Sarcoidosis is a systemic disease that can affect various organs and tissues of the human body. The pathology occurs everywhere and affects patients of all ages. However, according to the observations of specialists, young and middle-aged women are more often affected by the disease.
What is pulmonary sarcoidosis?
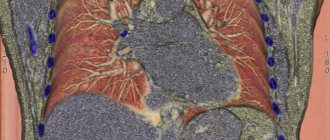
The second name of the pathology is Besnier-Beck-Schaumann disease. It belongs to the group of benign granulomatosis, accompanied by damage to the mesenchyme and lymphatic tissue. In order to understand what sarcoidosis is, it is necessary to imagine a small round formation, a granuloma - this is exactly what the pathology looks like on an X-ray image. Over time, epithelioid granulomas can grow and spread to other tissues and organs. In 90% of cases, the pathology affects the lungs, trachea, and intrathoracic lymph nodes.
Externally, changes in the lungs are similar to those observed with tuberculosis. With a detailed and careful study of granulomas, the absence of caseous necrosis is noted. In addition, in sarcoidosis, granulomas do not contain mycobacteria, which makes it possible to differentiate the disease if tuberculosis is suspected. Pulmonary sarcoidosis is characterized by the fusion of formations that form large and small foci of pathology.
Pulmonary sarcoidosis - causes
It is often not possible to establish the specific cause that caused sarcoidosis of the lungs and intrathoracic lymph nodes. None of the existing theories of the development of the disease provides reliable information about the nature of the disease. Experts make the following assumptions:
1. Infectious theory.
According to her, the cause of sarcoidosis is pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the respiratory system. Among them:
- mycobacteria;
- spirochetes;
- mushrooms;
- histoplasma;
- protozoa.
2. Genetic predisposition
– there is research data confirming the possibility of transmission of the disease by inheritance. This is confirmed by cases of familial sarcoidosis.
3. Impaired immune response
– the disease can be caused by malfunctions of the immune system, which is activated when exposed to exogenous (viruses, bacteria, chemicals) and endogenous (autoimmune reactions) factors.
These theories give reason to assume that the disease sarcoidosis is a disease of a polyetiological nature. It develops under the simultaneous influence of several reasons. At the same time, it is not always possible to identify the main one - the one that provoked changes in the lung tissue. It is worth noting that the disease sarcoidosis is not contagious - transmission from the patient to other people does not occur. However, there is an increased risk of developing sarcoidosis in people of certain professions:
- agricultural workers;
- doctors and medical staff;
- sailors;
- chemists;
- millers;
- firefighters.
Pulmonary sarcoidosis - symptoms
Many patients, when visiting a doctor, do not suspect that they have sarcoidosis - the symptoms of the disease are erased and non-specific. Such people complain of constant malaise, fatigue, and weakness. Against the background of such symptoms, there is a decrease in appetite and a decrease in body weight. Many patients note the appearance of fever not associated with a cold, night sweats, and lack of sleep. About 50% of cases of the lymphoglandular form of pulmonary sarcoidosis are characterized by the absence of symptoms. The second half of patients complain about:
- chest pain;
- painful sensations in the joints;
- cough;
- changes in the skin;
- shortness of breath;
- lesions of peripheral lymph nodes.
Degrees of sarcoidosis
Based on the results of the X-ray and the symptoms of the disease, doctors distinguish the following degrees and stages of pulmonary sarcoidosis:
- 1st degree (intrathoracic lymphoglandular form)
– characterized by bilateral, asymmetrical enlargement of bronchopulmonary or tracheobronchial lymph nodes. - Grade 2
– the presence of infiltrate in the lung tissue with damage to the intrathoracic lymph nodes. - Grade 3 (pulmonary form of sarcoidosis) – characterized by fibrosis of the lung tissue; There is no enlargement of intrathoracic lymph nodes. The progression of the disease leads to the formation of conglomerates against the background of increasing pneumosclerosis and emphysema.
Pulmonary sarcoidosis - complications
The lung disease sarcoidosis requires special long-term therapy. Patients with this diagnosis are forced to remain under dispensary observation for a long time even after completing the course of treatment. Such attention to patients with sarcoidosis is due to the high risk of complications. Many of them are accompanied by impaired breathing, which can be fatal. Common complications of pulmonary sarcoidosis include:
- emphysema;
- bronchial obstruction syndrome;
- respiratory failure;
- eye damage.
Causes of development, symptoms and methods of treatment of lymph node cancer
The lymphatic system is a collection of many lymph nodes and vessels that perform the protective function of the body. Lymphocytes are formed in the lymph nodes, which form a barrier that prevents viral and bacterial agents from entering the human body, oboleznjah reports. There are a large number of lymph nodes in the cervical, axillary and groin areas. Four percent of all cases of oncological pathologies occur in the lymphatic system. The pathological process can be localized in one or more lymph nodes. Lymph node cancer can occur as an independent disease, in which foci of cancer cells are located exclusively in the lymphatic system, or in the form of metastases to distant organs. There are local and general symptoms of the disease. Local symptoms include: enlarged lymph nodes, increased sweating during sleep, increased body temperature to subfebrile levels and a feeling of discomfort in the area of localization of the pathological process.
The diet for pulmonary sarcoidosis is gentle and includes fresh vegetables and fruits, broths, soups, fish and chicken. It is better to exclude bread from the diet. You should also limit your use.
Sarcoidosis - diagnosis
Outwardly, Beck's sarcoidosis (another name for pulmonary sarcoidosis) may not manifest itself in any way. This explains the situation when pathology is detected during the next preventive examination of the lungs - fluorography. In the image, doctors detect characteristic signs of sarcoidosis:
- fibrosis;
- emphysema of pulmonary tissue;
- focal dissemination.
In parallel, there is a change in the results of laboratory tests:
- moderate increase in ESR;
- leukocytosis;
- eosinophilia;
- increased titer of alpha and beta globulins.
Pulmonary sarcoidosis is often determined by a positive Kveim reaction. Thus, at the site of intradermal injection of a specific sarcoidosis antigen in a volume of 1–2 ml, a purplish-red nodule is formed. This result indicates sarcoidosis and requires appropriate therapy.
Authorized Products
The diet for pulmonary sarcoidosis includes vegetable/meat/fish soups based on a non-concentrated decoction with the addition of buckwheat, pearl barley, wheat, and barley. It is allowed to include whole grain porridge in the diet. Foods rich in animal/plant proteins must be present in sufficient quantities - dietary types of meat (turkey, chicken, rabbit, white/red fish, low-fat cottage cheese, chicken eggs, legumes, nuts, soy).
An important place in the diet is given to vegetables (zucchini, cabbage, carrots, celery, eggplant, onions, garlic, beets, radishes, tomatoes, cucumbers, asparagus, peppers, garden herbs) and various fruits/dried fruits, which provide the body with necessary vitamins and macro/ microelements.
Among fats, preference is given to various virgin vegetable oils and unsalted butter. It is useful to include nuts, seeds, whole grain bread, and bran in your diet. Useful drinks include rosehip decoction, herbal and green teas, freshly prepared vegetable/fruit juices, non-carbonated table mineral water, fruit drinks and compotes.
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| green peas | 5,0 | 0,2 | 13,8 | 73 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| boiled broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 4,0 | 27 |
| kohlrabi cabbage | 2,8 | 0,0 | 10,7 | 42 |
| red cabbage | 0,8 | 0,0 | 7,6 | 24 |
| watercress | 2,3 | 0,1 | 1,3 | 11 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| olives | 0,8 | 10,7 | 6,3 | 115 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| green beans | 2,0 | 0,2 | 3,6 | 24 |
| zucchini | 1,5 | 0,2 | 3,0 | 16 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
Fruits | ||||
| avocado | 2,0 | 20,0 | 7,4 | 208 |
| pineapples | 0,4 | 0,2 | 10,6 | 49 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| figs | 0,7 | 0,2 | 13,7 | 49 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| plums | 0,8 | 0,3 | 9,6 | 42 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| blackberry | 2,0 | 0,0 | 6,4 | 31 |
| strawberry | 0,8 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 41 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| seeds | 22,6 | 49,4 | 4,1 | 567 |
| dates | 2,5 | 0,5 | 69,2 | 274 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oatmeal with water | 3,0 | 1,7 | 15,0 | 88 |
| pearl barley porridge on water | 3,1 | 0,4 | 22,2 | 109 |
| boiled brown rice | 2,6 | 0,9 | 22,8 | 110 |
| barley porridge on water | 2,3 | 0,3 | 15,7 | 76 |
Dairy | ||||
| dairy products | 3,2 | 6,5 | 4,1 | 117 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| steamed chicken breast | 23,6 | 1,9 | 0,0 | 113 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| boiled fish | 17,3 | 5,0 | 0,0 | 116 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| sardine | 20,6 | 9,6 | — | 169 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| peasant unsalted butter | 1,0 | 72,5 | 1,4 | 662 |
| corn oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot compote | 0,5 | 0,0 | 21,0 | 85 |
| Pineapple juice | 0,3 | 0,1 | 11,4 | 48 |
| Orange juice | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| cucumber juice | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,5 | 14 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
* data is per 100 g of product
A diet for pulmonary sarcoidosis involves excluding from the diet fatty meats, ham, smoked/semi-smoked sausages, waterfowl meat, white rice, pasta, sweets (sugar, jams, waffles, chocolate, preserves, cakes, cookies, pastries, sweets) , dairy products (cheese, sour cream, cream), semolina porridge, various pickles and pickled products, fast food.
The consumption of animal/cooking fats, mayonnaise, margarine, and vegetable-milk mixtures is not recommended. The consumption of table salt is limited, spicy and fried foods, canned fish, packaged juices, carbonated and alcohol-containing drinks, and strong coffee are completely excluded from the diet.
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| pickles | 0,8 | 0,1 | 1,7 | 11 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| white boiled rice | 2,2 | 0,5 | 24,9 | 116 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| vareniki | 7,6 | 2,3 | 18,7 | 155 |
| pancakes | 6,3 | 7,3 | 51,4 | 294 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| bagels | 16,0 | 1,0 | 70,0 | 336 |
| buns | 7,2 | 6,2 | 51,0 | 317 |
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| brewer's yeast | 12,7 | 2,7 | 0,0 | 75 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| salt | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| tomato sauce | 1,7 | 7,8 | 4,5 | 80 |
| vinegar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 5,0 | 20 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| sour cream 18% | 2,5 | 18,0 | 3,6 | 184 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
| ham | 22,6 | 20,9 | 0,0 | 279 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 28,2 | 27,5 | 0,0 | 360 |
| pork sausages | 11,8 | 30,8 | 0,0 | 324 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Eggs | ||||
| hard-boiled chicken eggs | 12,9 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 160 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| semi-finished fish products | 12,5 | 6,7 | 14,7 | 209 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| tuna | 23,0 | 1,0 | — | 101 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| coffee | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 2 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Pulmonary sarcoidosis - treatment
According to the observations of specialists, detected sarcoidosis is often accompanied by spontaneous remission - the symptoms and manifestations of the disease disappear on their own. Given this feature, doctors establish dynamic monitoring of the patient for 6–8 months. This helps to make a prognosis, determine how to treat sarcoidosis in a particular case, and determine the need for specific therapy. Indications for drug treatment are:
- progressive sarcoidosis;
- generalized forms of the disease;
- damage to the intrathoracic lymph nodes;
- dissemination of lung tissue.
Sarcoidosis - recommendations
When sarcoidosis is diagnosed, treatment is developed individually, depending on the form of the pathology and its stage. The basis of therapy is hormonal drugs. The course of administration can reach 6–8 months. Prednisolone reduces the manifestations of sarcoidosis and normalizes respiratory function. At the same time, the following groups of drugs are used as part of complex therapy:
- anti-inflammatory – Indomethacin, acetylsalicylic acid;
- immunosuppressants – Azathioprine, Chloroquine;
- antioxidants – Retinol, Tocopherol acetate.
To achieve the effect as quickly as possible, especially when carrying out hormonal therapy, doctors recommend adhering to certain rules:
- dispensary observation;
- taking potassium supplements;
- restriction in food intake of table salt.
Treatment of pulmonary sarcoidosis without hormones
Besnier's disease can be treated without the use of hormonal drugs only in the early stages. In the absence of pronounced tissue changes and normal respiratory function, pulmonary sarcoidosis is treated without steroids. In such cases, the therapy is complemented by physiotherapy, which helps to alleviate the patient’s well-being, reduce cough and chest pain. Doctors prescribe iontophoresis and electrophoresis to the chest area. In this case, special solutions are used (aloe with novocaine, for example), which reduce pain.
Treatment of sarcoidosis with folk remedies
Many patients who supplemented the treatment of sarcoidosis with the use of folk remedies managed to reduce the duration of therapy. However, it must be remembered that before using any prescription, you must consult a doctor.
Lilac tincture
Ingredients:
- fresh lilac flowers – 1/3 cup;
- vodka – 200 ml.
Preparation, use
- The flowers are poured with vodka, closed tightly and placed in a dark place.
- Insist for 7 days.
- The resulting infusion is rubbed onto the chest and back 2 times a day. Use 2 teaspoons of tincture per procedure.
Herbal infusion
Ingredients:
- nettle – 40 g;
- St. John's wort – 40 g;
- goose cinquefoil – 10 g;
- chamomile – 10 g;
- string - 10 g;
- plantain – 10 g;
- celandine – 5 g;
- water – 500 ml.
Preparation, use
- The herbs are mixed.
- The resulting mixture in the amount of 1 tbsp. spoons are poured with boiling water.
- Leave for 1 hour.
- Strain and take half a glass 3 times a day before meals.
Features of nutrition during illness
There are no specially prepared diets for sarcoidosis; they occupy a secondary place in prevention and treatment. But following the recommendations of specialists, every patient is obliged to balance their diet for sarcoidosis. There is a lot of advice on a healthy diet, including for those receiving hormonal treatment. By eating healthy foods, you can avoid complications that are possible with the use of glucocorticoid hormones.
Practice has proven that a diet for sarcoidosis not only improves the patient’s condition, but in some cases relieves the disease. Of course, diet alone cannot cure a disease, but it plays an important role in prevention and treatment.
In order for nutrition to simplify the course of the disease, experts recommend adhering to the following rules:
- The disease is inflammatory in nature, and any inflammation thrives when eating foods rich in carbohydrates. It is better to eradicate from your daily diet:
- sweets;
- sweet carbonated waters;
- candies.
flour products (cakes, sugar, cakes, baked goods made from yeast dough);
If you don’t have enough willpower to get rid of such foods right away, do it gradually so that the body does not get stressed. Do everything one by one: replace sugar with sucrose, eat biscuits, replace water with fresh homemade compote.
The consumption of certain products is permitted within reasonable limits. Even the healthiest foods can be harmful if consumed in large quantities.