What are adenoids
Adenoids are enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsils.
Normally, the organ protects the bronchopulmonary system from the penetration of bacteria along with air from the external environment. As the disease develops, the tonsils lose their original functions, block the lumen of the nasopharynx and cause breathing problems. Adenoids are a barrier to infections that try to enter the body through the nasal cavity
Adenoids are folds of lymphoid tissue. In children who have not yet reached the age of seven, they perform the function of protecting the body from pathogenic agents. Adenoids do not allow pathogenic bacteria and viruses to penetrate the respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract.
After some time, the palatine tonsils begin to perform this function. The adenoids gradually die off. They stop working completely by the age of 16.
It was previously believed that adults did not have adenoids. But modern diagnostic methods have been able to confirm the opposite. Almost every third person has these formations that can affect the breathing process.
Over time, lymphoid tissue may increase in size. Its growth is promoted by colds and viral diseases. The more often a person gets sick, the higher the likelihood that his adenoids will enlarge.
Considering these features, it can be said whether adenoids are present in adults or not.
USEFUL: How to increase a child’s immunity if he is sick? Read more…
Causes of adenoiditis
According to the international classification of diseases, adenoiditis belongs to the section “Chronic diseases of the tonsils and adenoids”, ICD 10 code – J35.
Regarding the reasons that provoke the pathology, the main factor is infection. Most often, the disease develops due to the penetration of viruses into the body. In this case, adenoiditis manifests itself as one of the symptoms of acute respiratory viral infection; it is difficult to make a diagnosis in this condition due to the contiguity of the symptoms.
The second infectious reason why pathological vegetations appear is bacterial lesions. As an independent disease, it rarely develops; more often it manifests itself as a secondary infection against the background of a viral process. Due to infection by bacteria, with untimely diagnosis and improper treatment, purulent adenoiditis develops. This condition is life-threatening for the patient; the pus spreads to other nearby organs.
Non-infectious causes of adenoiditis include allergic manifestations or unfavorable living conditions. Pathology appears due to the penetration of an allergen into the body, inhalation of polluted air, high humidity or, conversely, dryness in the room.
If the disease is not given due attention in the early stages of the process, it becomes sluggish. Chronic adenoiditis in childhood is not a death sentence, since the nasopharyngeal tonsil tends to shrink. By the time of puberty, it practically disappears as an organ, only the basal part remains. But this does not mean that adenoids can not be treated. Pathology triggers irreversible processes in the body, the consequences of which are unpredictable, including death.
How to treat adenoids in adults?
Treatment of inflamed adenoids in adults involves therapeutic manipulations that combat the root cause of the disease. To alleviate the patient’s condition, means are used aimed at reducing the inflammatory process and the size of overgrown formations.
The medicine is taken before or after meals (the dosage is determined individually for each patient)
Conservative treatment helps restore nasal breathing and eliminate the symptoms of adenoids in adults.
It is recommended to carry out conservative therapy at the first stage of the disease. At later stages it will have minimal effect.
The patient is prescribed a whole range of medications that cope with the root cause of the pathology and its painful symptoms. For adenoids, adults are prescribed the following medications:
- Antibiotics (“Amoxiclav”, “Amosin”).
- Nasal rinsing solutions (“Furacilin”, “Chlorhexidine”).
- Vasoconstrictor drops (“Nazol”, “Protargol”).
- Homeopathic remedies to support the immune system (Sinupret, Lymphomyosot).
Before prescribing the drug, the doctor must make sure that the patient has no contraindications to such therapy. If the drug does not provide improvement, then it is replaced.
Surgical treatment
Removal and treatment of adenoids is carried out only according to indications that are identified in a person during diagnosis. There are several ways to excise the affected tissue. The optimal treatment option is selected by the attending physician.
Reference! The operation to remove the adenoids is called adenotomy.
Several options for radical treatment of pathology are offered, since inflamed adenoids in adults are removed in different ways:
- Classic operation. During surgery, overgrown tissue is removed with a Beckman knife. In its upper part there is a blade with which basic manipulations are performed. The total duration of radical treatment usually does not exceed 40 minutes. Rehabilitation takes the patient about 10 days.
- Endoscopic removal. A minimally invasive method for treating adenoids in adults. During the operation, devices are used, the actions of which are controlled by a specialist, since everything is displayed on the monitor.
- Laser therapy. One of the modern methods that is practiced in many clinics. The main advantage of the treatment is the absence of bleeding after tissue excision and a short rehabilitation period.
If a patient needs advice, he can always ask a doctor about how to treat adenoids.
Traditional methods
Inhalations can be done at home using the “old-fashioned” method or you can purchase a special device at the pharmacy
In the early stages of adenoid development, treatment with folk remedies is allowed. This treatment option must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Note! Folk remedies must be used in combination with traditional therapy, since as a monotherapy they give little result.
Essential oils help cope with swelling of soft tissues and a runny nose. Inhalations are carried out with them, which help prevent the development of infection and other complications.
For inhalation, you need to pour hot water into a bowl, then add a few drops of essential oil to it. You need to breathe over this container for about 5-7 minutes.
Flushing helps eliminate mucus that accumulates in the nasopharynx. The procedure is carried out with antiseptic solutions. The most effective is chamomile decoction. A saline solution can also give good results. It is recommended to wash them every 3-4 hours to achieve the best effect.
First degree adenoids in adults can be treated conservatively. This means that with the help of vasoconstrictors it is possible to remove nasal congestion. The doctor also often prescribes eucalyptus tincture for mouth rinsing and antibiotics for difficult cases.
Second and third degree adenoids are difficult to treat with medication, so the doctor performs surgery to remove the lymphoid tissue. However, the operation is performed only on patients who cannot breathe through their nose at all and experience discomfort.
If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, the following consequences may occur:
- The patient may experience problems with breathing and smell. It is extremely difficult to breathe through the nose, so the function is performed only through the mouth.
- Constant illnesses of acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections and colds.
- Ear diseases, pain in the ear area.
- Mucous and purulent discharge. Nasal congestion, headaches, dizziness and inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Doctors recommend starting treatment as quickly as possible, otherwise complications may appear that are not amenable to complex therapy. It is also very important to determine the cause of adenoids.
Diagnosis of the disease
Typically, an adult turns to an ENT doctor when he has recurring sinusitis or increased snoring at night prevents him from getting enough sleep and reduces his ability to work. In order to establish the exact cause of such pathologies, the otolaryngologist must not only examine and collect complaints from his patient, but also need to conduct a series of examinations.
To identify disorders in the nasopharynx, use:
- Posterior rhinoscopy . A special mirror is inserted into the patient’s mouth, allowing a clear view of the vault of the throat.
- Radiography . An enlarged tonsil is visualized on a photograph of the skull taken in a lateral projection.
- Computed tomography . This study allows you to obtain images showing the structure of the palatine tonsil and nearby structures in a three-dimensional image.
- Endoscopy . A flexible instrument with a miniature video camera at its end is inserted through the nose or mouth. The image is displayed on the monitor, and the doctor clearly assesses the condition of the oropharynx.
If a malignancy is suspected, a biopsy is indicated. The diagnosis is made only based on the totality of all examinations.
What complications may arise?
The most common complications are respiratory arrest and suffocation during sleep. They occur because air cannot pass through the respiratory tract normally. This is prevented by enlarged adenoids. The situation gets especially worse during inflammation.
Infection from inflamed adenoids can spread to neighboring organs. In this case, the following complications may occur:
- Acute otitis media of the middle ear. This complication often occurs in patients with adenoiditis. Inflamed tonsils block the mouths of the auditory canals, which connect the middle ear cavity and the nasopharynx.
- Acute pharyngitis, laryngitis, bronchitis, tracheitis. They can develop if mucous and purulent discharge from the adenoids gets into the throat.
- Acute inflammation of the sinuses.
- Angina. The inflammatory process occurs in the oropharyngeal tonsils.
Inflammation of the tonsils increases the risk of developing infectious diseases of the respiratory system. In advanced cases, bacteria can damage the mucous membranes and lead to their replacement. Sometimes adhesions block the airway. The development of chronic bronchitis is often observed.
Due to the blockage of the auditory tubes and the spread of infection, there is a risk of developing otitis media. The inflammation most often affects the middle or inner part of the ear. In the future, this can cause infection of the membranes of the brain.
The consequences of adenoids are irreversible. As a result of respiratory failure and oxygen starvation of organs, systemic deviations develop. These include heart failure. With a severe, long-term course of the disease, the oval of the face changes. This is fraught with breathing problems and the development of concomitant pathologies.
Pharyngeal tonsil and its functions
Tonsils are collections of lymphoid tissue localized in the nasopharynx and oral cavity. There are 6 of them in the human body: paired - palatine and tubal (2 pieces each), unpaired - lingual and pharyngeal. Together with lymphoid granules and lateral ridges on the posterior wall of the pharynx, they form a lymphatic pharyngeal ring surrounding the entrance to the respiratory and digestive tracts. The pharyngeal tonsil, the pathological growth of which is called adenoids, is attached at its base to the posterior wall of the nasopharynx at the point where the nasal cavity exits into the oral cavity. Unlike the palatine tonsils, it is not possible to see it without special equipment.
Tonsils are part of the immune system and perform a barrier function, preventing further penetration of pathogenic agents into the body. They form lymphocytes - cells responsible for humoral and cellular immunity.
In newborns and children in the first months of life, the tonsils are underdeveloped and do not function properly. Later, under the influence of pathogenic bacteria, viruses and toxins constantly attacking the small organism, the active development of all structures of the lymphatic pharyngeal ring begins. In this case, the pharyngeal tonsil is formed more actively than others, which is due to its location at the very beginning of the respiratory tract, in the zone of the body’s first contact with antigens. The folds of its mucous membrane thicken, lengthen, and take on the appearance of ridges separated by grooves. It reaches full development by 2–3 years.
As the immune system develops and antibodies accumulate after 9–10 years, the pharyngeal lymphatic ring undergoes uneven reverse development.
The size of the tonsils decreases significantly, the pharyngeal tonsil often completely atrophies, and their protective function is transferred to the receptors of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. Share the article on social media. networks:
Treatment without surgery
If the disease has just appeared and has minor symptoms, then drug treatment will be the best treatment option. The first degree is amenable to conservative therapy, so the doctor tries to strengthen the immune system with the help of medications.
Complex therapy includes the following points:
- Using saline solutions, rinse the nasal passages. To do this, take a glass of water and a spoonful of soda, then mix everything. It is recommended to rinse at least three times a day.
- Anti-inflammatory and painkillers are also instilled into the nose, which remove mucus from the nose, relieving the person of a runny nose.
- Therapeutic gymnastics, massage.
- Physiotherapy (laser therapy, UHF therapy, electropheresis).
- Balanced diet and taking vitamin complex.
Treatment with folk remedies has proven itself excellent in medicine. For this, essential oils of cedar, eucalyptus, mint, and cloves are used. Mix everything in a single container and breathe in the fumes for 12 minutes. You can take various decoctions internally. However, it is worth remembering that only a doctor can prescribe medicines and medications.
In the early stages, agents are used to help cope with inflammation and tissue enlargement. If the lumen is severely narrowed, the processes located in the nose and pharynx are removed.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are used to prevent tonsil enlargement. Preference is given to sprays for local treatment. They reduce tissue sensitivity and prevent the disease from progressing to the next stage.
Histamine receptor blockers can be used to shrink tonsils. Medicines suppress the synthesis of new cells and promote the elimination of processes. After normalization of the immune system, there is a chance of tissue shrinkage.
Additionally, auxiliary and symptomatic drugs are used. They prevent the development of infections, reduce the risk of complications and alleviate the general condition.
Vitamins are most often used to strengthen the immune system.
In case of infection, antibiotics and antiviral agents are prescribed.
If there is mucous discharge, nasal rinsing preparations can be used.
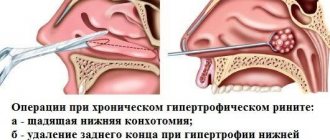
Surgically
Adenoid removal is performed in the following cases:
- Stage 3 of the disease;
- severe narrowing of the lumen of the respiratory tract, accompanied by attacks of suffocation;
- ineffectiveness of conservative therapy;
- hearing impairment;
- recurrent infectious diseases that are difficult to treat;
- change in the shape of the skull.
Local anesthesia is used for the procedure. General anesthesia may be used.
It is allowed to treat adenoids with folk remedies in the early stages. These methods must be combined with standard therapy, as they are not effective enough. If further treatment without surgery is impossible, the use of folk remedies is stopped due to inappropriateness.
Essential oils are used to eliminate swelling and runny nose. Inhalations reduce the risk of developing infectious diseases. To carry out the procedure, use a bowl of hot water or a clean cloth. In the first case, add 2-3 drops of oil to the liquid, bend over the container and breathe in the vapor for 5-7 minutes.
To remove mucus, rinsing is carried out. It is advisable to use a decoction of chamomile, as it is more delicate, but in extreme cases, you can prepare a saline solution. 1 tbsp. l. crystals are dissolved in a glass of warm water. The prepared solution is injected into the nostrils using a syringe. Washing is carried out every 3-4 hours.
Currently, there are no medications that would make adenoids smaller. Therefore, the main treatment is surgery.
Medication therapy is aimed at relieving inflammation in the nasal cavity and restoring nasal breathing. To do this, it is recommended to rinse to clear the mucus from the nose.
After the washing procedure, antibacterial sprays are used. When the adenoids become inflamed during acute respiratory viral infections, antiviral drugs are prescribed, and when the temperature rises, antipyretics are prescribed.
If problems with adenoids began due to allergies, then you need to take antiallergic drugs. In more severe cases, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Physical therapy may be used in addition to drug treatment. For adenoids, procedures such as:
- Ozone therapy. It is aimed at eliminating bacteria and viruses.
- Laser therapy. It allows you to improve blood circulation and relieve inflammation.
It is advisable to carry out drug treatment of adenoid vegetations in adults in the case of slight proliferation of lymphoid tissues. It should be understood that with grades 2 and 3 hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil, there is practically no chance of its reduction. If surgical intervention is contraindicated due to the patient’s health, treatment of ENT pathology is carried out using the following drugs:
- anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents - “Poviargol”, “Bioparox”, “Protargol”;
- antiallergic drugs – “Erius”, “Zirtek”, “Suprastin”;
- vasoconstrictor nasal drops - “Naphthyzin”, “Sanorin”, “Galazolin”;
- preparations for darkening the oropharynx - Faringosept, Ingalipt, Hexoral;
- immunostimulating drugs - Bicyclovir, Copaxone, Laferon.
Important! A drug treatment regimen can only be prescribed by a specialist and only after a diagnosis has been made.
At the stage of regression of inflammatory reactions in the nasopharyngeal tonsil, physiotherapeutic methods of therapy can be used. Magnetotherapy, UHF therapy and ozone therapy increase local immunity, thereby reducing the risk of relapse of septic inflammation of the ENT organs.
Surgery is a radical treatment method during which a specialist removes adenoid vegetations. If drug therapy brings only temporary relief from the symptoms of ENT pathology, the patient is prescribed an adenotomy. The absolute indications for surgery are:
- 2 or 3 degree of development of adenoid vegetations;
- lack of therapeutic effect from drug therapy;
- hearing impairment leading to the development of conductive hearing loss;
- frequent relapses of tonsillitis and retronasal tonsillitis.
The operation should not be performed on patients suffering from diabetes mellitus, blood diseases and cardiovascular pathologies, as this can lead to death.
Before surgery, the nasopharynx is cleared of pathological secretions and pathogenic agents with antiseptic solutions. The enlarged tonsil is excised with an adenotomy under local anesthesia. During the operation, a thin round knife is inserted into the nasal cavity, with the help of which the surgeon captures and cuts off the adenoid vegetations.
It takes no more than 20 minutes to complete all the necessary manipulations, after which the operated tissues are treated with an antimicrobial drug. To reduce the likelihood of pathogenic flora developing in the nasopharynx, the patient should take antibiotics and immunostimulating drugs for 2 weeks. In the absence of postoperative complications, the patient is discharged from the hospital on the 3rd day after adenotomy.
Adenoid grades
Clinical manifestations of ENT pathology largely depend on the degree of proliferation of adenoid tissue. A slight increase in the immune organ causes virtually no discomfort; pathological symptoms, such as dry cough and snoring, appear only at night. The second and third degrees of hypertrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsil significantly worsens the patient’s quality of life and entails complications.
| Symptoms | 1st degree of hypertrophy | 2nd degree of hypertrophy | 3rd degree of hypertrophy |
| pharyngeal tonsil size | adenoid vegetations cover only 1/3 of the choanae (nasal passages) and the vomer (a bone that is part of the nasal septum) | hyperplastic tissues cover up to 50% of the vomer and choanae | the enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsil almost completely blocks the nasal passages and the mouth of the Eustachian tube |
| hearing impairment | absent | slight hearing loss | due to blockage of the auditory canal, a sharp decrease in hearing is observed, which entails a decrease in pressure in the tympanic cavity; accumulation of effusion in the middle ear often causes the development of catarrhal otitis media |
| nasal breathing disorder | difficulty in nasal breathing is observed only at night when the patient takes a horizontal position | snoring during sleep, difficulty breathing through the nose | the patient is constantly forced to breathe through the mouth, so the overgrown adenoid vegetations almost completely block the nasal canals |
| accompanying symptoms | dizziness immediately after sleep, lethargy, headaches | frequent rhinitis, mucus running down the walls of the throat, sore throat, dry cough | constant opening of the mouth, difficulty swallowing, frequent relapses of respiratory diseases, mucous discharge from the nasal passages, headaches, eustachitis, nasal voice |
| features of therapy | drug treatment | drug and physiotherapeutic treatment | excision of hypertrophied tissue |
Adenoids can cause chronic inflammation of the mucous membranes in the nasal cavity and laryngopharynx, which leads to the development of sinusitis, bacterial pharyngitis, laryngotracheitis, etc.
Adenoids in adults very often occur against the background of chronic rhinitis and sinusitis. Inflammation of the tissues of the nasopharynx stimulates the activity of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, which begins to produce an excess number of phagocytes and T-lymphocytes. Prolonged irritation of the immune organ by pathological mucus leads to an increase in its size and the development of ENT pathology.
Depending on the degree of growth, 3 stages of the disease are distinguished. The treatment regimen and prognosis depend on the size of the adenoids.
First
Pathological tissues block the lumen by 1/3. At this stage, patients rarely seek help because they do not notice the symptoms. Due to the relatively small size of the tonsils, discomfort does not bother patients during the day, so the quality of life does not deteriorate. Symptoms appear at night when lying in a horizontal position.
Second
Enlarged tonsils block 2/3 of the lumen. This leads to a sharp deterioration in the quality of life. At stage 2, the disease does not pose a threat, so conservative methods are preferred in treatment. However, the risk of tissue enlargement remains.
Third
The tonsils are blocked by 70% or more. The symptoms are severe, the pathology is accompanied by attacks of suffocation. The last stage is life-threatening. When choosing a treatment regimen, preference is given to surgical methods.
Symptoms
The signs of adenoids in an adult are slightly different from those in children. The fact is that the human body in adulthood is already formed, so the disease minimally affects the facial bones and chest. However, pathology still makes itself felt:
- Colds, runny nose, nasal congestion. All these factors reduce the sense of smell.
- Snoring, snoring and poor sleep.
- Problems with hearing and speech.
- Changing the timbre of your voice.
- Sinusitis.
- Cough, irritation of the nasopharynx.
- Dizziness, headaches.
- Purulent discharge from the nose.
- Increased body temperature.
- Malaise, lethargy.
Each person's symptoms may be different; they do not necessarily show all the signs of adenoids. The main thing is that the person at this moment feels discomfort and breathing problems. Doctors call this disease adenoiditis.
When the tonsil reaches its maximum size, it prevents a person from breathing normally. Then an adult may develop problems such as a slightly open mouth, nasal sound, pain in the ears, hearing loss and frequent colds. Patients with asthma suffer the most severe illness. In this regard, you need to immediately undergo examination in the hospital in order to begin treatment as soon as possible.
Doctors also distinguish three degrees of the disease:
- The first degree is almost invisible. Only at night can you feel snoring and sniffling.
- When the second stage of adenoid disease occurs, more obvious signs of adenoid disease appear. A person breathes through his mouth even during the day.
- As for the third degree, doctors identify the following symptoms: purulent nasal discharge, breathing problems (choking), dry cough, increased body temperature.
It is worth noting that only a doctor can determine the extent of adenoids. After examination and diagnosis, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis, which helps to create a treatment plan.