Cervical erosion is a pathological, but benign process, manifested in the form of rounded red formations localized in the area of the cervical mucosa; the diameter of such formations can reach about two centimeters. Cervical erosion, the symptoms of which manifest themselves in the form of characteristic formations, can exist in several varieties, being congenital erosion, true erosion or pseudo-erosion.
- Description of the disease
- Types of erosion
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
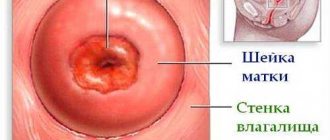
Cervix
The vagina and the uterus, hidden inside the woman’s pelvis, are connected to each other by the cervix. From the vagina one can see her external os, which is normally covered with pink epithelium. There is a canal inside the cervix, and the wall of the organ consists of three layers:
- external;
- muscle, consisting of fibers arranged in a circle;
- inner, epithelial layer.
Each of them has its own purpose. Muscular layer - provides compression and sealing of the cervix, protecting the uterus and its contents from infection and fluids.
The inner layer lining the uterine canal consists of a single layer of cells that have a specific, cylindrical shape. They are colored in a specific red color and form a velvety surface; the purpose of such cells is to secrete mucus, which tightly clogs the cervix. The epithelium covering the cervix from the vaginal side has a different structure. Its cells:
- flat, with dense walls, a core inside;
- arranged in several layers;
- tightly closed.
In the lowest, basic row of cells, located at the border of the muscle and epithelial layers, a continuous process of division of existing cells and the birth of new cells occurs. Layers of “fresh” cells rise, squeezing out the aging ones, ensuring complete renewal of the mucous membrane over a short period of time. This process ensures the healing of large and small damage that occurs on the mucosa during life.
The period of such renewal is individual for each woman and depends on the condition of her body.
In some cases, there is a disruption in the functioning of the layer of cells, they cannot be restored as quickly as necessary to maintain their integrity, and ulcerations appear on the cervix. The base layer of epithelium becomes too thin and weak for infection. Such destruction is defined as cervical erosion.
Types of erosion
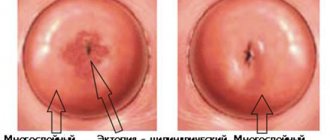
Patients whose doctor has diagnosed the disease are interested in what cervical erosion will look like (photo), erosion, what is it?
Externally, the damage takes the form of scratches or rounded wounds covering the mucous membrane of the cervix, and defects found on the mucous membranes are usually red.
True erosion
Wounds occur in varying depths and sizes. If lesions:
- observed on the upper epithelial layer;
- do not penetrate deep;
- leave the basal layer intact;
- no infection was detected on the mucous membranes and there was no pronounced inflammation;
- with a fairly strong body, they will be able to grow over themselves, the upper layer of the epithelium will be restored.
When pressing on the wound with an instrument, the doctor may observe slight bleeding - this condition is called true erosion. A doctor can rarely see such a lesion - usually defects of this kind heal within 10-14 days.
If the damage is deep, reaching the basal layer of cells or penetrating below, healing can proceed in two ways:
- a scar will form at the site of the damage, which will make the cervix more rigid and prevent it from stretching during childbirth, which may result in its rupture;
- the defect will not be overgrown with flat epithelium, characteristic of the cervix, but with cylindrical, “velvet” epithelium, which normally should not leave the internal canal of the cervix. This epithelium is located in one layer and produces thick mucus, which is not typical for the cervix.
Types of disease
True
This is one of the common gynecological diseases, the causes of which lie in mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the cervix during childbirth, rough sexual intercourse, and abortion. It is observed around the outer or sometimes on the back side of the pharynx, less common on the lip. The disease manifests itself in the form of defects in the mucous membrane and is visually observed as a red spot with clear limited edges, which is located against the background of pink healthy mucosa. Erosion can remain at this stage for 1 to 2 weeks, after which it turns into pseudo-erosion, but the possibility of it developing into oncology is quite low.
Congenital
During intrauterine development of the fetus, congenital erosion of the cervix may occur. Its cause lies in improper differentiation of the uterine epithelium. With this pathology, the mucosal defect looks shiny, smooth, round or irregular in shape, without inflammation. No discharge is observed from the cervical canal. Such erosion usually occurs in teenage girls or young adults and often disappears on its own. But if the disease is discovered during an examination, then it requires mandatory treatment, although its degeneration into oncology is very rare.
Pseudo-erosion
At this stage, a pathological change in the mucosa occurs, in which columnar cells finally replace the usual multilayered squamous epithelium. Progressive, stationary and healing stages of the disease can be distinguished. Progressive pseudo-erosion is characterized by the formation of glandular-type structures and their displacement into the vaginal area. The stationary stage is characterized by the formation of cysts, and the healing stage begins after the inflammation subsides. Pseudo-erosion can exist for several months or even years, and, as a rule, does not go away without treatment. Particular concern is caused by women who have been diagnosed with human papillomavirus, and patients who have an atypical cell structure. In such cases, the risk of cervical cancer increases significantly.
Ectopic cervix
Condition of the cervix after treatment
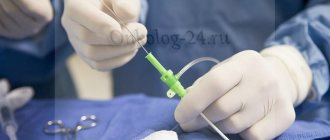
When carrying out conservative treatment, the condition of the mucous membrane can change - its layer is restored or a scar is formed. After removing the inflammatory processes, to accelerate the restoration of the squamous epithelium layer, cauterization of the affected area is used.
After the procedure, epithelial restoration processes are activated - leukocytes and other cells are drawn into the burn area, enhancing regeneration.
At the site of erosion, a crust forms, which falls off within 10-15 days, revealing part of the mucous membrane, which will fully recover within 45-60 days. When using the radio wave method, not a scab, but a thin film appears on the surface of the treated area.
Preparation for cauterization
Despite the fact that a woman is constantly examined by a doctor during treatment of erosion, before undergoing surgical treatment of erosion she must be sent again for:
- analytical blood tests;
- studies to detect sexually transmitted infections, syphilis;
- analysis for hepatitis and HIV;
- biochemical and general clinical blood tests;
- smear examination for pathogenic flora; colposcopy.
Cauterization is carried out only after good test results.
Contraindications to the procedure are the woman’s condition, infection with sexually transmitted infections, systemic diseases in the acute stage.
The main contraindications for cauterization are as follows:
- inflammation of the internal genital organs;
- identification of sexually transmitted infections;
- presence of bleeding or spotting;
- blood count abnormalities;
- diagnosing neoplasms in the internal genital organs and in the erosion zone;
- bearing a child and breastfeeding;
- the period immediately after childbirth;
- diabetes;
- presence of an installed IUD;
- presence of a pacemaker;
- diagnosis of papilloma virus;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- exacerbation of systemic diseases.
Colposcopy
To accurately diagnose the condition of the cervical cells, it is necessary to examine them under magnification. For this, colposcopy is used, a method that involves examining the organ under a microscope (with the possibility of additional lighting) and a mirror.
To ensure a quality examination, the doctor cleans the cervix. To do this, the vagina is treated with a cotton swab moistened with a solution of vinegar or Lugol.
This treatment makes the lesions more contrasty and allows you to better see the erosion of the uterus and what the lesion looks like.
Causes of cervical erosion
The causes of cervical erosion are quite varied. The following come to the fore:
- acute and chronic infectious diseases of the reproductive system. The causative agents of these diseases can be: staphylococci, enterococci , streptococci, ureaplasma, E. coli, gardnerella, mycoplasma, chlamydia. Fungal infections (candidiasis), especially in chronic form, can also cause the development of an erosive process;
- previous exposure to certain chemicals: intimate hygiene products, lubricants;
- traumatic injury to the uterine cervix due to:
- performing gynecological diagnostic, therapeutic and other manipulations - curettage, abortion, childbirth;
- aggressive sexual intercourse.
Provoking factors for the development of the disease
Factors that are not direct etiological causes, but significantly increase the risk of developing pathology, are:
- early intimacy, when the full formation of all cellular structures has not occurred (incomplete maturation of the mucous membrane), and hormonal balance has not been established;
- primary and secondary immunodeficiencies;
- diseases accompanied by hormonal imbalance;
- poor genital hygiene.
Cervical erosion, the causes of which can be both external (trauma) and internal (infections), is most common in those women who are most susceptible to the above predisposing factors.
Causes of the disease
- Mechanical injuries that occur as a result of rough and frequent sexual intercourse, as well as during abortion and childbirth. With physical impact, the stratified squamous epithelium begins to thicken, which leads to the subsequent formation of an inflammatory process.
- Sexually transmitted infections. Among these are the papilloma virus, genital herpes and other diseases.
- Incorrect and untimely treatment of genital tract infections.
- Early onset of sexual activity, late onset of sexual activity.
- Rare sexual contacts, or, conversely, frequent changes of partners.
- Current disturbances in hormonal status, disturbances in the menstrual cycle.
- Changes in the immunological scale (decrease in immunity).
- The presence of inflammatory diseases relevant to the pelvic organs (oophoritis, salpingitis, endometritis, etc.).
- A combination of some of the above reasons.
The occurrence of the disease in elderly patients is possible due to the pressure exerted by the uterine ring. In addition, there is also “physiological” erosion, determined in young women (up to 25 years), which has a tendency to heal independently.
Symptoms of cervical erosion
Signs of cervical erosion can have varying degrees of severity. Some women, regardless of age, do not even suspect that they have this pathology, since clinical symptoms are absent or completely scarce.
Others highlight vivid symptoms characteristic of diseases of the reproductive system.
The clinical symptoms of the disease are based on the following phenomena:
- discharge from the genital tract with impurities of a characteristic brown or yellowish tint, not associated with a specific phase of the cycle (see photo above);
- discomfort, varying degrees of intensity, itching, burning, accompanying the process of urination;
- vaginal dryness;
- pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- liquid, fairly abundant discharge of a green, yellow color with a sharp, rather unpleasant odor, as well as pain over the womb of a pulling nature appear when the cause of erosion is an acute inflammatory process;
- spotting brown discharge outside of menstruation itself, which was not there before, is observed when inflammation spreads to the area of the uterine wall and appendages.
Even if the patient has no symptoms of cervical erosion, but upon examination the doctor discovers a brightly colored spot that is significantly distinguished from the surrounding tissues, then the need for a detailed examination increases significantly.
Effective treatments
In each specific case, the method of erosion therapy is selected by doctors individually. But it is necessary to get rid of the pathology in the first phase of the menstrual cycle (about 6-8 days).
Today there are effective ways to successfully and painlessly treat pathology:
- conservative chemical coagulation (treatment of erosion with special medications that corrode pathological cells);
- cryodestruction (exposure to erosion cells with liquid nitrogen);
- diathermocoagulation (cauterization of pathology with high-frequency currents).
- radio wave treatment;
- cauterization of erosion with laser;
- in some cases, surgical treatment - radical, local intervention, very painful and traumatic for the woman, but in modern medicine this method of treatment is practically not used - it has been replaced by more effective and painless methods.
In folk medicine, there are also recipes and tips for getting rid of cervical erosion, based on the use of medicinal plant components.
NOTE!
The choice of treatment method for erosion must be carried out by a gynecologist, since such diseases are a rather delicate area where you should be extremely attentive and careful.
Classification
Having an idea of what an erosive lesion is, attention should be paid to the types of pathological process. So, depending on the reasons for the appearance and nature, all damage to the mucous membrane of the uterine cervix can be divided into 2 large groups:
- true erosion - violation of the integrity of the normal epithelium;
- pseudo-erosions or ectopia - characterized by abnormal (not necessarily pathological) development of the mucosal epithelium. That is, there is some shift in the border zone between the cells of the epithelium lining the uterine canal (here it is single-layered) and the epithelium that is located on the surface of the vaginal part of the cervix (multilayered). In many cases, ectopia is not dangerous, but is a normal physiological state of women at different age periods of life.
Sometimes you can come across the concept of congenital erosion of the cervix. In this case, we are also talking about ectopia, which does not have a negative effect on a woman’s health.
Among all true erosions, several groups of pathological processes can also be distinguished, the causes of which can also vary from hormonal imbalances to mechanical damage. These include:
- endometriosis - displacement with overlapping of cells of the uterus and cervical canal of different cytological structures;
- ectropion - displacement of the epithelial zone that lines the mucous membrane of the cervical canal into the vaginal cavity. It is a consequence of intense mechanical impact (late abortions, severely complicated labor);
- leukoplakia – hardening of the epithelium in any area of the mucosa;
- polyps and condylomas of viral origin , localized in the area of the cervical canal.
As for pseudo-erosions, they are classified by appearance depending on the type of growth:
- glandular;
- papillary;
- cystic;
- papillary;
- combined.
Signs of cervical erosion may vary depending on its specific subtype and the nature of its location.
How does erosion affect pregnancy?
Cervical erosion is an unpleasant, but still possible and quite common combination with pregnancy.
The period of conceiving and bearing a child in a woman diagnosed with erosion proceeds naturally, but difficulties may be observed during childbirth - the damaged cervix loses its elasticity and ability to stretch, and ruptures easily - this can cause serious bleeding that threatens the life of the mother in labor.
Therefore, most often a pregnant woman is offered not to cauterize, but simply to treat the pathology - a more serious intervention must be carried out after childbirth.
IMPORTANT!
Since erosion causes a defect and damage to the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, thereby creating a natural obstacle to a woman’s pregnancy, this disease becomes one of the most common causes of female infertility.
Diagnostics
Erosion of the vagina or that part of the cervix that is closest to it - diagnoses that a doctor can first make after a manual examination in the mirrors.
However, in order to make a final diagnosis, the gynecologist should not rely only on external signs of cervical erosion and complaints made by the patient.
The diagnostic algorithm for this disease consists of conducting such laboratory and instrumental research methods as:
- examination of a smear taken from the vagina to determine its qualitative and quantitative composition. Not only the type of pathogenic microflora (if present) is determined, but also the approximate quantitative value. In addition, this method allows you to count the number of leukocytes in a smear and roughly determine the degree of inflammation and neglect of the pathological process;
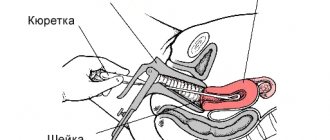
- cytological analysis of material taken from the vagina - analysis of cells taken by scraping from different parts of the mucous membrane. With this study, altered cells can be identified;
- full (extensive) colposcopy - used to identify cells changed by the erosive process, as well as the boundaries of the pathological focus. This method uses special dyes that change color depending on what medium they come into contact with. This is what prompts the doctor to assume a particular diagnosis. During colposcopy, iodine solution and 3% acetic acid are widely used. These solutions cause discomfort and a burning sensation only if they get into areas with a wound surface or ulcers. Colposcopy is a mandatory diagnostic test when determining tumor or inflammatory processes. Uterine erosion is determined using hysteroscopy;
- inoculation of the collected material to identify the causative agent of infection and determine its antibiotic resistance. It is carried out with the aim of prescribing the most rational therapy with a narrow-spectrum antibacterial drug;
- PCR, ELISA and RIF analysis to identify the infectious agent;
- biopsy - taking a biopsy sample (a section of affected tissue) to determine its cellular composition and identify atypical (cancerous) cells;
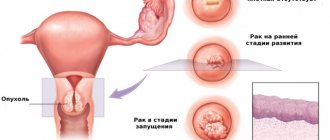
- histology - allows you to evaluate the structure of cells, and if it changes, determine the possible causes of their degeneration, as well as predict the further development of the pathological process.
Purpose of treatment
When diagnosing, the doctor is obliged to determine what led to the occurrence of erosion in the patient and the degree of her aggression. Usually the doctor does not name the type of lesion, does not inform the patient what causes cervical erosion and what treatment methods exist, although this is important for maintaining the woman’s health. Anxiety pushes a woman to independently search for information, leading to unnecessary worries and worries.
A preliminary diagnosis of erosion is made after examining the cervix by a doctor in the speculum. Then the gynecologist takes the obligatory smear and refers the woman to a series of tests. To determine a woman’s condition, the following is carried out:
- colposcopy or magnification studies of the cervical mucosa, as a result of which it is possible to determine the total area of the affected mucosa, the nature of the lesion, and remove a piece of mucosal tissue for histological examination;
- bacteriological culture of a smear to identify pathogenic microflora and fungal infections;
- cystoscopic examination of scrapings from the cervix and its canal;
- establishing the presence of pathogens of viral hepatitis and human papillomavirus in the body;
- determining the presence in a woman’s body of infections transmitted through sexual contact (chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia);
- general clinical and biochemical blood tests.
It is important to identify atypical cells in a smear. By these we mean cellular formations that differ in shape, structure and size from normal cervical epithelial cells. It is believed that such cells arise during an inflammatory process caused by viruses and bacteria, and tumors in tissues.
If the examination does not reveal pathologies transmitted through sexual intercourse, or inflammatory processes as a result of the addition of pathogenic vaginal flora, then no specific treatment is prescribed. The type of erosion does not matter.
The doctor’s wait-and-see attitude in this situation is explained by the fact that if the woman’s reproductive organs are healthy, erosion can drag on on its own, without treatment; unnecessary intervention can disrupt the natural balance of the body.
The doctor periodically examines the woman, monitoring the condition of erosion and conducting a diagnostic smear. Intervention will be required when atypical cells or signs of cervical dysplasia are detected.
If inflammatory changes or ulcers are detected on the surface of the mucous membrane, the doctor determines methods of treating cervical erosion
Treatment of cervical erosion
Treatment of cervical erosion is determined exclusively by a qualified specialist. Methods of influence are individual for each specific patient.
Before prescribing one or another method of exposure, the doctor finds out the causes of the disease. And only after this he decides whether surgical intervention is required in this case or whether conservative methods can be used.
In addition, in most cases, the defective area, the appearance of which is provoked by traumatic damage to the mucous membrane, has a small depth of penetration, goes away on its own and does not require aggressive medication.
Symptoms and treatment of erosion are 2 interrelated concepts. After all, the clinical picture often determines the direction of pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy.
Drug therapy
Conservative treatment of true erosion is based on the use of antibacterial drugs that have a detrimental effect on the isolated microorganism in the presence of infection.
Parallel use of drugs that restore the natural microflora is considered mandatory. These include products containing lacto- and bifidobacteria .
Surgical
Surgical treatment of the erosive process is prescribed within a period of time corresponding to the first week after the end of menstruation. This is because any operation must be carried out in the cleanest conditions possible.
Before carrying out any surgical intervention on the cervix (as on any other organ of the reproductive system), it is necessary to clarify the following: the good quality of the changed area, the presence of concomitant diseases.
The main methods of radical treatment of the disease are:
- Diathermocoagulation is the most effective method that guarantees complete removal of erosion (sometimes after repeated procedures). Its essence is to cauterize the affected area of the mucous membrane with an electric current. The disadvantages of diathermocoagulation are considered to be an aggressive effect on the mucous membrane, leaving behind scar changes, which can subsequently prevent pregnancy and complicate childbirth. The uterine cervix loses physiological elasticity, the risk of rupture increases;
- chemical coagulation - with this method, the eroded area is cauterized with a chemically aggressive substance. Solkovagin is most often used. This type of coagulation is used for small erosions and mainly in nulliparous young women. The disadvantages of the technique are: the lack of a 100% guarantee of complete recovery, as well as a long course of treatment, consisting of several procedures;
- Laser therapy is one of the most popular treatment methods, which is a priority for young women who are planning a pregnancy in the future. The big advantage is the absence of changes (scarring or adhesions) at the site of exposure;
- cryotherapy – removal of erosion by cauterizing it with liquid nitrogen. The manipulation is virtually painless and may cause only mild discomfort. The rehabilitation period lasts 1 month. At this time, the patient should completely avoid sexual contact and physical activity;
- radio wave radiation is the most gentle method of exposure, which does not require direct contact with the organ. In this case, a radio wave is sent to the changed area, which completely evaporates the damaged layer of epithelial cells. The rehabilitation period lasts about 1 month;
- electroexcision – complete excision of the neck with a special electric knife. It is used only if the disease becomes malignant.
Surgical treatment of cervical erosion in nulliparous women of reproductive age should, if possible, be delayed until pregnancy and childbirth.
This is due to the fact that after a radical method of influencing the defect, the risk of developing secondary tubal dysfunction, functional inferiority of the cervix and, as a consequence, infertility increases.
The formation of scars and deformations on the uterine cervix at the site of removal of erosion can also significantly interfere with pregnancy.
In addition, operated erosion of the vagina and cervix can cause premature birth even during pregnancy.
Non-traditional (folk remedies)
Regardless of the cause of cervical erosion, each patient should be prescribed comprehensive treatment. The use of traditional medicine recipes is also possible after prior consultation with a qualified specialist.
Currently, the most widely used means are:
- sea buckthorn oil, with which gauze swabs are moistened and inserted deep into the vagina before bed. Sea buckthorn oil has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect, and also prevents further growth of the damaged area. Use the product for 1-1.5 weeks;
- mumiyo, which is also used to soak tampons and insert them into the genital tract. The course of treatment is 7-10 days;
- mixture of herbs - mix oak bark, Chernobyl grass, birch leaves, chamomile flowers, eucalyptus leaves in equal proportions. 2 tbsp. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over spoons of the crushed mixture, let it brew for 2 hours under the lid, strain thoroughly. Use the resulting infusion for vaginal douching twice a day. The course of treatment is 1-2 weeks.
Diet
As for dietary nutrition for erosion, it is recommended to exclude sweets, flour products, gluten-containing foods, marinades and citrus fruits.
You should enrich your daily diet with foods containing fiber, biokefir, and yoghurts with live lactic acid cultures.
Types of treatment used
Erosion is a lesion that occurs as a result of a combination of a set of factors, therefore modern methods of treating cervical erosion are a set of measures aimed at creating conditions for the healing of lesions. There are:
- conservative therapy:
- surgical treatment methods;
- traditional medicine methods.
Conservative methods
Drug treatment is preferred in case of detection of erosion in nulliparous women; this is the first stage of therapy aimed at eliminating inflammation before the surgical stage of treatment.
To eliminate cervical erosion, treatment is carried out in the following areas:
- elimination of pathogenic microorganisms, normalization of microflora in the vagina, elimination of sexually transmitted infections and sexually transmitted diseases. Antibiotics and antimicrobials are used for this. The course is aimed at completely cleansing the vagina of pathogenic flora, and colonizing the vagina with beneficial microorganisms using a special class of drugs - eubiotics. The drugs are cultures of benign vaginal bacteria and are applied both topically and internally;
- removal of the altered epithelium of the cervix during pseudo-erosion (the affected area is covered with atypical cylindrical cells characteristic of the internal canal of the cervix, such “patching” covers the defect and does not allow the restoration of the correct, multilayered squamous epithelium of this area). Elimination of the “wrong” epithelium is done with the help of special medications that have the property of destroying cells with special substances. Medicines of this type include Solkovagin, Vagotil. It is possible to use hardware to eliminate altered epithelium (cauterization), which use various methods of influencing the mucosa;
- stimulation of lesion healing is carried out after the vagina is cleansed of harmful microflora and the layer of altered epithelium is removed. At this stage of treatment, drugs that improve tissue trophism and wound healing can be used. The standard preparations are Solcoseryl Methyluracil ointment, traditional medicine, used under the supervision of a physician. At this stage of treatment, various suppositories and douching are widely used;
- increasing the immune threshold of the body's protective properties, because it was their decrease that led to the uncontrolled development of pathogenic microflora, the possibility of infection with a number of sexually transmitted diseases, and the rapid restoration of affected tissues. To determine the causes of decreased immunity, the doctor involves a specialized specialist (therapist, endocrinologist, and others). To stimulate the properties of the body, therapy with vitamins, stimulants, traditional medicine, and regulation of lifestyle and nutrition are used. The most important factor for increasing immunity is reducing the stress load on the body and avoiding heavy physical labor.
Drug therapy can last from 14 days to six months, and in 9 out of 10 cases it confirms its effectiveness. The choice of medications and the method of treating erosion are chosen exclusively by the doctor. It is unacceptable for a woman to use any treatment methods on her own, even previously effective ones - after all, the cause of ailments can be the addition of an infection and an inflammatory process.
After the woman's condition has been stabilized, the doctor can move on to the second part of the treatment - cauterization, and determines how long it can take to do it.
Prevention
All preventive measures aimed at preventing diseases of the genital area are based on:
- regular examination by a gynecologist - at least once a year;
- having a regular sexual partner;
- treatment of acute and chronic diseases not only of the reproductive system;
- carrying out immunoprophylaxis in the autumn-spring periods;
- use of protective contraception.
Cervical erosion is not a death sentence, but, like any other disease, it is better to prevent than to treat.
Bloody discharge
As mentioned above, bleeding is the first obvious symptom accompanying the development of pathology.
Bleeding always occurs unexpectedly, for example, in the middle of the menstrual cycle, as well as with any injury to erosion (during an examination by a gynecologist, a woman douching, or during too harsh sexual intercourse).
After one of the treatment methods for cervical erosion (cauterization), light bleeding is a normal reaction.
The patient may bleed moderately for several weeks, as damaged areas of the mucous membrane are restored - such bleeding does not pose a danger to the woman’s health.
CAREFULLY!
Mechanical damage to the resulting scab (the natural protective film along the edges of the wound) can cause quite severe pathological bleeding, which can only be stopped in a hospital setting.
That is why doctors strictly prohibit patients from having sexual intercourse for a certain time after cauterization of erosion and recommend limiting physical activity.
Prognosis for patients
The prognosis for identifying erosion is favorable if it is diagnosed in the early stages of its development and treated in a timely manner.
Erosion is dangerous in women of any age because it is a favorable (provoking) factor for the development of malignancy in this place.
In addition, cystic cavities, scars, and polyps very quickly form at the site of damage, which in the future significantly complicate the possibility of achieving the desired pregnancy.
That is why it is extremely important to treat erosion immediately after identifying the disease.