Pneumonia without fever - this manifestation of pathology cannot be called rare, because there are a sufficient number of reasons that can provoke a process of this nature. The absence of body temperature does not mean that the disease is mild; often the patient is tormented by all the symptoms of the inflammatory process
What could be the cause of the pathology?
.
According to experts, pneumonia with a cough but no fever is quite dangerous. The danger is that the patient does not turn to a specialist for help, attributing the symptoms to ARVI, while the disease is rapidly progressing. In order to reduce the risk of complications of such a disease, you should familiarize yourself with its main causes and symptoms.
Definition of disease
Pneumonia is a serious, sometimes fatal disease. However, its manifestations do not always correspond to the severity of inflammation. This makes the situation even more complicated. Depending on what infectious pathogen caused the disease, pneumonia can be without fever, or almost without symptoms, or with the presence of severe and painful conditions. The “erased” course of pneumonia is a common occurrence in exhausted or weakened people.
This asymptomatic form of the disease is mistakenly taken for a not very dangerous problem. Sometimes a person does not even suspect that he has pneumonia, believing that he has a “mild cold.”
Pneumonia is a threat to the patient’s life, and the absence of fever and other symptoms only complicates the diagnosis and does not allow timely treatment to begin. This makes the situation even more alarming and may result in the death of the patient.
Symptoms of a latent form of the disease
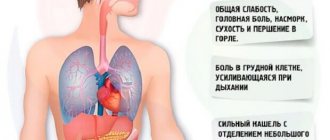
Pneumonia, which occurs without cough and high fever, is identified by the following symptoms:
- pale skin and a bright, unhealthy blush on the cheeks;
- prolonged aching headaches, worse in the evening and at night;
- chest pain when moving;
- sweating, aches in muscles and joints;
- shortness of breath at rest;
- tachycardia, thirst;
- intermittent breathing;
- fatigue, weakness.
It is especially difficult to diagnose pneumonia without a cough in children. Kids cannot explain what they feel and in what places they experience pain.
Parents should take their child to the doctor if they notice the following symptoms:
- drowsiness during the day, insomnia at night;
- educational lag;
- refusal of outdoor games;
- fatigue even after normal activities;
- apathy, poor appetite;
- moodiness, lethargy, frequent mood swings.
Night sweats without fever or chills is a good reason to consult a pediatrician.
Causes
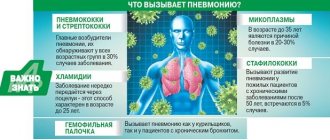
Pneumonia in most cases occurs due to human infection with pathogens, but it can also be non-infectious in nature. The causative agent of infectious pneumonia is most often bacteria, but viral, fungal inflammatory processes, as well as diseases caused by atypical microflora, can also occur. The most severe manifestations characterize the bacterial inflammatory process. But atypical pneumonia has mild symptoms and slow development.
The cause of a non-infectious inflammatory process can be:
- Sternum injury;
- Allergy;
- Exposure to toxic substances;
- Exposure to radiation.
Often the disease manifests itself as a secondary disease against the background of other diseases. The postoperative period poses a great danger to patients. Pneumonia can become a complication of bronchitis, “accompany” severe injuries or burns, food poisoning or inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
An almost asymptomatic, “erased” course of the disease is often found in patients weakened by existing ailments, who have been in a supine position for a long time. These could be, for example, paralyzed people, patients in the postoperative period. The weakening of the body's strength is the reason why temperature does not become a natural protective reaction to the inflammatory process developing in the lungs. Immunity decreases sharply after treatment for cancer or indiscriminate use of antibiotics.
The body does not react too actively to new manifestations of the inflammatory process if the patient already has chronic foci of infection.
Why is there no fever with pneumonia?
Cases of pneumonia without elevated fever are dangerous. When a person coughs but does not have a fever, he usually thinks that it is just a cold and there is no need to worry seriously. Meanwhile, inflammation is becoming increasingly widespread and continues to affect lung tissue.
The reasons why pneumonia can occur without fever are as follows:
- A decrease in the body's defenses is the main reason. Due to reduced immunity, the body loses the ability to adequately respond to the proliferation of pathogens. The process of increasing temperature is complex and multi-stage, requiring large amounts of energy and resources, and a weak body does not have them. Children and the elderly, HIV-infected people and people with other pathologies are at risk for developing pneumonia without fever due to reduced immunity. In particular, the presence of other inflammatory processes in the body depletes the immune system. After a long fight against infection and in the presence of several pathogenic foci at the same time, the body’s resources are exhausted - and the immune system does not respond to the emergence of a new foci of infection.
- Uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs. When taking antibiotics for a long time, microorganisms adapt to it, and the immune system is weakened. When using antibiotics that do not act on this particular pathogen of pneumonia, the same picture is observed. Similarly, if a person abruptly stops taking the correct antibiotic, interrupting the course, the immune system will not be able to suddenly begin to function fully, because. she has already “relaxed” while taking medication. This is why it is so important that the doctor prescribes the treatment and that the patient strictly follows the instructions, even if they feel better.
- Sometimes a single small focus of inflammation does not give rise to fever. As a result, a person does not notice the disease until the outbreak grows.
Symptoms
Depending on which microorganism is the causative agent of the infection, pneumonia can manifest itself in different ways. Clinical signs vary:
- Typical pneumonia. Its symptoms: rapid rise in temperature, cough with copious sputum, sometimes even with pus, pain in the lungs;
- Lobar pneumonia. The first symptoms: body temperature up to 39-40°C, shortness of breath. The inflammatory process causes severe pain in the area of the affected lung. With the development of the disease, the sputum becomes greenish, then orange, with possible bleeding;
- Atypical pneumonia. The symptoms of this disease are mild. The temperature is normal or slightly elevated. The cough is not severe, there may be a sore throat or malaise.
Symptoms may be expressed implicitly or completely absent due to the characteristics of the immune system of the sick person, the presence or absence of concomitant diseases. Also, the symptoms may be false and initially determined as bronchitis. In this article you can familiarize yourself with the differences between pneumonia and bronchitis. Pneumonia should be feared if cough (even mild), shortness of breath, discomfort in the lungs, and headache do not go away within a week. This condition of the patient can be observed after a prolonged cold. Feeling better, the temperature is not elevated, but a cough, a feeling of constant thirst, weakness, an unhealthy blush with pale skin should alert you.
Turning the torso in a patient with pneumonia may be accompanied by pain. Even minor physical activity during pneumonia with mild symptoms and without fever causes severe sweating, shortness of breath, and rapid heartbeat. It should be noted that rapid breathing is also one of the main signs of the disease. Cough with pneumonia without fever manifests itself in different ways. Sometimes - strong, dry, later with phlegm. Sometimes it is painful, but not too severe, with shortness of breath. This may be a symptom of airway obstruction.
With pneumonia, the patient often develops characteristic breathing, accompanied by some whistling. Trying to take a full breath is difficult.
Pneumonia (pneumonia) in adults - definition of the disease
Pneumonia or pneumonia is a very insidious infectious disease, especially when it occurs with mild symptoms. Pneumonia affects the lungs and the patient suffers from cough, chest pain, shortness of breath and fever. It can rise sharply even to forty degrees. But occasionally there is an exception to the rule. A person does not observe any increase in temperature, and this is very bad, because inflammation continues its destructive work for the body. And in some cases there is no cough yet. Why is it possible for adults to get pneumonia without such a symptom as high fever? What can affect the clinical picture of the disease so much?
Possible complications
Pneumonia without fever and other severe symptoms, however, remains a dangerous disease. Inflammation of the lung tissue creates enormous problems throughout the body. Impaired gas exchange in the alveoli can lead to respiratory or oxygen deficiency.
Pneumonia sometimes causes severe pathologies of the respiratory system:
- Exudative pleurisy;
- Collapse of the lung lobes;
- Pulmonary edema;
- Gangrene or lung abscess.
The consequence of pneumonia can be various types of diseases of the cardiovascular system:
- Myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle);
- Endocarditis (inflammation of the inner lining of the heart);
- Heart failure.
Sometimes there is a danger of developing bacterial toxic or septic shock. One type of complication of pneumonia can be the development of psychosis.
Treatment
You should not try to cure pneumonia on your own, without consulting a doctor, even if it is not accompanied by fever. The absence of fever, severe cough and other severe conditions may create the illusion of “well-being.” However, this well-being is imaginary. The absence of temperature even aggravates the problem: the body does not resist the disease, the inflammatory process develops unhindered.
There are specially developed standards for the treatment of pneumonia.
Treatment methods in this case should be determined by a specialist. To combat pneumonia, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment with antibacterial drugs. This will help cope with the main cause of the problem - pathogenic microflora.
By medication
In order for a weakened body to better cope with the consequences of the pathological process, it is necessary to take additional medications:
- Expectorants;
- Bronchodilators that relieve shortness of breath;
- Drugs that provide anti-infective protection;
- Medicines that improve blood supply to the lungs;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Antihistamines.
Treatment of pneumonia without antibiotics is possible if the inflammatory process is viral in nature. This diagnosis must be confirmed by examination and tests. In other cases, the use of antibiotics is necessary.
Folk remedies
How appropriate is the use of traditional medicine to treat pneumonia without fever?
This issue should be discussed with a specialist. Traditional medicine techniques in some cases help speed up the healing process and alleviate the patient’s condition. The prescription of certain medications created according to traditional medicine recipes depends on the type of pneumonia and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Therefore, self-medication and lack of medical care is a huge risk for a sick person. Pneumonia, not accompanied by a rise in temperature, most often indicates a weakened immune system. Therefore, ineffective or incorrect treatment can lead to death. Folk remedies play a supporting role in the treatment of pneumonia.
Symptomatic treatment is carried out using the antipyretic, anti-inflammatory or cough-relieving properties of medicinal plants.
What kind of pneumonia can it be?
Fever is not the main symptom of pneumonia.
Pneumonia without fever is an extremely dangerous condition precisely because of the consequences. It passes without the development of pronounced symptoms, which leads to the fact that the patient is not always able to assume the presence of such a serious illness, attributing the deterioration in health to general weakness, a cold, and simply overwork.
While the patient does not take any measures in order to eliminate the inflammatory process of the lung tissue, it gains momentum and spreads, affecting ever larger internal spaces of the respiratory organs.
Attention! It is quite difficult to identify the symptoms of such pneumonia. The clinical picture can be quite blurry. Diagnosis of pathology in children is difficult, but timely identification of the disease is important in the treatment process.
In what cases is it necessary to visit a doctor?
The key feature of the disease is that such pneumonia does not have an infectious load for people, and for this reason the patient’s environment cannot become infected with it, but at the same time it has the classic nature of a cold.
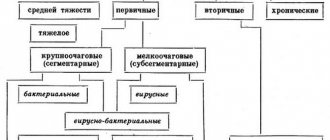
Pneumonia without an increase in temperature is classified according to various criteria and may have the character discussed in the table:
| The nature of the course of pneumonia | |
| Type of pathology | Description |
| Focal pneumonia | Determined as part of an x-ray examination, most often it is secondary. In the image it appears as darkened areas in the form of shadow loci of inflammation. The main provocateur is a recent infectious disease, such as ARVI, bronchitis, influenza, laryngitis, parainfluenza, bronchopneumonia. The complex of symptomatic manifestations is most often expressed by such negative reactions of the body as a cough, mostly of a non-productive nature, occasionally alternating with a wet one. Coughing attacks are deep and last for a considerable time. This type of pathological process requires treatment for 2-3 weeks, provided that antibacterial drugs are used. |
| Segmental pneumonia | Pneumonia of a segmental nature is characterized by the fact that the inflammation partially affects the lung, while the patient does not want to eat - he has a complete lack of appetite. Sleep disorders are observed. When this type of pneumonia occurs without fever, increased activity of the sweat glands is observed, cough may be completely absent, which significantly complicates diagnostic measures and makes it difficult to make a timely diagnosis. |
| Share | Lobar pneumonia implies that inflammation covers 1 or several lobes of the parenchymal component of the lung. |
| Drain pneumonia | It is characterized by a process that simultaneously covers several different lobe segments, with the merging of several foci into one significant locus of inflammatory damage. |
| Total pneumonia | It involves damage to one lung, but one entire lung is affected, or the pathological process occurs in two lungs at once. |
| Lobar type pneumonia | This type is characterized by the occurrence of pain in the area of the pulmonary parenchyma and abdominal area, which becomes more intense when coughing. In this case, the sputum may be rusty brown in color. |
| Staphylococcal pneumonia | It is destructive in nature and is an unfavorable form. Often not accompanied by an increase in temperature. Symptomatic manifestations include the urge to vomit, attacks of nausea, shortness of breath, coughing tremors with foul-smelling sputum mixed with pus. Wheezing is easily audible. With timely medical care, the disease can be completely cured, but only within a period of approximately 2 months. Further, rehabilitation and dynamic monitoring must be carried out. |
Important! Latent or pneumonia without cough and fever is the most dangerous. This disease has a relatively high mortality rate when compared with the classical inflammatory process.
Also, there is a difference in the localization of the inflammatory process: if it is on one side, then one-sided pneumonia without fever is diagnosed, and when the inflammation covers both lungs, then the diagnosis is “bilateral pneumonia”. There is also a difference in when pneumonia occurred by itself, that is, primary, and when pneumonia developed as a complication of another respiratory disease (secondary).
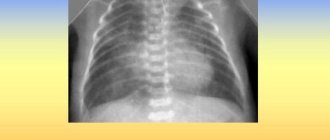
Clear signs of pneumonia are visible to the doctor on x-ray.
The main categories of pneumonia without fever are classified into the following types:
- Hospital, that is, the disease occurs after hospitalization was performed during the first days or after 3 days after the patient was discharged.
- Community-acquired, when the disease is in no way connected with infection within the walls of a hospital institution. This type is the most common.
- Pneumonia provoked by medical manipulations and interventions, that is, the introduction of etiopathogenic agents into the patient’s body during therapeutic and preventive procedures, surgical interventions, hemodialysis and parental use of medications.
- Aspiration, that is, foreign particles enter the larynx along with inhaled air or when ingesting food and liquids. Penetration due to sputum washings from the nasopharynx is also possible.
- Ventilation is the initial form of manifestation, up to 3 days, and the late version, that is, over 4 days, has a direct relationship with a person’s stay on artificial support of respiratory function, that is, on a ventilator.
- Atypical – when pneumonia is provoked by rarely encountered subspecies of pathogenic microorganisms, for example, chlamydia, mycoplasma, legionella.
- The cytostatic form occurs due to infusion or oral administration of pharmacological drugs that have a cytostatic effect.
The photo in the article presents X-ray data that allows the doctor to correctly diagnose the patient.
Regardless of the listed reasons and their classification, there are some common factors that contribute to the onset of pneumonia.
Attention! Pneumonia without characteristic symptoms often occurs in children and the elderly due to instability of the immune system. Treatment instructions for these categories of patients do not change, but it is extremely important to act in a timely manner. Only a pulmonologist, after carrying out diagnostic measures, will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and approve a treatment plan.
Prevention
Latent pneumonia or a disease without pronounced symptoms is a consequence of general weakness of the body or reduced immunity. Therefore, measures to strengthen the body’s immune system are a necessary condition for the prevention of pneumonia. The immune system is suppressed by systematic and excessive stress, poor diet and lack of regular physical activity, unsystematic use of antibiotics, and bad habits.
The following set of measures is recommended to prevent pneumonia:
- Sufficient and regular physical activity;
- Proper nutrition, including a number of foods that strengthen the immune system;
- A lifestyle that reduces excessive nervous overload;
- Hardening procedures;
- Preventing unsystematic use of medications;
- Getting rid of bad habits.
It is necessary to ensure that a person has a lot of positive emotional impressions in his life. Only regular and targeted actions to normalize lifestyle can give the necessary and long-term results.
How to distinguish bronchitis from pneumonia in an adult
The symptoms of SARS in children are described here.
how to treat if a child has snot like water //drlor.online/diagnostika-lechenie/otek/sopli-kak-voda-u-rebyonka-opasno-ili-net.html
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pneumonia includes a number of objective, laboratory and instrumental research methods that help to collect a complete picture and establish the correct diagnosis.
To make a diagnosis, you must consult a doctor and undergo appropriate tests
The doctor conducts a thorough examination, percussion and auscultation of the lungs.
Upon examination, attention is drawn to the lag of the right half of the chest, pallor of the skin and visible mucous membranes. Herpetic rashes are possible on the face.
The patient's breathing is rapid, shallow, with flaring of the wings of the nose.
A dull percussion sound is detected over the affected area. There is an increase in vocal tremors, which intensifies as inflammatory changes increase.
During auscultation of the lungs on the right side, weakened vesicular or bronchial breathing, crepitus, fine moist rales, and pleural friction noise are noted.
X-ray examination of the lungs is of particular diagnostic value.
The most informative diagnostic methods include:
- X-ray examination of the lungs;
- clinical blood test;
- microscopic examination of sputum;
- bacteriological culture of sputum with determination of antibiotic sensitivity.
An X-ray examination reveals an area of darkening corresponding to a lobe or segment of the right lung.
A clinical blood test reveals leukocytosis with a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, and an increased ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
Anatomically, the right bronchus is shorter and wider than the left, and therefore infection spreads through it more often.
In order to determine the cause of right-sided pneumonia, before starting therapy, sputum is cultured on a nutrient medium, which makes it possible to determine the type of causative agent of the disease and its sensitivity to antibiotics. To preliminarily determine the possible pathogen, a microscopic examination is also carried out.
If atypical pneumonia is suspected, serological tests are necessary.
During the diagnostic examination, it is important to assess the severity and prognosis of the disease in order to take this into account when deciding where to treat the patient. For mild cases of pneumonia, outpatient treatment is possible; for moderate and severe cases, hospitalization in a hospital is necessary. It is also important to take into account concomitant diseases that may be in the acute stage or decompensation.
If pneumonia occurs in a child, mandatory hospitalization is required.