Causes
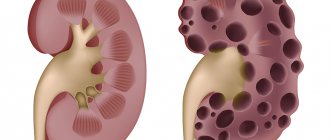
Urates are a type of stones that are formed during urolithiasis as a result of metabolic disorders of uric acid, sodium and potassium, which precipitate. Physical properties of urates:
- color from yellow to brown;
- smooth surface;
- form in the kidneys, bladder and ureter;
- can form conglomerates, acquiring a coral-like shape;
- create preconditions for the development of pyelonephritis and renal failure.
The main reason for the formation of urate stones is a disruption in the process of formation and excretion of urea, sodium and potassium. Metabolic disorders can be a genetic pathology and can be inherited.
Also, the formation of urates is caused by poor nutrition, lack of B vitamins, low fluid intake or poor quality. Long-term use of certain medications can also lead to sedimentation of urea, potassium and sodium in urine.
The external environment also negatively affects the human condition: hot living conditions, difficult and harmful working conditions, a sedentary lifestyle, bad habits and diets disrupt metabolism and lead to the formation of stones in the urinary system.
The acidity of urine plays a major role in the formation of urates. In some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, acidification of urine may occur (acidity changes), resulting in sedimentation of urea, potassium and sodium in the organs of the urinary system.
How to dissolve urate stones in the kidneys?
For diagnostically confirmed uric acid stones, groups of medications are used that affect the formation, growth and breakdown of urates:
- Xanthine oxidase inhibitors inhibit the active enzyme that converts uric acid.
These include the anti-gout Allopurinol and its analogues: Allozyme, Allopin, Zilorik, Milurit, Remid, Sanfipurol.
Allopurinol
- Uricosuric drugs inhibit the absorption of uric acid in the renal tubules, thereby promoting its excretion in urine and through the intestines.
They require sufficient fluid intake into the body, thereby increasing the load on the kidneys.
Represented by Benzobromarone and analogues: Dezurik, Hipurik, Urinorm, Etamid.
- For the treatment of renal lithiasis - the destruction of uric acid stones - the complex drug Blemaren, consisting of citric acid, potassium bicarbonate, and sodium citrate, is widely used.
Capable of alkalizing urine to 6.6-6.8 pH - the most suitable conditions for the breakdown of uric acid urates.
Its complete analogues: K-Na hydrogen citrate, Soluran; incomplete: Marelin, Magurlit, Urodan.
The choice of a drug to destroy stones and inhibit the process of lithiasis is made by the attending physician after assessing the state of the function of the urinary system, determining the nature and size of the stone, and existing concomitant diseases.
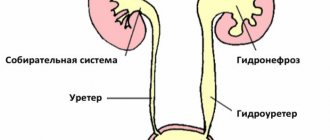
Unauthorized prescription of diuretics threatens the stone to move from its place, blockage of the ureter, the development of acute renal colic and subsequent infectious inflammation.
Lack of results of conservative therapy, large urate are indications for:
- minimally invasive - using pinpoint punctures in the kidney - surgical interventions: laparoscopy, nephroscopy;
- contact lithotripsy - through natural orifices. Using a urethroscope, it is possible to detect, crush with a laser beam and remove uric acid stones from the ureter.
Abdominal surgery is indicated only for giant coral-shaped urate stones and in cases where gentle methods are unavailable or contraindicated.
Signs
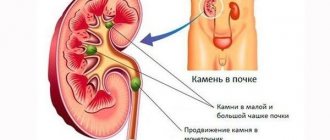
With urate stones, the clinical picture may be completely absent. The first signs most often appear when stones reach large sizes or when they move through the organs of the urinary system. The first sign of the disease is pain in the lumbar region. The movement of urates is accompanied by renal colic (sharp girdling pain, which may be accompanied by vomiting, chills and fever).
Changes in the physicochemical properties of urine should also alert the patient. With urolithiasis, the urine changes color. Reddish color, impurities and streaks of blood indicate the movement of solid formations. The loss of a white precipitate may be a sign of the onset of the development of an inflammatory process in the kidneys as a result of stagnation of urine.
The process of urination itself is also disrupted: the number of urges increases, the volume of urine decreases, the process of emptying the bladder is accompanied by pain, cutting and burning in the groin area and lower abdomen.
An alternative method to get rid of kidney stones
A modern non-surgical method for the destruction of urate stones of directed action is external shock wave lithotripsy.
Ultrasonic pulses pass through tissues unhindered; the focused energy impact is applied only to the working area - the calculus, provoking vibration and subsequent collapse of its crystal lattice.
Subsequently, urate stones, destroyed to the state of small fragments and sand, are excreted naturally through urine.
Performing lithotripsy
Indications for extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy are:
- stones ranging in size from half a centimeter and not exceeding two centimeters in diameter;
- the possibility of their visualization;
- renal colic due to urate movement.
The procedure is not indicated for:
- the presence of acute purulent infections;
- impaired blood clotting ability or taking anticoagulants;
- obesity degree III-IV;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- concomitant pathologies at the stage of decompensation;
- monthly expirations;
- detection of oncology;
- during the period of bearing a child.
Rehabilitation treatment after the procedure includes, if indicated, painkillers, prophylactic use of antibacterial agents or phyto-antiseptics.
It is necessary to observe a drinking regime: up to one and a half to two liters of liquid per day to facilitate the excretion of sand and small fragments with urine.
Diagnostics
Urate kidney stones are more common in patients aged 20 to 50 years, among whom men predominate. To diagnose stones of urate origin, laboratory and instrumental research methods are used.
During diagnosis, it is important to do a urine test. The presence of stones will be indicated by sediment, color, density and acidity. Important indicators are protein, red blood cells and white blood cells. An increase in the level of the latter may be a sign of the onset of the development of inflammatory pathologies of the urinary system.
A blood test will help determine the general condition of the patient. During diagnosis, special attention is paid to the presence of leukocytes and changes in erythrocyte sedimentation rate. An increase in these indicators indicates the presence of inflammatory diseases of various nature in the patient.
The nature and location of stones can be determined using ultrasound. An ultrasound machine allows for good visualization of urate stone. Less commonly used is magnetic resonance therapy or computed tomography.
If there are indications or insufficient data obtained during ultrasound, the patient is sent for urography. This is one of the methods for examining the kidneys using x-rays after intravenous administration of a contrast agent.
Diseases and possible complications
An exacerbation often begins suddenly, when a fragment of a stone enters the ureter.
The pathology does not give visible manifestations for a long time, being asymptomatic. An exacerbation often begins suddenly when a stone fragment enters the ureter. Renal colic occurs, accompanied by the following accompanying symptoms:
Apaan Mudra for the treatment of diseases and restoration of the kidneys
- intense pain in the lumbar region of a unilateral or encircling nature;
- irradiation of pain along the urethra, radiating to the inner thigh, lower abdomen and genitals;
- the pain is difficult to relieve, and the most effective are antispasmodic (relaxing the smooth muscles of the urethra) drugs;
- the condition is accompanied by reflex reactions of the body: fever, chills, sometimes nausea, single vomiting;
- the patient cannot find a suitable position that alleviates the condition.
If the ureter is not completely blocked, the urine may turn pink, which indicates significant damage to the urethral mucosa by the stone.
Complications of urate nephrolithiasis include excessive growth of stones with the formation of coral stones, paralyzing renal activity and leading to uremia - intoxication of the body with nitrogen-containing substances (urea, uric acid). Injury to the mucous membrane of the pelvis or ureters from stones can cause inflammation with the possible addition of a bacterial infection. In this case, complications of nephrolithiasis include pyelonephritis (sometimes purulent) and urethritis.
Treatment
Treatment of urate kidney stones is based on compliance with medical recommendations regarding nutrition, drinking regimen, physical activity and medication. If indicated, the doctor recommends crushing the stones through surgery.
Diet
For kidney stones of urate origin, a special diet is prescribed, which helps normalize metabolic processes. The foods consumed should balance the salt balance and change the acidity level of the urine. This will help dissolve the stones in the urine.
If you have urates, it is recommended to avoid pork, veal, their offal and fish. It is also not recommended to use strong meat broths. Canned, salty, smoked and sweet foods are prohibited.
Sour fruits, vegetables and berries are prohibited (cabbage, sorrel, spinach, raspberries, cranberries, figs and others). Mushrooms, sweet baked goods, coffee and cocoa-containing products are prohibited during treatment.
You can replace prohibited foods with dairy, nuts and seeds, eggs, cereals, sweet fruits and vegetables.
Drinking regime
It is also important to drink more than two liters of water. A sufficient amount of liquid helps wash out and dissolve the stones. Mineral water should be alkaline, which helps reduce urine acidity.
It is important to know that alkaline water is used exclusively in the presence of uric acid stones. Alkaline waters are contraindicated for stones of phosphate, cystine, oxalate, and xatine origin.
Drug treatment
The urologist prescribes medications to dissolve kidney stones. This type of stones is most easily amenable to gentle drug therapy. Effective remedies are Fitolit, Urolesan, Phytolysin and Citrate ointment.
Phosphates
The main component of such stones is calcium salts of phosphoric acid.
Formations can be detected during X-ray radiation.
The stones have a loose structure and a smooth surface, which eliminates the possibility of injury to internal organs.
The color of phosphates varies from grayish to white.
The main reason for the appearance and growth of phosphates are infectious diseases occurring in the urinary system. The vast majority of infections enter the urinary tract from the intestines. Thus, the acidity of urine changes sharply and becomes alkaline, which leads to the development of pathology.
Why are phosphate kidney stones dangerous? Doctors say the main danger of phosphates is their growth rate. As a result, the calculus fills the entire cavity of the kidney.
Diet for phosphate stones
In such a situation, the only possible method of treating the pathology is surgery, and even removal of the kidney. The technique of crushing formations is also successfully used, this is due to their fragile structure.
Specialists often use phosphates in the treatment of their ability to dissolve as a result of changes in the acidity of urine. To do this, it is recommended to use special mineral waters, medications and adhere to a therapeutic diet.
The causes of urolithiasis are often hereditary.
Symptoms of kidney stones
— diagnosis of the disease, pathogenesis of stone formation. Let's consider possible complications - cystitis, urethritis, renal failure.
Kidney stones can form due to metabolic disorders. Read about what factors cause predisposition to the disease in this article.
Prevention
The main preventive measure is sufficient consumption of clean water - 2 or more liters per day. Alkaline mineral water is recommended to cleanse the body and improve metabolic processes.
It is important to eat right, avoid frequent consumption of fatty, canned, salty, smoked foods. Minimize carbonated sweet drinks, coffee, cocoa and foods high in cocoa.
An active lifestyle plays an important role, which helps to cope with congestion in the body and improve metabolism.
Urates are one of the most common types of stones in urolithiasis. Formed as a result of metabolic disorders of urea, potassium and sodium. The formation of stones is accompanied by pain, difficulty urinating and gastrointestinal disorders. The basis of treatment is diet and sufficient water intake. Medicines are widely used to dissolve urates. If indicated, surgery to crush the stones is necessary.
By what methods are they identified?
The most common method for diagnosing the presence of kidney stones is ultrasound. It clearly shows the size and location of the stone. The only drawback of this method is that it is impossible to determine from ultrasound whether it is a urate stone or some other one. Therefore, a number of additional studies are prescribed :
- General blood analysis. Indicates the possible presence of inflammatory processes (if the level of leukocytes is elevated).
- Analysis of urine. It is used to determine the pH level (acidic, alkaline, neutral). Also, an increased level of white blood cells in the urine may indicate an infection.
- X-ray using contrast agents. A regular x-ray “does not see” urate, and therefore it is necessary to introduce contrast.
- CT (computed tomography). Allows you to determine the density of the formation and, accordingly, its chemical composition.
- Urography – x-ray of the urinary tract.
It is worth noting that a 100% chemical analysis of the stone can only be done after it has been scraped or removed .
Uric acid and nutrition
Uric acid usually dissolves in the blood, but when it doesn't, crystals form in the urine. Uric acid crystals may clump together to form deposits in the kidneys or urinary tract, may also be removed in the urine, or in other cases these crystals will settle in the joints causing a very painful condition known as gout.
When these problems arise as a result of high levels of uric acid in the blood, in addition to the indicated treatment, you need to take special care of your diet, since most of this acid comes from the food consumed.
Foods to lower uric acid levels
Foods low in uric acid include rice, tapioca, artichokes, pumpkin, beets, corn, flour, bread, grains, pasta, beets and onions, eggs (no more than three per week), sugar and its derivatives, coffee , tea and low-fat dairy products, potatoes (peeled only), cereals, carrots, beets, cucumbers, pumpkin, green apples, watermelons, lemons, white cabbage, onions, garlic (daily), dill, olive oil and other vegetables, bread (white, black), eggs (up to 3 pieces per week), You can eat lean beef or poultry: chicken, turkey, rabbit (cook until foam appears, drain the water, fry and cook in foil; meat can be baked in the same way with fish), preferably fried, in the oven or on the grill but in moderation, avoid eating meat every day. Consuming plenty of pineapple helps reduce and control uric acid levels. It is important to drink as much water as possible per day, green tea if possible, more than 2 liters, as water helps flush uric acid crystals from the body and prevents them from accumulating and forming stones.
| Next > |