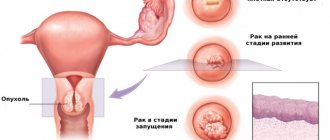
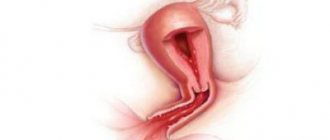
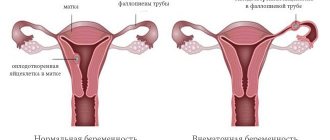
What is cervical pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy that occurs in the cervical canal of the uterus is called cervical.
It is extremely rare in medical practice. Doctors have identified two options for the development of pathology:
- True cervical - the fertilized egg is located in the mucous membrane of the uterine canal, without going beyond its limits. Pregnancy can develop up to 4 weeks of gestation, but ends in spontaneous abortion;
- Cervical-isthmus - the embryo is attached in the upper segment of the canal in the isthmus region. With this type, gestation can last up to 24 weeks, less often – up to 40 weeks.
With VSB, the egg and embryo penetrate the mucous membrane of the isthmic-cervical region of the uterine isthmus. Chorionic villi penetrate the muscles of the reproductive organ and grow deep into the myometrium.
This condition is life-threatening for the pregnant patient.
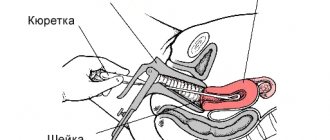
In case of ectopic pregnancy, the walls of the uterus are scraped in the cervix - the fetus is not viable.
Varieties of the disease
When a fertilized egg implants outside the uterine body, it is called an ectopic pregnancy. It is customary to distinguish the following varieties:
- pipe;
- ovarian;
- abdominal;
- cervical
The tubal form is considered the most common variant of ectopic pregnancy. Its diagnosis, as a rule, does not cause difficulties for doctors. The remaining three options are rare.
The most dangerous among them is the cervical location of the fetus. It is extremely difficult to detect, and complications in the form of bleeding can appear at any time. Pathology occurs in one of two options:
- Cervical-isthmus pregnancy (embryo development is observed in the isthmus area). With this position of the fertilized egg, it can last up to 16-24 weeks.
- True cervical pregnancy (fertilized egg is localized in the cervical canal itself). It can develop up to 12 weeks and end in spontaneous abortion.
To avoid such a problem, you need to know why it occurs.
Factors that provoke cervical pregnancy
The main cause of this rare pathology is a violation of oogenesis due to uterine anomalies.
In order for a cervical (distal) pregnancy to take place, factors are needed that influence the descent of the embryo into the cervix.
These include the following pathologies:
- fibroids of the uterine body;
- insufficiency of the isthmic-cervical canal;
- medical abortions for a number of indications in the anamnesis;
- Caesarean section operation;
- adhesive process of uterine tissue;
- in vitro fertilization;
- complicated previous births;
- large blood loss;
- gynecological operations.
Abnormal fertilization in the cervix is characterized by an unfavorable outcome for the woman.
Symptoms
SB has no specific signs. In some cases, pregnant women reported the following symptoms:
- primary signs of pregnancy: nausea, change in taste, mood swings;
- bloody spotting from the vagina: scanty and copious;
- absence of menstruation;
- mild pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent (rarely painful) urination;
- general weakness of the body and lethargy.
Symptoms characteristic of interruption of SB:
- cramping pain;
- dizziness;
- hyperhidrosis;
- fainting;
- open bleeding.
Clinical picture
It is quite difficult to suspect pathology in the early stages. The first ultrasound according to the obstetric protocol is prescribed at 12 weeks. By this time, if the fertilized egg has not attached to the walls of the uterus, a miscarriage has already occurred.
What signs of cervical pregnancy should a woman pay attention to? Often the pathology does not manifest itself at all. In rare cases, a woman consults a doctor with complaints of irregularities in the female cycle or periodic bleeding from the vagina. The latter can have a different character and be moderate or abundant. Bloody discharge, as a rule, is observed only in the first weeks. Then all unpleasant manifestations disappear.
The listed symptoms of cervical pregnancy are also characteristic of other pathologies. These include incipient miscarriage and complicated pregnancy. It is in these areas that doctors first begin their diagnostic search. However, they consider the cervical localization of the embryo last.
Spontaneous miscarriage always begins with bleeding. It can very quickly acquire a profuse form. This complication is dangerous for the health of the woman herself. If not given immediate medical attention, it can be fatal.
What to do if you notice symptoms of the disease
It is impossible to independently detect pathology based on existing signs.
Sometimes even doctors do not suspect cervical pregnancy due to the non-prevalence of the pathology. If spotting brown discharge appears, you should seek help as soon as possible.
If gestation is interrupted and bleeding occurs, the pregnant woman needs emergency hospitalization. It's about saving her life.
The insidiousness of such gestation lies in the ingrowth of villi into the endothelial layer of the cavity. This leads to the melting of muscle tissue.
Timely seeking medical help will prevent unwanted consequences for the patient.
Diagnosis of pathology
Making a diagnosis in early gestation is quite difficult.
The absence of clinical signs and symptoms of the process complicates diagnosis. To detect pregnancy in the isthmus, a specialist must have a wealth of experience and knowledge.
To establish a diagnosis, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Gynecological examination using speculum. The uterus, unlike the cervical canal, remains unchanged. The embryo is palpated behind the internal os.
- Two-manual gynecological examination - the uterus does not correspond to the gestational age, moreover, it does not change at all - the pathological process is concentrated in the cervical canal. The cervix is soft and eccentrically positioned.
- Transvaginal ultrasound is the main diagnostic method. A specialist may not immediately notice the presence of a fertilized egg in the wrong place, so an abdominal examination is not enough - intravaginal diagnostics is used.
On the device monitor, the diagnostician detects the following ECHO changes:
- the fertilized egg is absent in the uterine cavity;
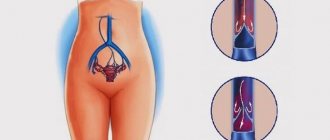
- dilated uterine canal;
- the uterus changes, taking on the appearance of an hourglass;
- the embryo is found in the lumen of the internal pharynx;
- the egg tissue adheres tightly to the mucous membrane, penetrating deep into its structure;
- in case of long-term pathology, the ultrasound diagnostician evaluates the condition of the mucous membranes and the degree of chorion ingrowth.
Causes
The causes of occurrence are most often associated with various pathologies of the uterus, when obstacles arise for the implantation (introduction) of a fertilized egg into the endometrium (inner layer) and it descends lower, attaching to the walls of the cervical canal. These include:
- previous medical abortion;
- previous cesarean section;
- uterine fibroids;
- Asherman's syndrome (formation of adhesions in the uterine cavity);
- IVF-induced pregnancy;
- various congenital anomalies of the uterus.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment of displaced pregnancy depends on the severity of the patient and the presence of associated symptoms. In most cases, diagnosis is made when bleeding occurs.
The only way to stop massive profuse bleeding is hysterectomy - complete removal of the uterus.
Other treatment methods are used with timely diagnosis and absence of bleeding:
- Conservative treatment consists of injection of methotrexate. The drug in a volume of 50 ml is injected into the fertilized egg, and then intramuscularly every other day. Treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting, since there is a high risk of bleeding;
- Surgical intervention using minimally invasive methods.
Such methods help preserve the reproductive organ and preserve its main function:
- hysteroscopy;
- laser coagulation;
- embolization of uterine arteries;
- suturing the pharynx of the Central Committee.
Scientists at the Sechenov Clinic have developed effective methods with minimal trauma to the uterine tissue:
- clipping of arteries - temporary closure of blood access to the uterus;
- vacuum aspiration. In the same way, postpartum cleansing and curettage of the walls of the uterus is carried out for medical reasons for up to 12 weeks;
- cervical tamponade with a balloon catheter. Bleeding is stopped by squeezing the vascular walls.
Ectopic pregnancy of the cervical canal of the uterus is characterized by increased mortality.
If left untreated, death occurs as a result of blood loss, or less commonly, blood poisoning.
Symptoms
Cervical ectopic pregnancy symptoms have clinical signs often characterized by the influence of gestational age. They also depend on the level of embryo implantation. In frequent situations, after the cessation of menstruation, most women notice the appearance of spotting. This bleeding process can be heavy or moderate. In some cases it can be profuse. In rare cases, patients experience scanty discharge.
This type of pregnancy is characterized by the absence of pain. However, as it develops, sudden blood loss may begin. Varicose nodes located in the cervical region of the uterus can provoke the appearance of this situation. The circumstance may be complicated by hemorrhagic shock. In most cases, patients also have DIC syndrome.
The isthmus-cervical type is not characterized by such pronounced symptoms. Most often, in this case, placenta previa is implied.
Disease prevention
To prevent the development of a dangerous disease it is necessary:
- visit a gynecologist at least 2 times a year;
- treat gynecological problems;
- use contraception to prevent unwanted pregnancy;
- carefully monitor the menstrual cycle;
- avoid casual sex;
- follow proper nutrition;
- undergo full rehabilitation after gynecological operations, including acute coronary syndrome and natural childbirth.
Preventive measures will not provide a 100% guarantee, but they will significantly reduce the risk of developing pathology.
Is it possible to get pregnant after pathology?
Whether pregnancy is possible after suffering distal ectopia depends on the method of eliminating the problem.
If radical measures were taken and the reproductive organ was not preserved, then pregnancy becomes impossible.
If the uterus was preserved, then at least 1 year must pass before the onset of a new pregnancy. During this time, the woman will regain her strength and her reproductive organs will be in order.
The chances of getting pregnant are individual and depend on the cause of the disease, the severity and age of the patient.
The need for surgery
After obtaining the desired effect from Methotrexate, doctors excise the fertilized egg using a hysteroresectoscope. The operation is performed using intravenous anesthesia. Its main advantage is the ability to preserve the reproductive organ. The procedure lasts about 20-30 minutes. Approximately 50% of patients while taking Methotrexate manage to become pregnant again naturally.
Some clinics today use another option for eliminating cervical pregnancy. This is a low-traumatic operation, which consists of the following stages:
- Clipping of the uterine arteries to cut off the blood supply to the reproductive organ.
- Removal of the fetus from the cervix using vacuum aspiration.
- Cervical tamponade with a Foley catheter (a drainage device with a balloon at one end).
Unfortunately, no treatment method is perfect. Therefore, it is better to prevent the development of pathology and take care of your health.