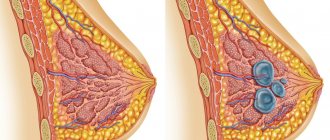
Today, according to statistical studies, about 70% of women suffer from mastopathy. This disease is characterized by pathological changes in breast tissue. The risk of getting sick becomes much higher after 40 years of age. There are several forms of mastopathy, the division into which occurs according to the clinical manifestations of the disease. If proliferative processes (growth) of glandular and connective tissue occur in the patient’s breast tissue, and multiple compactions are formed, a diagnosis of “diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy” is made. Most often, the disease affects the upper parts of the mammary glands. This form of the disease is considered to be the initial stage of the disease.
What it is?
Fibrocystic mastopathy is a violation of the ratio of the connective and epithelial components of breast tissue, accompanied by changes of a proliferative and regressive nature.
It is customary to distinguish two forms of the disease:
- Non-proliferative form. With this form of the disease, cysts of different sizes form inside the breast: from a few millimeters to several centimeters. At the initial stage of development of the disease, the formation of structures resembling bunches of grapes occurs. As the pathology progresses, the process of increased collagen production begins, which leads to the compaction of connective tissue, its proliferation and the formation of scars. As a result, the lobules that represent the mammary gland stretch and cysts form inside them. The non-proliferative form of the disease does not carry a high risk of malignancy of the pathological process. It is no more than 0.86%.
- The proliferative form is characterized by the launch of the proliferation process, that is, the growth of epithelial and connective tissue through cell division. With proliferation of moderate severity, the risk of degeneration of the pathological process into malignant is 2.34%. With a pronounced degree of proliferation, these values increase to 31.4%.
If we look at the statistics of the disease in general, there is a tendency towards an increase in pathology among women all over the world. During reproductive age, the disease affects on average up to 40% of women. If you have a history of multiple gynecological diseases, then the risk of encountering mastopathy ranges from 70 to 98%.
The high-risk group includes women who suffer from hyperplastic pathologies of the genital organs. During menopause, diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy is less common. Up to 20% of women suffer from it. After menopause occurs, new cystic formations most often do not appear. This statistical fact is also further evidence of the direct involvement of hormones in the development of the disease. [adsense1]
Anatomy of the breast
To understand how diseases form and in what places they develop, you need to know the anatomy of the breast. Women's breasts are part of the reproductive function, as they are involved in feeding infants. Accordingly, any disturbances in them are associated with hormonal imbalances or abnormalities in the immune system.
The composition of the mammary gland is as follows:
- Epithelial tissue.
- Adipose tissue.
- Connective tissue.
- Vessels.
At one time or another in a woman’s life, the composition of the breasts will change, depending on functionality. During the reproductive period, there will be such a ratio of tissues to maintain its naturalness, roundness and elasticity. During pregnancy and lactation, there will be more adipose tissue, and the ratio of connective and glandular tissue will change. With the onset of menopause, the mammary gland changes its composition: there is more adipose tissue, connective tissue replaces glandular tissue.
In each period, the breast performs different functions, slightly changing the ratio of tissues. Such changes can provoke violations. If there is a hormonal imbalance in the body, then diseases often arise for which women seek medical help.
go to top
Causes of mastopathy
The main cause of mastopathy is considered to be a hormonal imbalance, consisting in increased production of the hormone estrogen.
Hormonal imbalances can also be caused by the following factors:
- Multiple abortions, the consequence of which is always severe hormonal disruption of the entire endocrine system of the body;
- Gynecological diseases, both inflammatory (endometritis, adnexitis) and tumors (uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, endometriosis);
- No pregnancies before age 30;
- The likelihood of mastopathy increases in the presence of endocrine diseases (thyroid dysfunction, diabetes mellitus), as well as diseases of the liver and biliary tract (hepatitis, cholecystitis, etc.)
- Refusal to breastfeed or its duration is too short (less than 6 months). If a woman breastfeeds her child for more than 6 months, this reduces the risk of developing mastopathy by 2 times.
Other contributing factors:
- Injuries to the mammary glands (impacts, severe compression);
- Psycho-emotional factors (depression, neuroses, stress, chronic fatigue syndrome);
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse, tanning fashion).
Clinically, there are two main forms of mastopathy: diffuse and nodular.
Symptoms
According to experts, the diffuse form of the disease is its initial stage. That is why the symptoms of the disease in some patients are quite blurred, as a result of which women may not pay due attention to their condition for a long time. However, without treatment, the disease progresses.
There are certain signs that allow one to suspect diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy in a patient:
- Swelling of the mammary glands and an increase in their volume.
- Chest pain. It has a dull, aching character and disappears after the onset of menstruation. Over time, the pain becomes more intense and lasting; it can be localized not only in the chest, but also radiate to the arm, shoulder or armpit. In some patients, even a light touch to the affected gland can cause pain. With further development of the disease, the pain becomes less significant.
- Enlarged lymph nodes located in the armpits.
- Loss of sleep, feelings of fear and anxiety.
- The appearance of discharge from the nipples. They can be very different: abundant or scanty, bloody or colorless.
- Changes in the skin of the nipples: cracks, retraction of the nipple or skin.
- The appearance of formations in tissues. They can be either multiple (resembling a bunch of grapes) or single. Such formations do not have clear boundaries and can be found in different places of the mammary glands.
The degree of manifestation of symptoms of diffuse mastopathy depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle: they make themselves felt most strongly in the second half of the cycle, and after the start of the critical days, the symptoms smooth out. For many women in later stages of the disease, pain and lumps remain regardless of the phase of the cycle. [adsense2]
Diffuse mixed mastopathy
The mammary gland is a paired organ. It is located in the area of the anterior chest wall between the ribs. The tissue of the organ consists of lobes and lobules. They are formed by the fusion of glands. The functioning of this organ is controlled by several hormones. These include estrogens, TSH, FSH, progesterone, luteinizing hormone, prolactin, thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy is a chronic disease of the mammary glands in which cysts form and areas of fibrosis appear. All tissues and organs are involved in the process. Otherwise, such mastopathy is called mixed, since it combines the signs of fibroadenomatosis and the cystic form.
This disease is diagnosed mainly in women of childbearing age (30-40 years). The prevalence reaches 40%. Diffuse fibrous mastopathy is often combined with gynecological diseases. One or both glands are involved in the process. The ICD-10 code for this pathology is N60. The danger of the disease lies in the possibility of malignancy. This rarely occurs.
Main risk factors
The development of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy of the mammary glands is based on hormonal imbalance. The reasons are a decrease in the level of progesterone in the blood and an increase in the concentration of estrogen. The latter is involved in the processes of fibrosis, that is, the proliferation of connective tissue. The mixed form of the disease does not occur without the participation of predisposing factors. These include:
- stress;
- insufficient sleep;
- depression;
- aggressiveness;
- ovarian pathology;
- abortions;
- miscarriages;
- inability to breastfeed the baby;
- late menopause;
- strict diet;
- injuries;
- polycystic disease;
- hepatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- hypothyroidism;
- endemic goiter;
- taking certain medications;
- overweight;
- hereditary predisposition;
- lack of regular sex life;
- sexual dissatisfaction;
- absence of pregnancies before the age of 30;
- early puberty;
- presence of bad habits;
- wearing uncomfortable bras;
- myoma;
- infertility;
- lack of ovulation;
- menstrual irregularities;
- endometriosis;
- lack of iodine in the body;
- brain tumors;
- diabetes;
- taking hormones.
Cystic mastopathy can be caused by an unhealthy lifestyle. The level of estrogen and prolactin largely depends on dopamine. This hormone is poorly produced against the background of depression and overwork. The content of prolactin and estrogen in the bloodstream increases, which leads to an increase in the duration of the milk ducts and active cell division.
A sharp change in hormonal levels is observed during abortions and miscarriages. The body is preparing for the birth of the baby. The volume of the mammary glands normally increases. During an abortion, the production of prolactin decreases and estrogen increases. The reverse development of tissues occurs unevenly. This is how cysts form.
Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy often appears against the background of trauma. This may include compression of the glands by clothing and injury. Bilateral mastopathy is often detected in people with thyroid pathology. The reason may also lie in damage to the hypothalamic-pituitary system. It is there that tropic hormones are synthesized. They regulate the functioning of organs, including the mammary gland. Mastopathy develops against the background of pituitary adenoma.
Clinical manifestations of mastopathy
The clinical symptoms of this disease are specific. The following signs are possible:
- breast tenderness;
- nipple discharge;
- presence of seals;
- breast enlargement on one or both sides;
- feeling of fullness;
- edema;
- pain;
- burning;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
The clinical picture consists of symptoms of cystic and fibrous mastopathy. The most common symptom is pain. It has the following features:
- appears before menstruation;
- becomes constant over time;
- dull, aching or twitching;
- varying intensity;
- radiates to the shoulder, axillary region and under the scapula;
- detected in 90% of sick women.
Pain occurs due to swelling and blood stagnation. Signs of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy include discharge. This sign is not permanent. Such women develop whitish or greenish spots on their underwear. Most often, discharge appears when pressure is applied to the nipple.
The presence of blood in the secretion is an ominous symptom. Upon palpation, small foci of compaction are determined throughout the entire thickness of the organ. Soreness is noted. Skin hyperemia, fever and deterioration in general health indicate the addition of a secondary infection. In such people, you can feel the cysts - they are soft, elastic, with clear boundaries, oval in shape, ranging in size from 0.2 to 5-7 cm. A burning sensation may be felt in the area of cyst formation. Their appearance is due to the expansion of the duct and the accumulation of fluid. Over time, a capsule appears. The duct is covered with connective tissue.
Mixed mastopathy and pregnancy
It is necessary to know not only what diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy is, but also how it affects pregnancy. This disease is not dangerous for the unborn child. Pregnancy is recommended for all women with mastopathy, as this leads to changes in hormonal levels and improvement in the functioning of the gland. Breastfeeding the baby is also recommended. This is the main remedy against mixed mastopathy.
During lactation, resorption of cystic formations may occur. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are the main treatment and preventive measures. If a woman was treated for mastopathy with hormonal medications and then became pregnant, therapy should be suspended, since many drugs have a negative effect on the fetus. This disease does not affect the process of conceiving a child.
Why is mastopathy dangerous?
Diffuse fibrocystic pathology (FCM) is a benign process that is characterized by abnormal development of mammary gland tissue. Some types of cells actively multiply (that is, proliferation occurs), others regress - as a result, the ratio of the connective tissue component and the actual active secretory tissue changes.
Despite the declared benignity of fibrocystic changes, mastopathy is a favorable background for the development of malignant oncological diseases, and therefore is classified as a precancerous condition. With active proliferation of cells in the affected gland, the risk of cancer reaches 32%. With less activity of the pathological process, the risk is reduced to 1%, but this indicator cannot be neglected.
The vast majority of cases of diagnosis of fibrocystic pathology occur in women of childbearing age whose mammary glands are active. During perimenopause, significantly fewer such pathologies are observed. Women pay almost no attention to the primary signs of the disease, since they are not expressed by serious pain and are perceived as temporary discomfort. However, with age, the disease progresses and can lead to dangerous consequences.
Forms of fibrous mastopathy
Fibrous mastopathy is called benign breast tumors - diffuse or nodular. In the first case, they are characterized by engorgement of the mammary glands, the appearance of dense areas, foci that do not have clear boundaries - this form is considered the initial stage of the disease. Another name is focal fibrous mastopathy.
In the nodular type of pathology, single or multiple areas of compaction have a contour. Separately, we consider the fibrocystic form of the pathology, which is characterized by the formation of cysts filled with fluid. The fibrocystic type of the disease is prone to degeneration into breast cancer, and therefore requires constant monitoring.
According to the localization of the compactions, the fibrous form of mammary gland mastopathy in women can be bilateral (both mammary glands - left and right) and unilateral. The disease is prone to symmetrical manifestations, as it is a consequence of hormonal disorders. Based on the severity of the pathological process, mild, moderate and pronounced fibroadenomatosis is distinguished. According to which component predominates in the mammary gland, they are classified:
- mastopathy with a predominance of fibrosis;
- mastopathy with a predominance of the glandular component;
- mastopathy with a predominance of cystosis;
- sclerosing adenosis;
- mixed type;
- fibrocystic mastopathy.
Until now, in modern medicine there is no exact classification of mastopathy, and existing descriptive terms and characteristics require improvement.
Diagnostics
Considering the technical capabilities of diagnostic medicine, identifying diffuse cystic mastopathy is not difficult. All middle-aged women must undergo screening or preventive examination. From the age of 35, breast ultrasound is performed once a year; from the age of 40, X-ray mammography is prescribed once a year.
If a woman has signs of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy, then diagnostic testing methods are prescribed by the doctor. Possible options:
- Consultation with an endocrinologist and oncologist.
- Anamnesis collection ─ general data, complaints, family history.
- Breast examination, palpation.
- Examination for gynecological diseases, taking smears.
- Ductography is an X-ray examination of the milk ducts using a contrast agent.
- Ultrasound examination, which evaluates benign and malignant formations with high accuracy.
- Biopsy of a lump or cyst ─ histological examination of the tissues of the formation.
- X-ray mammography is a study with a low radiation dose and minimal stress on the body.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) with contrast.
- Blood tests for hormones: TSH, fT4, LH, FSH, prolactin, estradiol, progesterone.
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
- Microscopic examination of nipple discharge
There is no degeneration of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy into cancer. The danger is that the disease prevents timely recognition of the presence of a malignant process in the breast. [adsen]
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
A set of measures carried out to diagnose FCD allows you to fully examine the woman’s condition and determine the extent of the disease in order to determine methods of treating the disease. This includes the following procedures:
- Ultrasound.
- Mammography.
- Blood analysis.
- A smear of nipple discharge.
- Hormone analysis.
- Puncture.
- Analysis for cell division activity when identifying cysts or formations.
- Ultrasound of the cervix and uterus.
Typically, a woman undergoes examination by a mammologist, gynecologist, dermatologist and endocrinologist. Treatment also involves combining several specialists. All doctors must coordinate treatment so that there are no interruptions, since the endocrinologist will prescribe hormonal treatment, and the mammologist will prescribe vitamins and avoidance of hormonal medications. To prevent such dissonance from occurring, comprehensive treatment is necessary, taking into account the opinions of all specialists.
Since mastopathy is a multifaceted disease, treatment depends entirely on the results obtained during diagnosis. Thus, for the nodular form of FCM, dishormonal treatment belonging to group A is prescribed.
If the blood test does not show an excess in the number of leukocytes, then non-hormonal treatment is prescribed, which the woman can follow at home. She also observes:
- Herbal medicine.
- Intake of red vegetables and fruits.
- Taking nonsteroidal drugs.
- Taking vitamins A, B, C, E.
- Enzyme therapy.
- Taking nutritional supplements.
Acupuncture and immunotherapy are carried out in the hospital. Dimexide and novocaine can also be prescribed. If a woman is being treated at home, she should not miss examinations with a doctor.
Also prescribed:
- Taking diuretics during the premenstrual cycle.
- Taking vitamins.
- Dieting.
- Selecting underwear of the appropriate size.
Hormonal treatment is mainly carried out in order to restore hormones in the blood that disrupt the gynecological and endocrine functions of the body. Abstinence from alcohol and tobacco, black tea and coffee, and table salt is also prescribed.
The duration of treatment can vary from 3 months to six months. This is determined by the severity of the disease, as well as the effectiveness of the treatment prescribed by doctors.
go to top
Treatment
The chosen treatment method for fibrocystic mastopathy depends on the stage of the disease. Basically, it is complex, that is, it is accompanied by taking medications, eliminating diseases that became the precursors of this disease, as well as following a diet and using folk remedies.
Treatment of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy of the mammary glands is carried out using non-hormonal medications.
These include the following:
- Treatment for FCM does not take place without taking vitamin-containing medications. In this case, you will need to take vitamins for a fairly long period of time. Particular attention is paid to vitamins of groups A, B, E and C.
- Preparations that contain a lot of iodine. These are “Iodine-active”, “Iodomarin”, “Klamin”. They help restore normal functioning of the thyroid gland. However, prescribing them to yourself is strictly prohibited.
- In case of severe pain due to breast disease, treatment is carried out using painkillers. For example, Diclofenac.
- Homeopathic remedies will help reduce the production of prolactin. “Mastodinon”, “Remens”, “Cyclodinone” have positive reviews. For the desired effect, it is necessary to take medications for at least six months.
- To reduce nervous tension, the patient may need sedatives and sedatives. Tinctures based on motherwort, valerian and other medicinal plants help very well.
Diffuse fibrotic disease of the mammary glands should include treatment that will be aimed at restoring the functioning of the hypothalamus-pituitary gland-ovaries. Most often, it is recommended to use hormonal drugs for this. These include the following:
- Oral contraceptives "Marvelon" and "Janine". The peculiarity of their reception is strict adherence to the instructions.
- Medicines based on gestagens. These include Utrozhestan, Duphaston, Norethisterone. It is best to take them during the second phase of the menstrual cycle. Otherwise the effect will not be as strong.
- Women over 45 years of age should take androgens. Such drugs include Methyltestosterone, Fareston and Tamoxifen. The duration of treatment is determined individually depending on each case of the disease.
- In advanced cases of the disease, it is advisable to use inhibitors that stimulate the production of prolactin for treatment. This is the drug "Parlodel".
It is advisable to carry out therapy for fibrocystic mastopathy only after a thorough medical examination, which will establish the variety of forms of breast disease. When diagnosing the cystic variety of the disease, it will be necessary to perform puncture and cytological examination of breast tissue. If the presence of a benign tumor is established, surgical intervention may be quite sufficient. [adsense3]
Symptoms of the disease
Clinical manifestations of breast disease depend on the stage. Fibrous mastopathy begins and is asymptomatic. At the initial stage, painful lumps appear before menstruation, when hormonal levels change, at which time an increase in breast volume is possible. After menstruation, the pain goes away.
The first symptoms of fibrous mastopathy can easily be confused with the usual soreness of the mammary glands in the premenstrual stage of the cycle. Over time, the symptoms intensify, swelling, density, swelling of the milk ducts and pain in the chest area are observed more often, and are not cyclical, but constant. In severe cases of the disease, severe pain appears when changing body position or light touch.
During self-examination of the mammary glands, clearly defined areas in the form of nodes or compaction of the mammary gland structure without obvious boundaries are palpated; pressure is often accompanied by a pain symptom. Mastopathy is accompanied by secretion from the nipples. The consistency of the liquid varies, as does the color of the discharge - transparent, greenish, whitish. Symptoms include deterioration of the physical and emotional state during the PMS period, inflammation of the axillary lymph nodes, which is determined independently by palpation.
Treatment with folk remedies
Mastopathy is a disease known since ancient times, so there are a lot of folk recipes. But it is important to remember that this method can only cure the disease in the early stages of its development and taking into account the doctor’s recommendations.
Tinctures. Prepared using herbs that are infused with alcohol. You can prepare them yourself or buy them ready-made at the pharmacy:
- alcohol tincture of boron uterus;
- tincture of pine nut shells;
- propolis tincture.
Decoctions. They help normalize hormonal levels, cope with tumors and get rid of associated inflammatory diseases occurring in the body. The herbs are infused in boiling water and taken orally. For the treatment of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy, it is recommended to drink herbal decoctions:
- burdock root;
- boron uterus;
- red brush to regulate the functioning of the thyroid gland;
- yarrow;
- chagi.
Lotions and compresses. Herbal compresses should be applied to the chest overnight for several weeks to achieve the following results:
- burdock leaf compress;
- cabbage compress with honey;
- flatbread made from rye flour;
- pumpkin compress;
- compress of grated beets and honey.
The use of traditional methods for the treatment of fibrocystic mastopathy should also be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician. Herbal medicine implies the ability to prepare decoctions from several herbs at once or use ready-made mixtures that can be purchased at a pharmacy.
Treatment methods for mastopathy
Treatment of mastopathy is prescribed by the attending physician. Traditional medicine is permissible only with the permission of the attending physician and only as an auxiliary therapy. Treatment methods for mastopathy are usually conservative. Surgical intervention is used for nodular mastopathy, in the presence of cystic formations and intraductal papillomas. Refusal of treatment, as well as self-medication for mastopathy, is dangerous and leads to oncology.
Glandular fibrous mastopathy is the most common form of mastopathy. In terms of severity, it is classified as the mildest. Most often, this disease is diagnosed in girls and young women of childbearing age.
The peculiarity of glandular fibrous mastopathy is its asymptomatic course; the manifestation of the disease is felt several days before the onset of menstruation by soreness in the mammary glands and their engorgement.
With the start of a new cycle, the breasts return to normal. The doctor can detect pain on palpation and some density of breast tissue only immediately before the onset of menstruation, but the rest of the time the breast remains unchanged.
Very often, women attribute such phenomena to periodic ailments and miss the onset of the disease. When the development of fibroglandular mastopathy follows the type of tumor, a movable nodule may form in the mammary gland. It does not cause concern and often goes unnoticed by patients, but is easily identified by a medical specialist upon palpation. Therefore, to identify breast pathologies in the early stages, constant systematic examination by a gynecologist and mammologist is very important.
Treatment of glandular fibrous mastopathy includes:
- symptomatic treatment
- normalization of hormonal levels
- treatment of existing endocrine diseases
- stabilization of the central nervous system
- normalization of liver and kidney function
- elimination of existing genitourinary diseases
- reduction or removal of fibrous formations
Diet
The therapeutic diet should contain products to stabilize hormonal levels. Food should be rich in fiber (greens, grains).
It is important to take natural estrogen (legumes, cabbage of all varieties). Vitamin therapy strengthens the immune system and gives the body strength (citrus fruits, raw vegetables and fruits). Natural iodine is a cure for mastopathy. Eating fish, seafood, liver and sour milk will replenish the body with phospholipids. It is necessary to drink 2 liters of plain water, this will help to quickly restore metabolic processes.
Most often, giving up your usual unhealthy lifestyle helps cure any illness. Fibrocystic mastopathy is easier to prevent, and this requires a timely visit to the doctor. At the initial stage of the disease, it is easier to defeat the disease.
Treatment of fibrocystic mastopathy
To ensure that the symptoms of the disease are relieved, it is advisable to conduct a competent diagnosis and consult a doctor. An integrated approach is used to treat this disease, including changes in diet, the use of comfortable underwear, the use of vitamins, anti-inflammatory and sedatives, and in some cases the use of hormonal and homeopathic medications.
Nutrition correction
It is advisable to completely eliminate products that can affect the formation of fibrous tissue and the appearance of fluid in the structure of the cyst. Doctors often recommend giving up coffee completely and limiting the consumption of tea, chocolate, and sweets. Many experts believe that any pathology of the mammary glands occurs as a secondary phenomenon after the formation of disorders in the intestines. It is advisable to completely eliminate constipation and normalize the bacterial flora.
Visible signs of breast
If you have been diagnosed with mastopathy, it is advisable to eat foods that contain the maximum amount of fiber. Eat vegetables and fruits, greens daily. Drink enough water. Get rid of bad habits, in particular, drinking alcoholic beverages.
On a note! Do not cook foods that are too fatty; it is advisable to completely exclude from your diet foods that can irritate the gastrointestinal tract.
Using the correct underwear
If you suffer from mastopathy, it is advisable to review your entire wardrobe, in particular your underwear. Measure your measurements carefully to avoid purchasing clothes that are uncomfortable. Pay attention to all elements of the underwear, make sure that the clothes do not cause discomfort.
Clinical manifestations of types of mastopathy
Vitamins
Useful microelements are necessary to improve the condition of the immune system, stabilize hormonal levels, and also activate the endocrine system. Experts recommend primarily using vitamins B, A, E for mastopathy. Use the drug Aevit (dosage: 1 capsule per day for 30 days) or Triovit (dosage: 1 capsule per day for 2 months).
Diuretics
If the disease is not treated in time, most patients suffer from edema. They may spread throughout the body. To get rid of negative effects, it is enough to use light diuretics. It is advisable to stop using medications and replace them with special teas based on medicinal herbs.
On a note! You should reduce the amount of salt consumed daily.
Development of mastopathy
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Doctors often advise using Nise , Diclofenac , which allow you to completely get rid of pain. Unpleasant sensations intensify before menstruation. It is advisable to use these drugs if you experience severe discomfort. A course of therapy with nonsteroidal drugs for mastopathy is not provided.
Sedative drugs
Necessary to eliminate psychological stress factors, which allows you to reduce the intensity of the symptoms of the disease in a short time. Use an infusion of valerian or motherwort . You can use special teas. Many people use sage tea . To prepare it, place 1 tsp. chopped herbs in 1/2 tbsp. boiling water, brew, then take 2-3 times a day.
Etiology of fibrocystic mastopathy
Hormone therapy
If a hormonal imbalance occurs in the body, the functioning of the mammary glands without disturbances is impossible. It is necessary to monitor the level of estrogen and progesterone. With mastopathy, the amount of hormones increases, which causes the mammary glands to grow. Medicines necessary to suppress estrogen activity should be used. Doctors often prescribe Toremifene and Tamoxifen .
To suppress the secretion of excessive amounts of hormones, oral contraceptives are used, in particular Marvelon . With their help, you can eliminate the increased production of almost all female hormones and stabilize the functioning of the endocrine system.
Diagnosis of mastopathy
Non-hormonal drugs
To restore the balance of hormones and reduce the intensity of breast growth, Mammolen . The drug is made on a plant basis and is used to increase the amount of female hormones.
Homeopathy
These medications help reduce the amount of prolactin without significant side effects. Doctors usually prescribe Remens , Mastodinon .
Clinical breast study
Iodine preparations
It is used in this case if, together with mastopathy, women suffer from disorders of the thyroid gland. Doctors prescribe them for severe hypothyroidism. If autoimmune mechanisms are activated in the body, these medications are not prescribed. Popular drugs from this group: Iodomarin , Mamoclam .
Surgery
In some cases, drug therapy does not produce the expected effect. A decision is made to perform surgery. Surgery is also mandatory if an oncological tumor develops.
On a note! In order to promptly detect fibrocystic mastopathy, it is advisable to regularly undergo diagnostic examinations and consult a doctor if symptoms of the disease occur.
Fibrocystic mastopathy has a conditionally favorable prognosis. If the disease is not treated, the pathology will progress. It is worth starting therapy as early as possible, since the patient’s condition with this disease worsens upon reaching the age of 30 years. If you carry out proper treatment, you can avoid the occurrence of a cancerous tumor and other complications of mastopathy. The left side in the lower abdomen hurts, study the link. What can hurt in the left lower abdomen, read our article.
Prevention and possible complications
Compliance with preventive measures reduces the risk of the disease and promotes a speedy recovery if it occurs. These include: giving up bad habits, avoiding stressful situations, choosing the right underwear, maintaining an active lifestyle, reducing salt consumption, timely treatment of diseases of the pelvic organs.
It is important to competently select hormonal contraceptives and regularly visit an oncologist and mammologist (at least once a year). Breastfeeding a child for more than 6 months reduces the risk of developing cancer by 2 times.
All women, including healthy ones, need to learn how to check their mammary glands on their own. This advice is especially relevant in the periclimacteric period (after the age of 45). This is done by visually examining the breast in the mirror and feeling it while lying down and standing. If any abnormal lump is detected, you should consult a doctor.
Despite the benign course, fibrocystic changes are a favorable background for the development of malignant diseases. With active proliferation (growth) of affected cells, the risk of cancer is 32%. With less activity of the pathological process, the risk decreases to 1%.