What is a needle biopsy and how is it performed?
A biopsy is the intravital removal of abnormal tissue for further microscopic examination. It is carried out in various ways, but the safest and most informative is to obtain a biopsy using a puncture. This method has a number of undeniable advantages, namely, good tolerance by patients, a minimum of side effects and high information content.
This biopsy is performed in one of two ways:
- Fine needle. This type is classic and in medical terminology is called fine-needle aspiration puncture biopsy. A characteristic feature of this diagnostic method is aspiration (sucking) of the contents of the pathological neoplasm using a disposable syringe with a thin needle. A fine-needle biopsy lasts no more than a minute and is well tolerated by all patients.
- Thick-needle. This type of diagnostic test is called trephine biopsy. It makes it possible to obtain a biopsy sample of a slightly larger size (volume), since a thick needle with a cutting end is used for the procedure.
A biopsy is performed by puncture, both when it is necessary to study a shallow tumor, and in the case of taking cells or liquid secretion from deep layers of tissue. In the latter case, the procedure must be monitored using ultrasound, which helps to avoid medical errors and prevent possible complications.
Postoperative period
After a cervical biopsy, the woman is given a certificate of incapacity for work for a period of up to 10 days. The operation does not affect your overall health. After taking the material for analysis, discharge is observed for 3-4 days; when curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, bleeding can persist for up to 7 days.
A short-term increase in temperature is possible, however, if hyperthermia exceeds 37.5 ° C, you must consult a doctor, due to damage to the integrity of the epithelium, an inflammatory reaction may occur.
During the first week, pain in the lower abdomen is observed; in order to relieve the unpleasant symptom, the doctor prescribes analgesics.
Possible complications
If all safety measures are followed, complications are practically not observed. However, given that a biopsy is a micro-operation, complications are possible, namely:
- inflammation due to infection of the wound surface;
- bleeding due to damage to the vascular network;
- scarring or formation of pathological tissue in the case of a circular biopsy.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
A biopsy performed by puncture is the safest medical examination of tissue structures to detect cells that have undergone the process of malignancy. Typically, a piece of tumor is collected under ultrasound control, which increases the effectiveness of the procedure.
The main indications for this research method are:
- Identification of the nature of abnormal changes in tissue structures and liquid components of pathological areas localized in various internal organs, skin and muscle fibers.
- Monitoring of therapeutic measures carried out to eliminate a previously identified pathological process.
- Determining the prognosis of the course of the disease and establishing the possibility of a complete cure.
It has a targeted biopsy and a number of contraindications, both absolute and relative.
It is strictly unacceptable to carry out such a procedure in the following cases:
- the patient is in a comatose state;
- the patient’s disagreement with its implementation, expressed in refusal to sign a mandatory preliminary agreement;
- a person has a history of a number of diseases that cause blood clotting disorders;
- intolerance to medications used for aseptic treatment and local anesthesia.
Relative contraindications, i.e. the undesirability of carrying out this procedure, but the possibility of performing it with the permission of a doctor to save the patient’s life, include acute infectious and inflammatory processes developing in the body, a febrile state and insufficiency of the functioning of certain internal organs (cardiovascular, renal etc.).
"Liquid biopsy" [edit | edit code ]
Liquid biopsy is the informal name for a new technique for identifying tumor cells and their DNA in a patient’s blood. Until the beginning of 2014, the technique was considered exclusively laboratory and inapplicable in practical oncology. In February 2014, a study was published [1], the authors of which were able to show the promise of liquid biopsy for the early detection of various types of cancer [2] [3].
This procedure, according to scientists, can revolutionize the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, as it greatly facilitates the early detection of tumor cells before symptoms appear. A liquid biopsy helps the doctor see the big picture and understand how cancer cells spread in the body, while a regular biopsy only provides information about the local tumor.
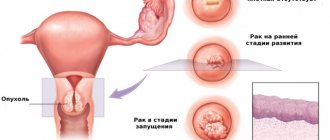
A biopsy is a diagnostic procedure performed to obtain a tissue sample (biopsy) from a “suspicious” location, such as a tumor or polyp. A biopsy is necessary to confirm the diagnosis of cancer.
Needle biopsy for cancer
This type of research, in the presence of malignant pathologies in the body, is less dangerous than performing an incisional (surgical) biopsy of a tumor, which in most cases can provoke the process of metastasis of the primary tumor structure after taking a biopsy.
Carrying out a puncture biopsy if the patient has malignant cells is recommended in the following cases:
- the tumor structure is significant, but complete or partial resection of the organ is contraindicated;
- the process of malignancy has affected the lymphatic system (in this case, invasive intervention can cause the activation of malignant cells, and their spread with the lymph flow to nearby tissues and organs, so biopsy of the lymph nodes through puncture becomes the method of choice).
Worth knowing! Despite the fact that performing a puncture does not injure the organ damaged by oncology, before using this procedure it is necessary to irradiate the tumor structure, which will reduce the risk of the spread of metastases.
Puncture
This procedure involves a puncture carried out in the desired part of the body with a specially designed, hollow needle. The target of action may be a specific organ, cavity or blood vessel. Puncture is used for different purposes. One of them is related to diagnostics. In this case, it is possible to remove biological material from the body (in a small amount), the study of which helps to identify the disease. Sometimes, through a puncture, special coloring substances are introduced into the area under study, which is necessary in some situations to perform x-ray diagnostics.
Puncture is also used as a therapeutic method. For example, it allows you to deliver medicine directly to a problem area. In addition, this is a way to pump out pathological fluid or air accumulated somewhere in the body, as well as to perform rinsing.
From which organs can a puncture be taken for examination?
Puncture collection of biopsy material, despite the safety of the procedure, cannot always be performed.
Most often, a targeted biopsy is prescribed when tissue from the following organs affected by the pathological process is required for histological examination:
- kidney;
- lungs;
- liver;
- mammary gland;
- lymph nodes;
- stomach and pancreas;
- any part of the intestine.
But most often a puncture biopsy of the thyroid gland is prescribed. Taking biopsy material from this secretory organ using a puncture is the most optimal way. A biopsy performed on the thyroid gland using the puncture method avoids any pathological consequences.
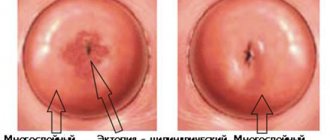
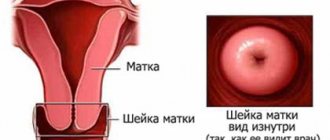
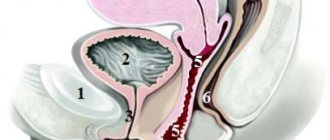
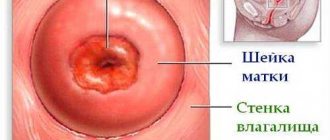
Cervical biopsy methods
There are many techniques used to perform a cervical biopsy. The classification is based on the method used to collect the sample. There are several different methods for cervical biopsy:
- Colposcopic (or puncture). In this case, tissue is collected using a very thin needle, and the material for examination is examined under a microscope.
- Radio wave. To take a sample for analysis, use the Surgitron apparatus.
- Laser. Such a biopsy involves removing areas of tissue using a laser, i.e., a laser knife.
- Conchotomnaya. The principle of sampling is very similar to colposcopic. They differ in that instead of a needle they use a conchotome - a special surgical instrument that looks like scissors with pointed edges.
- Loopback (loopback). To take the material, a very thin wire is used, twisted into a loop, through which a weak electric current is passed.
- Wedge-shaped (conization of the cervix). This type of biopsy is one of the few that is an advanced analysis (the vast majority are performed specifically). A triangular piece (wedge-shaped) is taken from the cervix, the study of which gives the most complete result about the problem at hand.
- Circular (circular). A type of wedge biopsy. The material is collected using a laser or scalpel. The research material itself includes not only cervical tissue, but also part of its canal.
- Trephine biopsy. The essence of the method is that the material to be studied is taken from several affected areas at once.
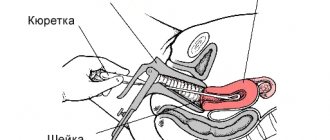
- Curettage of the endocervical canal. This biopsy method is fundamentally different from the above, since it involves curettage of the cervical canal (not the uterus itself).
Can a needle biopsy be trusted?
The reliability of a biopsy performed through puncture sampling of biological material is of interest to many. According to the unequivocal opinion of experts, this diagnostic study has a high degree of information content, but its results may contain errors. The appearance of false-negative or false-positive indicators can be influenced by both some external factors and the general condition of the person, which is why, before making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a repeated sampling of biopsy material and a number of additional instrumental and laboratory tests.
Biopsy analysis: when is it needed?
A biopsy is recommended in cases where other research methods are insufficiently informative. It not only determines the benign or malignant nature of the formation, but also provides information about the severity of the disease. A biopsy test is prescribed if diagnostics are necessary for all types of soft tissue.
Here are just a few indications for a biopsy, the most common in medical practice:
- focal and diffuse pathological processes affecting the liver,
- abscesses of the splenic region,
- carcinomas in the pancreas,
- malignant type of lymphoma, as well as metastasis in the lymph nodes,
- kidney tumors
- cysts on the thyroid gland,
- hematomas,
- precancerous conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, chest organs and others.
There are separate indications for performing a biopsy of the chorion (outer membrane of the fetus):
- hereditary pathological processes,
- genetic abnormalities present in at least one of the parents,
- late pregnancy,
- the presence of chromosomal disorders in first children.
When a biopsy test suggests pain or discomfort, anesthetic methods are used.
The rules for skin care after analysis are different and depend on the location of the sample, but in most cases the bandage is removed within a day after the test, and water procedures are possible after 2-3 days.
Diagnostic equipment, what is it?
To ensure that the biopsy is safe for humans and does not provoke the development of any complications, specialists carry out the procedure only with the help of special equipment. Currently, oncologists in most clinics use a modern disposable needle biopsy kit.
It includes the following tools:
- Needles for puncture biopsy of three types (cutting, modified, aspiration). The set includes cannula needles (pointed at one end of the tube) of various diameters.
- Disposable plastic guides (syringes) for 20 and 30 ml;
- Test tubes filled with saline and ampoules with lidocaine.
- Gel for filling the space between the ultrasound sensor and the skin.
In addition to disposable kits, biopsy guns are used to carry out this diagnostic procedure, allowing shots to be fired with a thin, sharp needle, which acquires high speed and cuts tissue at the site of the lesion. With the help of such a gun, puncture biopsy of soft tissues of various internal organs is effectively performed: liver, prostate, mammary, pancreas and thyroid glands, kidneys, etc.
In most specialized oncology clinics and specialized medical centers, ultrasound-guided puncture biopsy is performed using the latest equipment used to visualize manipulations performed on internal organs - Kretz 530 and HP SONOS-5500 ultrasound scanners.
Causes of bleeding and preventive measures
During the procedure, the integrity of the mucous membranes and underlying layers of the cervix is partially disrupted. After the biopsy, there is a period of recovery and healing, which may be accompanied by various adverse reactions and disorders, including bleeding.
The doctor must inform each patient about such consequences of the manipulation, as well as indicate possible more serious complications. During the recovery period after a biopsy, each woman should follow a number of recommendations that will significantly reduce the period of spotting.
These include the following:
- Use sanitary pads, which should be changed every 3 hours.
- Don't douche.
- Do not use tampons.
- Refuse to visit public places such as bathhouses, saunas, swimming pools, and open reservoirs.
- Avoid intense physical activity.
- For the period specified by the doctor, refuse sexual intercourse.
- Do not take medications that contain acetylsalicylic acid, which thins the blood and increases its secretion.
- It is prohibited to use medications in the form of vaginal suppositories and ointments.
Important! You should consult a doctor if you notice any suspicious symptoms.
Important! You should not be afraid of minor bleeding and light spotting after a biopsy in the first 10 days. Excessive bleeding is a dangerous symptom indicating the development of complications.
Preparation for collecting biopsy material using puncture
A puncture biopsy is a fairly informative diagnostic method, but correct results can only be obtained with its help if the patient is properly prepared for the biopsy procedure.
Carrying out a biopsy on each internal organ requires specific preparatory measures, the specifics of which will be announced by a specialist, but there are a number of general rules:
- stopping taking medications that reduce blood clotting;
- abstinence from alcohol 3 days before the procedure;
- correction of the diet with the exclusion of fatty and heavy foods, as well as hot spices and various seasonings, except for herbs.
Worth knowing! When prescribing this procedure, be sure to consult with the specialist who will perform it, and take into account during the preparation process all his recommendations, voiced individually to each specific patient.
Warning and dangerous symptoms, assistance measures
There are a number of manifestations that are a serious signal and indicate the development of biopsy complications.
- blood is released, colored bright scarlet;
- discharge of blood with clots;
- copious discharge;
- persistence of discharge, including light discharge, after a biopsy for 10 days or more;
- temperature rise above 37.5⁰С. During the first 2 days, the temperature can reach 37-37.4⁰C as a normal short-term reaction to minor tissue inflammation. Exceeding these indicators, as well as prolonged hyperthermia, is an alarming signal;
- the appearance of an unpleasant, purulent odor in the discharge indicates the addition of an infection;
- yellow or yellow-green discharge (a symptom of inflammation and infection);
- severe pain in the lower abdomen, which is cramping in nature;
- nausea and vomiting;
- severe weakness;
- headaches, dizziness;
- tachycardia;
- decreased blood pressure;
- menstrual irregularities;
- heavy and prolonged menstruation;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
It is important to understand that self-medication is unacceptable. If you detect at least one of these signs, you should immediately contact a doctor who will prescribe correct and effective treatment.
- wound healing;
- antibacterial;
- enhancing blood clotting;
- restoring the volume of lost plasma (intravenous solutions);
- iron supplements for the treatment and prevention of anemia;
- hemostatic agents;
- antiseptics.
Blood losses, especially massive ones, threaten not only a woman’s health, but also her life. Timely treatment is the key to the patient’s quick recovery.
How is a needle biopsy performed?
As a rule, a diagnostic procedure, the purpose of which is to take samples of soft tissue and fluid from pathologically changed areas of the body through puncture, is performed on an outpatient basis. A puncture biopsy is usually performed under ultrasound guidance, which allows the specialist to visually monitor all his actions, avoid medical errors and prevent the occurrence of possible consequences and serious complications.
Adult patients are usually given local anesthesia, which reduces the sensation of pain when puncturing the skin and soft tissues, while small children undergo this biopsy under general anesthesia. This allows the doctor to perform the necessary manipulations while the child is under the influence of the medication and does not make unexpected movements.
The procedure technique is as follows:
- A point (there may be several) is marked on the skin with a marker in the area of the future puncture.
- Hair is shaved off the skin (if there is any in this area) and disinfection is carried out with an antiseptic, as well as, if necessary, local anesthesia with Lidocaine.
- Under visual control, a biopsy needle is inserted percutaneously and quickly advanced to the abnormal area.
- A certain amount of biological material is collected, after which the doctor removes the needle, stops the bleeding if necessary, and seals the puncture site with a bandage. A bandage is usually not required.
The resulting biopsy is smeared onto a glass slide and sent to the laboratory for further microscopic examination.
How does the procedure work?
Since there are quite a few ways to perform an operation, the doctor’s actions in each of them will be slightly different. Which method to choose is decided in each individual case with each patient individually.
To perform a biopsy, the patient is placed in a regular gynecological chair. General anesthesia is performed in rare cases; as a rule, local anesthesia is most often used, and the patient is always conscious.
The instruments that will be used during the operation depend on how the cervical biopsy is performed, i.e., using what method the material for research will be taken.
First, the doctor inserts a speculum into the vagina. This will allow him to see the cervix, where a bright light is then directed. Using cervical biopsy instruments, the doctor removes suspicious tissue and sends it for testing. The procedure does not take much time: half an hour is usually more than enough. After this, the patient is quietly allowed to go home.
In some cases, a cervical biopsy is performed in the hospital under general anesthesia. Only the doctor can decide whether the patient needs hospitalization. In cases where he determines that it is still needed, his advice is followed unquestioningly. The operation time increases and can be up to one and a half hours. After the biopsy, the patient may be asked to remain in the hospital for observation for 1-2 days.
Deciphering the analysis results requires the specialist to have appropriate training, so only a doctor can do this.
Results of histological and cytological examination of the material
After a needle biopsy is performed, laboratory examination of the biopsy sample takes several days.
The pathologist's response may contain the following information:
- Norm. There are no cells with abnormal changes in the studied material.
- Non-malignant changes. There are altered cellular structures, but there are no signs of malignant degeneration.
- There is an oncological lesion. The material under study contains cells with an altered shape and structure that arise during the process of malignant degeneration.
- Not enough information. The amount of biopsy material submitted for examination was not enough to determine the pathological process, so the procedure must be repeated.
Important! If, as a result of examining tissue taken from internal organs using a puncture type of minimally invasive procedure, pathological signs are discovered, you should not immediately make a terrible diagnosis. Their appearance does not always indicate the development of a serious disease.
When to see a doctor
Discharge is considered pathological and requires medical attention if there is:
- increased pain;
- temperature increase;
- the appearance of pus, scarlet blood;
- increasing the number of discharges;
- signs of anemia: pallor, tachycardia, weakness, changes in blood tests;
- deterioration of general condition;
- discharge of yellow, black or green clots;
- the appearance of smearing red marks after the complete disappearance of all discharge.
These signs indicate the development of infectious or inflammatory complications during the procedure.
What diseases can be detected with a puncture biopsy?
Conducting research is not permissible for all diseases that develop in internal organs; for example, in case of heart pathologies, puncture biopsy sampling is unacceptable.
Using this procedure, the following diseases can be identified:
- benign processes in the mammary gland and other internal organs;
- a number of infectious and inflammatory lesions;
- non-oncological blood pathologies;
- diseases of the spine.
Worth knowing! Often a puncture procedure is prescribed to examine the male reproductive gland, testicle or prostate. But in this case, histological analysis is most often carried out not with the aim of detecting a benign or malignant tumor, but to identify the cause of male infertility or to collect sperm for their further use in an artificial insemination program.
Goals and objectives of biopsy [edit | edit code ]
Biopsy is the most reliable research method if it is necessary to determine the cellular composition of tissue. Taking tissues and then examining them under a microscope makes it possible to determine the exact cellular composition of the material being studied. A biopsy is a test included in the diagnostic minimum for suspected cancer, and is complemented by other research methods, such as X-ray, endoscopic, and immunological.
An essential circumstance determining the need for a biopsy is the need to determine treatment tactics for cancer. Treatment of oncological diseases requires traumatic, often disabling interventions: surgical operations, radiation therapy, administration of toxic chemotherapy drugs, which does not allow starting treatment without reliable confirmation of the diagnosis, which is a histological or cytological examination of biopsies.
For example, for rectal cancer located in the lower sections, a radical treatment method is to perform abdominoperineal rectal extirpation - an operation that involves removing the rectum and forming a colostomy (unnatural anus). If there is no clear certainty in the diagnosis, such an operation cannot be performed. If after the operation it turns out that there was no malignant tumor, the question naturally arises about the need for performing a traumatic intervention. The same goes for breast cancer, stomach cancer, lung cancer and other malignant tumors.
Consequences and care after the procedure
Performing a biopsy using a puncture usually does not cause any complications, but in some cases certain negative consequences may occur:
- the appearance of a large amount of blood at the puncture site due to injury to a blood vessel located in the immediate vicinity;
- development of the inflammatory process due to infection of the wound by bacterial microflora;
- needle damage to the tissue structure of an internal organ;
- deterioration of the patient's general condition.
To avoid any complications, it is necessary to perform this procedure only by a qualified specialist who will carry out all manipulations under the control of medical video equipment. In addition, you should pay close attention to the recovery period. After the procedure is completed and a certain amount of biopsy is sent for further histological or cytological examination, the specialist who performed the puncture will necessarily give the patient a number of recommendations. In each specific case they are different, but basically they come down to a temporary reduction in physical activity and monitoring your well-being.
Possible complications
A cervical biopsy often frightens women with possible complications. They arise due to a violation of the surgical technique, the patient’s condition, or the presence of unidentified contraindications. Such complications may be:
- inflammatory process in the cervix and vagina - occurs with intense pain, pathological discharge, menstrual dysfunction;
- scar formation: extensive tissue removal leads to the formation of scar adhesions on the surface of the cervix;
- cervical orifice stenosis;
- infection of the uterine cavity, endometritis;
- pyometra - accumulation of pus in the uterine cavity due to a violent inflammatory and infectious process;
- bleeding from the wound surface;
- pain syndrome: due to surface trauma, a spasm of the muscle fibers of the uterus and the vessels feeding the epithelium occurs, which is expressed in a moderate pain syndrome.
The most common complications of a biopsy are vaginal discharge due to inflammation or infection and bleeding.
Where can I undergo the procedure, what is its cost and patient reviews?
Despite the fact that a puncture biopsy is considered a fairly simple, minimally invasive operation, the choice of a medical institution for its implementation should be approached very seriously. It is best to perform the procedure in private clinics and public cancer centers that are licensed to perform this procedure.
The price for this test varies depending on the organ on which the biopsy procedure will be performed and the status of the clinic. There are many reviews about this study and they are all unambiguous: the doctor’s performance of the necessary manipulations in each specific case does not cause significant pain and is not accompanied by discomfort.