequent pelvic surgical operations, adhesions and scars begin to form inside, which form a film. It is she who can prevent the fertilized egg from entering the uterus.
- Tumors in the area of the uterus, ovaries and pelvis, having a benign or malignant basis.
- When using hormonal drugs, an imbalance of hormones in the body may occur.
- Consequences of using an intrauterine device.
- Inflammatory processes of the urinary system.
- A large number of sexual partners.
- Long-term infertility.
- Pregnancy after 40 years.
- Abnormal structure of the pelvis.
Diagnostics
Girls who are predisposed to such a pregnancy should receive a correct diagnosis of their condition. The following procedures are carried out:
- During a small pregnancy, even an ultrasound is not always able to make a correct diagnosis, so doctors use blood tests for hCG. During intrauterine pregnancy, the amount of the substance will be sufficient and will increase every few days. And with an ectopic pregnancy it will be much lower.
- In the later stages, an ultrasound examination can show the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, which indicates internal hemorrhage. This requires urgent surgery.
- Sometimes pregnant women may be prescribed laparoscopy, which can confirm the diagnosis and immediately eliminate the problem, remove the embryo, without heavy surgical intervention.
Necessary examinations after a regressing pregnancy
The minimum examinations after a regressing pregnancy include:
— Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
— Blood test for hormones (usually a test for sex hormones is taken, a test for other hormones is taken if there are any symptoms indicating a possible disruption of the hormone-producing organs);
— Analysis for infections;
— Spermogram (the child has two parents; the reasons for a regressive pregnancy can be found not only in the mother).
This list can be significantly expanded depending on the specific situation; it should be individual for each woman, depending on the results of a general examination, the nature of menstrual function, heredity, and the presence of any diseases in the past or present.
For repeated regressing pregnancies, the examination is more detailed. An examination for antiphospholipid syndrome and a study of the karyotype (set of chromosomes) of the father and mother are required.
Treatment
How to treat progressing pregnancy? There are two ways:
- The first method is surgery, termination of pregnancy. But in a gentle way - laparoscopy. In this procedure, part of the organ is removed along with the embryo. After this, the woman may well become pregnant again.
- The second method is done in late pregnancy. In this case, as a rule, the pipe may already rupture and there will be bleeding. In this case, a completely damaged organ with an embryo is recovered. After such an operation, it is difficult for a woman to become pregnant again.
Consequences
After a frozen pregnancy, a woman faces two problems:
1. Chronic endometritis . The main danger that awaits a woman after all the manipulations performed is the development of an inflammatory process in the uterine cavity. The result of a regressing pregnancy is often chronic endometritis. In this condition, the menstrual cycle is disrupted and acyclic bleeding from the genital tract occurs. Chronic pelvic pain may occur. Chronic endometritis can significantly complicate a woman’s life and cause poor health in the future.
Sluggish inflammation of the uterine mucosa is dangerous not only because of its unpleasant symptoms. Against the background of chronic endometritis, secondary infertility often develops. The damaged endometrium becomes thinner, and the fertilized egg does not find a place for implantation. Miscarriage occurs in the early stages of pregnancy. Even if the embryo takes root, in the later stages endometritis becomes the cause of placental insufficiency, leading to the formation of chronic hypoxia and delayed fetal development.
2. Hormonal imbalance . Failure of the menstrual cycle is another common complication after a regressive pregnancy. Sharp changes in hormone levels mean that the body cannot always recover on its own. The ovaries do not begin to function fully. There is a delay in menstruation, intermenstrual bleeding appears. Endocrine disorders in a woman's body can also lead to infertility.