Often diagnoses mycosis of the throat and respiratory organs, which is caused by the mold fungus Aspergillus. When a person becomes ill, he or she is concerned about toxic-allergic manifestations of a chronic course. It is quite difficult to identify the disease on your own, so at the first unpleasant symptoms from the respiratory system you should consult a doctor, undergo laboratory tests and comprehensively treat aspergillosis.
Classification of aspergillosis
Depending on the route of infection by fungi, several types of aspergillosis are distinguished:
- endogenous (autoinfection);
- exogenous (airborne or alimentary transmission);
- transplacental (vertical route of infection);
Aspergillosis also differs in the localization of its pathological processes:
- bronchopulmonary (including pulmonary aspergillosis);
- aspergillosis of ENT organs;
- aspergillosis of the skin, eyes and bones;
- septic, or generalized aspergillosis.
According to statistics, approximately 90 percent of all cases of aspergillosis occur due to primary infection of the respiratory tract, as well as the lungs. About five percent are due to infection of the paranasal sinuses. In addition, involvement of other human organs in the pathological process is diagnosed in almost five percent of people susceptible to infection.
Prevention
Black mold is most often found by residents of old houses or corner apartments in high-rise buildings, so in rooms of this type, inspection of the walls should be carried out as carefully as possible. Aspergillus likes to hide behind loose wallpaper, tiles, and clogged ventilation. At least once every three months, you need to do a general cleaning of the sanitary unit using antibacterial agents and grout.
Do not allow dampness in the basement of the house or the appearance of deposits of rotting vegetables. Wooden shelves and ceilings in damp rooms are unacceptable. If there is a section of the wall in the house that regularly becomes covered with mold, despite all measures, you need to pay attention to the integrity of the wall in this place.
Causes of aspergillosis
The causative agents of aspergillosis in the human body are some types of mold fungi Aspergikkus, which have the names:
- A.flavus;
- A.niger;
- A.clavatus;
- A.nigulans.
Aspergilli, molds, have several properties:
- are aerobes and heterotrophs;
- can grow at temperatures up to 50 degrees Celsius;
- They can be preserved for a long time by freezing and drying.
Under environmental conditions, Aspergillus can spread almost everywhere - in water, air, soil.
The most favorable places for the spread and “prosperity” of the aspergillosis virus are:
- ventilation and shower systems;
- humidifiers and air conditioners;
- old books and things;
- damp walls and ceilings;
- long-stored or spoiled food products and waste;
- agricultural or indoor plants.
In most cases, human infection with Aspergillus occurs through inhalation. In other words, by inhaling dust containing fungal mycelium. Those most at risk of infection are workers in weaving and paper spinning enterprises, agricultural workers, flour millers and pigeon breeders, as pigeons are susceptible to aspergillosis.
A contact route of infection with aspergillosis through damaged skin or mucous membranes is also possible. The route of alimentary infection cannot be ruled out if a person consumes products contaminated with Aspergillus.
Medicine knows cases of auto-infection. Activation of fungi located on the skin, mucous membrane of the respiratory tract or pharynx occurs.
Typical risk factors for aspergillosis include the following:
- immunodeficiency;
- chronic diseases of the respiratory system (tuberculosis, COPD, bronchial asthma, etc.);
- diabetes;
- burns;
- dysbacteriosis;
- use of antibiotics, cytostatics, corticosteroids;
- use of radiation therapy.
Pathogenic effect of Aspergillus spp. per person
The entry point for infection in the vast majority of cases is the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. At first, aspergilli are located superficially, then deepen, causing ulceration of the mucous membrane.
Aspergillosis, site of injury
1) Even a healthy person who inhales a large concentration of Aspergillus spores can develop pneumonia - interstitial pneumonia. A distinctive feature of interstitial pneumonia in aspergillosis is the formation of specific granulomas consisting of giant epithelial cells (the so-called epithelioid cell granulomas). Aspergillus granulomas (aspergilloma) have a spherical shape and are centrally located foci of purulent inflammation, in which there are fungal hyphae, and giant cells along the periphery. The localization sites for aspergilloma are the upper parts of the lungs, which is confirmed by x-ray. Fungi are found in the affected mucous membrane of the bronchi, in the cavities of the lungs, bronchiectasis foci and cysts; in this form the fungi do not penetrate into the lung tissue (non-invasive aspergillosis).
2) In parallel with damage to the respiratory system with aspergillosis, there is a decrease in the immunological reactivity of the body (immunodeficiency). Cases of complications of concomitant diseases of internal organs, mucous membranes and skin are described. An example would be lung abscesses, chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis, lung cancer, tuberculosis, against the background of which a pulmonary form of aspergillosis occurred, which, of course, caused a complication of the main process. Recent decades have shown the incidence of aspergillosis in immunocompromised individuals (HIV-infected, cancer patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy, organ recipients).
3) One of the possible lesions with aspergillosis is damage to internal organs and systems (invasive aspergillosis), which occurs in the vast majority of cases against the background of a significant decrease in immunity. Up to 90% of patients with this lesion have two of three possible features: • the number of granulocytes in the blood is less than 500 cells in 1 μl; • therapy with high doses of glucocorticosteroids; • therapy with cytostatics. In invasive aspergillosis, aspergilloma can form in internal organs. The introduction of fungi occurs hematogenously (through the bloodstream). The lungs are affected first, followed by the pleura, lymph nodes and other internal organs. A peculiarity is the possibility of the formation of abscesses at the site of granulomas in most cases. The nature of the process resembles septic, in which the mortality rate is quite high (up to 50%).
4) Allergic restructuring of the body - fungal antigens are powerful allergens that can cause allergic reactions with predominantly damage to the bronchopulmonary tree.
Symptoms of aspergillosis
Today, one of the most typical forms of infection is pulmonary aspergillosis. Any initial stages of the disease of bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in most cases are disguised as a clinical picture of bronchitis or tracheobronchitis.
Let's define the main first symptoms of aspergillosis:
- restless frequent cough with grayish sputum;
- coughing up blood;
- weakness throughout the body;
- weight loss
If the aspergillosis disease process spreads to the lungs, a pulmonary form of mycosis develops, otherwise called aspergillus pneumonia. If the disease passes into the acute phase, the following signs of deterioration in the body's condition are noted:
- chills;
- cough with copious discharge of purulent mucous sputum;
- chest pain;
- active shortness of breath;
- There is a distinct musty smell when breathing.
Microscopic examination of sputum reveals Aspergillus spores and mycelial colonies.
If we talk about infection of the human respiratory system by fungi, the following types of diseases can contribute to infection:
- pulmonary fibrosis;
- emphysema;
- cyst;
- lung abscess;
- sarcoidosis;
- tuberculosis;
- histoplasmosis;
- hypoplasia;
- pulmonary aspergilloma;
- mycoses.
In case of untimely treatment, a person’s death may occur due to pulmonary hemorrhage or asphyxia.
The next type of infection is aspergillosis of the ENT organs. The disease can occur as:
- external or otitis media;
- rhinitis;
- sinusitis;
- pharyngitis;
- tonsillitis.
In the case of aspergillus otitis, the first thing that occurs is hyperemia, peeling and itching of the external auditory canal. Over time, the ear canal will begin to fill with a loose gray mass containing threads and fungal spores.
Spread of aspergillosis to the eardrum is often observed, accompanied by sharp stabbing pains.
Ocular aspergillosis can take the following forms:
- conjunctivitis;
- ulcerative blepharitis;
- nodular keratitis;
- dacryocystitis, etc.
Possible complications appear in the form of ulcers in the cornea, glaucoma, and loss of vision.
Features of therapy
Drugs
The treatment regimen for each patient is individual.
An early case of detection of aspergillosis is eliminated with the help of medications, which are prescribed to each patient individually and in a special dosage. This is due to the fact that many medications are contraindicated or cause side effects. The duration of drug treatment depends on the type of aspergillosis and its stage. The main groups of medications used for aspergillosis.
- Antifungal drugs that eliminate pathogenic microorganisms and suppress their activity: Vfend;
- "Voriconazole";
- "Amphotericin B";
- "Itraconazole";
- "Fluconazole".
Surgical intervention
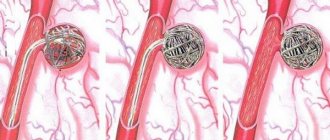
During the operation, damage to the blood vessel is repaired.
If invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is not amenable to drug treatment or has become complicated, then surgical treatment is prescribed. The procedure involves resection of injured internal organs. With correct surgical procedures, the patient does not experience complications. During the procedure, a catheter is passed through the vessel, which reaches the aspergilloma. Then a special substance is injected through this catheter, blocking the vessel, as a result of which the bleeding stops.
The operation is indicated if the patient coughs up a large amount of blood, but the lungs are still functioning.
Diet for aspergillosis
This type of disease requires a special diet. Blue cheeses and other similar foods are strictly contraindicated for the patient. It is necessary to consume fresh berries and fruits in large quantities to strengthen the immune system. Food should be high in calories, but you should not overeat. It is necessary to maintain a drinking regime and avoid starvation.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional therapy will only eliminate the symptoms of the disease for a while.
Aspergillosis in the sinuses and other parts of the body is difficult to treat with folk remedies. Alternative therapy can be used as an auxiliary therapy and after consultation with the attending physician. Some natural components have anti-inflammatory and antifungal effects, and also strengthen the immune system. Healing teas, infusions and decoctions can be prepared from them and taken orally or for treating the skin. The following folk remedies for aspergillosis are distinguished:
- birch leaf;
- flax seeds;
- medicinal lovage;
- wormwood;
- cherry branches.
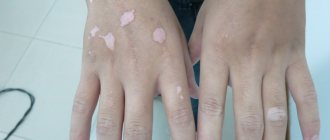
Skin aspergillosis
This form of the disease is characterized by:
- erythema;
- infiltration;
- brown scales;
- itching.
As skin aspergillosis develops, the nail plates may become partially deformed or destroyed, changing their normal pink color to brownish-green or dark yellow. Crushing nails is also quite possible.
Aspergillosis of the gastrointestinal tract can occur in the body under the guise of enterocolitis or erosive gastritis. This type of aspergillosis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- moldy smell from the mouth;
- constant nausea;
- vomit;
- diarrhea.
The generalized form of aspergillosis develops in the case of hematogenous dissemination of bacteria from their primary focus to other organs and tissues. In the case of this form of aspergillosis, the following types of diseases occur:
- aspergillus endocarditis;
- encephalitis;
- meningitis;
- abscess of the brain, liver and kidneys;
- myocardial abscess;
- damage to the bones, ENT organs, and gastrointestinal tract by aspergillosis disease;
- Aspergillus sepsis.
The lethal outcome in the septic form of aspergillosis is very high, so timely and correct treatment of the disease can save the patient from death.
Morphology and physiology of Aspergillus niger
What kind of mushroom is Aspergillus niger? They are able to take root and grow into a colony even at temperatures above +40 0C. The speed at which mushrooms ripen when capturing large territories is simply unique - within three days. The mushrooms darken, acquiring a characteristic dark gray or black color, as the conidia - microscopic formations at the top of the thickened conidial head of the parasitic organism - mature.
The morphology of Aspergillus niger implies several strains of black mold, which chooses premises, food products or even the human body as its habitat.
Diagnosis of aspergillosis
Depending on one or another form of aspergillosis, the patient is referred for consultation to specialists of the appropriate profile:
- pulmonologist;
- otolaryngologist;
- mycologist;
- ophthalmologist.
In the process of treatment and diagnosis of aspergillosis, the greatest attention is paid to professional history, as well as the presence or absence of chronic pulmonary pathologies or immunodeficiency. If bronchopulmonary aspergillosis is suspected, a specialized X-ray of the lungs, bronchoalveolar lavage and bronchoscopy with analysis of collected sputum are performed.
The basis for the correct diagnosis of aspergillosis is a whole range of laboratory tests, and the following components serve as the material for the study:
- sputum;
- water from the bronchi;
- scrapings from nails and smooth skin;
- discharge from the ear canal and sinuses;
- imprints of the surface of the human cornea;
- feces, etc.
In addition, the aspergillosis virus can be detected using a microscope, PCR, culture and serology. It is also possible to conduct medical allergy skin tests.
As practice shows, differential diagnosis of the disease in pulmonary aspergillosis is carried out exclusively in the presence of inflammatory diseases of bacterial or viral etiology. Aspergillosis of the nails and skin is similar to rubromycosis, athlete's foot, syphilis, actinomycosis and tuberculosis.
Treatment
Pharmacological treatment of aspergillosis is based on the use of amphotericin B and voriconazole. In addition, surgical removal of the affected areas is possible.
Regardless of the type of disease, failure to respond to treatment can lead to death.
Complications of aspergillosis can include respiratory failure, bleeding in the lungs, bile duct blockage, and kidney damage.
The information presented in this article is intended for informational purposes only and cannot replace professional advice and qualified medical care. If you have the slightest suspicion that you have this disease, be sure to consult your doctor!
Clinical course
Infection occurs mainly through airborne dust. Additional ways for infection to enter the body are poor-quality food and wounds on the skin. Penetrating into the respiratory system, the fungi actively multiply and form colonies. This leads to the following processes in the body of a sick person:
- development of inflammatory processes;
- penetration of moldy fungi into the mucous membrane, lung tissue and bronchi;
- proliferation of connective tissue in lesions;
- necrosing inflammation;
- internal bleeding;
- accumulation of gases in the area between the lungs and the wall of the chest cavity.
Doctors distinguish several tissue reactions to the penetration of the virus: the proliferation of epithelial tissue of the tuberculoid type, the appearance of scars and pus in various organs, as well as a serous-desquamative reaction. The latter develops against the background of other infectious diseases and weakened immunity.