Causes of the disease
If a cyst is discovered during diagnosis, then identifying the cause of its presence is much more difficult. With acquired character:
- after mechanical impact,
- after injury,
- various lesions and damage to the kidneys and urethra,
- infections.
In approximately 5% of all cases, the cyst can begin to develop in the womb, and also appear in people who have a genetic predisposition.
Recurrent infections of the genitourinary system, tuberculosis, and high blood pressure are factors that can trigger the appearance of tumors in the kidney. The cyst, increasing in size, begins to put pressure on the bladder.
The progressive growth of a cyst can lead to unpleasant consequences - its rupture, as a result of which the contents accumulated in its internal cavity will spill into the human abdominal cavity.
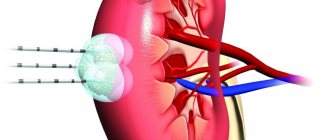
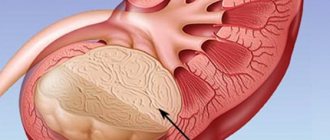
What does renal parenchymal cyst mean? This is a urological disease in which capsules filled with yellow liquid appear in the kidneys. They are diagnosed on the right kidney or on both kidneys at once. This disease affects men over the age of forty, although women are no exception.
Who is at risk?
What is it, a parenchymal cyst of the right kidney is supposedly a urological type of disease. It is characterized by a capsule formation on the kidney filled with yellow liquid. The shape resembles an oval or sphere, often formed only on the right kidney or on both sides of the urinary organ. It mainly occurs in men over 40 years of age. This does not at all exclude the risk of the disease among the female population.
With this pathology, a cavity is formed directly in the kidney tissue (parenchyma), which is filled with serous contents. Hence the name - renal parenchymal cyst. These formations can be either single or multiple.
The cyst can be congenital or acquired. A congenital change in kidney tissue develops due to mutations that cause the fetal renal tubules to fuse together. This happens when a woman drinks alcohol, drugs, or smokes during pregnancy.
Important. Some toxic substances and infections have such a negative effect.
The causes of the acquired type of cyst can be chronic infections of the excretory system, high blood pressure, inflammation of the prostate gland, and kidney stones.
Other causes of neoplasms in the renal parenchyma:
- injuries, blows to the kidneys, other damage;
- hereditary predisposition;
- clogging of the kidney tubules with salt;
- kidney tuberculosis;
- BPH.
Important. Doctors consider chronic pathologies that have not received sufficient treatment to be common causes of renal parenchyma degeneration.
Several factors are involved in the development of pathology. The process of appearance of a parenchyma cyst can be described as follows:
- formation of free space between tissues;
- filling this space with liquid;
- production of collagen by tissues around the cavity, which becomes insoluble, as a result of which the tissues are rejected from the space and take on the shape of a capsule.
Why do cysts occur?
At the moment there is no single point of view on the etiology of the described disease. There are only hypotheses and guesses. Few of them have an evidence base.
One of the powerful factors stimulating the appearance or growth of a cystic neoplasm is the influence of the mother’s health on the developing organs of the fetus. This may be a previous infection, especially a viral one. Alcohol and nicotine-containing products increase the likelihood of developing cysts and other formations in the kidneys.
A significant proportion are cases of genetic predisposition. This applies more to polycystic kidney disease. Parenchymal cystic cavities in this situation damage the kidney tissue to a large extent. There is a recessive and dominant form of pathology. The first of them is usually incompatible with life.
Acquired cysts appear for other reasons.
- inflammatory diseases of the renal parenchyma;
- nonspecific or specific infection;
- urolithiasis disease;
- hypertensive changes in the kidneys;
- inflammatory process in the prostate gland, as well as hyperplasia of its tissue.
For adequate prevention of cystic kidney disease, it is necessary to exclude the above factors. But this is quite difficult to implement today.
Kidney stones can provoke the development of a parenchymal cyst in the kidney
Reasons for appearance and varieties
A large number of tumors and tumor-like formations can develop in the kidney. The latter include cysts.
These are cavity structures that have their own walls. Cystic cavities are usually filled with serous contents.
When complicated, they may contain blood and even pus. Parenchymal cysts are not associated with urinary structures.
Unlike sinus cavities. In this case, they communicate with the urinary elements and may contain urine, including infected urine.
Formations are found both on the right and on the left. But more often they can be detected in the parenchyma of both kidneys. Polycystic disease is a special situation when cysts are located on both sides and their number is more than 4.
Signs of pathology
Most often, the cyst develops in the body completely asymptomatically, so over a long period of time it increases in size and affects the kidneys. The patient, not knowing this fact, will not be able to prevent its development in time.
When the cyst grows and reaches a large size, it will begin to put pressure on the neighboring internal organs, and this fact does not go unnoticed by the patient, as severe pain will appear, which will intensify with increasing loads and playing sports.
There are situations when a person does not suspect that he has a cyst in the parenchyma of the kidney until he undergoes an ultrasound examination of the organ during the examination. The news will be unexpected for him.
However, this can happen if the disease is at the initial stage of development and the cyst does not exceed twenty millimeters. Then it does not manifest symptoms, or they are so weak that the person simply does not notice them. But if the size of the formation exceeds two centimeters, then the following manifestations are possible:
- Frequent urge to empty the bladder.
- Pain in the lumbar region.
- Immediately after sleep, swelling appears.
- Violation of the composition of urine.
- Lethargy and general malaise.
- Insomnia.
However, a parenchymal cyst of the right or left kidney does not always manifest itself with these signs; they can be symptoms of other pathologies.
Often other kidney diseases have the same symptoms. But to know exactly what disease you have, you should undergo an examination.
Usually, there are no special symptoms. Often the patient may not even suspect the presence of such a phenomenon.
At times, a parenchymal cyst of the right kidney (as well as the left) can manifest itself as aching and nagging pain in the kidney area. Accordingly, the area of pain localization will indicate which kidney is affected.
If the pain is on the right side, then it is the right side, and if it is on the left, this indicates damage to the left kidney. With physical activity and sports training, such pain can noticeably intensify.
Naturally, pain will be more pronounced on the side where the tumor is located.
In addition to pain, the patient may be bothered by the following symptoms:
- increased blood pressure;
- hematuria (blood in the urine);
- urinary disturbance.
Clinical manifestations
Taking into account the absence of nociceptors (pain receptors) in the parenchymal mass, the symptoms of the described pathology occur only in three cases.
- Large formations that put pressure on the renal capsule.
- Complicated course - suppuration or hemorrhage into the cavity.
- Reduced pain threshold.
A parenchymal cyst of the right kidney simulates damage to the liver, pancreas, gall bladder or appendix. The patient is experiencing pain in the right lumbar region. It can be different in character. If the parenchymal cyst of the right kidney reaches a large size, the patient complains of dull, constant pain. It does not depend on movement. If the cyst suppurates, a sharp or throbbing pain appears. Sometimes it makes it difficult to move, since any movement, coughing, or sneezing is accompanied by severe pain. As a rule, there is no irradiation.
Symptoms of the disease
The development of a cyst can occur unnoticed by the patient, and the cyst itself is accidentally discovered during examination. When it grows to a large size, the patient begins to feel pain due to its pressure on adjacent organs. The main symptoms of a renal cyst are: pain in the lower back with sudden movements, the appearance of blood when urinating, impaired urine outflow, enlargement of the affected kidney, pain in the bladder area.
When the patient's immunity is weakened, an infection develops, causing inflammation. In this case, all the symptoms of infectious pyelonephritis appear: pain when urinating, general weakness, fever, pain in the lower back and abdomen.
When analyzing urine, red blood cells and casts are detected, and the number of leukocytes increases. If treated incorrectly, the disease progresses to chronic renal failure.
Its characteristic symptoms are frequent urge to urinate, increased blood pressure, and severe thirst. Large formations can compress important renal vessels, leading to necrosis of renal tissue.
Sometimes a person may not suspect anything about the presence of kidney diseases until he decides to undergo an ultrasound of the genitourinary system. What he may find out about completely by accident or also unexpectedly after an annual medical examination at his place of work.
This often happens if the kidney formations are less than 1–2 cm in diameter. In this case, the patient may have no symptoms at all or may appear, but in a mild form. When a cyst formed on the kidney may manifest itself with the following symptoms if it increases in size by more than 20 mm:
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Aching or nagging pain in the lumbar region. Characteristic of subcapsular cavitary renal formations.
- Observation of swelling in the face, arms and legs after waking up.
- Changes in the composition of urine.
- Constant feeling of fatigue, general malaise.
- Symptoms of restless sleep.
If such symptoms are observed, it must be taken into account that they may not always indicate the presence of a parenchymal cyst. Often such ailments can indicate other kidney problems. Which can only be determined using diagnostic techniques.
A renal parenchymal cyst does not have any obvious signs. With a small size of the tumor, a person does not feel discomfort. If a cyst has formed in the right kidney, increases in size, and begins to put pressure on the bladder, then urination may become more frequent. Such neoplasms are accidentally found during an examination for another reason.
The cyst begins to manifest itself with distinct symptoms when its diameter increases to 2 cm. The parenchyma is compressed, the functioning of the organ is disrupted, and there is a malfunction in the functioning of the entire excretory system.
Symptoms of the presence of parenchymal cysts are very mild. The patient may not feel anything and live his normal life. This asymptomatic course of the pathology is observed over a very long time. Cysts are often diagnosed incidentally during an ultrasound examination for another reason.
When the formation begins to rapidly grow and put pressure on the accompanying organs, the patient begins to feel unpleasant manifestations. Renal parenchyma cysts are characterized by the following signs:
- pain in the lower back, intensifying after physical exertion and sudden movements;
- lower blood pressure readings increase;
- there are traces of blood in the urine;
- depending on the side of the lesion, the right or left kidney, circulatory impairment occurs;
- problems with urination;
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- increase in kidney size.
With a weak immune system, infection may occur. In this situation, the patient will experience manifestations of pyelonephritis: loss of strength, frequent urge to go to the toilet, dull regular pain, increased body temperature.
Symptoms
The disease develops slowly over many years. Such a tumor is most often discovered by chance when the patient comes to see a specialist for another reason. Symptoms of parenchymal kidney cysts appear when the formation is large, which is explained by pressure on neighboring organs. May be observed:
- pain in the lumbar region of a pulling and stabbing nature (most often this symptom is observed with a subcapsular cyst);
- high blood pressure;
- problems with urination (pain, frequent urge);
- increased fatigue, weakness;
- blood in urine;
- kidney enlargement.
These signs are not specific, that is, characteristic specifically of a cystic formation. That is why it is necessary to carry out full-fledged instrumental diagnostics.
Diagnostic methods
Before prescribing therapy for a kidney cyst, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis, and for this you should undergo various studies.
If during the procedures it is not possible to obtain the correct answer, then the patient is prescribed additional studies.
Only after them can we talk about the correct diagnosis.
Complaints and anamnestic data do not provide valuable information for making a diagnosis. Moreover, even objective research is uninformative. Intraparenchymal formations are visualized by ultrasound. But the identified structures do not always turn out to be cystic.
Functionalist doctors often wonder: parenchymal cyst of the left or right kidney - what does it look like on ultrasound. It is usually an anechoic or hypoechoic formation. The contours are clear. The structure is often homogeneous.
Even if the ultrasound picture is beyond doubt, further examination should be carried out, especially if the identified structure is large. A tomography is performed.
In controversial situations, puncture of the organ at the location of the cystic cavity is indicated. A pathological examination will determine the nature of the formation.
To do this, check the cellular composition and biochemical parameters of the biopsy sample. The disadvantage of the study is compliance with the conditions (operating room), high price and duration of the procedure.
Another examination method necessary to exclude cancer is to determine the concentration of tumor markers. But you shouldn’t trust this method completely. It has low specificity but high sensitivity.
Diagnosis of cystic formations in the kidneys
Ultrasound examination is a screening method for determining the described pathology in renal tissue. It allows you to evaluate the structure, size and other echographic parameters of the cyst in real time.
What does a cavity formation look like on the screen of an imaging specialist conducting ultrasound diagnostics? It should be anechoic, that is, black in color. A focal formation usually has delineated boundaries; they are quite clear when the formation is benign.
The walls of the cysts should be thin, there may be expansion, but it is uniform. Otherwise, there are reasons to assume the presence of a malignant tumor. Another important echographic feature is dorsally enhanced ultrasound, which evaluates the ratio of the sound density of the cystic formation and adjacent kidney tissue.
A complex cyst acquires an elongated contour. Its shape is usually irregular and deformed. The cavities of the formation are filled with liquid, sometimes heterogeneous contents. There are partitions of varying thicknesses; the formation has several chambers, but at the same time there is a single common wall.
The X-ray image is intended to complement diagnostic procedures in order to finally determine the tactics of patient management and assess the prognosis of the disease. A contrast study will provide additional information about whether there is a connection between the cystic cavity and the pyelocaliceal system of the organ.
With radiography, cysts can be classified according to their location:
There are no special drugs for therapy today. The left kidney cyst, like the right kidney cyst, cannot resolve on its own. Only its growth can stop. The only method of getting rid of cysts today is resection of the formation along with the kidney tissue. The pathology itself is harmless. It just requires careful attention and timely observation.
Treatment methods
A cyst may not require treatment when nothing is bothering you.
If the cyst is “silent”, then observation by a urologist is required at least twice a year.
Considering the specifics of the development and progression of a parenchymal tumor, as well as the fact that medicine cannot give clear answers to the question of what symptoms clearly indicate the disease, a cyst can manifest itself in different forms and progress over many years.
Medicine knows of cases where a parenchymal cyst developed over decades of a person’s life, beginning to grow and show signs of its pathogenic intervention only when the sick person reached adulthood.
Any type of cyst on the kidneys is not a good sign and requires attention. Even the slightest benign formations on the kidneys can eventually develop into large tumors, provoke inflammation, disrupt the functioning of internal organs and transform into malignant cancers. If you don’t know what a parenchymal cyst of the left kidney is, if there is a delay in treatment, the tumor can rupture.
Usually, if the diameter of the cyst is less than 4 cm, treatment is not prescribed. Periodically (once every six months) they do an ultrasound, go to a consultation with a urologist to monitor the rate of growth and development of cysts. Sometimes such dynamics can last for years if the cyst does not grow, or does not grow quickly. In this case, for a normal life, it is enough for the patient to maintain a healthy lifestyle, not to get too cold, protect himself from infections, and watch his diet.
When treating a kidney cyst, patients are given recommendations on proper nutrition:
- Fluid retention in the body is associated with salt consumption. Excess liquid can cause swelling and increased blood pressure, so it is recommended to consume salt in small quantities.
- There should be a minimum amount of protein in the daily menu.
- Since the mechanisms for removing fluid from the body are disrupted, swelling appears, you need to reduce the amount of water you drink.
- It is necessary to remove spicy, fried, alcohol, and strong coffee from the diet.
- Eat at least 5 times a day, in small portions and regularly.
Following a diet is very important, as it makes it easier to restore the functioning of the urinary system and eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
If the cyst size is 6 cm or more, it is necessary to perform a puncture.
The puncture procedure is not long, it takes about 20 minutes. Local anesthesia helps relieve pain.
A needle is inserted into the cavity of the tumor in order to pump out its contents. The fluid removed from the cyst is sent for analysis.
Then a substance is injected that causes a chemical burn to the walls of the cyst (alcohol or iodine). At this time, the doctor sees all his actions on the ultrasound screen.
After such manipulation, primary urine no longer fills the cavity. This helps prevent the cyst from forming again.
With this treatment option, there is a risk of developing fibrosis (seals, scars appear, organ tissues are transformed due to chronic inflammation), the walls of the parenchymal formation and the tissues that are adjacent to it.
If the cyst is large, a drainage is installed through which alcohol is injected into the cavity. This procedure is carried out once a day for three days.
A positive feature of the drainage method is that it is performed outside the hospital and under local anesthesia. However, subsequently the risk of cyst recurrence is about 30%.
After puncture, cysts often appear again due to structural features and location (inflammation, calcification of the walls, formation with numerous chambers, varying thickness).
Another treatment method is conservative. Its essence is to reduce the symptoms of the disease without affecting its course. The patient takes medications that help relieve pain, lower blood pressure, and relieve inflammation. The effectiveness of this method is low.
There are also non-traditional methods for treating parenchymal kidney cysts. Doctors often recommend adding herbal medicine to the main treatment. The effectiveness of medicinal herbs has been confirmed in practice.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor sends the patient for a full examination. The final diagnosis is made taking into account all the symptoms.
A cyst can be identified by palpation, because it leads to an enlargement of the kidney and a change in its structure. A blood test reveals anemia and a decrease in the amount of functional proteins.
When analyzing urine, the presence of leukocytes and erythrocytes in it is revealed, as well as a decrease in its specific gravity. The main method for diagnosing renal cysts is ultrasound.
It is this that allows you to determine the location, size and nature of the neoplasm.
If the presence of malignant cells is suspected, the doctor will prescribe an x-ray examination. With such a study, the cyst manifests itself as a neoplasm that does not have blood vessels. Computed tomography is considered the most modern and reliable diagnostic method.
The uncomplicated course of the disease is not subject to therapy. Urologists and nephrologists insist on dynamic monitoring. An ultrasound examination of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space should be performed every six months.
It is important that the kidneys are examined by the same specialist. When ultrasounds are performed by different people, disagreements can occur. But in both cases, the patient should ask for a film on which the cyst is printed, so that he can then present it to the treating doctor during the next ultrasound examination.
For renal parenchymal cysts, treatment is required only if there is a complication. It is performed by urologists or surgeons. The puncture is simply called igniopuncture. But it is applicable for small cysts without signs of suppuration. When pus accumulates in the cavity, the cyst and part of the kidney are removed (resection). In parallel, systemic antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
Detection of parenchymal cysts should direct the patient to long-term dynamic monitoring of the condition of the kidneys. Every 6 to 12 months, an ultrasound scan of the kidneys is performed so as not to miss signs of developing complications or malignancy (degeneration into a tumor).
If the formation is small (up to 4 cm), treatment is not carried out. Observational tactics are used.
Once every six months the patient undergoes an ultrasound scan and visits a urologist. The growth of cystic neoplasms is monitored.
In some cases, this may take several years. The patient must follow a diet, lead a healthy lifestyle, and avoid hypothermia and infection.
Let us remember - parenchymal cyst of the left kidney, that this is a formation that does not bother the patient with symptoms. You can live your whole life under the supervision of a doctor; this is better than surgery.
The principles of dietary nutrition are quite simple. You should not consume a lot of salt, because it retains fluid in the body and causes edema and high blood pressure. You should also eat less protein foods. To reduce tissue swelling in conditions of poor functioning of the excretory system, you need to drink less fluid.
It is necessary to exclude fried, fatty, spicy foods from the menu. These dishes provoke the consumption of large amounts of liquid. You need to eat at certain times 5 times a day in small portions. By following a diet, it is easier to restore the functioning of the excretory system.
Conservative treatment with drugs includes the use of anti-inflammatory, uroseptic, and antibacterial drugs. The patient must follow the recommendations for prevention to avoid complications and infection of the body.
Timely treatment and removal of parenchyma cysts leads to rapid recovery and preservation of the organ due to the regenerative ability of the parenchyma. If the size of the cyst is no more than 5 cm and it is benign, no intervention is performed.
For regular monitoring of the patient's condition, periodic examination is indicated. Today, surgery is the most optimal solution for treating parenchymal cysts of both the right and left kidneys.
It is best to perform surgery on patients at a young age.
Ultrasound-guided puncture is the most popular treatment method. In this case, using a needle, the contents of the formation are removed, into which a special substance is introduced for gluing surfaces. This is an invasive technique that is accompanied by local anesthesia.
Laparoscopic surgery is a non-invasive innovative method that allows you to completely remove a parenchymal cyst. The surgical technique involves introducing a special substance to expand the surgical field, after which a laparoscope is inserted.
Laparoscopic resection can be performed, that is, removal of the parenchyma cyst along with part of the kidney tissue. After the operation, the patient is prescribed treatment with antibiotics and painkillers.
If necessary, treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed. Sutures are usually removed one week after surgery.
To prevent the occurrence of complications, the patient is shown breathing exercise.
In very severe cases, when tissue necrosis develops, kidney removal or nephrectomy is performed.
Surgery
Indications for operations:
- Lack of results after complex therapy.
- A growing tumor that threatens the patient’s life because kidney function is impaired.
- The appearance of inflammation and pus in the cyst.
- The beginning of the death of kidney tissue.
The operation can be performed in different ways, which are chosen by the doctor. For example, if the cyst does not develop without complications, neighboring organs do not suffer from it, then a puncture can be performed. To do this, the doctor makes a puncture in the skin.
After this, a sclerosing substance is introduced, only this procedure is done using an ultrasound machine.
Such operations include laparoscopy, which is also performed through a puncture in the skin.
However, it should be remembered that these methods are good when the kidney does not undergo any complications. But if the neoplasm threatens the health or life of the patient, then the doctor prescribes removal of the damaged organ or part of it.
wmedik.ru
Medications
Therapy for kidney cysts is carried out with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. All of them help in the treatment of kidney diseases. An intraparenchymal kidney cyst will be eliminated in the same way.
But it is worth noting that all medications, dosages and courses of therapy will be prescribed to the patient only on an individual basis. This choice will depend on the patient's condition during the therapy itself.
Almost always, more attention is paid to preventive measures so that there are no relapses and deterioration in health in the future.
Classification of renal parenchymal cyst
Kidney tissue is represented by a complex structure. Under the influence of certain factors, it can grow, fence off from the renal tubules and transform into a cyst. Parenchymal formations are divided into:
- Intraparenchymal renal cyst - localized in the thickness of the renal structure.
- Peripelvic (sinus) - located in close proximity to the pelvis, but does not communicate with it.
- Cortical - located in the parenchyma layer of the same name.
- Subcapsular - localized under the renal capsule.
- Multilocular – multi-chambered and rare.
Possible complications
The most serious and common theoretical consequence of having a cyst in the kidney is its rupture. Even a small external or internal impact can lead to rupture.
Accompanying this factor is the outflow of the contents of the cyst cavity into the abdominal cavity, which causes the abdominal cavity to become inflamed. Inflammation of the abdominal cavity is a serious condition that requires mandatory surgical intervention.
In addition to rupture of the cyst, its suppuration may also develop. Symptoms manifest as weakness, acute pain in the lumbar region and fever. This condition will also require surgery and subsequent antibacterial treatment.
When the cyst becomes very large, it will begin to compress, which will lead to a change in the vascular structure of the kidney. The functioning of the kidneys will be impaired, and in addition to this, self-poisoning of the body will occur due to renal failure (the blood becomes infected with kidney toxins as a result).
Most often, this variant of the development of the disease is associated with bilateral kidney damage, although it is possible that only one kidney is affected.
The most serious consequence of a cyst can be the transformation of a benign pathology into a malignant one.
A doctor can tell you what a parenchymal cyst of the left or right kidney is, especially if he diagnosed you with such a diagnosis. After this, you need to undergo annual examinations. This should be done in order to detect changes in the cyst in time and begin effective treatment.
If the patient decides not to treat this pathology, then over time suppuration occurs, from which neighboring organs can become infected. Because of this, other complications will appear in the body, for example:
- A disease may occur in which the gradual death of the renal parenchyma occurs.
- Kidney failure will occur.
- The lining of the organ will rupture, causing internal hemorrhage.
All these complications will greatly worsen the patient’s situation. Therefore, doctors advise not to put off visiting a doctor, but to do it as soon as possible. Otherwise, the outcome will be fatal.
If your doctor has diagnosed you with a parenchymal cyst of the left kidney, you must undergo diagnostic procedures every year for preventive purposes. This is necessary in case of detection of changes in the structure of education and timely treatment if necessary.
The point is that such a pathology, if left untreated or improperly treated, can cause suppuration, thereby causing infection of nearby organs. Which can also cause the development of the following complications:
- Provoke renal hydronephrosis.
- Kidney failure.
- Lead to rupture of the membrane of the formation, thereby causing internal hemorrhage of the organ.
Which, in turn, can greatly affect a person’s quality of life. For this reason, you should not delay visiting a doctor and receiving timely treatment. In the worst case scenario, this can be fatal.
How does a cyst form in the left kidney and what are the symptoms of the disease?
A cyst does not form immediately, but over a certain number of stages. First, a void forms between the tissue layers of the kidney. The formed cavity immediately begins to fill with serous fluid. Those tissues that surround the cavity produce insoluble collagen. As a result, the cyst separates from the tissue and turns into a capsule. At subsequent stages, the neoplasm may be complicated by hemorrhage or suppuration. This depends on several factors: the size of the cavity, how close it is to the surface of the organ, whether there are other kidney diseases, and the causes of the cyst.
In congenital cysts, the reasons for their development cannot be identified. And for those purchased they are as follows:
- past illnesses of the kidneys and some other organs: among such diseases, most of them belong to urolithiasis and pyelonephritis; — external factors (injuries, bruises, blows, radiation).
The disease almost always has no symptoms, only in rare cases do some appear that serve as harbingers of the disease, but cannot be diagnosed based on them. For this purpose, a survey is used.
The patient may experience the following symptoms:
- Pain. When the cyst reaches a certain size, in rare cases, pain begins in the place where the tumor is located. But it also happens that the pain is felt in completely different organs: in the spleen, liver, and so on. - Increased blood pressure. If the parenchyma is compressed by the cyst, the patient's blood pressure increases. Parenchymal cysts can be recognized precisely by this indicator. - Temperature. If the cyst is complicated, then the patient’s body temperature rises. - Hematuria. Blood in the urine is observed in case of infection of the cyst.
It is worth knowing that only after a full examination does the doctor refer the patient for treatment.
Nutrition during this period of life
A parenchymal cyst of the right kidney, like any other disease, takes a lot of vitality from a person, and the recovery time after an illness is quite protracted. But in order for the body to recover faster and the kidney to start working at full capacity, it is necessary to adhere to a specially prescribed diet. It will be beneficial for the kidneys and the entire urinary system.
The essence of such a diet is to avoid salt, or it can be consumed, but only in minimal quantities. You should also not eat fried or fatty foods, and exclude protein from your diet. In addition, smoked meats and spices should not be consumed. The patient is also advised to give up bad habits and drinking strong coffee and tea.
It follows from this that for a complete recovery a person needs to balance his daily diet. It should contain only natural and fresh products, as well as fresh vegetables and fruits.
Use legumes with caution because they can cause gas. It can have a detrimental effect on the patient's condition.
For pathologies such as parenchymal kidney cysts, in addition to drug and surgical treatment, the patient should follow a special diet. First, you need to limit your salt intake.
This requirement is especially important for patients with impaired renal function. If the patient has peripheral edema, the amount of fluid consumed should be limited.
If a kidney cyst does not lead to such symptoms, you should not limit the amount of fluid you drink.
In addition to salt, a patient with a kidney cyst is advised to avoid certain other foods. These include: hot seasonings, fatty and fried foods, alcoholic drinks (in particular beer). You need to exclude chocolate, coffee and some seafood from your diet. Smoking has a negative effect on the kidneys.
Patients suffering from kidney disease should limit their intake of heavy protein foods.
Protein breakdown products are especially dangerous for people with parenchymal kidney cysts. Therefore, if a kidney cyst is detected, the patient should reduce the amount of such food consumed to facilitate the functioning of the organ. This will reduce the amount of harmful substances formed in the body, which is especially important in case of kidney failure.
Following a strict diet for kidney and bladder diseases is an essential part of the treatment of these pathologies. But don’t think that you can get rid of a cyst only through diet. In any case, it will have to be combined with medication and even surgical treatment.
prokistu.ru
Prevention and prognosis
The outcome of the disease depends on the size of the formation and the development of complications. If measures to eliminate the pathology are taken on time, the prognosis is favorable. For small cysts that are asymptomatic, the prospects are also comforting. Patients are monitored by nephrologists. When polycystic or multilocular neoplasms are diagnosed, the prognosis worsens, as the likelihood of malignancy and the appearance of renal failure increases. With radical therapy, complications and recurrent episodes are rarely recorded. People who have had an organ removed should follow a special diet and reduce physical activity.
There is no specific prevention of parenchymal cysts. In order to prevent the development of the disease, it is recommended to treat concomitant diseases in a timely manner and undergo periodic examinations.