- February 27, 2019
- Pregnancy
- Sofia Ermakova
Diagnosis of pregnancy pathologies in the early stages is complicated by the diversity of the clinical picture. Some patients experience mild pain in the lower abdomen with minor discharge from the genital tract, others are hospitalized with hemorrhagic shock. Therefore, in all women of reproductive age, when complaining of discomfort in the lower abdomen, ectopic pregnancy is first excluded.
General information about ectopic pregnancy
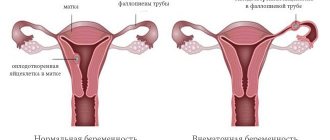
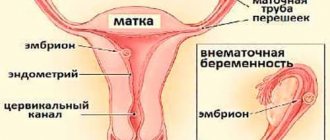
A normal pregnancy begins to develop when the fertilized egg implants in the uterine cavity. After the fusion of germ cells in the fallopian tube, the egg moves into the uterus, where the necessary conditions are provided for the development of the unborn child. The gynecologist determines the gestational age based on the height of the fundus of the organ. Thus, in the absence of an embryo, the normal dimensions of the uterus are about 8 cm in length and approximately 5 cm in width.
Pregnancy at six weeks can already be diagnosed by a slight enlargement of the reproductive organ. By the eighth week, the uterus has expanded to approximately the size of a woman's fist, and by the sixteenth week it is located somewhere in the middle between the womb and the navel.
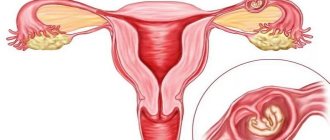
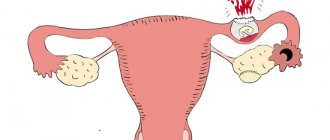
But in some cases, the fertilized egg is attached not in the uterine cavity, but in the tube, abdominal cavity or ovary. This is a serious pathology that is dangerous due to complex consequences and recurrence. A progressive ectopic pregnancy can cause rupture of the organ where the egg develops and be fatal. Cases of ectopic pregnancy have recently increased fivefold. In 7–22% of women, repeated abnormal pregnancies were noted, which in more than half of the cases leads to the development of secondary infertility.
Areas of fetal location in pathology
Based on indirect signs, the gynecologist determines uncharacteristic symptoms and manifestations. But an accurate diagnosis is possible only based on the results of ultrasound diagnostics.
Pipe zone
The most common option. Due to pathology of the fallopian tubes, the fertilized egg cannot enter the uterus and attaches to the wall of the tube. There it begins to develop and grow. The danger lies in rupture of the fallopian tube and bleeding as a result.
What this pregnancy looks like on video:
Abdominal space
A rare form in which the fetus is visualized in the abdominal cavity on ultrasound. There it attaches to any organ or abdominal wall, disrupting work and vital functions.
Options for having a child with this pathology are possible, but very rare. The child finds himself unprotected in free space, which negatively affects his development. At the same time, its growth provokes a malfunction in the functioning of internal organs.
Cervical zone
The fetus is located in the cervix of a pregnant woman. This form is rare and very life-threatening.
Ovarian zone
During fertilization, the egg does not leave the ovary, but begins to develop in it. This can lead to ovarian rupture and internal bleeding.
Risk factors
The risk of ectopic pregnancy is higher in patients who are at risk. Inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs can cause pathology, and sexually transmitted infections play a significant role. About 64–83% of women with an ectopic pregnancy have previously had chlamydia.
It is believed that the use of intrauterine contraceptives can also cause similar pathologies. According to some data, 18–20% of patients presenting with symptoms of ectopic pregnancy used contraceptives. Hormonal pills also increase the likelihood of such pathologies.
Quite often (up to 25%), improper attachment of the fetus is found in women who have undergone surgery on the appendages. A risk factor is the first pregnancy resulting from IVF. The transport function of the tube is disrupted in case of tumor-like formations of the ovaries and oncological diseases of the pelvic organs. A history of endometriosis, hormonal imbalances, endocrine diseases, and frigidity can contribute to the occurrence of an ectopic pregnancy.
Classification of ectopic pregnancy
Most often, the fertilized egg during an ectopic pregnancy is attached to the tube (according to various sources, up to 95–99% of cases). Ovarian pregnancy occurs in 0.1-1.3% of patients, cervical pregnancy - 0.1-0.4%, abdominal pregnancy - 0.1-0.9%. Attachment of the false membrane to the accessory horn of the uterus (this occurs in 0.2-0.9% of cases) is intrauterine, but the clinical picture is similar to the manifestations of uterine rupture. Multiple ectopic pregnancies are possible as a result of IVF, but in practice they are extremely rare. In this case, one fertilized egg is located in the uterus, the other outside the organ.
Diagnostic measures
The doctor may suspect an ectopic pregnancy based on the woman's complaints during the examination. In the area where the embryo is implanted, it is sometimes possible to feel a small lump, which, when touched, causes sharp pain. However, accurate diagnosis can only be made using instrumental and laboratory methods used in combination.
When using an intravaginal sensor, the embryo becomes visible on ultrasound only after 4 weeks. A transabdominal examination performed through the abdominal cavity will show pathology only at 6–7 weeks. The embryo looks like a dark oval vesicle (pictured).
A fetus implanted outside the uterus is not always visible, so indirect signs will help determine the pathology. An ultrasound specialist in case of an ectopic pregnancy will see: (more details in the article: how is an ectopic pregnancy determined?)
- absence of the fetus in the uterine cavity in the presence of signs of conception;
- small, inappropriate increase in size of the uterus;
- false ovum;
- corpus luteum cyst;
- the appearance of fluid inside the uterine cavity.
The diagnosis made during ultrasound can be clarified using a blood test. After implantation, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin increases. It triggers physiological processes in a woman’s body necessary for the development of the fetus and stimulates the production of other hormones. In the early stages of ectopic pregnancy, the indicator may not differ from normal values, however, as the period increases, the concentration of hCG decreases (we recommend reading: indicators of hCG levels by week during ectopic pregnancy). Progesterone levels will also be low. Such deviations are also observed when there is a threat of spontaneous abortion or frozen pregnancy.
Diagnosis of interrupted abnormal pregnancy
With abnormal attachment of the fertilized egg, there are four possible pathology development options:
- progressive ectopic pregnancy;
- non-developing ectopic pregnancy;
- pregnancy terminated spontaneously;
- pregnancy interrupted as a result of a ruptured tube.
The consequence of an interrupted tubal pregnancy is often hemorrhagic shock. There is pain on palpation of the anterior abdominal wall. Sometimes even with hemorrhagic shock the pain may be insignificant. In 15% of cases, patients report discomfort in the collarbone or shoulder due to nerve irritation. Differential diagnosis of cyst rupture and splenic rupture is necessary.
Accuracy of ultrasound diagnostics
In fact, diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy is not so easy; in the early stages it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with various diseases of the reproductive system and more. If there are only indirect signs, it is important to conduct a comprehensive assessment of all survey data.
Ectopic pregnancy should be differentiated from the following pathological conditions:
- appendicitis;
- ovarian cyst, its rupture, torsion and other pathologies;
- uterine fibroids;
- corpus luteum cyst;
- volumetric processes in the organs of the genitourinary system.
Modern methods of surgical interventions for ectopic pregnancy make it possible to preserve women's fertility in full. To do this, it is only necessary to diagnose the pathology in time and carry out qualified treatment.
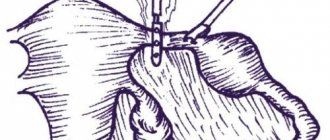
The following methods of interrupting the pathological process are known in medicine: extrusion, salpingotomy, tubectomy, laparoscopy. After the operation, ultrasound confirms that the fertilized egg has come out completely.
Less often, under the influence of unfavorable factors, the zygote is pushed out of the tube in the opposite direction and settles on the wall of the peritoneum or in the ovary. In the latter case, fertilization occurs before or immediately after the release of the egg. This pathological phenomenon is fraught with ovarian rupture.
Diagnostics
Does an ultrasound show an ectopic pregnancy? Ultrasound examination is the leading method for diagnosing pathology. As for the clinical picture, one can suspect a developing tubal pregnancy first by minor abdominal pain, which increases as the period increases, delayed menstruation, dark or bright red discharge from the genital tract, abdominal pain on palpation, uterine enlargement less than the expected gestational age (determined by a gynecologist ). An ectopic pregnancy at 5 weeks usually becomes visible on an ultrasound, so if you contact a specialist early, you can avoid the serious consequences of the pathology.
Inaccuracies and complications
And yet, concerned women are interested in whether an ultrasound will show an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages in all cases? Or are there errors? No one can give a 100% guarantee due to the following reasons:
- Too short a pregnancy does not physically allow one to determine whether there is an embryo in the uterine cavity or not.
- Limited range of ultrasound machine capabilities.
- Imperfection of the equipment used and its possible malfunction.
- The specialist performing the diagnostic procedure did not have sufficient qualifications and experience.
Sometimes an accumulation of fluid or a blood clot in the uterus looks like a fertilized egg and the specialist mistakenly determines intrauterine pregnancy. The woman calms down accordingly, and if the internal bleeding is insignificant, then a pathological pregnancy can proceed hidden for a long time and at the same time not have pronounced symptoms.
A frequent option for further developments is rupture of the fallopian tube. This happens suddenly and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- A sharp pain is felt in the lower abdomen, mainly on the side where the fertilized egg was attached to the tube. The pain radiates to the rectum area, as well as the right collarbone.
- Often there is a false urge to defecate or loose stools appear. The abdomen is swollen and painful on palpation.
- Decreased blood pressure, severe weakness, even fainting. With severe bleeding, hemorrhagic shock develops.
- Pale skin and mucous membranes, shortness of breath, cold sweat.
- Apathy, lethargy, rapid, weak pulse.
Treatment in this case involves immediate surgery. The damaged fallopian tube is removed laparoscopically, and if hemorrhagic shock occurs, then by performing a laparotomy (open access to the abdominal cavity).
Ultrasound with the introduction of a vaginal sensor is considered the most accurate diagnostic method in determining ectopic pregnancy. But you shouldn’t expect a 100% guarantee from him either. Not in all cases this pathology will be visible and the correct diagnosis will be made. It is advisable to combine ultrasound diagnostics with other methods for greater accuracy.
- February 27, 2019
- Pregnancy
- Sofia Ermakova
Diagnosis of pregnancy pathologies in the early stages is complicated by the diversity of the clinical picture. Some patients experience mild pain in the lower abdomen with minor discharge from the genital tract, others are hospitalized with hemorrhagic shock. Therefore, in all women of reproductive age, when complaining of discomfort in the lower abdomen, ectopic pregnancy is first excluded.
Differential diagnosis of pathology
If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, the specialist will conduct a differential diagnosis. It is necessary to exclude other pregnancy-related diseases in the patient. This can be a spontaneous threatening abortion, complete or incomplete abortion, hydatidiform mole, infected abortion, and the like. Or diseases not associated with pregnancy (inflammation of the appendix, rupture of the cyst, genital tract infection, renal colic, ovarian torsion, acute salpingitis, uterine bleeding). Laboratory tests and ultrasound examination are usually prescribed. Ultrasound shows an ectopic pregnancy already in the early stages, which allows for a correct diagnosis.
Further tactics
If an ectopic pregnancy is visible on an ultrasound, the woman is sent to a gynecological hospital to terminate it.
It is impossible to carry the fetus to the birth of a healthy child, and a delay of even one day threatens the life of the mother. Gestational age determines medical tactics.
Termination of pregnancy can be done in several ways:
- Medical abortion is a procedure where special drugs artificially induce a miscarriage in a woman. Use can only be in early pregnancy; it allows you to preserve the fallopian tube intact.
- Laparoscopic intervention - several punctures are made in the abdominal wall, special instruments are inserted into the pelvic cavity, with the help of which the fallopian tube is cut, the embryo is removed, and the tube is sutured and preserved. Both of these methods do not affect a woman’s ability to subsequently conceive and bear a child.
Laparoscopic surgery for ectopic pregnancy
- Laparotomy surgery has to be performed when an ectopic pregnancy can be determined after the rupture of the fallopian tube, the onset of bleeding, and when there is a threat of peritonitis. An emergency incision is made and the damaged tube is removed along with the embryo. The likelihood of getting pregnant in the future is reduced by 2 times compared to healthy women.
When there is at least some hope that the fertilized egg will descend from the fallopian tube into the uterus, the hospital doctor will take a wait-and-see approach and monitor signs of the disease using an ultrasound procedure.
Laboratory diagnostic methods
In case of ectopic pregnancy, blood tests for hCG content, progesterone concentration, and a general clinical analysis are indicated. In case of abnormal attachment of the fertilized egg, the results of hCG in the blood or urine are positive. With normal attachment in the first few weeks, the content of the beta subunit doubles approximately every two days, with an ectopic level it grows more slowly. Usually blood is donated over time at intervals of 48 hours. In 85% of tubal pregnancies, the hormone concentration increases less than twice.
The level of progesterone in normal pregnancy already in the first weeks exceeds 25 ng/ml. When ectopic, the concentration remains below 5 ng/ml. But this does not allow us to accurately establish the fact of improper attachment of the fertilized egg and distinguish an ectopic pregnancy from fetal death during an intrauterine one. In addition, in a large number of patients with suspected tubal pregnancy, progesterone levels fluctuate between 5 ng/ml and 25 ng/ml, which reduces the diagnostic value of the study.
As for the results of other laboratory tests, the white blood cell count can increase to 10-15 thousand μl-1, and hemoglobin and hematocrit often remain normal even with intra-abdominal bleeding.
Blood tests and combination of methods
Along with ultrasound diagnostics, pathology can be judged quite accurately by the results of a woman’s blood test for hCG. Here, signs of ectopic pregnancy suggest a certain level of hormone in the blood. If it is lower than it should be during a normal pregnancy, it is highly likely that we are talking about pathology. In other words, it is worth finding an ectopic pregnancy using several examinations at once.
Experienced gynecologists advise women to combine several approaches at once in order to accurately draw conclusions based on their results - whether it is an ectopic pregnancy or not. Such approaches include ultrasound, pregnancy test, and hCG blood test. In addition, the doctor will be able to name other tests that interest him. Early diagnosis of pathology contributes to successful treatment and the opportunity to give birth to a healthy child in the future.
Often such pathologies end in spontaneous miscarriages, so the gynecologist is in no hurry to prescribe an operation, but only observes. Further, if a miscarriage does not occur, special means are used that cause a miscarriage. This is called a medical abortion. The last method, surgical intervention, is prescribed when the timing of the pathological condition does not allow choosing milder methods of intervention.
Signs of ectopic pregnancy on ultrasound
Intrauterine (normal) pregnancy is in very rare cases combined with a pathological one (one case in 10–30 thousand), therefore, on ultrasound, a reliable sign of a normally developing pregnancy is the detection of an embryo in the cavity of the genital organ. At what date will an ultrasound show an ectopic pregnancy? When examining through the abdominal wall, a fertilized egg can be detected in the uterus at six to seven weeks. If diagnosis is carried out with a vaginal sensor, then at 4.5-5 weeks. This allows you to exclude or confirm the presence of pathology.
An ectopic pregnancy on ultrasound is confirmed by the detection of a fertilized egg outside the cavity of the muscular organ. Indirect signs are the absence of intrauterine pregnancy, an increase in the size of the reproductive organ in the absence of an embryo in the cavity or organic changes, visualization of a formation in the appendages, detection of fluid in the pelvis (typical of 50-75% of cases), detection of a cyst or false ovum.
Can an ultrasound detect an ectopic pregnancy? This diagnostic method is the most reliable. In the majority of patients (about 76%), the pathology is detected before contacting a gynecologist. An ectopic pregnancy is most often detected by ultrasound between the sixth and ninth weeks. Early diagnosis allows you to avoid most complications. Therefore, it is recommended to perform an ultrasound examination to exclude ectopic pregnancy in the second week of missed menstruation or earlier.
Detection of ectopic pregnancy during pregnancy up to 12 weeks (in the early stages)
Many women are concerned about how early an ultrasound examination shows pathology. An undeniable advantage is the fact that ultrasound diagnostics makes it possible to determine pathology at a very early stage. Already in the fifth week, you can see using ultrasound the location of the embryo outside the uterus. It is precisely because of the above that ultrasound is extremely important as a diagnostic method and an aid in making a diagnosis. It is also worth noting once again that, given the possibility of detecting pathology in the early stages, women should not ignore ultrasound; timely medical assistance in an unfavorable case can reduce negative consequences to a minimum, saving the health and life of a woman.
In this 28-year-old patient, no fetus was detected, but ultrasound doctors found an accumulation of fluid in the right fallopian tube - a sign of ectopic pregnancy
The danger of pathological pregnancy
The consequences of pathological pregnancy are divided into early and late. Early complications include complications during gestation itself. This may be a pipe rupture followed by bleeding, hemorrhagic and painful shock. In most cases, a tubal abortion occurs, that is, detachment of the fertilized egg and its release into the uterine cavity or abdominal cavity. This poses a threat to the patient's life. An ectopic pregnancy can cause infertility (a late complication) or even lead to death if the pathology is not detected in time.
Consequences
So, if an ultrasound shows the presence of a disease, then it is important not to waste time. Indeed, in case of delay, various complications are possible. In particular:
- Severe internal bleeding due to the release of the embryo into the abdominal cavity. In such a situation, the fetus stops developing and harms the woman’s internal organs.
- Fallopian tube rupture. This consequence may well be fatal. Indeed, in the event of a rupture, internal bleeding, firstly, is very strong and the body loses a lot of blood, and, secondly, it is difficult to detect - the blood enters the uterine rectal cavity and accumulates there.
- Infertility. Occurs in 30 cases out of 100. As a rule, it is a consequence of a rupture of the fallopian tube and untimely consultation with a doctor.
- Relapse of the disease. Its probability is about 20%. However, this consequence cannot be excluded.
In half of the cases, the next pregnancy is likely to proceed normally. However, conceiving a child is not recommended for at least six months after the end of treatment. During the period of abstinence from conception, you should be very careful about contraception and first consult with your doctor.
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
When choosing a treatment method, the woman’s intention to plan a pregnancy in the future, the development of the adhesive process (this increases the risk of re-abnormal attachment of the fertilized egg), gynecological and obstetric history are taken into account. If pathology is re-identified in a preserved pipe, removal of the pipe is required. And the feasibility of preserving the appendages is also taken into account (depending on the degree of pathological changes). In case of severe bleeding, the only option is often abdominal surgery and removal of the fallopian tube. With early diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy by ultrasound, there is a chance to completely preserve reproductive function.
What to do?
After an ultrasound examination, additional diagnostic methods may be needed to confirm or exclude fetal freezing.
After diagnosing a pathological pregnancy, the fertilized egg is removed by surgery. Next, the woman goes through a rehabilitation period (restoration of the functions of the reproductive system, examinations, relief of inflammation, and other manipulations prescribed by the gynecologist).
Practice shows that after removing the dead fetus and complete recovery, the chances of getting pregnant are quite high. In order to become a happy mother in the future, you need not to delay the problem, consult a doctor and follow all instructions
Prevention of ectopic pregnancy
To prevent the development of pathology, one should prevent the development of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs and treat gynecological diseases in a timely manner. Before a planned pregnancy, it is recommended to undergo a comprehensive diagnostic examination and treat existing chronic diseases. During sexual activity, you need to use reliable methods of protection and avoid abortion.
If it is necessary to terminate a pregnancy, it is better to give preference to low-traumatic methods in the optimal time frame. A medical abortion must be performed by a qualified specialist in an institutional setting. After an ectopic pregnancy, the recovery process needs to be monitored by ultrasound. To preserve reproductive function, a woman should be observed by a gynecologist and follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Indications and contraindications
The attending physician should decide whether to conduct an ultrasound examination if an ectopic pregnancy is suspected. It is he who is informed about a number of indications for such a procedure.
- Absence of menstruation for a certain period of time in a woman planning to conceive a child.
- Presence of signs of pregnancy (nausea, loss of appetite, drowsiness, enlargement and increased sensitivity of the mammary glands).
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen, rectum or thighs, bleeding from the genital tract.
- Confirmation of pregnancy during the test.
- History of a previous ectopic pregnancy.
- A burdened gynecological history (chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases, surgical interventions on the pelvic organs, peritonitis, and so on).
Interesting: Mom has 1 positive, dad has 2 negative, what will the child have?
There are no absolute contraindications for ultrasound; there are restrictions for performing the procedure using transabdominal or transvaginal methods. In each specific case, the specialist chooses the method of performing ultrasound examination. Ultrasound is not recommended if:
- damage to the skin in the area where the sensor is placed;
- signs of bleeding from the genitals, menstrual bleeding;
- surgical interventions with vaginal sutures;
- an unfilled bladder during transabdominal examination interferes with visualization of the genitourinary system.
Symptoms and causes
The onset of pregnancy leads to a gradual restructuring of all organs and systems in the female body; the hormonal background must ensure the preservation of the emerging life. Therefore, the desires and behavior of a pregnant woman change noticeably: original taste preferences, a constant desire to sleep, a changeable emotional background are integral companions of the expectant mother at first.
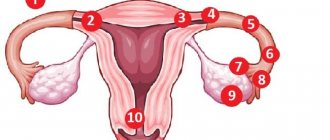
Normally, a fertilized egg enters the uterine cavity from the fallopian tube, where the process of implantation into the endometrium begins. There are a number of factors that interfere with this process, and then the fertilized egg is attached in any other places. Depending on the place of attachment of the embryo, ovarian, tubal, cervical or abdominal localizations are distinguished.
In the pathological course, most often - in 90% of cases - the zygote (fertilized egg) does not reach the uterus, but remains in the fallopian tube. This organ is not designed for the development of a child, therefore, as the embryo grows, it ruptures.
Less often, under the influence of unfavorable factors, the zygote is pushed out of the tube in the opposite direction and settles on the wall of the peritoneum or in the ovary. In the latter case, fertilization occurs before or immediately after the release of the egg. This pathological phenomenon is fraught with ovarian rupture.
Cervical and abdominal localizations are much less common. Attachment of the zygote to the cervix is an extremely dangerous phenomenon, characterized by a high risk of death. Often, in order to save the patient’s life, the surgeon decides to remove the uterus, which means for her the loss of reproductive function.
The abdominal location of the embryo is also a dangerous condition. It can develop if a fertilized egg, during the process of movement, ends up in the peritoneal cavity, becomes fixed there and begins to develop. The second scenario is a consequence of a tubal abortion, when, having come off the fallopian tube, the zygote enters the abdominal cavity and is implanted there.
The reasons for atypical egg implantation include the following factors:
- infectious and inflammatory processes along the route of the developing fetus;
- the presence of adhesions, synechiae and scars in the pelvic organs;
- intrauterine contraceptive systems (spirals) lead to the development of endometrial edema, which prevents implantation;
- history of medical abortions;
- signs of hormonal disorders in a woman’s body (not only an imbalance of sex hormones);
- tumor processes in the reproductive organs (both benign and malignant).
There are objective signs for suspicion of the existence of an ectopic pregnancy, which the doctor will identify during examination and communication with the woman.
- The size of the uterus does not correspond to the expected period of development of the embryo after fertilization (every week the volume of the organ increases, and in the absence of a fertilized egg in the uterus, myometrial growth does not occur).
- The level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is not high enough (when performing routine pregnancy tests, the result may be negative if there are subjective signs of pregnancy).
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen or rectal area.
- Thick viscous brown discharge.
- An ultrasound examination reveals no fertilized egg in the uterine cavity.
If there is minimal suspicion of a developing ectopic pregnancy, ultrasound diagnostics should be performed and ectopic localization should be identified.