Ectopic pregnancy
Normally, a fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus, where the embryo will develop in the future. Many factors contribute to this. And if at least one of the conditions changes or is violated, the risk of ectopic pregnancy increases.
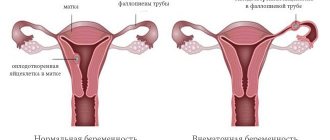
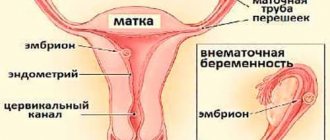
An ectopic pregnancy is a severe pregnancy pathology in which the fertilized egg is implanted (fixed) not in the uterine cavity, but outside it. This phenomenon is dangerous because no other organ is able to provide conditions for the development of the fetus. After attachment, the fertilized egg can begin to develop normally, which is accompanied by the formation of the placenta, amniotic sac and other embryonic organs. In order for the placenta to receive nutrition, it needs to form a connection with the blood vessels of the pregnant woman. And if the vessels of the uterus are not capable of forming such a “connection,” then the vascular network of other organs is destroyed, which is accompanied by bleeding. In some cases, the growth of the fertilized egg can cause organ rupture (for example, if implantation occurs in the fallopian tube) or damage.
An ectopic pregnancy carries a great risk to the life of the pregnant woman and, unfortunately, cannot ensure the successful development of the fetus. Therefore, its occurrence is always an indication for surgical intervention.
Find out what the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are at an early stage.
How to find out if pregnancy is intrauterine after IVF?
The first symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy cannot serve as a reliable reason for treating the pathology. To ensure that the fertilized egg is not implanted correctly, diagnostic procedures should be carried out in a medical hospital.
Examination by a gynecologist
Depending on the severity of the woman’s condition, the gynecologist examines her in a gynecological chair. The data obtained in this way are not final, but allow the specialist to assess the patient’s condition.
Blood test for hCG
An important step in diagnosis is the determination of the beta subunit of hCG. This subunit is specific with its own schedule of changes in concentration depending on the duration of pregnancy. With beta-hCG levels
In addition to blood tests, ultrasound is used to diagnose ectopic pregnancy.
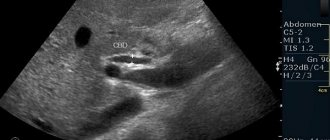
If the embryo is absent from the uterus with a positive hCG reading, one should think about its abnormal placement. The most accurate method is Doppler ultrasound. The image obtained in this way allows you to accurately determine the location of the attachment of the fertilized egg. It is performed transvaginally if the patient’s condition is appropriate and there is no severe bleeding.
Laparoscopy
If the results of previous studies are insufficient or questionable, laparoscopy is sometimes prescribed. The essence of the procedure is to examine the pelvic cavity, in particular the fallopian tubes, using a laparoscope (a telescopic tube with lenses connected to a video camera, the image is transmitted to the screen). The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
What is the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy during IVF?
The probability of an ectopic pregnancy with IVF ranges from 2 to 10%. Even if a woman follows all the doctors’ recommendations, there is no guarantee that this pathology will not develop. Knowing this, specialists treat their patients very carefully so as not to miss the development of complications.
Can there be an ectopic pregnancy during IVF if the fallopian tubes are removed? Even then, there is a risk because the pipes are not completely removed. And in the remaining area or on the border with the uterus, the fertilized egg can also attach, contributing to the development of an ectopic pregnancy.
Types of pathology
Experts divide ectopic pregnancy into several types depending on the site of attachment of the egg.
It can be implanted in the following places:
- In the area of the removed fallopian tube.
- Inside one of the pipes. Such a pregnancy may rupture the tube as the fetus grows.
- In the area of the cervix. It is rare, and the embryo can develop in this way for quite a long time.
- On the ovaries. Often occurs during IVF as a result of hyperstimulation of ovulation.
- In the abdominal cavity. It is very dangerous for a woman’s life and can lead to tissue necrosis, sepsis, and peritonitis.
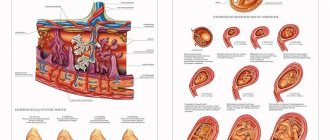
In most cases (8 out of 10), the fetus is attached to the fallopian tube, much less often this occurs in the peritoneum. The main danger of improper implantation is injury and rupture of the organ, as well as internal bleeding. If nothing is done, everything can end in death.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy after IVF
After the fertilized egg is transferred into the uterine cavity, some time passes before the fertilized egg implants into the uterine wall. During this time, migration of the embryo may occur. Doctors identify several possible causes (risk factors) of ectopic pregnancy after IVF:
- Ovarian hyperstimulation. This is the use of drugs to stimulate ovarian function. Dosages are not always calculated accurately, and in some cases a woman may be too sensitive to the drug due to the characteristics of her body. At large dosages, internal edema of various organs, including the fallopian tubes, may develop. The villi, which usually move to move the egg toward the uterus, are no longer able to fully perform their function. And if a fertilized egg gets into one of the tubes, it will not be able to return back to the uterus.
- Operations on the fallopian tubes. Modern surgery strives to ensure that intervention in the patient’s body is minimal. And it's not just about the cosmetic effect. Connective tissue forms in the area of the operation, ensuring healing of the organ. But she does not take on the function of this organ. That is why, if one of the tubes has been operated on or touched, the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy increases.
- Congenital changes in the organs of the reproductive system (deformations of the fallopian tubes, uterus). During intrauterine development, some organs may develop with minor or significant deviations. For example, anomalies of the uterus include a rudimentary horn and a bicornuate uterus. If the embryo is implanted in the area of the rudiment or horn, this pregnancy will also be pathological.
- Diseases of the uterus and appendages of an inflammatory nature. They lead to a decrease in the functionality of organs.
- Changes in hormonal levels. One of the dishormonal pathological disorders is endometriosis. It occurs when endometrial cells enter the fallopian tubes and even the abdominal cavity with menstrual blood. There these cells take root, forming islands. They directly have a pathological effect on the functional activity of the reproductive organs.
- Failure to comply with doctors' recommendations after the IVF procedure.
The main stages of IVF
Before we find out why an ectopic pregnancy occurs after IVF, let us recall the main stages of the procedure. After all, the risk of pathology largely depends on the correctness of their implementation. Patients who are indicated for artificial insemination are carefully examined to identify all contraindications. If inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system or sexually transmitted infections are diagnosed, they are treated. When the woman is healthy, an ovarian stimulation protocol is determined. It can be long or short. The duration of the short protocol is 10-14 days, the long one is 20-25 days. In some cases, if there are contraindications, they try to obtain eggs without stimulation.
When the follicles are mature (determined by ultrasound), they are punctured. The eggs are placed in a special medium, mixed with sperm, and fertilization lasts 12-24 hours. Then the embryo is transferred to a thermostat, where it is incubated for 2-5 days. During this period, the woman is prescribed progesterone and estrogens to prepare the uterine wall for implantation. Insufficient development of the endometrium can cause an ectopic pregnancy.
Embryo transfer is done 3-6 days after puncture. It is carried out in an operating room, but without hospitalization of the patient. Immediately after completion of the procedure, the woman can go home. On the fifth day, progesterone levels are monitored to adjust maintenance therapy. On the 14th day after the transfer, an hCG test is performed. It is he who can indicate that a pathology has arisen. An indirect sign is a significant increase in basal temperature. The expectant mother should carefully monitor her condition so as not to miss dangerous symptoms, which will be discussed below.
Types of ectopic pregnancy during IVF
Based on the location of the implanted fertilized egg, the following types of ectopic pregnancy are distinguished:
- Tubal pregnancy. It develops in 95-98% of cases. The severity depends on which part of the tube the egg is attached to. The most favorable option is to place the fertilized egg in the wide (ampullary) part of the tube.
- Ovarian pregnancy.
- Abdominal pregnancy. In this case, the embryo is attached to some organ of the abdominal cavity. Since the pain in this case is not very pronounced, and the location is quite difficult to determine using ultrasound, this type of ectopic pregnancy is one of the most dangerous.
- Cervical pregnancy. It occurs when the fertilized egg leaves the uterus, but at the last moment attaches to the cervix. But such a pregnancy occurs extremely rarely.
- Pregnancy developing when fixed in the rudimentary uterine horn. Since the embryo is located in the uterus, such a pregnancy may not be detected for a long time. But since it is still pathological, the fetus will not be able to fully develop.
Features of ectopic
One of the problems of ectopic conception with in vitro fertilization is the high probability of heterotopic pregnancy. In this condition, one embryo develops inside the uterus, as expected, and the other develops outside the uterine body. This is observed when several embryos are transferred; in search of a place to attach, one fetus may move into the tube.
In such a situation, specialists are faced with a difficult task - they need to remove the fallopian tube with the embryo attached to it, while preserving the fertilized egg inside the uterus. But this is not always possible. Fortunately, the frequency of such cases is one in 30 thousand. It is to prevent such a situation that in some countries, removal of the fallopian tubes is considered one of the mandatory points of the IVF protocol.
Symptoms of ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy
The manifestation of signs of ectopic pregnancy after IVF depends on the stage of the pregnancy itself. If it has just begun to develop, and the pregnant woman generally feels relatively well, then the symptoms are no different from those of a normal pregnancy. In the case when a tube ruptures or damage to another organ occurs, which is accompanied by bleeding, the presence of an ectopic pregnancy can already be assumed.
Signs of developing ectopic pregnancy:
- absence of menstruation;
- nausea;
- decreased or increased appetite;
- increased fatigue, drowsiness;
- irritability;
- increased sensitivity to different odors;
- enlargement of the mammary glands.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy that indicate termination of pregnancy:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, which occurs mainly on the side where pregnancy develops. Often it can spread to the rectum and extend to the lumbar region.
- When a large amount of blood accumulates in the abdominal cavity, the abdomen may increase slightly in volume. This is also accompanied by severe abdominal pain.
- Bloody issues. They may be spotty or watery. In general, their number is small, since most of the blood accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
- Signs indicating loss of a large volume of blood: pallor, dizziness, decreased blood pressure, vomiting. The woman may even lose consciousness. Such symptoms develop if an ectopic pregnancy is not detected immediately.
Treatment
The main goal of treatment is to remove the pathologically located embryo. There are no other solutions to this problem. Two main approaches to treatment have been developed, each with their own characteristics.
Drug therapy
During this procedure, hormonal drugs are prescribed that cause abortion. These are drugs such as mifepristone and others. They cause active rejection of the endometrium, along with the embryo.
The method is quite traumatic, has a bad effect on the body, hormonal balance, and injures the mucous membrane. Subsequently, taking such a drug increases the likelihood of developing an ectopic pregnancy. It is rarely prescribed even for natural conception. And even less often - during in vitro fertilization, when the body was artificially hormonally prepared for conception.
In addition, it is not applicable in the case of a heterotopic pregnancy, when it is possible to “save” one embryo.
Surgery
The fertilized egg can be removed surgically. This is done laparotomically or laparoscopically. In the case of IVF, VMB can be diagnosed early, when the size of the embryo is not large. This allows it to be removed laparoscopically. But if the embryo is large, this method is not suitable. And I have to do abdominal surgery.
The method helps with significant periods of VMB. And also, with its help, you can remove only one pathological embryo, preserving the others.
How is an ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
An ectopic pregnancy is usually detected more quickly during IVF, since the first screening is prescribed earlier than during a normal pregnancy - 3 weeks after fertilization of the egg. Doctors focus on two main points about examining a woman:
- Elevated hCG levels, which indicate the presence of gestation.
- The absence of a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity, which is detected by ultrasound.
Sometimes on an ultrasound it is possible to see changes in the appendages, which indicates the location of the fertilized egg. And in some cases, it is possible to determine the presence of fluid (blood accumulation) in the abdominal cavity.
How to recognize by tests and ultrasound
At the moment when the embryo is fixed, the chorion (future placenta) begins to secrete the hormone - hCG. As the period increases, its level will increase. It is hCG that any rapid test reacts to, even if the fetus is fixed in the wrong place.
Experts may suspect an ectopic pregnancy during IVF if a small amount of the hormone is present in the blood. Each period corresponds to a certain amount of hCG. And if it does not grow with the fetus, it means there are some pathologies.
Doctors diagnose ectopic pregnancy using the following criteria:
- HCG should double every 2 days. If this does not happen, suspicions arise. You should know that test results can only be assessed over time.
- An ultrasound does not detect a fertilized egg in the uterus. In the very early stages, it may not be visible with ultrasound, so do not get upset ahead of time. The study should be carried out approximately a month after embryo transfer.
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
It is possible to treat ectopic pregnancy with medications. However, doctors choose this method only if it is not possible to perform the operation (there are contraindications). These drugs are highly active and, accordingly, have many side effects, including on the reproductive system. Therefore, the choice of surgical intervention in this case is more preferable. Depending on the location of the embryo, the presence of complications and the woman’s desire to become pregnant again in the future, surgeons choose the method of intervention.
- Laparotomy. Access to the abdominal cavity is achieved through a large incision. The indication for such an operation is the patient’s serious condition, symptoms indicating loss of a large volume of blood. In this way, the surgeon can quickly stop the bleeding and further stabilize the woman’s condition.
- Laparoscopy. This operation is minimally invasive. Interventions in this case are minimal, which provides a good cosmetic effect and faster healing. By inserting a laparoscope into the abdominal cavity through small incisions, the surgeon can remove the embryo. If the pregnancy is short and the tube is not damaged, then you can get by by cutting the tube (it will not be removed). In some cases, it is possible to save part of the fallopian tube. But if it ruptures, it is necessary to remove the fertilized egg along with the tube.
After the operation, the woman’s condition must be monitored to avoid possible complications. Drug treatment is also prescribed, which is aimed at preventing the development of the inflammatory process, as well as restoring reproductive function.
Heterotopic pregnancy
A specific condition for VMB after IVF may be heterotopic pregnancy. In this condition, several embryos are attached, for example two. In this case, one is located pathologically ectopic, and the other is normally located in the uterine cavity.
Heterotopic pregnancy
The main difficulty for doctors in this case is to preserve the embryo in the uterus. But remove the ectopic. This cannot always be done. Of course, this condition almost never develops in the absence of fallopian tubes. That is why in a number of European countries with a high level of healthcare development, their removal is a mandatory condition for IVF.
Is it possible to get pregnant after an ectopic pregnancy?
Is it possible to have repeat IVF after an ectopic pregnancy? Of course, the woman will be able to get pregnant again. But after an ectopic pregnancy, you must wait six months. During this time, reproductive functions are restored. It is also very important to be much more attentive to your health. Most likely, preparations for another pregnancy will be much more serious.
To avoid ectopic pregnancy in the future, you must follow these recommendations:
- Prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases of the genital organs or treat them promptly and thoroughly.
- Monitor the general condition of the body.
- Create a proper diet for yourself.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Expert
- Latest articles
- Feedback
About the expert: +MAMA
We are the friendliest site for moms and your babies. Questions and answers, unique articles from doctors and writers - we have it all 
- Oligohydramnios during pregnancy -
- A newborn's eye is festering -
- When does the fontanelle close in newborns?
- Nutrition after childbirth -
- Headache during pregnancy -
- How to lose weight after childbirth -
- Second screening during pregnancy -
- Precursors of childbirth in multiparous women -
- How long do newborns sleep?
- How to remove belly fat after childbirth -
See all
Recovery period
If the organ into which the fetus was implanted was preserved, then improper attachment of the embryo may recur. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to carry out restorative therapy. It should be remembered that a woman should not become pregnant for the next six months, otherwise irreparable harm to her health can be caused.
Before surgery, examination and preparation of the pregnant woman is necessary. Afterwards, the woman is monitored, medications are administered through an IV, and antibacterial treatment is given. Doctors advise the patient to be active (move more and walk outdoors).
In order to restore the body as much as possible, postoperative recovery should begin in the first 12 hours. This is because adhesions begin to form at this time. Their appearance can be avoided using laser radiation or a magnetic field (quite effective methods).
Also, after an ectopic pregnancy during IVF, women are advised to:
- use contraception for the next six months;
- do hydroturbation, in which medications are injected into the fallopian tubes;
- stay physically active and avoid stress.