Congestive pneumonia is a secondary inflammatory disease that develops against the background of existing ventilation and hemodynamic disorders. It should be noted that the disease has no restrictions regarding age and gender, but is most often diagnosed in elderly people and bedridden patients.
- Etiology
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Complications
- Prevention
The clinical picture of congestive pneumonia in patients at the initial stage manifests itself in the form of ARVI, so most patients do not seek medical help in a timely manner, which leads to the development of life-threatening complications.
Diagnosis of the disease is based on a visual examination of the patient and laboratory and instrumental examination methods. Treatment of congestive pneumonia is complex, with mandatory antibiotic therapy. Self-medication is unacceptable; there is a high risk of not only complications, but also death.
According to the international classification of diseases of the tenth revision, this disease belongs to the section “Unspecified pneumonia”, which is why it will have its own code - ICD-10 code J18.
Etiology
The main pathogens of pneumonia
We should separately highlight people who are at risk:
- forced bed rest for bone injuries;
- old age, namely over 60 years;
- with chest deformation;
- with curvature of the spine.
In addition, it is noted that congestive pneumonia most often develops in cancer patients in the postoperative period.
Most often, unilateral pneumonia is diagnosed with localization in the lower part of the right lung, but in some cases there may be a bilateral nature of the lesion.
Regardless of what caused the development of such a pathological process, treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor; unauthorized medical measures are extremely dangerous for health and life in general.
How to recognize congestive pneumonia?
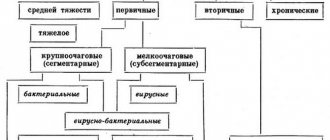
Pneumonia is a disease that affects the lung tissue. Pneumonia is divided into 2 types: primary and secondary. Primary ones are infectious in nature. Secondary ones develop in other serious diseases. Congestive pneumonia most often develops against the background of heart failure.
The mechanism of pneumonia is complex. It all starts with a violation of the venous outflow of blood. The latter penetrates through the vessels, sweating the alveoli. All this leads to swelling and inflammation. Over time, normal tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue. The outcome of congestive pneumonia can be pulmonary sclerosis and the appearance of brown induration.
Often the disease occurs latently, and the symptoms are mild. To make a diagnosis, the following studies are carried out:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- urine test;
- electrocardiography;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
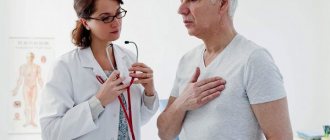
- percussion and listening to the lungs;
- pressure measurement;
- counting pulse and respiratory rate;
- Ultrasound of the pleural cavity;
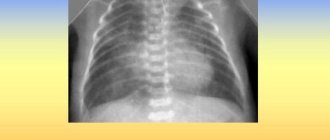
- X-ray examination of the lungs.
Taking an anamnesis is of great importance. When listening to the lungs, pneumonia is indicated by hard breathing and the presence of fine wheezing. The main diagnostic method is radiography. It allows you to identify signs of inflammation (changes in the structure of the lungs, the presence of linear shadows, accumulation of hemosiderin, expansion of the roots of the lungs). Changes in the blood are insignificant.
If cardiac pneumonia is suspected, a sputum examination is performed. Cells with hemosiderin can be found in it. The patient's indications of the presence of heart pathology are important for establishing a diagnosis. To confirm the diagnosis of heart failure, stress tests are performed, blood gas composition is examined, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, and ventriculography are performed.
Diagnosis of the disease
Detection of the disease begins with a medical examination. Diagnosis is complicated by the presence of somatic symptoms in the patient. Doctors should not lose sight of the likelihood of developing congestive pneumonia in patients and monitor the general condition of the person.
Diagnostics is based on several methods:
- auscultation;
- X-ray examination of the lungs.
When listening, the hardness of breathing and the presence of wheezing, both dry and wet, finely bubbled, are determined.
X-ray shows a decrease in tissue transparency and an increase in the pattern of the lungs. An outline of the lesion or a line with a slightly expanding root may be detected.
The following examinations are also prescribed as diagnostic measures:
- Ultrasound of the pericardium and pleura;
- ECG;
- Echo-CG;
- blood sampling for general examination;
- blood chemistry;
- microscopy of sputum to identify cells affected by hemosiderin.
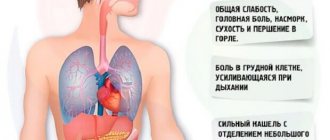
Symptoms
The danger of congestive pneumonia in elderly people and other patients is that at the initial stage of development of the clinical picture it is similar to ARVI. Therefore, targeted treatment therapy is usually not started in a timely manner.
In general, the symptoms of pneumonia are characterized as follows:
- low-grade or elevated body temperature;
- cough - dry at the beginning, later productive, with the release of viscous sputum;
- shallow breathing;
- increasing weakness, shortness of breath;
- fast fatiguability;
- headache, dizziness;
- exacerbation of symptoms of the underlying factor;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- noisy breathing;
- increased heart rate;
- unstable blood pressure.
It should be noted that congestive pneumonia in older people is often disguised as the underlying disease, outwardly manifesting itself only in the form of a slight deterioration in well-being. Therefore, in bedridden patients, it is very important to properly prevent this disease, including breathing exercises.
Causes of occurrence in older people
In a immobile patient, congestion easily occurs in the pulmonary alveoli. Among the predisposing factors to the development of the disease are:
- chronic diseases of the bronchopulmonary system;
- bad habits;
- low physical activity;
- oncology;
- decreased immune system;
- allergic asthma;
- hypothermia;
- circulatory disorders in the cardiovascular system;
- bacteria, viruses and fungal infections.
The risk group for hypostatic pneumonia includes older people. The reason why this pathology is dangerous for the elderly is age-related changes and natural impairment of pulmonary ventilation.
Those who have suffered diseases of other organs and systems are also susceptible to pulmonary disease:
- bronchitis, sinusitis, flu;
- diabetes;
- pathology of the heart muscle;
- mitral stenosis;
- kidney inflammation.
Often, congestive pneumonia occurs in older people who have undergone surgery. This is explained by postoperative pain, in which the patient breathes shallowly and shallowly. This increases the accumulation of fluid in the lung organ and can cause complications.
We recommend additional reading: Basic methods of treating dropsy on the legs in older people
Etiological factors
Not everyone knows why pneumonia develops against the background of heart pathology. Extensive congestive pneumonia can be a complication of the following heart pathologies:
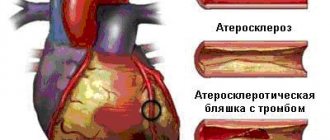
- coronary disease (heart attack);
- atherosclerosis;
- cardiosclerosis;
- mitral valve stenosis;
- arrhythmias;
- hypertension.
In all these diseases, hemodynamics are impaired. Against this background, the drainage function of the bronchi worsens. Sputum accumulates in their lumen, which serves as a favorable factor for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Pulmonary ventilation is also impaired. In most cases, congestive pneumonia affects the lower lobes of the lung.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that congestive pneumonia does not have specific symptoms, a comprehensive diagnosis is required to make an accurate diagnosis. As a rule, diagnostic measures consist of two stages. First of all, a physical examination of the patient is carried out with the collection of a personal history and clarification of the current clinical picture.
- blood sampling for general and biochemical analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- sputum collection for microscopic examination;
- chest x-ray;
- Ultrasound of the pleural cavity;
- ECG;
- EchoCG.
Based on the results of the diagnostic program, the doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis and, therefore, prescribe effective treatment.
Definition of disease
Hypostatic pneumonia is also known as congestive pneumonia. This is a more serious form of ordinary pneumonia, when, due to gravity, blood and transudate accumulate in the lowest parts of the lungs. Just like with ordinary pneumonia, the problem is accompanied by inflammation of the lung tissue.
This form of the disease is more dangerous than the usual one. The probability of death is quite high (according to some estimates, it reaches 50%), so its treatment must be approached with the utmost seriousness.
Signs of cardiac pneumonia
Congestive pneumonia in most cases proceeds less violently than the primary form of pneumonia. The severity of symptoms depends on the following factors:
- degree of disturbance of blood flow and ventilation;
- severity and stage of the underlying disease;
- addition of a secondary infection.
Symptoms may not appear immediately, but several days or even weeks after bed rest. Congestive pneumonia is divided into early and late. In the latter case, symptoms appear after 2-6 weeks. If inflammation occurs due to heart failure, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- moderate increase in body temperature;
- productive cough;
- hemoptysis;
- weakness;
- dyspnea;
- malaise;
- poor tolerance to physical activity.
Additional symptoms of the disease are tachycardia, forced body position, and cyanosis of the skin. Doctors know the dangers of congestive pneumonia. If left untreated, this disease can lead to the development of pleurisy and pericarditis. In the latter case, inflammation of the pericardial sac is observed.
Causes and symptoms
It is known that the lungs are a paired organ that is located in almost the entire chest cavity. They represent the main device of the respiratory system. Depending on the phase of breathing, the size and shape of the lungs change.
In addition to the above-mentioned inactivity, one of the causes of stagnation is also heart failure - blood is not pumped by the heart, resulting in stagnation of blood in the venous system of the lungs, which extends from the left side of the heart.
If the pressure invariably increases in the area of the blood vessels, then a large amount of blood penetrates into the alveoli. This causes a decrease in gas exchange, which subsequently results in shortness of breath, and in the worst case, the person begins to suffocate.
So, in addition to a decrease in physical activity, there are several reasons for stagnation:
- Heart diseases that weaken the heart muscle, as well as heart attacks.
- Shrinkage or insufficiency of the heart valves.
- A sharp increase in blood pressure, or hypertension.
- This condition is sometimes the result of taking medications.
- Kidney failure.
- Poisoning with poisonous gas.
- Serious injuries.
- Long stay at altitude.
At first, congestion in the lungs can be confused with pneumonia. There are many cases where it is difficult to diagnose the disease in the early stages.
The doctor's examination proceeds as follows:
- temperature is measured,
- breathing is heard,
- a blood test is performed;
- An x-ray of the lungs is prescribed.
Based on the above studies, appropriate treatment is prescribed. If a person has a weak immune system, then the disease can progress on the third day. The following symptoms are identified:
- usually a person’s temperature is normal and does not rise significantly;
- breathing quickens, tachycardia develops;
- the patient speaks slowly, stopping, and is characterized by cold sweat;
- A cough with the appearance of blood, in the worst case - bloody foam, is also characteristic;
- there are complaints of weakness and fatigue, it is difficult to lie down on a low pillow, while sitting, shortness of breath goes away over time;
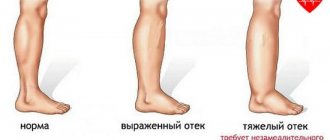
- the skin has a pale tint, the area between the nose and lips is bluish, swelling appears in the legs;
- It is also possible that pleurisy may occur as a result of hypoxia or other pathologies.
Also characteristic are incessant wheezing, gurgling sounds in the chest area, which can be heard without even using a stethoscope. If a person experiences initial symptoms of congestion in the pulmonary tract, then it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor.
What are the treatments?
Treatment of congestive pneumonia is complex and includes the following measures:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- breathing exercises and exercise therapy course;
- special food.
Breathing exercises for pneumonia
In most cases, treatment of such patients is carried out in a hospital setting; therapy with folk remedies at home is ineffective and can lead to the death of the patient.
Drug therapy includes taking the following drugs:
- antibiotics - they are prescribed exclusively on an individual basis, the dosage regimen and dosage are strictly prohibited from changing;
- diuretics;
- mucolytics;
- expectorants;
- antipyretics (if necessary);
- antiviral;
- vitamin and mineral complex;
- to improve the metabolism of the heart muscle and cardiac glycosides (for heart failure);
- immunomodulatory.
As for additional treatment methods, the patient may be prescribed the following:
- breathing exercises;
- back massage;
- oxygen therapy;
- exercise therapy exercises;
- inhalation.
In more complex cases and if conservative treatment methods are ineffective, the doctor may prescribe bronchoscopy or bronchoalveolar lavage.
Treatment of congestive pneumonia should be comprehensive. It includes the use of antimicrobial drugs (antibiotics), oxygen therapy, immunomodulators, and expectorants.
The latter make it possible to improve sputum discharge and normalize bronchial patency. From this group of drugs, Acetylcysteine, Ambroxol, Bromhexine are used. In case of edema, diuretics (Furosemide) are indicated. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type of pathogen. The most commonly prescribed drugs are penicillins, macrolides, and cephalosporins. It is preferable to administer antibiotics intramuscularly.
Additionally, chest massage can be performed. Therapeutic gymnastics plays an important role in the treatment of congestive pneumonia. If you have the opportunity to get up and walk, you need to do it more often. Persons with strict bed rest are required to periodically change positions and perform various exercises. For a sick person to recover, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease that led to pneumonia (heart failure).
If necessary, therapeutic bronchoscopy and thoracentesis can be performed. If you follow all the doctor’s instructions, the infiltrate in the lungs will resolve. Prevention of cardiac pneumonia includes regular position changes and exercises for patients who are on long-term bed rest and cannot walk. Breast massage is provided.
Prevention
Bedridden patients need to pay special attention to methods of preventing the development of pneumonia:
- give a semi-sitting position;
- change body position at least 4 times a day;
- do massage (cupping, percussion).
It is important to try to give the patient a semi-sitting position
In order to prevent the development of congestive pneumonia, you need to monitor the patient’s diet. His diet should contain sufficient amounts of vitamins and minerals. If a person has poor appetite, vitamin complexes are indicated for him.
Breathing exercises as a method of preventing congestive pneumonia
Another method of preventing congestive pneumonia is breathing exercises. This is a vital procedure on which rehabilitation depends.
Breathing exercises have a general tonic effect, have a positive effect on the patient’s mental state , and also allow:
- prevent lung muscle atrophy;
- restore lung function after an illness;
- stimulate the functions of the cardiovascular system;
- prevent the occurrence of blood clots and the development of pathologies of the urinary system.
In order to prevent the development of congestive pneumonia, the patient must perform the following exercises:
- The patient, while inhaling, raises his arms up and hugs his shoulders, and while exhaling, returns to the starting position (performed while lying on his back);
- The patient, while inhaling, raises his arms with his palms up, and while exhaling, lowers them along the body;
- the patient turns his head in both directions simultaneously with short inhalations and exhalations;
- the patient clenches his hands into fists and places them against his belt, sharply lowers them down as he inhales, and returns them to their original position as they exhale.
Inflating balloons and blowing air into a tube placed in a glass of water also has a good effect (allows you to ventilate the lower parts of the lungs).
All exercises should be done smoothly and slowly, without overstraining the chest muscles. If the patient is tired or his condition worsens, classes must be stopped.