Treatment of segmental pneumonia in adults depends on the extent of the lesion. Segmental pneumonia is in second place after focal inflammation. Represents a lung lesion that does not extend beyond the segment. Find the answer Are you having a problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
The site provides reference information. Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious doctor. Any medications have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required, as well as detailed study of the instructions! Here you can make an appointment with a doctor.
Treatment in adults
Treatment methods for pneumonia directly depend on the severity, extent of tissue damage and the etiology of the disease itself. If the patient experiences increased sweating, this usually indicates an improvement in the condition, but not with pneumonia.
Sweating indicates that a fever has begun, which often accompanies pneumonia. Often, excessive sweating occurs before a sharp rise in temperature; the patient must urgently take antipyretic drugs so as not to aggravate the problem.
If there is increased sweating and loss of strength, it means the disease has not been completely cured, it can develop into a chronic form.
Depending on the course of the disease, doctors prescribe treatment methods such as:
- Antibacterial therapy;
- Taking antiallergic drugs;
- Taking medications containing adrenaline if the patient experiences suffocation or Quincke's edema;
- Artificial ventilation;
- Detoxification therapy to alleviate the patient’s condition;
- Expectorants;
- Bronchodilators;
- Oxygen therapy;
- Chest massage;
- Breathing exercises.
Effective treatment methods
The disease is quite insidious, there seems to be nothing special in the treatment, but if the necessary moment is missed, the outcome can be sad.
With such a diagnosis, the patient should not neglect the proposed conditions of inpatient treatment; only strict, daily monitoring by a specialist will help him recover from polysegmental pneumonia without any special complications.
The patient should be prescribed one of the following antibiotics:
- Penicillin;
- Cefazolin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Erythromycin;
- Ofloxacin;
- Cephaloridine;
- Azithromycin;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Cefaclor;
- Levofloxacin.
It is necessary to prescribe medications that promote the removal of sputum (mucolytic agents):
- Ambrobene;
- Gerbion;
- Lazolvan;
- Acestine;
- Ambroxol;
- Sinupret;
- Bronchoval;
- ACC;
- Deflegmin;
- Bromhexine;
- Fluditek.
Regardless of the type of inflammation, the attending physician prescribes a course of vitamin therapy to maintain the body’s immune system, anti-inflammatory and cardiovascular medications.
In severe cases of the disease, oxygen therapy (in cases of respiratory failure) and the administration of intravenous glucose-saline solutions (in cases of severe intoxication of the body) may be indicated.
The patient should radically reconsider his usual lifestyle, it is necessary:
- Maintain bed rest (sleep more);
- Completely give up bad habits (drinking alcohol and smoking);
- Provide additional aeration of the room in which the patient is located;
- Eat a balanced diet by the hour;
- Maintain a drinking regime, since fluid intake helps remove harmful substances from the body.
Fighting at home
Mild forms of the disease can be treated at home. An exception to the rule will be patients who, in addition to pneumonia, have other concomitant diseases, or lonely elderly people.
If treatment is carried out at home, then for a complete recovery it is necessary to flawlessly follow all the doctor’s instructions.
At home, you should follow several important rules that will help you cope with the disease much faster:
- Bed rest;
- Drink plenty of fluids;
- Eating healthy foods rich in vitamins and microelements;
- Taking vitamins.
For the patient, follow a routine, have access to fresh air, and take care of your own hygiene. Traditional recipes based on natural ingredients can help cure pneumonia at home.
Thanks to their medicinal components and healing properties, they help the body quickly cope with the disease and restore strength.
Several effective recipes:
- Hazelnuts and red wine to remove phlegm from the body. Mix peeled nuts and red wine in equal proportions (0.5 kg each), put on low heat, and boil for 25 minutes. Take the infusion on an empty stomach, one spoon three times a day.
- Figs and milk. Pour a glass of milk over several figs and place on low heat. Boil for 15-20 minutes, drink one glass every day after meals.
- Badger fat against pneumonia. Take a few spoons an hour before meals three times a day. Use this remedy for one month, after taking a short break, start taking it again. You can mix badger fat with milk and honey to make it tastier.
- Raspberry tea helps fight cough. Brew raspberry bush twigs and drink instead of tea. You can add raspberry jam and honey.
- Herbal collection. Mix licorice root and hoofed grass, anise, pine buds, and fennel in equal proportions. Take 4 tablespoons of the resulting mixture, add a glass of water, leave for half an hour. Strain and drink three times a day.
How is the diagnosis made?
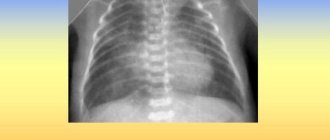
To diagnose lung disease and make a diagnosis, the segmental type of pneumonia must be confirmed by laboratory tests and images (X-ray or ultrasound, in additional cases MRI). At the first visit to the clinic, the doctor examines the patient and collects complaints. The presence of symptoms of inflammation is established.
A chest x-ray is required. Additional indicators of pneumonia are the results of laboratory tests of blood and sputum. The chest may be tapped to detect muffled sounds. The X-ray image shows a “collapse” of the lung, indicating a segmental type of disease. There will also be dark areas visible in the image. These are tissues with pathology.
A blood test only helps to record the fact of inflammation without establishing the cause and its type. To confirm pneumonia, it will be necessary to determine the type of causative agent of the disease. The most effective antibiotic is also determined after testing the sensitivity of bacteria to drugs.
Causes of pathology
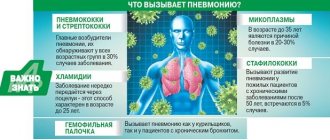
The segmental form of pneumonia is an inflammatory process that occurs in the right or left, or simultaneously in segments of both lungs. The cause of this disease will be various viruses, fungi and bacteria.
The disease is dangerous, because it will cause many other diseases of the body, even lead to death, if left untreated.
The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets; when a patient sneezes or coughs, they spread bacteria and microorganisms that enter the body of a healthy person and begin to multiply.
Inflammation in segments of the lungs begins due to a decrease in the level of body defense. This can happen during colds or sudden hypothermia. A common cause of segmental pneumonia is the multiplication of the pathogen in one part of the lungs.
Causes of the disease in adults:
- Frequent inflammation of the walls of the lower respiratory tract, which is accompanied by overgrowth of defects with connective tissue;
- The occurrence of vascular spasms during smoking;
- The presence of deformed bronchi;
- Decreased immunity, impaired blood supply.
The unresolved segmental form of pneumonia is characterized by the development of connective tissue in the lung. During its development, it shrinks, which leads to compression and deformation of the lymphatic and blood vessels, and then the bronchi.
This leads to stagnation of secretions in the bronchi, where infection begins to actively develop. When blood vessels are compressed, this leads to disruption of tissue nutrition and difficulty in lymphatic drainage.
Consequences and complications
In cases of untimely contact with a specialist, and in the rhythm of life this is a common story, a patient diagnosed with polysegmental pneumonia (especially if it is characterized as bilateral) may acquire complications of the following types:
- Endocarditis;
- Meningitis;
- Empyema of the pleura;
- Pericarditis;
- Serous and fibrous pleurisy;
- Lung abscess.
These diseases are life-threatening and difficult to treat.
It is better if a person is vigilant about his health and catches pneumonia in the early stages of its development.
The most dangerous consequences for human life from this disease are:
- Indications for surgical interventions;
- Death.
Getting rid of the acute form
Acute segmental form of pneumonia requires an approach to treatment.
The main method of treatment is antibacterial therapy, and when treated at home, the following are often prescribed:
- Macrolides;
- Penicillin drugs;
- Cephalosporins.
If the causative agent of the disease has not been identified, then doctors prescribe joint therapy, which includes antibiotics and additional medications.
The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and its characteristics. Recovery lasts 1-2 weeks, then the treatment drug is changed.
During acute pneumonia, the following treatment methods are used:
- Stimulation of immunity;
- Prescribing detoxification therapy;
- Taking antihistamines;
- Taking antipyretic and expectorant medications.
When the body has coped with the fever and intoxication, physical therapy begins.
Such treatment includes:
- Electrophoresis using potassium iodide and calcium chloride;
- UHF;
- Inhalations;
- Massage.
To reduce the size of the inflamed lesion, exercise therapy or an additional course of treatment is used. In order to properly treat the patient, it is necessary to undergo tests to obtain important laboratory, physical, and radiological data. Sometimes surgical intervention may be required if the disease recurs in the same segment.
https://feedmed.ru/bolezni/organov-dyhaniya/segmentarnaya-pnevmoniya-vzroslyh.html
What is polysegmental pneumonia
The polysegmental form of pneumonia is a limited inflammation and covers the lung tissue within the boundaries of several anatomical segments of one or two lungs (unilateral and bilateral pneumonia). Most often, preschool children (from 3 to 7 years old) are affected by the disease, but the pathology also occurs in older children and adults.
How does the polysegmental form differ from other forms of pneumonia?
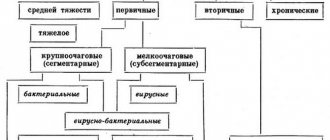
| Form of pneumonia | Distinctive features |
| Focal | The process involves one or more foci of infiltration up to 2 cm in size |
| Focal-confluent | Characterized by heterogeneous massive infiltration, consisting of several foci |
| Segmental | The process is limited to one anatomical segment of the lung tissue |
| Share | Inflammation develops in the lobe of the lung |
| Interstitial | The disease is characterized by pronounced changes in the interstitium of the lungs (usually in patients with immunodeficiency) |
Polysegmental pneumonia can be:
- unilateral (right- or left-sided): inflammation can occur in separate segments of different lobes of one lung, occurs in 95% of cases of this type of pathology;
- bilateral: segments in different lobes of both lungs are affected.
The following types of pneumonia are also distinguished:
- primary: occurs as an independent disease;
- secondary: develops against the background of an acute respiratory viral infection.
Left-sided form of the disease
The following symptoms are characteristic of segmental left-sided pneumonia:
- Chest pain of various etiologies, which intensifies with inhalation;
- Cough with a lot of sputum, which contains pus or blood;
- Sore throat that leads to coughing;
- Heat;
- Weakness;
- Dyspnea;
- Chills;
- Increased sweating;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Unreasonable agitation of the psyche.
Symptoms are characteristic of many diseases, therefore, for effective, timely detection of the disease and for treatment, an accurate diagnosis is necessary.
Left-sided lower lobe pneumonia can occur without obvious symptoms. It is characterized by general weakness of the body, loss of appetite and high body temperature.
Effective treatment of this disease requires the use of antibiotics. And to do this, you first need to identify the causative agent of the disease, which is difficult. A person’s nasopharynx contains many microbes and bacteria, which will often cause such a disease.
To identify the pathogen, the doctor takes a smear, but the results of the study come in 3-4 days.
At this time, the patient is prescribed a course of broad-spectrum antibiotics. They act much worse, but do not allow the disease to spread further. When the cause of pneumonia has been identified, a narrow-acting antibacterial agent is prescribed, which kills the very cause of the disease.
Diagnostics
The main method for diagnosing the disease is x-ray. The resulting images objectively display the affected segments and their location. Conclusions are made based on darkening in the images - this is one of the main signs of the disease. A spatial classification of polysegmental pneumonia is carried out: right-sided/left-sided/bilateral, upper lobe/lower lobe. Data on the volume of lesions is displayed.
Additional methods:
Physical examination
- physical examination will reveal wheezing, weak breathing, and airway defects;
- a clinical blood test will indicate pronounced symptoms of inflammatory processes in the body;
- fluorography;
- bacteriological studies of secretions (sputum);
- diagnosis of the state of the immune system;
- in cases of severe forms of the disease, serological and virological procedures are additionally performed.
All information received is taken into account when determining the type and dosage of medications. The diagnosis is determined only in conjunction with the external manifestations of the disease, in order to avoid confusion with other types of similar ailments.
Bilateral lung disease
The causes of bilateral segmental pneumonia will be viral forms that are transmitted by airborne droplets from person to person. After entering the body, they begin to actively multiply, especially in the case of reduced immunity.
This disease occurs when:
- Hypothermia;
- The presence of a viral infection;
- Lack of sleep;
- Allergenic conditions;
- Autoimmune pathologies;
- Chronic lung diseases.
The symptoms of bilateral segmental pneumonia are the same as those of ordinary pneumonia. They can appear immediately after infection, or after several days. The most dangerous thing is the absence of symptoms during such a disease; this prevents the disease from being detected in time, which leads to serious complications.
For effective treatment, drugs are selected individually, taking into account the following factors:
- Type of pathogen;
- The state of the body's protective function;
- Test results;
- The result of tests for sensitivity and tolerability of drugs.
Strong antibiotics are used for treatment, usually third or fourth generation cephalosporins. Combination drugs are often prescribed, which are much more effective.
Symptoms and diagnosis of segmental pneumonia in children
The symptoms of segmental pneumonia in children in the early stages are often similar to a common respiratory disease. The rate of development of the acute stage depends on the age of the child. In a newborn baby, pronounced symptoms appear several hours after infection, and in a teenager this period may last several days.
Main symptoms:
- severe weakness, refusal to eat and drink, nausea, sometimes vomiting, delirious state of consciousness;
- fever up to 39 degrees, which is difficult to bring down with antipyretics;
- At first there is a dry cough, but as the disease progresses, a wet cough develops with copious expectoration of green mucus;
- difficult moaning and wheezing breathing;
- shortness of breath, expressed mainly in children aged 1-6 years.
- the color of the lips may take on a bluish tint.
To make a diagnosis, a specialist uses the following methods:
- general and biochemical blood test, general urine test;
- isolation of part of the sputum to identify the causative agent of pneumonia through laboratory tests;
- culture of mucus from the throat or nose to determine sensitivity to antibiotics;
- X-rays of light;
- conducting an ECG.
The disease very quickly has a detrimental effect on a fragile child’s body, so timely making a correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment.
Focal pulmonary tuberculosis
Focal pulmonary tuberculosis is a form of secondary tuberculosis that occurs in the lungs and is characterized by inflammation of foci no larger than 1 cm in diameter.
Often the symptoms are mild or not expressed at all. Segmental pneumonia is often differentiated from this disease.
There are 2 forms of focal tuberculosis, and depending on them, treatment is prescribed:
- Active focal tuberculosis is treated in an anti-tuberculosis dispensary.
- Inactive tuberculosis - outpatient, under the supervision of a specialist.
For treatment, chemotherapy is used, lasting several months, with the following drugs:
- "pyrazinamide";
- "rifampicin";
- "ethambutol";
- "isoniazid".
If the disease is detected at an early stage, it is treated with streptomycin. The duration of the entire treatment depends on the form and severity of the disease; it lasts 6-9 months.
This disease rarely progresses, so doctors manage to cure 95% of patients if patients follow all the doctor’s instructions. The disease is highly treatable.
Anti-tuberculosis drugs are prescribed in optimal doses, and at the same time the doctor prescribes other drugs that help fight the disease. These are mainly vitamins and hormones.
The outcome of focal tuberculosis is favorable, fresh lesions resolve, and changes in the body do not pose a serious threat to health. But, if treatment is not started on time, or focal tuberculosis is not completely cured, then serious complications are possible.
The disease can develop into:
- Tuberculoma;
- Chronic form of tuberculosis;
- Infiltrative tuberculosis;
- Cavernous tuberculosis.
Right-sided and left-sided segmental pneumonia
The anatomical structure of the lungs is such that the right one has 10 segments, and the left one 8. Children's segmental pneumonia most often affects the left lung. One or more segmented areas of the organ are affected. Right-sided segmental pneumonia occurs extremely rarely in children; bilateral disease occurs even less frequently.
| Right-handed | Left-handed |
| This localization of pneumonia makes it possible to make a diagnosis more accurately and quickly, as it has more pronounced symptoms. Therefore, the necessary treatment and disease control are prescribed earlier. Inherent mainly in the adult population, it is easier to treat. May have a negative effect on the liver. | Since important organs are located on the left side, the danger of the disease for the baby increases. With this location of pneumonia, the doctor examines the x-ray more carefully, as it becomes difficult to make a diagnosis. The organ that may suffer from the disease is the heart (development of tachycardia). Timely treatment will not allow complications to arise in the child’s body. |
If the disease develops in a child under 12 years of age, hospital treatment is recommended, since many medications at such an early age should be taken only under the supervision of medical personnel.