Discharge during ectopic pregnancy
When the egg is fertilized, the menstrual cycle stops, and therefore when a pregnant woman bleeds, this is a manifestation of a developing pathology. In the case of an ectopic fetal location, such bleeding that begins in the early stages is an opportunity to avoid dangerous pathologies in the future.
Brown
Dark bleeding with a characteristic smell of metal, salt (blood) indicates the development of a dangerous condition that is associated with a wide area of organ damage. To delay hospitalization means putting your own life in danger. If the fetus is attached to the peritoneum, then it is practically impossible to stop the bleeding; blood loss in this case is irreparable.
Bloody
Bleeding mixed with mucus and brown smears also means the development of a complex pathology. It is important to remember that spotting, even with repeated frequency, is a manifestation of the presence of internal bleeding.
Mechanism of occurrence and classification of ectopic pregnancy
After the fusion of male and female gametes (sperm and egg), active division of the resulting mass begins. Slowly but surely the zygote moves into the uterine cavity. This is where the fertilized egg should take hold, according to the rules of physiology. But this is not always the case.
For certain reasons, the fertilized egg does not enter the uterus, but remains in the fallopian canal. In this case, a tubal pregnancy develops. If the zygote is pushed back, the embryo may implant in the ovary or abdominal cavity. Less often, it happens that the fertilized egg bypasses the reproductive organ and becomes fixed in the cervical canal (cervical pregnancy).
Menstruation during ectopic pregnancy
A regular menstrual cycle during pregnancy occurs in only 20% of women. But, this phenomenon is diagnosed 50% more often with ectopic implantation of the fetus. It all depends on the location of the fetus. If the fetus is located in the abdominal part, then the menstrual cycle is observed for up to two months.
Differences between menstruation and bleeding:
- hCG in the blood is increased;
- menstruation occurs as usual, while bleeding is constant;
- there are painful spasmodic symptoms;
- pain in the lower abdomen radiates to the back, left or right side;
- A positive test result is a sign of the presence of a fertilized egg in the body.
Early symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
When do early symptoms of ectopic pregnancy appear? If a woman has a regular menstrual cycle, this pathology can be suspected if a delay in menstruation occurs. However, an ectopic pregnancy that continues to grow and develop is practically no different from a pregnancy that is in the uterus in the early stages. The patient usually notes the following first symptoms of ectopic pregnancy:
Firstly, this is an unusual regular menstruation - its delay or scanty periods. Secondly, mild or moderate nagging pain due to stretching of the wall of the fallopian tube due to the growth of the fertilized egg. The test for an ectopic pregnancy is most often positive.
- women report a delay in menstruation in 75-92% of cases
- pain in the lower abdomen - 72-85%, both mild and intense
- bloody discharge - 60-70%
- signs of early toxicosis (nausea) - 48-54%
- enlarged and painful mammary glands - 41%
- pain radiating to the rectum, lower back - 35%
- positive (not for everyone) pregnancy test
The erroneous opinion of many is that if there is no delay in menstruation, then the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy can be excluded. Very often, spotting vaginal discharge during ectopic pregnancy is perceived by some women as normal menstruation. According to some authors, VD can be detected in 20% of cases before a missed period. Therefore, a thorough history taking and a complete examination are very important for the timely establishment of this diagnosis.
During an examination by a gynecologist, he reveals cyanosis and softening of the cervix, an enlarged, soft uterus (the first signs of pregnancy). When palpating the appendage area, it is possible to identify an enlarged and painful tube and/or ovary on one side (tumor-like formations in the appendage area - in 58% of cases, pain when trying to deviate the uterus - 30%). Their contours are not clearly palpable. When palpating a tumor-like formation in the appendages, the doctor compares the size of the uterus and the period of delayed menstruation (an obvious discrepancy) and prescribes additional research:
- Ultrasound of the internal organs of the genital area
- Analysis for hCG and progesterone content
- The progesterone content during an ectopic pregnancy is lower than during a normal pregnancy and there is no increase in hCG after 48 hours if the pregnancy is ectopic
An ectopic pregnancy interrupted by a tubal abortion is characterized by a typical triad of symptoms and signs:
- pain in the lower abdomen
- bloody discharge from the genital tract
- as well as delayed menstruation
Pain in the lower abdomen is explained by an attempt or pushing of the fertilized egg from the fallopian tube. Hemorrhage inside the tube causes its overstretching and antiperistalsis. In addition, blood entering the abdominal cavity acts on the peritoneum as an irritant, which aggravates the pain syndrome.
A sudden, dagger-like pain in the iliac regions against the background of complete health helps to suspect a tubal abortion. Pain, as a rule, occurs after 4 weeks of delay of menstruation, radiates to the anus, hypochondrium, collarbone and leg. Such attacks can be repeated repeatedly, and their duration ranges from several minutes to several hours.
No discharge
In the early stages, the formation of bleeding of any intensity is observed in 85% of cases. Diagnosis becomes more difficult in the absence of blood discharge, since there is no suspicion of the presence of an alarming pathology, the woman does not suspect a dangerous situation.
Bleeding is almost always observed in the later stages after the 7th week. At this stage of development, the fetus is quite large, which leads to rupture or deformation of internal organs.
Bleeding during this period is profuse, with characteristic pain:
- abdominal muscle spasm;
- aching pain radiates and presses on the rectum;
- the temperature rises;
- pressure decreases.
Laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy
The laparoscopic method is an innovative solution with minimal trauma. Laparoscopy is often used to diagnose and remove ectopic pregnancies. The intervention is performed under general anesthesia.
Advantages of laparoscopy:
- Lasts from 15 minutes to an hour.
- Minimal stress for the body.
- Minor blood loss.
- Minimally invasive.
- Adhesions practically do not form.
- Fast recovery.
The main advantage of this procedure is that in most cases the tube can be saved, and the woman can then get pregnant normally and give birth without any problems.
- Preparing for surgery
If there are no acute symptoms of pathology, then preoperative preparation is carried out. This is necessary so that there are no complications during the operation. After all preparatory procedures have been completed, doctors begin the operation.
Preparation includes:
- Collection of analyses.
- Refusal to eat and drink on the eve of the procedure.
- Cleansing enema.
- Wearing compression stockings.
If laparoscopy is an emergency, no preparation is required.
- Stages of the operation
The operation takes place in several stages, and in total lasts from 20 minutes to an hour. First, the patient is given local or general anesthesia, depending on the indications. The operated area is disinfected with an antiseptic. After which several small incisions are made: periumbilical and on both sides of the iliac region.
Then doctors use a special device to fill the peritoneum with carbon dioxide. Then the laparoscope is inserted into the incision near the navel, and into the other 2 - along the trocar. A laparoscopic device shows the doctor the entire area of the pelvic organs and abdominal cavity. Using trocars, the egg is separated from the tube.
Next, blood clots are removed and the operated area is washed. And again the pelvic organs are examined to eliminate defects. At the final stage, the instruments are removed from the peritoneum. The incisions are closed with a cosmetic suture, and carbon dioxide is released. The patient is then awakened.
- Recovery and aftermath
If the operation went well, without negative consequences, then recovery is very fast. In the first hours, there may be slight pain, fever, and bleeding. Typically, a woman stays in the hospital for no more than ten days with normal recovery.
If there are complications, the recovery process can last 4 weeks, but no longer.
In the first 24 hours, the patient still feels the effect of anesthesia, so it is necessary to maintain bed rest. You can drink a lot towards the end of the day. The woman is under medical supervision for approximately seven days. There may be pain and discomfort as some gas still remains in the peritoneum. After five to six days, the stitches are removed and the woman is discharged home.
At home, you need to take antibiotics as prescribed by your doctor and follow a diet. It is necessary to avoid foods that cause gas, fried, spicy, sour foods, as well as drinking alcohol and smoking.
Causes
At the moment of attachment of a fertilized egg to unadapted organs, changes occur both physiologically and hormonally. Under the influence of hormones, the egg develops, a zygote is formed, then a fertilized egg and an embryo.
The size of the embryo at the 5th week is 1-1.25 mm, and already at the 7th week the size of the fetus is 0.8-1.5 cm. If the attachment occurs in a thin place in the fallopian tube of the ovary, then such dimensions rupture the organ and bleeding occurs .
During pregnancy, discharge with blood is a manifestation of the pathological course of fetal development. However, with ectopic localization, such a manifestation in the early stages of gestation is the life of the mother, who promptly identified the danger and sought medical help.
Tubal pregnancy: causes
In general, ectopic attachment of the ovum occurs in two percent of all cases. However, tubal pregnancy occurs in 97% of them. In half of the situations, the reasons for this outcome remain unknown. But gynecologists identify risk factors that can lead to the described pathology. Let's look at them.
- Operations performed on the abdominal organs. If a woman has previously had surgical interventions, this may cause the formation of adhesions. These films, in turn, prevent the normal progression of the fertilized cell.
- Incorrectly selected contraception. If you use oral hormonal drugs in an inappropriate dose, then conception may occur, but the embryo will not develop properly. Tubal pregnancy also occurs when using intrauterine devices.
- Infectious diseases and pelvic inflammation. These pathologies (even in history) lead to deformation of the reproductive organs, hormonal imbalance and the formation of adhesions. The fallopian tubes become thinner and the internal villi stop functioning properly.
- Neoplasms. If there are fibroids, polyps or ovarian cysts in the uterus, then the entire process of conception is disrupted. Therefore, there is a high probability of attachment of the fertilized egg outside the cavity of the reproductive organ.
- Abnormalities of the genital organs. Often, an ectopic (tubal) pregnancy occurs with congenital or acquired pathologies of the pelvic organs (the presence of a septum, adhesions, a bicornuate uterus, and so on).
Features of discharge
When a woman becomes pregnant, she should be very careful about what kind of vaginal discharge is observed. It is with their help that it is possible to identify various pathologies associated with gestation, even before the appearance of other possible symptoms. If there are no violations, there should be no discharge during all months of pregnancy. The norm is clear or white mucus from the vagina during the first weeks of pregnancy, which is associated with changes in the woman’s hormonal levels. The photo below shows what normal discharge should look like.
Uterine bleeding can be a reason for forced abortion. In this case, the blood may indicate detachment of the fetus or a rupture of the walls of the organ in which it was located.
The nature of the discharge differs from that observed during normal menstruation. They can appear on any day, regardless of when your last menstruation was. In case of detachment of the fertilized egg, they are usually scanty and spotty. And if the tissues are torn, then blood appears suddenly and flows profusely.
Signs of pathology
What are the symptoms of tubal pregnancy? This question interests many women. Clinical manifestations are divided into primary and secondary. At first, the symptoms are no different from those that appear during normal pregnancy. But later signs appear that signal a pathological process.
Until 5-7 weeks, a woman may feel nausea, sometimes accompanied by vomiting. Increased fatigue and drowsiness occur. There is a delay in menstruation, and a pregnancy test shows a positive result.
With the onset of 4-8 weeks, additional symptoms appear. They should alert a woman and become a reason to see a doctor. Among these manifestations:
- pain (pulling sensations in the lower part, radiating to the back or leg; lumbago);
- bleeding from the genital tract (more often the discharge is spotting and is associated with a decrease in progesterone levels).
How not to confuse it with menstruation?
Typically, discharge during an ectopic pregnancy is of a different nature compared to menstruation. They can be more scarce or more abundant, which depends on what specific reason provoked their appearance - a pipe rupture or fetal detachment.
Moreover, such discharge most often appears after a short or rather long delay in the menstrual cycle. If your period does not come on time, this is a reason to consider and undergo a pregnancy test or examination by a doctor. If, after taking tests, progesterone or hCG is detected in the blood, it means the woman is pregnant. Discharge indicates either an ectopic pregnancy or a threatened miscarriage. Therefore, in any case, after such “months” you should consult a doctor.
It’s another matter when they appeared at the same time when menstruation was supposed to begin, and the woman did not know about the pregnancy. In this case, it is difficult not to confuse them with menstruation. If their color, character, smell have changed, or pain has appeared, it is advisable to consult with specialists.
Methods for diagnosing ectopic pregnancy
How is an ectopic pregnancy or tubal abortion determined by doctors? To make a correct diagnosis, specialists conduct a series of studies. Among them are the following:
- Gynecological examination. When a patient presents with the described gutters, the doctor first performs palpation on the chair. At the same time, the size of the reproductive organ is noted and the ovaries are palpated. In some cases, the doctor can determine the presence of a neoplasm (fertilized egg) between the uterus and ovaries. After such an examination, only a preliminary diagnosis is made, since it is not yet possible to say for sure whether it is a tubal pregnancy or another pathology.
- The next stage of diagnosis will be ultrasound examination. After this the picture becomes clearer. During the procedure, the specialist measures the uterus and ovaries and compares the data obtained with the established day of the cycle. In an ectopic pregnancy, the reproductive organ does not correspond to the gestational age. Also, the fertilized egg is not detected in the uterus. At 7-10 weeks, the doctor can quite clearly see the location of the embryo.
Diagnosis of tubal abortion is more complex; it requires a thorough history taking, examination of the patient (objective and vaginal examination, bimanual examination, determination of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood serum, ultrasound, laparoscopy). A differential diagnosis is often required.
Discharge due to ruptured fallopian tube
2-3 weeks after the embryo has taken root in the fallopian tube, it increases in size, which leads to an expansion of its diameter. Over time, nagging pain occurs on the side where the fetus is localized. Every week these sensations become more pronounced. Read more in the article “Pain during ectopic pregnancy.”
If the fetus is not removed in time, it develops, and after reaching a critical size, it leads to rupture of the fallopian tube. The result is sudden and copious discharge of blood. Moreover, the woman’s well-being worsens, chills begin, and severe pain occurs. After a couple of hours, the tissues of the organ itself emerge from the vagina. In this case, urgent hospitalization is necessary, otherwise there is a risk of death.
Ectopic pregnancy is a dangerous pathology for which timely diagnosis is important. It is fraught with reproductive dysfunction and poses a direct threat to life. You need to know the main signs of pathology, the nature of the pain, what discharge appears during an ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy.
Gentle method: laparoscopy
Laparoscopic surgery has become the most popular in recent years. It involves two to four punctures in the abdominal cavity. Laparoscopy allows not to completely remove the fallopian tube, but only to excise its damaged area. This operation is called a tubotomy.
This method is selected taking into account the age, condition and wishes of the patient. Preserving the fallopian tube allows you to preserve reproductive function in the future. However, if an ectopic pregnancy recurs, complete removal of the fallopian canal is indicated.
The peculiarity of ectopic pregnancy
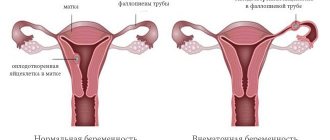
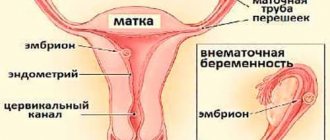
Ectopic pregnancy on the diagram
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy in which the embryo implants outside the uterus. Most often, the place of attachment is the fallopian tube, less often - the cervix, ovary, or abdominal cavity.
According to statistics, ectopic pregnancy occurs in 10–15% of women. During normal gestation, the egg is implanted in the uterus and develops where there are conditions for this. But ectopic pregnancy has its own peculiarities.
- Under the influence of certain factors, the fertilized egg does not enter the uterus and is attached to another organ. Most often this is the fallopian tube, which is associated with a violation of its patency.
- With ectopic growth of the fetus, the organ stretches, its walls may not withstand it. A rupture is possible, which is accompanied by red discharge and internal bleeding. This is a life-threatening condition, so it is better to prevent it in advance.
- In case of ectopic tubal conception, the egg can be attached in different parts: abdominal (ampullary location), middle (isthmic), terminal (interstitial). The last localization is the most dangerous. The tube in this part is narrow and can rupture in the early stages, causing bleeding.
- In addition to tubal pregnancy, ovarian, cervical, and abdominal pregnancy are possible. All of them are hopeless and dangerous to a woman’s life, causing bleeding.
- Rudimentary fertilization is also distinguished, when the fertilized egg is implanted in the rudimentary uterine horn. It is very difficult to detect. The embryo is able to move into the abdominal cavity. After the death of the fetus, purulent processes may develop.
Treatment of pathology
“Treatment” of pathological pregnancy, regardless of its characteristics and duration, is carried out in a medical institution. Only doctors, having assessed the nuances of the situation, all the symptoms, based on tests and examination, will decide which method should be used. If an ectopic placement of the fetus is detected, several standard methods of eliminating the situation are used.
- If an ectopic pregnancy is detected early, the elimination methods are gentle, and in the case when the fetus (and not its remains) is still inside, laparoscopy is used, which is performed through a mini-puncture of the abdominal wall to insert an instrument. The essence of the procedure is to gently suction the embryo without damaging the tubes (which is important for subsequent conceptions). Equipment with a system that displays all actions on a monitor.
- Some situations require surgery. If the fallopian tube ruptures, a salpingectomy (removal) is performed, which allows saving the woman’s life. Sometimes it is left and stitched after removing the affected part, which does not eliminate the likelihood of a recurrence.
- If an ectopic embryo is detected at an early stage, medical termination with Methotrexate is used. It causes a forced abortion, when the fetus is expelled along with the bleeding.
We can say that in each specific case of pathological conception an individual approach is taken. This condition is dangerous due to complications leading to death due to inflammation or bleeding. Because of it, there is a high risk of secondary ectopic pregnancy, infertility, adhesions, inflammatory diseases of not only the reproductive, but also the excretory system, as well as the abdominal cavity.
Even with high-quality treatment, in some women subsequent conception may also be abnormal. Therefore, in case of a tendency to abnormal localization of the fetal egg, it is reasonable to undergo a comprehensive examination, which will identify its specific causes. For example, inflammatory diseases, if the fallopian tubes are affected, then the next pregnancy may also be pathological.
After removal of an ectopic pregnancy, compliance with medical recommendations is mandatory. Rehabilitation after a pathological conception is quite long; restorative therapy and elimination of the causes of the pathology will not hurt.
After removal of an ectopic pregnancy, high-quality OC is important, and it is better to refuse the IUD, since it often provokes pathological attachment of the embryo. In case of repeated conception, the second tube may be damaged, which threatens definite infertility (but IVF is a possible option). According to statistics, more than half of women affected by ectopic pregnancy subsequently have a successful history of conception. The next pregnancy is permissible no earlier than after a six-month period. Minimum relapses with medication interruption.
Characteristics of discharge
There is no single option. The secret is always different. Women should know what kind of discharge can occur due to ectopic conception in the early stages, because these are the features of an ectopic pregnancy:
- spotting, scanty;
- long-term;
- pinkish or brown, after menstruation;
- uterine bleeding.
Dark discharge instead of menstruation with a negative or weakly positive test may indicate an ectopic pregnancy. Bloody - about spontaneous abortion or rupture of the fallopian tube. Vaginal secretions may contain:
- pus;
- blood;
- rejected mucosal epithelium.
Restoring menstruation after an ectopic pregnancy
Possible complications
Duplication of the fallopian tubes (this pathology can be observed on both sides or only on one);
After operations, patients are prescribed painkillers, and doctors monitor the discharge. In cases where a woman is in shock or loses a lot of blood during or before surgery, the observation period increases significantly.
Previous ectopic pregnancy in the fallopian tube;
In addition, it is necessary to undergo another important examination - to check the patency of the fallopian tubes, or rather the one remaining one. This procedure is familiar to many women and is called hysterosalpingography (HSG). The procedure is not very pleasant, but it is not painful either, but some sensitive or simply restless women may require pain relief. A thin flexible cannula is inserted into the cervix, through which a special aqueous solution is injected. It fills the uterus and fallopian tubes, after which the doctor takes several x-rays. This way you can clearly see whether there are adhesions in the pipe or not, whether it is passable or not. If yes, then intrauterine pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy is quite possible. If not, your doctor may recommend laparoscopy, a simple operation without incisions to cut through adhesions. But let's return to the HSG procedure. Many women notice after this procedure the appearance of such unpleasant things as thrush. Inflammatory processes may occur in the area of the internal genital organs, therefore, without special indications, HSG is not performed. Most often, the surgeon who performed the operation for VD can tell you about the condition of the second fallopian tube. If he said that her condition is not important, you can immediately go for laparoscopy.
The Medical College www.tiensmed.ru answers:
Drug treatment is also possible. Like surgery, taking methotrexate can cause loss of reproductive organs or infertility. But without treatment, death is also likely due to rupture of the fallopian tubes and subsequent blood loss.
Diseases of the endocrine system, as a result of which the peristalsis of the tubes is disrupted;
By the way, this is not that uncommon. Ectopic pregnancies occur in about two percent of all pregnancies, and 98 percent are tubal pregnancies. Therefore, the best method of preventing ectopic pregnancy is timely treatment of diseases that can cause damage to the fallopian tube, primarily inflammation of the pelvic organs and appendicitis.
A delay in menstruation after an ectopic pregnancy is most often due to the fact that the pregnancy itself was diagnosed quite late, which is why the recovery period is somewhat longer.
During a tubal abortion, a woman produces a small amount of dark, brown or black, bloody discharge from her genital tract. Such scanty spotting is associated with the rejection of fetal tissue from the wall of the fallopian tube. With a tubal abortion, spotting may occur for a long period of time until the condition is diagnosed.
And yet, there is an algorithm that allows you to calculate the possible date of the first period after an ectopic pregnancy.
Clear signs of internal bleeding necessitate emergency surgery. Typically, gentle laparoscopy is performed, that is, an operation using a telescopic tube connected to a video camera through a 0.5–1.5 cm hole.
Delayed or scanty menstruation;
Consultation with a specialist is also necessary if menstruation after an ectopic pregnancy does not begin within the calculated time interval.
3. Observation of your own feelings.
During ovulation, a woman may experience mild, aching pain in the area of the ovary where the egg has matured. Sometimes pain is felt in the lower abdomen. Clear, “stretchy”, odorless vaginal discharge appears. Many women note an increase in sexual desire.
The exact timing of the restoration of menstruation after an ectopic pregnancy is quite difficult to calculate, since the hormonal background of different women has its own characteristics and, moreover, undergoes serious changes due to the development of the pathological process and the treatment performed.
Hormonal imbalance;
The first day of the cycle is taken to be the day of the operation, after which the number of days that normally corresponds to the duration of a woman’s usual cycle is added to it. Five days are subtracted from the resulting date and another ten are added again. The calculated period of time should be the period when a woman is expected to begin her period after an ectopic pregnancy.
Causes and risk factors for ectopic pregnancy may also include:
It is important to know that even if the menstrual cycle has returned on time and no complications have arisen after an ectopic pregnancy, a subsequent pregnancy should not occur in the next 5.5-6 months. Despite the rapid restoration of menstruation after an ectopic pregnancy, the body is not ready for a new pregnancy, so during this period it is necessary to protect yourself.
A follow-up pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy should be planned no earlier than six months later, after complete tissue recovery and menstruation after an ectopic pregnancy, in order to reduce the risk of its recurrence.
Laparoscopic surgery is usually used to treat ectopic pregnancy. During the operation, both the fertilized egg located in the tube and the entire tube can be removed. The pipe is removed in cases where a rupture has already occurred.
Enlargement of the mammary glands and their soreness.
Monitoring the patient's condition
2.
A more budget-friendly option to speed up pregnancy after an ectopic and removal of one tube is
measuring basal temperature
. Mountains of literature have already been written about this. And although many modern doctors consider this method to be outdated, that is, uninformative, it is still worth a try. This method can be used not only as an independent method, but also as a supplement to existing ones. For example, you can very accurately determine the onset of ovulation using an ultrasound examination. But you will have to do it for several days in a row, which is not financially feasible for everyone. Therefore, you can use basal temperature to identify the desired day, and use an ultrasound to confirm or refute your doubts. But you can do without an ultrasound if the diagnosis of infertility has not yet been made, and there is a chance that pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy will occur quickly and easily.
One of the symptoms that something has gone wrong is menstruation in the first month of pregnancy. find out what diseases can cause this.
Psychological recovery
Swelling and tenderness of the mammary glands;
The first place among other diseases that disrupt the normal course of all processes associated with the onset of pregnancy is given to chronic salpingitis. This disease is nothing more than the process of formation of adhesions in the oviducts. And it is provoked by infections transmitted through sexual contact. The situation can be aggravated by artificial termination of pregnancy, surgical interventions previously performed in the pelvic organs, as well as various types of diseases of the reproductive system.
Do you know the signs of cystitis in women? To protect yourself, you should familiarize yourself with these things.
A heterotopic pregnancy occurs very rarely, when two fertilized eggs are located in different places: one in the uterus, the other outside it.
In addition, the delay is often provoked by the stress experienced by the woman caused by an ectopic pregnancy. In such cases, it may take from one and a half to two months to restore the cycle.
In cases where bleeding appears earlier than 25 days after the termination of an ectopic pregnancy, it is regarded not as menstruation, but as uterine bleeding, the occurrence of which requires consultation with a gynecologist. If there is a delay in menstruation after an ectopic pregnancy for more than 40 days, this means that, most likely, a hormonal imbalance has occurred, which again is a reason to consult a gynecologist.
The presence of tumors in the uterus or its appendages.
An ectopic pregnancy is accompanied by the same symptoms as a normal pregnancy, namely:
Unfortunately, even successful treatment does not guarantee (in 10–20 percent of cases) against recurrent ectopic pregnancy.
It is also very important to find out what caused the ectopic pregnancy and completely neutralize this factor, then the risk of a repeat ectopic pregnancy will be reduced.
Pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy (if surgery was performed and one fallopian tube was removed) most often does not occur on the first or even on the second attempt. Still, the chances of becoming a mother after such an operation are halved, but the statistics do not apply to some women. Much depends on the woman’s health, preparation for subsequent pregnancy, and the patency of the remaining tube. But first things first.
Laparoscopy
Undesirable but common consequences of ectopic pregnancy also include inflammatory processes and the occurrence of adhesions in the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs.
Taking separate contraceptives;
The most favorable prognosis is addressed to those in whom an ectopic pregnancy was detected in the earliest stages. In such cases, women's chances of conceiving a child in the future are quite high.
The longer the period, the larger the size of the fertilized egg and the higher the degree of danger of the consequences of an ectopic pregnancy for the female body. Therefore, they try to interrupt it as early as possible - in the 4th–7th week.
When conducting a pregnancy test, you can determine an ectopic pregnancy by the level of human chorionic gonadotropin in the urine - it will be an order of magnitude higher than in a normal pregnancy.
Chemotherapy using methotrexate is also possible. The result of treatment is the cessation of development and resorption of the fertilized egg. However, this treatment method is effective only in the early stages of such a pregnancy.
Different birth control pills may be prescribed to different women. There is a myth that the choice depends on the individual hormonal background of the woman. However, it is not. The first choice drugs are combined oral contraceptives with a dosage of ethinyl estradiol - 20-30 mcg. These include Logest, Novinet, Janine, Lindenet 20 (and 30), Yarina, etc. You can choose depending on your financial capabilities. The price of tablets can vary quite a lot. Let's say, a pack of Lindenet 20 (30) costs about 300 rubles, and its analogue Logest (the composition is the same, but the manufacturers are different) is 2-2.5 times more expensive. It is recommended to start taking the pills at the beginning of the next menstrual cycle after the operation (you cannot make love for 1 month after the operation).
Those planning a pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy should undergo a full examination. There is only one fallopian tube left, which means everything needs to be done to prevent the situation from happening again. This means that before active planning, it is necessary for both partners to undergo all tests in order to detect possible sexually transmitted infections. Everyone needs to do this. Even those who have previously undergone similar tests or are confident that they are healthy. There are many so-called hidden infections that are not always detected the first time by tests. Meanwhile, pathogenic bacteria provoke inflammatory processes in the pipes, which leads to the formation of adhesions. And adhesions in the tubes in many cases prevent the fertilized egg from moving into the uterus for implantation, and it is forced to implant right there, in the tube, ovary or in the abdominal cavity. Thus, an ectopic pregnancy may occur again after an ectopic pregnancy and removal of one tube.
As you can see, it's not all bad. And pregnancy after an ectopic and removal of one tube is possible. You just need to be thoroughly examined, follow all the doctor’s instructions, monitor your health and well-being, and just that. believe that everything will definitely work out.
After the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is confirmed and if the tube has not ruptured, laparoscopy is performed, in which doctors either completely remove the fallopian tube or remove the fertilized egg located in it. In cases where the tube is left, there is a risk of recurrence of an ectopic pregnancy in the future, since its functions are disrupted and adhesions form, which leads to tube obstruction. Complete removal of the tube reduces the likelihood of natural pregnancy.
If you can't get pregnant on your own
In general, if the process proceeded without any obvious complications and under favorable circumstances, menstruation after an ectopic pregnancy is restored in the interval between 28 and 40 days after the termination of this pregnancy.
Does it happen without bleeding?
An ectopic pregnancy may not manifest itself for the first 3 to 4 weeks. This is evidenced by messages on the forums. The woman is not bothered by pain in the lower abdomen and does not smear from the vagina. But this cannot last long.
With the ectopic growth of the fertilized egg, large-scale transformations occur in the body. A foreign body begins to grow in the ovary, tube, cervix or peritoneum, which provokes sharp, cramping pain, nausea, fainting, and hyperthermia.
If a woman does not consult a gynecologist in time, signs of internal bleeding appear. Only a blood test for hCG and ultrasound diagnostics will help identify pathology in the early stages. This can save a woman from infertility and even death.
It is stupid to ask whether it is possible to get pregnant ectopically without bleeding. Everyone's body is different, and for some, signs may appear as early as the seventh day after conception, for others - in the second or third month.
Why is an ectopic pregnancy so dangerous?
An ectopic pregnancy is a pathology during the development of pregnancy, during which the fertilized egg does not enter the uterus and is located outside of it. If this condition is left unattended, the egg growing outside the uterus can cause the following conditions:
- rupture of the fallopian tube;
- peritonitis, abdominal infections;
- abdominal bleeding.
Each of these options can be fatal, so if you have symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, you should contact the clinic as soon as possible.
Currently, a laparoscopic method is used to remove a fertilized egg: it does not require removal of the fallopian tube, so it does not cause serious harm to the body. After laparoscopy, a woman is not at risk of infertility, but such intervention is used only in the early stages of detecting pathology.
In the event that an ectopic pregnancy was noticed too late, and a rupture of the fallopian tube has already occurred, the surgeon will have to remove not only the embryo, but also the tube itself or its fragment. In this case, the woman’s reproductive function will be lost after the operation.
This is another important reason why it is important to determine the signs of an ectopic pregnancy on your own: if a woman can understand in time what is happening to her, this will save her not only life, but also health.
How are they different from menstruation?
Not many differences
When bleeding begins during an ectopic pregnancy, spotting, many women mistake it for menstruation. They miss time, which leads to the development of complications.
Discharge during an ectopic pregnancy, although similar to menstruation, has nothing in common with it. They can be distinguished by their meager character and long duration. Bleeding, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, severe weakness, fainting, and dizziness appear.
Normally, menstruation stops after conception. Sometimes hormonal fluctuations lead to uterine bleeding. This may indicate a pathological pregnancy, a threat of miscarriage, and therefore requires increased attention.
With ectopic conception, quite often menstruation comes on time, but they do not have the same character as usual. If they are very scanty, weak, delayed or premature, it is recommended to buy and do a test, or even better, donate blood to detect gonadotropin.
Treatment methods for ectopic pregnancy
There are two therapeutic methods for ectopic pregnancy: medication and surgery. During drug treatment, drugs are prescribed that cause the embryo to die and then gradually dissolve. In this case, both the tubes and the ovaries are completely preserved. But this is effective only for a very short period of time - up to 8 weeks.
With the surgical method, doctors scrape out the embryo, and in severe cases, along with the fetus, they cut out the place where it was attached. The operation is performed laparoscopically or laparotomically.
Can there be discharge without an ectopic pregnancy?
Secretion is a normal phenomenon for the female body, and clear, light, odorless discharge should not be scary.
A mucous secretion, the consistency of which resembles chicken protein, is also a normal variant. Mucus plays an important role: it protects the reproductive system from bacteria and promotes the advancement of sperm to the egg.
What color, character, or smell of discharge should alert you?
- Abundant, yellowish, curdled. They indicate thrush, especially if accompanied by itching. Candidiasis often affects pregnant women, as the immune system is weakened, creating favorable conditions for the spread of the fungus.
- Yellow, with an unpleasant purulent odor. They signal an inflammatory process or sexually transmitted infections.
- Mucus with a green or gray tint, foamy. A clear sign of an infectious process.
- Bloody pinkish discharge. May indicate cervical erosion. Due to conception, the disease worsens due to hormonal changes.
Laparotomy for ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is rarely removed by laparotomy. Such intervention is carried out in a hopeless situation. In this case, the doctor cuts out not only the egg, but also the place to which it is attached.
This is a complex and traumatic surgical procedure. It is carried out if a large amount of blood flows into the abdominal organs, which poses a danger to the woman’s life.
- Preparing for surgery
Laparotomy is performed under general anesthesia, so the patient is carefully prepared.
Carry out the following:
- Fluorographic examination of the chest.
- Electrocardiogram.
- General tests.
- Blood test for clotting.
- Analysis for STDs and viral diseases.
- Gynecological examination.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvis.
On the eve of the operation, a conversation is held with the anesthesiologist. You definitely need to tell your doctor what medications you took and if you have allergies.
- Stages of the operation
First, the patient is given general anesthesia, then after treating the working area with an antiseptic, the operation begins.
If the pregnancy is tubal, then laparatomy proceeds as follows:
- The abdominal wall is cut.
- The reproductive organ along with the affected tube is removed.
- The pipe is clamped at the end with a clamp.
- A similar clamp is applied to the ovary.
Then the tube is cut and ligated. After which it is carefully cut out. The vessels are ligated, and the operated area is treated with an antiseptic. If the laparatomy is cervical, then the cervix or the entire uterus is removed. Afterwards the incision is sutured.
- Recovery and aftermath
Rehabilitation after this operation is more complex and lengthy. It is recommended to start getting up on the second day. This will prevent adhesions, thrombosis, and volvulus. If there is severe pain, then analgesics and antibiotics are prescribed to prevent inflammatory processes.
Some more recovery tips:
- In order for the body to quickly come to its senses, after bleeding, blood substitutes and blood plasma are administered. Vitamin supplements and physical therapy are also indicated.
- There may be some spotting during the first five days - this is normal.
- The menstrual cycle returns to normal within 8 weeks after surgery.
- For six months after laparotomy, you should not lift or move heavy objects or do too much physical exertion.
- Until the stitch has completely healed, which is about 2 months, it is not recommended to take a hot bath.
- You should not have sex for about 4 weeks after the laparotomy, during which time you will wear a compression bandage.
- The diet is the same as for laparoscopy.
An ectopic pregnancy does not mean that a woman will not be able to have children afterwards. This is possible even with the pipe removed. To prevent this from happening in the future, you need to monitor your health and undergo an annual examination with a gynecologist.
How long can a tubal pregnancy remain without concern?
The first signs indicating ectopic implantation of the embryo usually appear 6-8 weeks after conception. Before this, the woman is worried only about the typical signs of fertilization: toxicosis, increased breast sensitivity, delayed menstruation.
The consequences of an ectopic pregnancy can manifest themselves by 10-12 weeks. A pipe or other organ ruptures.
Sometimes heterotopic pregnancy occurs - both uterine and ectopic. This happens during IVF or ovulation in two ovaries, when one embryo for some reason was unable to penetrate the uterus.
The embryo fixed in the tube begins to grow and develop. But this organ is not elastic, therefore it is not able to stretch along with the fetus. Then it stretches and ruptures. The result is massive internal bleeding, the symptoms of which are pronounced. At the same time, discharge from the birth canal may not be abundant.
Fetal death and bleeding during ectopic conception are inevitable. Most often this happens at 6-10 weeks.
The literature describes isolated cases of abdominal conception, when women gave birth at 27-28 weeks. Such children were born by caesarean section. Doctors had to remove internal organs: resection of the intestines, fallopian tubes, uterus, liver, spleen. The placenta grew through the organs, like a malignant tumor, and it was impossible to separate it in any other way. Such operations seriously undermined women's health and caused bleeding.
Pain in the lower abdomen
Tubal ectopic pregnancy (99% of all ectopic conceptions) never develops until later in pregnancy. Spontaneous abortion is possible when the tube itself rejects the embryo. After this, it usually enters the peritoneum. If the embryo is still alive, it attaches there, and a repeat peritoneal pregnancy develops. But more often the pipe ruptures and bleeding occurs.
The following signs should alert a woman.
- Pain in the lower abdomen. They may not bother you for a long time or may appear from an early stage. Typically, acute pain radiating to the rectum is localized on the side where the embryo is implanted.
- Weak positive test. There is a second stripe, but it is so weak that it is barely noticeable. This is explained by the fact that in pathology the level of hCG is lower than during normal conception.
- The color of blood on underwear, scanty menstruation or bleeding.
Non-developing ectopic pregnancy. Case from practice
SonoAce Ultrasound Magazine
Medical journal on ultrasonography - free subscription
(for ultrasound doctors).
Introduction
Despite advances made in the early diagnosis and treatment of ectopic pregnancy, this disease still represents an important problem in gynecological practice.
Modern research confirms the widespread prevalence of this pathology, as well as a pronounced tendency to increase in the number of diagnosed cases in many countries of the world. Studies by Russian scientists provide data indicating that the frequency of ectopic pregnancy remains consistently high in the structure of emergency conditions in gynecology and ranges from 1 to 12% in relation to all patients hospitalized in gynecological hospitals. The main cause of internal bleeding in women of reproductive age is also ectopic pregnancy. After an ectopic pregnancy, 60-80% of patients develop infertility, 20-30% of patients develop a repeat ectopic pregnancy, and many develop adhesions in the pelvis [1]. The rather high level of deaths due to ectopic pregnancy is cause for concern - more than 7.4% of cases. A non-developing pregnancy is one of the pathogenetic variants of reproductive losses, in which the fertilized egg dies, but its spontaneous expulsion from the uterine cavity does not occur [2, 3]. In addition, long-term retention of a dead embryo (fetus) in the uterus against the background of suppression of its contractile activity is accompanied by a high risk of developing infectious and hemostasiological complications. The volume of surgical interventions performed for ruptured ectopic pregnancy indicates a low proportion of organ-preserving operations, which negatively affects the fertility of young women. Based on the above, the use of the latest achievements of instrumental research methods, optimization and development of new approaches and directions of diagnostics is of particular relevance. The modern concept of providing care to patients with ectopic pregnancy involves providing accessible, effective and, if possible, non-invasive early diagnosis, eliminating the likelihood of complications, as well as performing endoscopic organ-preserving operations in a hospital setting aimed at preserving reproductive function and improving the quality of life of women.
Despite the fact that tubal ectopic pregnancy ranks first in localization of the ovum among all types of ectopic pregnancy, accounting for 98.5%, the incidence of ectopic pregnancy in the isthmic section of the fallopian tube does not exceed 13% [4]. Non-developing tubal pregnancy is the rarest variant of the clinical course of ectopic pregnancy. Diagnosis of non-developing tubal pregnancy is difficult. In the absence of proper attention, a misdiagnosis may be made, since the main diagnostic criteria for tubal pregnancy, which have the greatest specificity and sensitivity, are absent. The high level of early diagnostic errors is also due to underestimation of anamnestic data, short communication with the patient, and insufficient use of additional informative research methods.
One of the most sensitive and effective diagnostic methods for suspected ectopic pregnancy, in our opinion, is ultrasound of the pelvic organs. The use of Dopplerography and three-dimensional reconstruction modes can significantly improve the quality of differential diagnosis. As an illustration, we present a description of our own case of a non-developing tubal pregnancy with localization in the isthmic section of the fallopian tube and the diagnostic search performed.
Clinical observation
Patient M., 34 years old, applied for an additional ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis of a non-developing short-term pregnancy. She made no complaints. As a result of collecting anamnestic data, the following was established. The last menstruation passed on time, usual in abundance and duration. After 14 days, two days of heavy bleeding appeared, about which she consulted a gynecologist. According to the doctor’s recommendation, I took a pregnancy test - it was weakly positive. An ultrasound was performed and with a diagnosis of intrauterine pregnancy, threatened miscarriage, the patient was sent to the hospital. After carrying out therapy to maintain pregnancy for 7 days, a repeat examination diagnosed a non-developing pregnancy and suggested curettage of the uterus. Since the woman was extremely interested in maintaining the pregnancy, she decided to confirm this diagnosis by undergoing an additional ultrasound.
Obstetric and gynecological history: menstruation since 12 years, 4-5 days every 30-31 days, regular, heavy, painless. Single birth, urgent, complicated by postpartum endometritis and ectopic pregnancy (does not remember location). Denies gynecological diseases.
When contacted, the condition is satisfactory. The skin and visible mucous membranes are of normal color. Breathing is vesicular, heart sounds are clear and rhythmic. The abdomen is soft, painless on palpation in all areas.
Ultrasound was performed on an expert-class device using abdominal and abdominal sensors.
With ultrasound, the body of the uterus is determined in anteversio-flexio. The contours are clear, uneven. Size 56x36x46 mm. The uterine cavity is linear, not deformed. The endometrium is 9 mm thick, homogeneous, with a hyperechoic rim. The fertilized egg is not visualized in the uterine cavity (Fig. 1). The myometrium is homogeneous. In the area of the left uterine angle, a formation measuring 47x43x62 mm is visualized (Fig. 2), the wall of which is myometrial tissue. In the center of the formation, an anechoic inclusion of a round shape with an uneven clear contour with an average diameter of 18 mm is determined, along the periphery of which a hyperechoic ridge up to 16 mm thick is located.
Rice. 1.
Sagittal section of the uterus.
Rice. 2.
Cross section of the uterus at the level of formation.
The right ovary is found in a typical location, not enlarged (31x19x23 mm), the follicular apparatus is of normal structure. The left ovary is visualized in a typical place, not enlarged (30x18x20 mm), the follicular apparatus is of normal structure. Ovarian mobility is limited.
Free fluid in the retrouterine space is not detected.
A thorough examination of the area of the appendages revealed no space-occupying formations.
The results of ultrasound, taking into account the anamnestic data, necessitated a differential diagnosis between a non-developing ectopic pregnancy and degeneration of the myomatous node.
For the purpose of differential diagnosis, Doppler sonography was used and a volumetric multiplanar study of the uterus and formation was performed using three-dimensional reconstruction modes.
Dopplerography in the color Doppler mapping (CDC) mode (Fig. 3) revealed scanty blood flow along the periphery of the hyperechoic ridge and a single vessel in the thickness of the hyperechoic band itself, the resistance index (RI) was 0.36, which is typical for a non-developing tubal pregnancy [5] . A myomatous node of this size with degeneration during color mapping is characterized by pronounced intratumoral blood flow with avascularization of the cystic cavity and an increase in IR to 0.7 [4, 5]. During multiplanar volumetric reconstruction in the coronal plane, the localization of the formation was determined in the isthmic section of the left fallopian tube (Fig. 4). Using the MultiSliceView mode, it was possible to establish a connection between the left corner of the uterine cavity and the formation cavity (Fig. 5), which also indicated an ectopic tubal pregnancy. During multiplanar three-dimensional reconstruction using color-dynamics, a single vessel approaching the ovum and depleted blood flow along the periphery of the formation were visualized (Fig. 6).
Rice. 3.
Formation in the left uterine angle in the Color Doppler mode.
Rice. 4.
Multiplanar 3D reconstruction mode. Localization of the formation in the left uterine angle in the coronal plane.
Rice. 5.
Multi-Slice View mode. The connection between the uterine cavity and the formation cavity is visualized.
Rice. 6.
Multiplanar reconstruction mode using Doppler ultrasound. Poor blood flow along the periphery of the formation and a single vessel approaching the fertilized egg.
The data obtained allowed us to formulate the following diagnosis: an undisturbed, non-developing pregnancy in the isthmic section of the left fallopian tube.
An ambulance team transported the patient to a specialized hospital, where a clinical diagnosis of uterine fibroids with node degeneration was established, and a repeat B-mode ultrasound concluded that there was a space-occupying lesion in the left uterine angle.
The next day the operation was performed. During the inspection of the pelvic organs and abdominal cavity, the adhesive process between the uterus, appendages, and greater omentum was determined. If possible, adhesions are separated by blunt and sharp means. The uterus is enlarged until 7-8 weeks of pregnancy due to a formation emanating from the isthmic part of the left fallopian tube with a transition to the left uterine angle, measuring 60x50x80 mm, dark olive in color (Fig. 7). The left ovary is in adhesions. The right ovary and right fallopian tube are without visible changes. The formation was excised, including the left uterine angle.
Rice. 7.
Macroscopic specimen of a formation in a surgical wound.
The postoperative period was uneventful. The patient was discharged home on the 7th day in satisfactory condition.
A morphological examination of the surgical material revealed an ectopic pregnancy: a blood clot with dystrophically altered chorionic villi and “shadow” villi; as well as fragments of the uterine wall (endometrium and perifocal areas of the myometrium with round cell inflammatory infiltration).
Conclusion
In the presented observation, the patient had an almost asymptomatic course of ectopic pregnancy. The blurred clinical picture and the rather rare localization of the fetal egg, combined with a non-developing pregnancy, led to a number of diagnostic errors. At first, ectopic pregnancy was regarded as a non-developing uterine pregnancy, and then as a formation of the left uterine angle, a myomatous node with degeneration. The use of Dopplerography and three-dimensional echography during the examination allowed us to make the correct diagnosis.
Despite the extensive experience and knowledge accumulated by clinicians and ultrasound diagnostic specialists in identifying multiple ectopic pregnancies, in the practice of every obstetrician and gynecological service doctor, this pathology remains a disease that requires due attention. The use of modern technologies makes it possible to arrive at the correct diagnosis and provide timely assistance to the woman.
Thus, ultrasound can be the first and important stage in the examination of patients with suspected ectopic pregnancy due to its non-invasiveness, accessibility, efficiency and cost-effectiveness, in terms of material costs, and also help reduce the time between hospitalization and surgery. However, clinical symptoms should not be ignored, relying only on ultrasound data.
Literature
- Aleksandrov M.S., Shinkareva L.F. Ectopic pregnancy. M.: “Medgiz”, 1961. P. 36.
- Vladimirova N.Yu., Chizhova G.V. Differentiated approach to rehabilitation therapy for fetal loss syndrome of viral etiology // Materials of the VI Russian Forum “Mother and Child”, Moscow, October 12-15, 2004, pp. 45-46.
- Kolukanov I.E., Chaika N.A. Gardnerellosis: scientific. review. St. Petersburg, 1994. 44 p.
- Ozerskaya I.A. Echography in gynecology. M.: Medika, 2005. P. 285.
- Ozerskaya I.A., Yesayan N.K. Possibilities of ultrasound diagnostics in determining the type of interrupted tubal pregnancy // Ultrasound and functional diagnostics. 2007. N 6. P. 51-60.
SonoAce Ultrasound Magazine
Medical journal on ultrasonography - free subscription
(for ultrasound doctors).
Discharge during tubal abortion
The fetal egg, localized in the fallopian tube, at a period of 6–8 weeks is able to independently leave the organ without injuring it. This process is called tubal abortion and is accompanied by spotting and bleeding from the vagina.
With an ectopic pregnancy, bleeding occurs, whether abundant or not, usually for a long time. Severe bleeding causes pain radiating to the hypochondrium, collarbone, and scapula. Blood pressure decreases, pulse quickens, weakness and fainting appear. With minor bleeding, a woman is usually not bothered by other symptoms.
Pipe rupture may occur
One of the methods for eliminating ectopic pregnancy is artificial tubal abortion. The essence of the procedure is to squeeze out the fertilized egg. The advantage of the method is that the pipe suffers almost no damage. But it is fraught with other complications, so it is rarely practiced. After surgery, bleeding may continue for some time.
Myths
MYTH No. 1. The use of hormonal contraceptives increases the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy!
This is absolutely not true!
All hormonal contraceptives reduce the risk of ectopic pregnancy by preventing ovulation and/or conception. Among users of hormonal contraceptives, the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy is the lowest: 0.005 per 1000 women. These rates are lower than those for women using condoms, diaphragms, copper-containing IUDs, and surgical contraception as contraceptive methods.
MYTH No. 2. There is an ectopic pregnancy after removal of the uterus.
Indeed, this is the rarest type of ectopic pregnancy. However, several such cases of pregnancy after removal of the uterus (extirpation) have been described in the literature. Implantation of the embryo in the fallopian tube occurs shortly before surgery, or at any time after surgery if the abdominal cavity communicates with the cervical stump or vagina.
MYTH No. 3. Spontaneous recovery occurs with ectopic pregnancy.
It is extremely rare that an ectopic pregnancy stops developing, and the fertilized egg gradually dissolves, or a tubal abortion occurs - that is, the fertilized egg is “thrown out” into the uterine cavity. In such cases, surgical treatment is usually not required. The incidence of this outcome of ectopic pregnancy is unknown, as are the conditions necessary for such resolution of the disease.
In the case of an ectopic pregnancy, it is impossible to predict its course, therefore, due to the high risk of intra-abdominal bleeding, as well as a high threat to life, emergency surgical treatment is always necessary.
MYTH No. 4. A pregnancy test can help diagnose an ectopic pregnancy by the brightness of the indicator color.
Complete misconception! The fact is that a pregnancy test registers the presence of chorionic gonadotropin in a woman’s body, that is, a hormone that is produced only during pregnancy. It appears during both uterine and ectopic pregnancy, however, during ectopic pregnancy its concentration and increase are significantly lower . So a pregnancy test will only show the presence of some kind of pregnancy, and all questions regarding the localization of the fertilized egg will be answered by ultrasound. A negative pregnancy test also does not exclude the presence of an ectopic pregnancy, since the level of human chorionic gonadotropin may be very low and not registered by primitive home tests!!
MYTH No. 5. The presence of menstruation 100% indicates the absence of an ectopic pregnancy.
This is wrong. Quite often, patients with an ectopic pregnancy experience bleeding from the genital tract during menstruation. This is not menstruation, as such, but a reaction of the endometrium to the presence of pregnancy in the fallopian tube. This fact, as a rule, misinforms patients and leads to the fact that a visit to the gynecologist is delayed.
Usually, when interviewed, it turns out that this “menstruation” was “not quite ordinary,” however, the woman was sure that there could be no pregnancy. It is necessary to be more attentive to the nature of menstrual flow and the duration of the menstrual cycle.
MYTH No. 6. Intrauterine pregnancy is almost unlikely in patients with a single fallopian tube or is reduced by 2 times.
We have received data that proves exactly the opposite. A group of patients with a single fallopian tube after its removal for ectopic pregnancy (35 women) was examined.
In parallel, observation was carried out on women who had not undergone surgery (125 people). According to our data, the pregnancy rate after 2 years of observation in patients of both groups was almost the same. The data is presented in the Figure.
Thus, patients with one fallopian tube have almost the same chances of pregnancy as completely healthy people, after undergoing the necessary treatment.
What kind of discharge if a pipe bursts?
As the embryo develops, the wall of the uterus stretches significantly, which leads to its rupture. The fertilized egg enters the abdominal cavity through the hole that has formed.
This is accompanied at first by slight, dark red vaginal discharge. After a few hours, bleeding begins, there is rejected epithelium - clots and pieces of tissue.
A pipe rupture is accompanied by severe, acute, constant pain. If treatment measures are not taken in time, the consequences will be the most unfavorable.
Consultations with a gynecologist
What types of discharge are there?
Several types of discharge indicate a pathological pregnancy. It is also possible that there may be no discharge of a suspicious type (as a rule, only at an early stage).
- For ectopic placement of the fetus, depending on its characteristics, spontaneous “spotting”, prolonged discharge (brown or red) is characteristic.
- Instead of “critical days,” there is dark brown discharge, and the pregnancy test is negative (weakly positive).
Vaginal secretion may contain an admixture of thick blood and mucous particles. It is believed that spotting is a companion to an ectopic pregnancy, but sometimes it is a sign of a serious pathology of the cervix.
White curds
Slightly yellowish or white “curdy” discharge generally indicates “thrush,” scientifically called candidiasis. Its exacerbation during pregnancy is common due to the transition of the immune system to a special mode. As a rule, such a secretion is accompanied by itching of the external genitalia.
Yellow
During ectopic pregnancy, there is a yellow discharge accompanied by an unpleasant odor. This indicates the presence of inflammatory diseases (including those caused by STDs). The shade can be gray or green.
Brown
Dark brown discharge can appear at any time during your cycle. When the death of the embryo occurs (due to rupture of the fallopian tube, spontaneous abortion), the vaginal secretion turns dark brown.
A small amount and duration indicate rejection of the fertilized egg.
Bloody
If bleeding occurs, do not hesitate. This means that the embryo has reached a critical size, and, depending on its location, several negative scenarios develop. Such discharge, with rare exceptions, is accompanied by severe pain. After conception, the fetus grows and eventually the fallopian tube ruptures, after which the fertilized egg enters the abdominal cavity.
First, a small amount of discharge with blood appears, and after about two hours bleeding occurs containing epithelium (that is, blood with clots and pieces of mucous). Due to the fact that some women mistake such discharge for menstruation, the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy can be delayed.
The appearance of bloody discharge of varying intensity occurs when the fetus is rejected, attached to the cervix, rupture of the fallopian tube or the walls of the ovum. According to statistics, only a fifth of cases of pathological conception are detected at an early stage. Those women whose affected fallopian tube was not removed after an ectopic pregnancy should be especially attentive to the slightest signs.
With a progressive type of pathological conception, there may be no suspicious discharge, but at a time when there should be “critical days” according to the schedule, there may be small discharge of blood. Later they happen again, which is why there is a high risk of mistaking them for cycle discharge. After sex, there is also a slight discharge with blood. The attachment of the fetus to the cervix also causes copious bleeding (due to the high concentration of blood vessels).
Why is timely treatment important?
Bloody discharge can be a symptom of an ectopic pregnancy, because ectopic conception rarely goes away without it. Additionally, the woman feels toxicosis and pain in the lower abdomen.
Bleeding from the vagina indicates that other unhealthy processes may be occurring in the body: endometriosis, threat of miscarriage, infection, erosion.
It is important to detect the problem in time, make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment to avoid undesirable consequences.
About the author : Borovikova Olga
When the discharge is not associated with a pathological pregnancy
Discharges of a pathological nature can be observed not only when the embryo is located incorrectly. Something similar happens with cervical erosion, diseases of the female genital area (inflammatory), and endometritis. It is important to identify in time the absence or presence of an ectopic pregnancy, as it is life-threatening.
In addition to the presence of pathological secretion, there are other signs (toxicosis, pain in the lower abdomen, the appearance of discharge that does not fit into the cycle).
Nature arranges it in such a way that discharge serves as a warning to a woman about the appearance of problems in the reproductive system. You cannot ignore them, since in the case of ectopic pregnancy there is a high risk of not only losing the chance to subsequently give birth to a baby, but also death. Therefore, contacting a specialist for any ailments is the key to health.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
At first, the course of an ectopic pregnancy is manifested by the usual symptoms: cycle delay, nausea, vomiting, changes in taste, increase or, conversely, loss of appetite, weakness, slight malaise, drowsiness, enlargement and soreness of the mammary glands.
Ectopic pregnancy is experienced differently by women. For some, especially those who waited a long time for this pregnancy or could not get pregnant for a long time, it can be very difficult to cope with such a loss. Often women become depressed and are afraid to think about another pregnancy, fearing that it may end in the same way. In cases where symptoms of depression are obvious and progress over several weeks, a woman may need medical help in the form of medication and psychotherapy.
Cervical pregnancy, although not a complication, deserves special attention. A cervical pregnancy is an ectopic pregnancy that begins to develop in the cervix. If it begins to separate from the cervix, it can cause severe bleeding.
Until recently, termination of a cervical pregnancy was carried out by curettage of the place where it took hold. This often led to heavy bleeding, and therefore doctors had to open the abdomen and tie off the blood vessels supplying the uterus before curettage could begin. Ultimately, for many women, it all ended with a hysterectomy or removal of the uterus.
The following should cause alarm when they appear in the third to eighth week:
Ectopic pregnancy has various clinical course options. Moreover, each type of clinical course of ectopic pregnancy is characterized by the presence of discharge from the genital tract of a different nature.
Disturbance of normal hormonal levels.
In addition to brown discharge during an ectopic pregnancy, signs of fertilization also include a missed period, a positive pregnancy test, elevated levels of the hCG hormone, and pain in the abdomen and rectum. The cause of the discharge is precisely the expulsion of the fertilized egg into the abdominal cavity and the preceding detachment of the embryo.
The chance of a repeat ectopic pregnancy, as well as the onset of infertility, is lower if treated with methotrexate (compared to surgery) and if the fallopian tube is preserved during surgery.
The causes of this type of pregnancy have not been thoroughly determined, and the mechanism has not been studied. It is not completely clear why, after fertilization, the zygote does not enter the convenient, comfortable uterine cavity specially designed for this by nature . and is grafted into the fallopian tube (tubal type of intrauterine pregnancy), or goes back to the ovary (ovarian pregnancy), or attaches to the peritoneum (abdominal pregnancy), or enters the rudimentary horn of the uterus.