Cervical ectopia of the cervix: what is it?
Modern medicine uses such definitions as pseudo-erosion, endocervicosis, false erosion to designate the disease ectopia. Ectopic columnar epithelium of the cervix occurs in 40% of women, while more than 11% of all cases are congenital anomalies. Patients of childbearing age are at risk (up to 50% of all cases). A history of ectopia in women increases the risk of the formation of malignant tumors, as well as the development of various inflammations of the vulva.
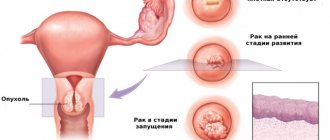
During a gynecological examination without the presence of ectopia, the cervix is covered with squamous epithelium in several layers. Using mirrors and internal examination, the cervical canal, which is covered with columnar epithelium, is revealed. In the presence of cervical ectopia, the photo demonstrates that the line between the epithelia is deformed and moves closer to the outer cavity of the vagina, being located either locally or in a circle, the picture is completely different.
Norm and pathology
Norm
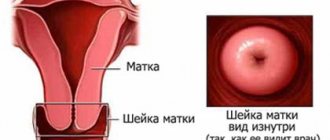
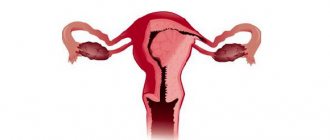
Normally, the inside of the cervix is lined with single-layer columnar epithelium. And the vagina is lined with stratified squamous epithelium. Accordingly, that part of the cervix that protrudes into the vagina is covered with vaginal (stratified squamous) epithelium (see photo).
Pathology
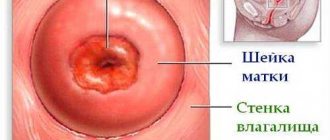
1) If there is an inflammatory process on the part of the cervix protruding into the vagina, then a bleeding defect in the mucous membrane appears and it looks red (see photo). This condition is called true erosion.
Remember: true erosion is always a pathology. And it always needs to be treated.
2) If part of the single-layer columnar epithelium from the inside of the cervix protrudes outward - into the vagina, then upon examination this part also looks red, since the single-layer epithelium is thinner than the multilayered epithelium (see photo). But this place does not bleed, since there is no mucosal defect.
This condition is called ectopia of the cervical epithelium (that is, what I talked about above). Another name is ectropion. Previously, in the USSR this condition was also called pseudo-erosion, or false erosion.
Remember: ectopia is not a pathology, it is a variant of the norm. And most often there is no need to treat it at all.
Classification of cervical ectopia of the cervix
Modern medicine defines several forms of ectopia, both by origin and localization, and by the course of the disease. Ectopia can be either a congenital disease (about 11% of all cases) or acquired. Signs of ectopia may be uncomplicated, which is the norm on an individual basis and does not require treatment; complicated ectopia is often caused by inflammation inside the genital organs, which also involves diseases such as colpitis and cervicitis. These diseases are infectious, their complete cure is necessary first of all. In the future, the prognosis of ectopia may not have any signs and a relapse may occur.
- When the structural and skin elements of the cervix change, as well as when their relationship is dysfunctional, cervical ectopia is ectropion.
- Based on histological characteristics, they are distinguished:
- pseudo-erosion;
- papillary - structural formations of the cylindrical epithelium of the uterus;
- glandular - ectopia with inflammation, abscess of glands with branching is noted.
Scarring during ectopia is accompanied by the transformation and renovation of the epithelium from cylindrical to flat. The process involves additional cells, which, through division, turn into an immature form, and then acquire a mature stage.
With colposcopy, it is possible to differentiate changes in the skin. Under negative conditions, cellular transformation may not have a logical conclusion. In this case, a relapse of ectopia occurs. It is also possible for a retention cyst of the cervix to appear if the pharynx has a skin growth of a metaplastic type.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the pathological condition involves the following methods:
- Carrying out an examination of the patient on a gynecological chair using a system of mirrors, which makes it possible to identify the red focus of the pathological process.
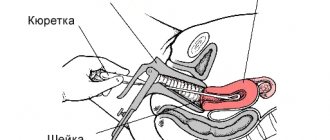
- Carrying out cytology - taking a smear and laboratory examination of the biopath. This will allow you to determine whether the tumor is malignant or benign.
- Colposcopy - using a colposcope, the doctor examines the mucous layer of the uterus and cervical canal.
If the pathological process is complicated by concomitant diseases, or there is a suspicion of oncology, a biopsy is performed.
We recommend reading - antibacterial drug Nolitsin 400 mg: instructions for use, use in gynecology.
Cervicometry of the cervix during pregnancy: what is it and how often should women do it? See the answer here.
Hysteroscopy of the uterus: venerolog-ginekolog.ru/gynecology/diseases/gisteroskopiya.html
Additionally, the doctor may refer the woman for the following studies:
- taking a smear for microflora.
- carrying out bacteriological culture.
- carrying out PCR analysis to detect sexually transmitted infections.
If a menstrual cycle disorder or female type of infertility is diagnosed, the patient is referred to determine the level of hormonal status, as well as an ultrasound scan.
Causes of cervical ectopia of the cervix
Cervical ectopia can develop in conditions of changes in the functional systems of the body, including:
- hormonal disorders;
- inflammatory processes;
- presence of injuries and damage to the genital organs;
- general decrease in immunity due to chronic diseases.
The causes of ectopia of the uterus are diseases of the reproductive system that occur in the patient’s history and which have relapsed. Such diseases include chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, vaginitis, endocervitis. Changes in the microflora of the vagina, a quantitative increase in opportunistic flora due to bacteria such as streptococcus, staphylococcus, E. coli, etc. - all this can lead to the development of ectopia. In addition, vaginal discharge provokes changes in the squamous epithelium of the cervix, where erosion forms. In the future, erosion is differentiated as ectopia.
Injuries and mechanical damage can cause ectopia. Difficult childbirth, surgical termination of pregnancy, douching, insertion of an IUD also increases the risk of pseudo-erosion and the development of the inflammatory process.
Hormonal imbalance in the body is also one of the causes of ectopia. Very often it is a concomitant disease with ovarian dysfunction, endometriosis, fibroma.
A decrease in the immune system and protective properties of the body can develop as a result of diseases such as diabetes and obesity.
The following conditions play an important role:
- early sexual life;
- frequent change of partners;
- unprotected sex;
- multiple births;
- multiple abortions.
All this is fertile ground for the occurrence of pseudo-erosion.
Treatment options
How to treat cervical ectopia depends on the form of the deviation and the extent of the pathological process.
Treatment is prescribed only in case of complicated pathology in order to prevent dangerous consequences. Congenital endocervicitis requires only regular monitoring.
If the disorder is accompanied by infection or an inflammatory process, treatment is aimed at eliminating them. In this case, antibacterial drugs, immunostimulants, hormonal agents and vitamin complexes are prescribed.
If conservative treatment does not have an effect, surgery is prescribed. Today, one of the following methods is used to combat ectopia:
- electrocoagulation. The method is only suitable for cases where a woman no longer plans a pregnancy. During the manipulation, the neck of the affected organ is cauterized with an electric current. As a result, the pathological area dies;
- radio wave surgery. To perform the manipulation, a special instrument is used – Surgitron. The waves penetrate the tissue and provoke the evaporation of the upper layer of the epithelium. No scars remain after exposure;
- cryotherapy. The essence of this method of therapy is the effect of cold on the affected areas. They are treated with liquid nitrogen;
- laser destruction. The laser beam affects only atypical cells and does not capture healthy tissue. This procedure is very effective - a successful outcome is guaranteed in 98-100% of cases.
For several weeks after surgery, precautions should be taken.
In particular, for several weeks you should give up:
- sexual intercourse;
- lifting weights;
- playing sports;
- use of tampons;
- douching.
After these procedures, if symptoms of complications appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of cervical ectopia
Symptoms and manifestation of ectopia are observed in a complicated form. As a rule, it is accompanied by diseases such as dysplasia, leukoplakia, and polyps. There may be a discharge that is whitish or mixed with blood in the presence of colpitis or endocirvicitis.
At the initial stage of a complicated form of ectopia, the patient may complain of changes in the nature and timing of the menstrual cycle, as well as the inability to become pregnant for a long time (1 year).
The uncomplicated form of cervical ectopia of the cervix does not have any special signs. During a gynecological examination, it is easily detected by a specialist.
Symptoms of pseudo-erosion
In the vast majority of cases, the patient is not bothered by any symptoms, especially in the initial stages and if the disease is mild. Pathology can only be detected by examining a gynecologist.
With a complicated form of pseudoerosion, the patient may experience some symptoms:
- The appearance of white spotting discharge.
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse.
- Itching of the genitals.
- Bleeding during or after sexual intercourse.
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
- Difficulties in conceiving a child.
Diagnosis of ectopic columnar epithelium of the cervix
Diagnosis of pseudo-erosion at the initial stage includes a primary gynecological examination by a specialist, thanks to which it is possible to identify the nature of ectopia - congenital or acquired. If the form is congenital and there are no complaints from the patient, further diagnosis and special treatment are not required. In the acquired form, it is necessary to evaluate the previous nature of the columnar epithelium of the cervix and compare it with changes in the vagina at the time of diagnosis.
Diagnostics using gynecological speculum and instruments reveals a violation of the epithelial line, the presence of a red inflammatory focus of the uterus, which can bleed when pressed.
Colposcopy and Schiller tests are mandatory measures to identify ectopia of the columnar epithelium of the cervix. These methods reveal the following indicators of the disease:
- transformation of uterine tissue into new structural compounds;
- the presence of a cylindrical zone of skin and a displacement of the connection line closer to the exit of the uterus;
- leukoplakia;
- punctuation;
- mosaic.
With the listed signs of ectopia, further diagnosis consists of:
- bacteriological culture;
- PCR diagnostics;
- microscopy;
- cytological examination;
- in some cases, a biopsy is indicated.
Additionally, studies of the ovaries are carried out, their functionality and the presence of possible hormonal disorders are determined. If any violations are detected, consultation with a gynecologist-endocrinologist is mandatory.
CAUSES OF CERVICAL EROSION
When a gynecologist tells a woman that she has cervical erosion, usually we are not talking about true erosion, since it exists for a short time (1-3 weeks) and the moment of its appearance is almost impossible to catch, but about cervical ectopia or pseudo-erosion. The most common causes of this cervical disease are:
- Sexual infections, vaginal dysbiosis and inflammatory diseases of the genital area.
- Early onset of sexual activity. The mucous membrane of the female genital organs finally matures by the age of 20-22. If an infection (especially HPV) interferes with this delicate process, the disease can practically not be avoided.
- Traumatic injuries during abortion and childbirth.
- Hormonal imbalances, ovarian dysfunction.
- Reduced protective functions of the immune system.
- Frequent change of sexual partners, aggressive sex, vaginal fisting, BDSM.
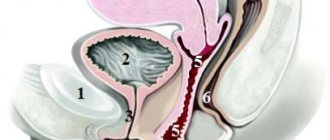
Photo of cervical ectopia: 1 - stratified squamous epithelium; 2 - columnar epithelium; 3 - junction between cylindrical and stratified squamous epithelium.
Pseudo-erosion or ectopia is a pathological lesion of the mucous membrane of the cervix, in which the usual flat stratified epithelium of the outer part of the cervix is replaced by columnar cells from the cervical (cervical) canal. No epithelial defect occurs in this disease. The single-layer epithelium from the canal comes out to the outer part and ends up in a completely different “habitat”. Under the influence of the acidic environment of the vagina and the reasons listed below, epithelial cells begin to grow more or less actively. This is how the lesion progresses.
The reason for the appearance of erosions on the cervix in young or nulliparous girls may be associated with the formation of hormonal levels, at some stages of which there is a risk of developing this pathology. In girls under 18 years of age, the congenital type of the disease is most often observed. In adolescents, disorders are possible due to the early onset of intimate relationships when the mucous membrane of the genital organs is not fully formed and due to hormonal changes and dysfunction of the body.
The main reason for the development of cervical erosion in adulthood is mechanical trauma during childbirth, pathological discharge (leucorrhoea) due to infections, installation of an IUD (intrauterine device), abortion and various hormonal changes.
HOW DOES EROSION APPEAR ON THE NECK?
The trigger for the development of cervical erosion is most often infection. Infection is promoted by various microtraumas, cervical ruptures during childbirth, trauma during abortion, as well as inflammation of the vagina and uterine appendages. The local inflammatory process of the mucous membrane is accompanied by increased secretion, that is, the formation of leucorrhoea. This leads to additional irritation and disruption of the normal structure of the mucous membrane of the cervix. The epithelium disappears, the surface of the mucous membrane is exposed - the so-called. "cervical erosion". She easily “perceives” the infection, and the blood vessels are damaged; a woman may even complain of spotting after sexual intercourse. This is how true erosion occurs.
It is irregular in shape, bright red in color and bleeds when touched. 1-2 weeks after its occurrence, true erosion either disappears or turns into “pseudo-erosion of the cervix” and the defect of stratified squamous epithelium is replaced by columnar epithelium of the cervical canal of the cervix.
Treatment of cervical ectopia
The complicated form of pseudo-erosion has several treatment options, depending on the nature of the identified disorders. Anti-inflammatory drugs must be prescribed. An individual contraceptive program is selected together with a gynecologist-endocrinologist. Hormonal imbalances in the body are also treated.
Treatment of cervical ectopia involves the possibility of undergoing various therapies:
- laser therapy;
- cryotherapy;
- radiosurgery;
- diathermocoagulation, thanks to which the internal inflammatory process of the cervix stops and ectopia recurs.
When diagnosing diseases of the genital organs, further treatment occurs on an individual basis, depending on the specific disease, nature and location.
Uncomplicated ectopia does not require treatment. A patient with a history of this disease should simply be under the supervision of a doctor and follow his recommendations, which should contribute to the regression of the disease. If signs of ectopia are detected, the woman needs to undergo an examination as soon as possible to identify pseudo-erosion of a complicated form.
Cervical ectopia: concept of the problem
Cervical ectopia is a gynecological pathology, which is characterized by displacement of the layer of cylindrical epithelium lining the cervix into the vaginal lumen itself.
Quite often it is called pseudo-erosion, although it has nothing in common with true erosion, since the integrity of the tissues in this case is not violated. Although, on the other hand, the epithelium lining the cervical canal extends to the very outer part of the cervix, and goes beyond physiological norms.
Prevention and prognosis of cervical ectopia
Cervical ectopia of the cervix has a positive prognosis when the disease is detected. The disease is monitored through colposcopy every six months, even in the absence of complaints about health.
Carrying out preventive measures consists of timely diagnosis and further treatment of any diseases that the patient has. Women who have endocrine disorders are at risk; they need constant monitoring by a gynecologist-endocrinologist to monitor the condition of the body and timely identify disorders.
Also, to prevent ectopia, constant examination by a gynecologist is necessary to detect infectious diseases of the genital organs.
Proper management of intimate life, properly selected contraception, avoidance of unwanted pregnancy - all these are the main preventive measures that must be observed.
Is it dangerous to health and life?
Although cervical ectopia can cause a number of unpleasant symptoms (for example, the appearance of discharge or pain), ectopia does not pose a direct threat and does not cause any health-threatening consequences . The only possible complication is the occurrence of an inflammatory process.
The area where ectopia is localized is the most vulnerable, and any infection that gets inside is a provoking factor for the occurrence of cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix). The main symptom of this disease is discharge with a strong unpleasant odor.
If symptoms appear, you should immediately seek help from a specialist. The disease cannot be the cause of cervical cancer. It is also not a cause of infertility.