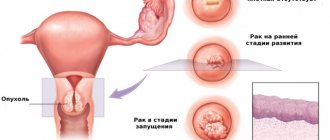
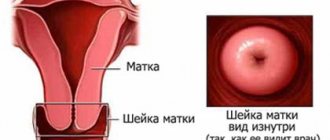
A polyp in the uterus is a benign neoplasm that is located on the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ. It can be either single or multiple.
A polyp grows quickly, and simply put, it is a type of wart that appears not on the skin surface, but on an internal organ - for example, in the cervix or in the endometrial layer of the uterus.
It is imperative to treat polyps, since lack of treatment can lead to undesirable consequences, including removal of the entire uterus.
In this article we will talk about whether polyps can be cured using conservative methods without surgery.
Causes of endometrial polyp in the uterus
More often they occur in women after 35 years of age, during the rapid onset of menopause. However, the disease occurs both in very young people who have never given birth, and in elderly people. This is a multifactorial disease, the main role in the occurrence of which is attributed to disturbances in hormone levels and chronic foci of infection in the endometrium.
Hormonal factor
An imbalance between estrogens and gestagens occurs more often in women with excess weight, endocrine diseases, against the background of polycystic ovary syndrome, endometriosis, and also after frequent terminations of pregnancy. Only fibrous polyps occur regardless of the woman’s hormonal status.
Estrogens are responsible for the formation of new endometrial cells in the first phase of the cycle. In the second phase, their level drops noticeably, and the concentrations of gestagens increase, which inhibit the proliferative effect of estrogens and promote the differentiation of tissues that have already formed.
With an excess of estrogens and a lack of gestagens, endometrial cells begin to divide randomly and foci of polypous growth appear. Gestagens do not restrain them, since their level is insufficient for this.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
Unstable levels of hormones provoke in women the formation of not only polyposis of the uterine cavity, but also hyperplastic processes in general, and also increases the likelihood of developing myomatous nodes.
Inflammation
The second important reason for the appearance of endometrial polyps in the uterus is a low-grade inflammatory process. It is believed that any pathology of the endometrium arises precisely against this background. And it is not necessary that a woman suffer from chronic adnexitis or endometritis; any surgical intervention (even an aspiration biopsy of the uterine cavity), exceeding the time limit for wearing an IUD, and other seemingly insignificant circumstances are sufficient.
Other reasons
Various endometrial injuries play a role. First of all, this applies to abortions, diagnostic curettages and other manipulations that involve entering the uterine cavity. Damage causes activation of enzyme systems in this area, which can lead to failure of cell growth and polyposis.
Diagnostic curettage
A number of endocrine diseases are associated with an increased risk of the formation of endometrial polyps in the uterine cavity. This happens due to impaired blood supply to tissues and changes in metabolism. Most often, endometrial pathology occurs in women with thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus, autoimmune disorders, heart and vascular diseases.
Polyposis can also be a consequence of long-term use of medications, especially hormonal ones, such as Dexamethasone.
Diagnostics
The main role in diagnosing this condition is played by ultrasound. When it is carried out using the transvaginal (and sometimes transabdominal) method, the polyp is clearly visualized on the device monitor. Based on this feature, we can conclude that it exists.
It is also extremely important to examine the neoplasm for histology. For him, part of the tumor is removed in one way or another, most often with the help of electrosurgery. Examination of such material for histology allows us to confirm or refute the presence of tumor markers in it. Thus, it is necessary to examine the adenomatous node in the uterus histologically in order to promptly begin treatment of the oncological process as it develops.
It is important to remember that if a patient of childbearing age is diagnosed with this condition, she will have to visit a gynecologist for diagnostic purposes for 5 years thereafter every six months. Moreover, regardless of whether the treatment was carried out and how successful.
Types: glandular, fibrous and others
Based on the histological structure of polyps, the following types are distinguished:
| Type of polyp of the uterine cavity | Short description |
| Ferrous | They originate from endometrial cells, which contain glands and produce mucous secretion. A type of simple glandular polyps is glandular-cystic. Both types are formed from actively dividing cells, and therefore have a high risk of malignancy in the future in the absence of proper treatment. Most often, endometrial glandular polyps occur in women around 40 years of age against the background of hyperestrogenemia, and sometimes they can go away on their own along with the sloughing endometrial cells of the uterine cavity. |
| Fibrous | They are formed from connective tissue and are represented by very dense formations in their structure. Fibrous endometrial polyps are one of the most harmless formations; they almost never degenerate into uterine cavity cancer. Their treatment consists only of removal and further monitoring of the condition of the uterine cavity. They do not have sensitive receptors for hormones, so they do not depend on their levels. |
| Glandular fibrous | This is a mixture of the two previous ones, one of the most common variants of polyps. In this case, the dense base, as a rule, is located close to the wall of the uterus, and the freely hanging end “floats in the cavity.” The difficulty with these polyps is that when removed, the “pedicle” may not be completely excised, which will lead to rapid re-growth. |
| Adenomatous | These are borderline formations between glandular polyps and adenocarcinoma of the uterine body (cancer). Therefore, identifying this type of polyposis is always a reason for a detailed examination and serious treatment, including surgery. |
| Placental | They form in women after any pregnancy, even if it was interrupted at a short term or successfully ended in childbirth. They are chorion tissue that remained in the uterine cavity and transformed into a polyp. Removal leads to complete recovery. |
In appearance, endometrial polyps can be wide-based or narrow, “hang” into the uterine cavity or be in the form of tubercles on the surface of the endometrium; they can be tiny (1-2 mm) in size and large - several centimeters.
Symptoms of appearance in the uterus
The clinical manifestations of polyps in the uterus largely depend on what parameters they have, their number, location, and the woman’s age. Sometimes they can be discovered accidentally during a routine ultrasound. Typical complaints include the following:
- Intermenstrual discharge . This could be spotting or heavy discharge. They can appear regardless of the day of the cycle, but more often on the eve of or after menstruation, as well as in the middle - during ovulation. The appearance of discharge after sexual intercourse or physical activity is typical.
- Heavy menstruation with clots . Polyps in the uterine cavity disrupt the contractility of the endometrium, thereby causing heavy periods. In addition, parts of the polyps may break off and come out.
- Pain . This is not a typical symptom for polyps. Pain in the lower abdomen of a pulling nature can appear with large polyps, as well as if it breaks away from the endometrium and tries to pass through the cervix to the outside. In the latter case, the woman notices increasing nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which goes away immediately after something like a small clot of mucus appears in the discharge - this is part of the polyp.
- Infertility . Polyps often interfere with conception. There are several reasons for this. Polyps in the uterine cavity can provide a mechanical obstacle to the path of sperm, which is dangerous, and also act as a spiral.
Watch this video about the causes and symptoms of polyps in the uterus:
Treatment
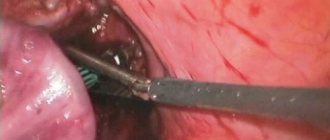
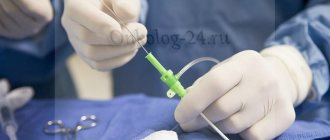
There is only one way to cure polyps in the uterus - to remove them surgically using hysteroscopy - a low-traumatic operation performed using special equipment. For very small formations with a diameter of less than 1 cm, it is permissible to use curettage. If the formation is large, it seems to “unscrew” and is removed, after which the site of injury is cauterized using an electric current.
Curettage procedure
After the actual removal has been performed, restorative therapy is necessary to protect the patient from infections and allow healing to proceed quickly. For this purpose, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, such as Metrogyl, Ceftriaxone, or narrow-spectrum antibiotics, when a smear on the microflora shows the presence of a specific pathogen.
In addition, the use of anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs (Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac) is necessary. They will help avoid the development of inflammation, quickly relieve existing ones and speed up healing. In addition, they have an analgesic effect and will help relieve some of the symptoms that develop after surgery.
Separately, it is worth considering the use of immunomodulatory and immunostimulating therapy. It allows you to restore and enhance both the general immunity of the patient’s body and local tissue immunity. This is necessary to avoid the addition of an infectious process and to increase the speed and ability of the tissue to regenerate. Drugs such as Likopid, Interferon, Viferon are used; Viferon vaginal suppositories are suitable for topical use.
In some cases, hormonal treatment is also required. It is prescribed strictly by a doctor after performing a hormone test. Typically, preference is given to progesterone drugs, as they reduce the negative effects of estrogen on the body, which is responsible for pathological tissue proliferation. The following drugs are used: Duphaston, Utrozhestan, Longidaza and others.
In rare cases, complete removal of the uterus is performed. It is necessary when there is a significant risk of developing malignancy. This happens with multiple relapses and the presence of the provoking factors listed above. Also indicated are adenomatosis and other changes in the endometrium, its atrophy. Also, women of post-reproductive age often undergo such intervention.
Uterus removal
Why is it dangerous for women?
Polyps in the uterine cavity can bother a woman for years - constantly or detected with some frequency; the consequences of the disease can be as follows:
- malignancy - first of all, caution should be exercised in case of polyps in menopausal women, as well as if adenomatous ones are detected;
- heavy periods - menstruation can be so significant that it will lead to a decrease in hemoglobin levels and anemia in a woman, causing weakness, lethargy, and decreased ability to work;
- infertility.
Polyp in the cervix
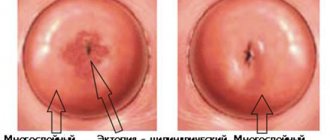
Cervical polyp is a common symptomatic gynecological pathology. A growth is formed due to abnormal growth of the mucous membrane .
If transformation into oncology is not observed, the polyp does not pose a danger to the woman’s life, but this does not mean that it does not have to be treated.
A polyp can lead to a number of complications that can significantly undermine a woman’s reproductive health.
The clinical picture of polyps begins to be accompanied by complications.
Most often, women consult a doctor due to infertility , but when the polyp increases in size, the symptoms may be as follows :
- menstrual irregularities;
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- bleeding during menopause;
- increase in the volume of leucorrhoea;
- pain and bleeding during intimacy.
If the polyp becomes infected and inflamed, the signs may be as follows::
- temperature increase;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- bleeding;
- bloody discharge with pus or mucus;
- weakness.
NOTE!
The presence of at least one of the listed signs is a good reason to contact a specialist for advice.
Is it possible to get pregnant with an endometrial polyp?
Functional polyps can be shed independently from the endometrium during menstruation and do not affect the likelihood of pregnancy. However, they can occur in girls who have not previously had any gynecological problems and become a cause of infertility. In this case, surgical treatment is necessary.
After the endometrial polyp in the uterus is removed, you can try to get pregnant within 2-3 months. And if the problem was hidden only in a polyp, you won’t have to wait long for pregnancy.
Polypoid growths exert their contraceptive effect in several ways:
- Creates an obstacle to the spermatozoon . In this case, even small polyps, but located at the mouths of the fallopian tubes or above the internal os of the cervix, prevent the passage of sperm to the egg.
- Acting like a Navy . This refers to fairly large and dense polyps in the cavity that interfere with normal implantation of the fertilized egg and negatively affect the endometrium, interfering with its secretory transformation.
Types
There are three forms of the disease:
- Diffuse, when the lesion is evenly distributed throughout the mucosa;
- Focal, when only certain areas are affected;
- Nodular, when a node of cells with a membrane is formed.
Treatment may vary slightly depending on the form.
There are different types of tissue changes in the uterus.
- Simple unexpressed form;
- Complex expressed form.
It is very important to correctly determine this type, since the need for further surgical treatment depends on it. For example, the oncological process develops much more often in a complex form (in 29% of cases) than in a simple form (in 8% of cases).
Diagnosis of the condition
You can suspect endometrial polyposis based on a woman’s complaints about heavy menstruation. However, these symptoms are also characteristic of other pathological conditions, for example, endometrial hyperplasia and submucous fibroids.
Polyposis can be reliably determined using ultrasound. However, it is informative to perform it on days 3-7 of the cycle. Performing an ultrasound in the second phase is fraught with overdiagnosis - normal endometrium may look like a polyp.
Multiple endometrial polyps according to ultrasound data
If endometrial polyps are suspected, a 3-D ultrasound is informative, as pathological growths in the uterine cavity can be more clearly seen.
Treatment without surgery
If the gynecologist decides that in a given clinical situation it is possible to postpone surgical treatment, then the woman is prescribed conservative therapy. As a rule, treatment of endometrial polyps without surgery involves taking the following medications:
- oral contraceptives or gestagen monotherapy according to the woman’s age and constitution;
- vitamin complexes - Time factor, Cyclovita, cyclic intake of vitamin E.
After two to three months of treatment, a control ultrasound of the pelvic organs is prescribed on days 3-7 of the cycle. If polyposis or even suspicion of it persists, surgical treatment is recommended.
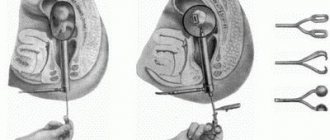
Hysteroscopy and other operations to remove endometrial polyps
Hysteroscopy is the “gold standard” in the treatment and diagnosis of endometrial polyposis in women of all ages. It is performed in a hospital setting, but does not require long-term hospitalization. As a rule, the woman can be discharged home the next day after the intervention.
A minimal examination is required to prepare for the procedure. Endometrial polyps in the uterus are removed by hysteroscopy using intravenous anesthesia - after the medicine is administered into a vein, the woman falls into deep sleep and does not feel pain.
Hysteroscopy is performed using a special instrument - a hysteroscope. This is a tubular manipulator of small diameter, inside of which there are conductors with various functions - a camera for viewing (everything that happens inside the uterine cavity is displayed on the monitor screen), tools for removing and cauterizing areas of the endometrium. Hysteroscopy allows the following:
- see polyps in the uterine cavity - their size, location, structure;
- remove them - the doctor precisely excises them and cauterizes the site of the “leg”, which minimizes the likelihood of relapse;
- The material is sent to the laboratory for examination, which allows further competent treatment to be prescribed.
Hysteroscopic removal of a polyp in the uterine cavity
If hospitals are not equipped with a hysteroscopic stand, routine diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity is performed - a standard operation to remove an endometrial polyp in the uterine cavity.
In this case, the doctor “blindly”, relying only on his own feelings, after adequate anesthesia, dilation of the cervical canal and insertion of a curette into the uterine cavity, successively “cleanses” all the walls, while theoretically the polyp should be removed. However, the procedure is fraught with the following:
- some growths may not be removed by accident;
- a “leg” often remains, which increases the likelihood of relapse of the disease.
Watch this video about the diagnosis and treatment of polyps in the uterus:
Uterine polyps and alternative treatment
Polyps of the uterine cavity and cervical canal are processes that have benign characteristics and occupy one of the leading places among the structure of gynecological pathology. Polyps can occur in various locations of the reproductive organ.
They can be observed in the uterine cavity, both on the anterior and posterior walls of the female reproductive organ; also the favorite location of these neoplasms is the fundus of the uterus close to the mouths of the tubes. One of the varieties of these hyperplastic processes are polyps of the cervical canal, which are located in the cervix itself, and also come from the columnar epithelium lining the mucous membrane in this part of the uterus.
According to their characteristics, uterine polyps are either glandular or fibrous formations, which have different ratios of these components. There are also adenomatous polyps, which alarm doctors in terms of their malignancy.
Recurrences of such neoplasms are extremely undesirable and carry increased risks of cancer pathology
The causes of polyps of the female reproductive organ are many pathological conditions, including hormonal dysfunction, which is the cause of various pathological conditions of both the reproductive sphere and somatic pathology, infectious and inflammatory diseases, and intrauterine manipulation. The most important factors in the pathogenesis of uterine polyps are hormonal and inflammatory factors. It is these influences that have a significant restructuring at the cellular level of the endometrium and endocervix, which entails a hyperplastic process.
The symptoms of a polyp in the uterus are quite varied. It may include spotting during the menstrual period, menstruation that is large in volume, intensity and duration, and pain.
Traditional medicine is quite wary of polyps. Some sources claim that polyps up to one centimeter, which do not cause any clinical symptoms, are treated and observed conservatively. However, most of these processes require surgical correction, that is, their removal.
Diagnosis of these pathologies is a gynecological examination, which will detect a polyp of the cervical canal, as well as an analysis of the clinical picture of the condition, which may prompt the doctor to use ultrasound diagnostics, with the help of which a preliminary diagnosis of a uterine polyp will be established. The final diagnosis will be established after polypectomy (removal of this hyperplastic neoplasm) and obtaining a histological report of the analysis of the removed material from the uterine cavity or its cervix.
Of course, any operation, even if not extensive, scares people. Representatives of the fair sex are looking for a variety of ways to relieve this condition, which is not associated with surgical intervention. Many women turn to alternative, folk medicine in the hope of obtaining a cure without the use of surgical tactics for the management of uterine polyps.
Traditional medicine recipes aimed at combating uterine polyps
In fact, homeopathy is not as harmless as many people think. Herbal preparations can both have a positive effect on the course of the pathological process and cause a lot of complications in case of overdose or improper use of these drugs. Of course, doctors of traditional medicine do not recommend putting herbal treatment in the first place. Homeopathy for uterine polyps can be used as an auxiliary treatment method,
as well as in the recovery period, and for further prevention of the development of such hyperplastic processes. Some herbal remedies may have the effects of phytoestrogens, that is, on the contrary, they act as an even greater influence of estrogen on the polyp, causing its growth and development.
You should not rely only on homeopathy for the reason that not a single doctor will take responsibility to say that this polyp is 100% benign. Some of these seemingly harmless polyps may represent an oncological process that does not cause any clinical symptoms. That is why the absence of traditional medicine is extremely undesirable in the management of patients with such diagnoses.
Celandine in the treatment of polyps
Celandine is a plant that in certain dosages can be quite an effective medicine and have a good therapeutic effect, and in other dosages it can be a real poison that can cause considerable harm to the human body. For uterine polyps, it is also used in the form of infusions for oral administration or douching.
In order to prepare a solution (infusion) based on celandine, you need to pour boiling water over the sprouts. The container in which the celandine is located must be wrapped in a gauze towel and left for 12 hours. The finished infusion is taken 3 times a day, ranging from 15 ml to 100 milliliters.
“Berry bouquet” in the treatment of polyps. Rose hips and lingonberries are quite effective in the fight against hyperplastic processes.
To prepare the active infusion, you need to take two tablespoons of lingonberries, 3 tablespoons of chopped nettle, as well as 3 tablespoons of rose hips. These ingredients should be poured with a glass of boiling water. This product infuses quite quickly, and after 4 hours the product can be taken. Each time a new infusion is prepared, which is drunk in an amount of 250 ml.
A tincture based on golden mustache is also used. To prepare, you need half a liter of good quality vodka, as well as 50 joints of this herb. It is crushed and filled with the required amount of vodka. This tincture takes much longer to prepare than previous recipes. These ingredients should be infused for a week, or even 10 days. After preparation, take 20 drops of tincture, which is diluted in 1/3 glass of water. The frequency of use per day is two, treatment is a month. However, therapy is not limited to one course. It is believed that 5 courses of such treatment are necessary to obtain a therapeutic effect.
Not only herbs are used to treat polyps in the uterine cavity. The most common garlic, which we love so much and is used quite often in the cooking of our country, and pumpkin seeds can be suitable for this. To prepare the product you will need 7 egg yolks, which must first be boiled, fresh pumpkin seeds, as well as vegetable oil in a volume of about 300-400 milliliters.
Pumpkin seeds are ground together with the yolks. This mixture must be mixed with vegetable oil and the resulting mass should be placed in a water bath for half an hour. After this mixture has cooled, it should be taken 1 teaspoon three times a day. Then 5 days break. Take the mixture until complete recovery.
The most common herb, which is very often used to treat gynecological pathologies, is boron uterus. Women use an infusion of Borovaya uterus, which is prepared by pouring one teaspoon with 150 milliliters of boiling water. After the infusion has cooled, drink 1/3 glass three times a day. Sometimes this herb is combined with wintergreen infusion.
Products based on herbal ingredients are used not only internally. A fairly good effect is obtained when using douching solutions. For preparation you will need two tablespoons of yarrow, rosemary leaves, as well as sage, four tablespoons of oak bark. The ingredients must be mixed and poured with boiling water in a volume of 2.5 liters. This mixture must be simmered over low heat for 30 minutes. After the mixture has cooled, it must be strained. The warm solution is used in the form of douches.
Also used for douching is a set of plant components such as St. John's wort, agrimony, celandine, and calendula. The ratio of components should be: 2-2-3-2. One tablespoon of this herb is poured into a glass of boiling water and left for 6 hours. The resulting infusion is filtered through gauze and used warm for douching. For each new procedure, a new solution is prepared.
However, traditional medicine also has some caution regarding douching. Indeed, if this procedure is performed ineptly, there is a high probability of washing out the normal flora, the appearance of an imbalance in the microflora and the appearance of colpitis - an inflammatory process of the vagina.
Of course, traditional medicine should not be perceived as a panacea and the main method of therapy for hyperplastic processes of the uterine cavity and cervical canal.
The true causes of such processes can never be stopped by using herbal remedies. Moreover, not every polyp is truly a benign neoplasm. The danger of missing an oncological process is the main reason why homeopathy should not be used as the main method of therapy. Thus, representatives of the fair sex are only wasting time and delaying the possibility of treatment through the use of modern achievements of science and technology.
In addition to such a dangerous pathology as cancer, a woman gets a lot of problems that arise from untimely and unqualified treatment of polyps:
- Infertility. This is a rather serious and complex psychological and medical condition that not every doctor or clinic can cope with, and not every representative of the fair sex can survive the inability to have offspring. As a result of disrupted hormonal levels and the presence of a polyp in the uterus, the endometrium is simply not suitable for a fertilized egg to attach to the surface of the uterine cavity.
With polyps located in the cervical canal, sometimes sperm simply mechanically cannot penetrate the uterus and meet the oocyte. This is the second reason for lack of pregnancy. - Heavy bleeding both during the period of desquamation of the epithelium, that is, menstruation, and in the intermenstrual period leads to an increase in the symptoms and pathogenesis of anemia - a reduced level of hemoglobin. The woman’s quality of life will be lost; she will begin to feel a feeling of constant weakness, fatigue, and inability to perform the amount of work previously performed. A decrease in oxygen delivery to organs and tissues leads to hypoxic changes, that is, a lack of oxygen in tissues and its consequences for all organs and systems. Depending on the severity of anemia, the function of organs and systems affected by oxygen starvation will change.
If pregnancy nevertheless occurs in the presence of a uterine polyp, then there is a high probability of the occurrence of such a pathological process of gestation as the threat of miscarriage and spontaneous abortion. This pathological condition is a hormonal and psycho-emotional stress for a woman, forcing her to withdraw into herself and experience the loss of her beloved child, who was still at the stage of intrauterine development.
Currently, a proven effective method of treating uterine polyps is their hysteroscopic removal - hysteroresectoscopy. Only by removing the polyp and sending it for histological examination can you get an accurate answer to the question of whether its nature is benign or malignant, as well as prescribe the necessary amount of therapy indicated in each specific case.
And homeopathic treatment can be used as maintenance therapy. And only after agreement with the attending physician, obstetrician-gynecologist.
Prevention of occurrence
Based on the histological response obtained after removal of the endometrial polyp in the uterus by hysteroscopy or conventional curettage, the doctor prescribes treatment aimed at preventing recurrence of the pathology. Almost always this is hormonal therapy. Only fibrous polyps do not require such treatment; only dynamic monitoring using ultrasound is necessary.
The following drugs are used:
- combined estrogen-gestagens - Janine, Diane-35, Regulon, Jess and others;
- pure gestagens - Duphaston, Utrozhestan, Visanne, Depo-Provera, Norkolut;
- agonists of pituitary gonadotropic hormones - Buserelin, etc.
The general principles of preventing the occurrence of polyps are sexual literacy, reliable contraception, and timely treatment of gynecological and endocrine diseases. A healthy lifestyle with normal body weight and a balanced diet plays an important role.
We recommend reading about how menstruation occurs with a polyp. From the article you will learn about what a polyp is, the characteristics of menstruation with a polyp in the uterine cavity and on the cervix, drug and surgical treatment. And here is more about the consequences of hysteroscopy when removing an endometrial polyp.
Endometrial polyps can occur in the uterine cavity even in nulliparous women. There are many reasons for this, but the main role is played by hormonal disorders and the chronic inflammatory process in the uterine cavity. The simplest and most reliable diagnostic method is pelvic ultrasound. Not all polyps need to be removed, and if necessary, it is better to give preference to hysteroscopy.
What complications may arise?
As a rule, when removing uterine polyps using hysteroscopy or laser surgery, the risk of complications is minimal. However, it is not always possible to resort to these methods for treating endometrial polyps, especially when it comes to emergency diagnostic curettage in case of bleeding. In addition, one cannot ignore the physiological characteristics of each individual woman.
Complications after surgery to remove polyps in the uterus.
- hematometer. This is the accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity as a result of a violation of its outflow, mainly associated with cervical spasm. If diagnosis is untimely and there is no treatment, pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply there, since the blood is a good breeding ground for them.
- perforation of the uterus. This is a through hole in the wall of the uterus, which leads to its communication with the abdominal cavity. Perforation can lead to a severe infectious inflammatory process with the development of peritonitis or to severe bleeding if a large vessel is damaged. As a rule, this situation occurs during diagnostic curettage. The doctor works blindly. This can happen during hysteroscopy/laser treatment if the work area is in an area of the uterus with scars and adhesions.
- adhesions and scarring. Occurs when the uterine mucosa is severely damaged or after an inflammatory process in it. Adhesions and scars disrupt the functioning of the endometrium and prevent the egg from attaching to it. This can cause infertility or ectopic pregnancy. As a rule, these complications occur after diagnostic curettage, where the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity is severely injured.
- inflammatory process in the uterine cavity. Occurs when bacterial flora gets into it. Therefore, doctors can prescribe antibiotics prophylactically.
Complications in case of untreated uterine polyps.
- uterine bleeding. As the polyp grows, blood vessels begin to grow in it. Their walls are quite permeable, which can lead to bleeding. As a rule, the amount of blood loss is small and can begin spontaneously and also end.
- infertility. The polyp can prevent the fertilized egg from attaching to the wall of the uterus, which leads to problems with conception.
- threat of miscarriage. The polyp can provoke placental abruption and thereby terminate the pregnancy.
- ectopic pregnancy. It can develop with multiple uterine polyps.
- malignancy. Malignant degeneration, which leads to an oncological process.
- chronic source of infection. Polyps are very vulnerable to pathogenic microflora and can become a chronic source of infection.
In approximately 10% of cases of surgical treatment, disease relapse occurs. The reason for this may be the individual characteristics of the body, incomplete removal of the polyp, a malignant process or a hereditary predisposition.
Take care of yourself and be healthy!