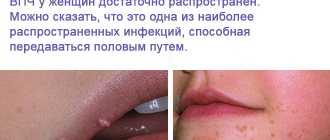
As a rule, even the patient has no idea that the patient has basal cell carcinoma on the nose. For a long time, a tubercle formed on the surface of the skin is perceived as a pimple or boil. The tumor does not bother or hurt. Only after consulting a doctor does it become clear that it is a cancerous tumor that requires appropriate therapy. Early treatment gives a positive prognosis for recovery. Due to the fact that the nose is the most protruding part of the face, a person immediately notices damage to the surface of the skin.
What is basalioma
This disease is cellular skin cancer. Most often, the pathology is located on the face, as well as on the scalp. Very often, a neoplasm can be mistaken for a boil or a pimple, so a person with such a lesion may not immediately see a doctor. But the disease is fraught with many dangers.
Skin basal cell carcinoma develops gradually in the presence of factors contributing to its appearance. The neoplasm looks like a small nodule, which can have different sizes. Pathology can be very dangerous, as it can destroy bone and cartilage tissue.
Types of basal cell carcinoma on the scalp
Below you see a list of types of skin oncology, as well as the main symptoms by which they can be diagnosed:
Flat - a plaque-type defect with clear roll-like edges that are slightly raised above the surface of the rest of the skin;
Nodular - a defect of pink color and round shape, bloody discharge often comes out of it;
Superficial - a pink spot, slightly protruding, with a shiny surface (this is the most benign variety of all listed).
Who most often experiences this problem?
Basal cell carcinoma of the face most often develops in elderly people over 50 years of age. Moreover, the pathology affects almost every second person after 65 years. Naturally, under favorable conditions for the disease, it progresses quickly.
It should also be noted that the pathology most often occurs in residents of the southern regions. Often, those who live in villages or work in the garden for a long time can detect a neoplasm. The fact is that these people are constantly exposed to sunlight. And all those who have very light skin need to be careful. As for men and women, the disease can occur equally often.
Nasal basalioma (causes of occurrence)
The exact cause contributing to the occurrence of malignant neoplasms has not yet been established. Experts suggest that the development of basilioma is facilitated by:
- the presence of similar diseases in relatives (hereditary predisposition);
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- light skin and hair (non-pigmented tissues are less resistant to external influences);
- work with harmful carcinogenic substances - pesticides, amines, arsenic;
- receiving high doses of radiation (including professional radiation from radiologists);
- impaired immune activity due to infection with HIV, hepatitis and other chronic infections.
In some patients, basal cell carcinoma may occur against the background of external well-being, even in the absence of the listed reasons. The individual characteristics of the body and the activity of its defense mechanisms are of great importance in the development of the disease.
Causes of pathology
Skin basal cell carcinoma is a serious disease that is provoked by many factors.
Among the reasons that influence the development of a neoplasm, the following can be identified: 1. Genetic predisposition.
2. Immune system disorders.
3. Excessive exposure to sunlight, radiation, and chemicals.
4. Bad environment.
5. Injuries.
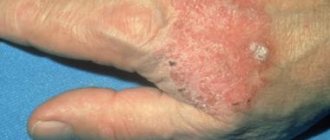
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma, can be located in different areas: on the back, chest, shoulders. However, most often it is located on the face (cheeks, chin, nose).
Causes of the disease
The reasons that cause the development of a malignant neoplasm are not yet known to doctors. Scientists have identified a number of factors that can provoke the formation of basal cell carcinoma. Reasons include:
- Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
- Tanning in a solarium for an extended period.
- In people with fair skin, basal cell carcinoma develops more often.
- Skin prone to sunburn and freckles.
- Interaction with industrial arsenic compounds associated with professional activities.
- Drinking water with high levels of heavy metals and arsenic.
- Exposure to the body of various carcinogenic elements - from soot, bitumen, paraffin wax, tar with resin and other petroleum products.
- Inhalation of substances after combustion of oil shale.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
- A gene disease associated with a mutation of the chromosomal series - albinism.
- The presence of a virus in the body - xeroderma pigmentosum.
- Gorlin-Goltz syndrome.
- Exposure of the skin to ionizing radiation.
- Chemical burns, scars and skin ulcers.
- Old age is considered an important factor in the development of basal cell carcinoma.
- Precancerous diseases - cutaneous horn, leukopenia, actinic keratosis and others.
Doctors recommend treating precancerous formations on the skin - this will prevent the formation of basal cell carcinoma and other dangerous nodules - melanoma or squamous cell skin cancer. Older people should be examined by a dermatologist annually.
Types of tumors and their symptoms
It must be said that the quantity and quality of symptoms depend on what type of pathology you suffer from. At the initial stage, you may notice a small reddish nodule, which is perceived as a pimple. Gradually, the size of the tumor increases, but you do not feel any pain.
As the tumor grows, a thin gray crust appears in its center. If it is removed, a small hole remains on the skin. It soon becomes crusty again. Naturally, over time there are more nodules, and they can merge into one formation.
As for the types of pathology, the following types should be distinguished:
1. Superficial basalioma of the facial skin. It has an oval or round shape and has a pink tint.
2. Ulcerative. It occurs as a result of erosive skin lesions or can appear independently. The affected area resembles an ulcer with high, hard edges.
3. Tumor. They are small nodules that can rise above the surface of the skin. Their surface is mostly smooth.
4. Pigmented. The lesion in this case has a bright shade.
5. Scleroderma-like basal cell carcinoma of the face. It has the shape of a white plaque.
There is also a classification of the disease according to the degree of development. That is, several stages can be distinguished:
- First. A small formation measuring 2 cm or less.
- Second. The size of the tumor exceeds 2 cm, and it can take root through the entire thickness of the skin.
- Third. The sizes may vary, but in this case the formation may already affect all soft tissues.
- Fourth. Here the tumor spreads to the cartilage and bones.
Classification
In the overwhelming majority of cases, patients develop a single lesion, and only five out of a hundred people have several basal cell tumors on the nose. Since the nose is the most protruding part of the face, the tumor appears on it most often. The absence of fatty tissue on the olfactory organ allows basal cell carcinoma to grow rapidly, growing into cartilage and bone tissue. Nasal basalioma is classified according to location, stages of development of oncological pathology and form of the disease.
Localization
With equal frequency, basal cell carcinoma can form on:
- bridge of the nose;
- tip of the nose;
- back of the nose;
- areas around the nostrils;
- nasal wings.
The neoplasm does not have a capsule or shell, so it very easily invades the surrounding tissues both in depth and in width.
Forms of the disease
In order to determine the morphological structure and shape of basal cell carcinoma, doctors perform a biopsy and histological examination.
In medical practice, there are the following types of basal cell tumors of the nose:
- Nodular-ulcerative basalioma is the most common. It is pink in color and round in shape. The tumor can bleed easily if touched. At the initial stage, the tumor is no more than 0.5 centimeters in size; in the center of the tumor there is a depression that can be covered with a crust. When the crust is removed, a bleeding abrasion is visible. As the tumor grows, it acquires a lobular structure. Basalioma is covered with a thin transparent skin, through which the capillaries that feed it are visible. The density of nodular basalioma is similar to cartilage. This type of tumor often becomes infected.
- Sclerodermal basal cell carcinoma of the skin of the nose appears as a white dense spot. Such basalioma can have different development, from sluggish to extremely aggressive and rapid.
- The warty form of basalioma consists of many nodules of dense consistency, which in appearance resemble a cauliflower inflorescence. The tumor rises above the skin and is lighter in color than healthy tissue. There is no vascular pattern on such a formation.
- The pigmented type of basal cell carcinoma is distinguished by its bright color and an ulcer in the center. The neoplasm has an edging of any shade, from flesh-colored to blue-black.
- Flat basalioma is a plaque that does not differ in color from the surrounding skin. The edges of the neoplasm are raised and have a pearlescent ridge. This type of basal cell carcinoma does not bleed or ulcerate, but it is very aggressive and can grow into deeper layers in a short period of time.
- The superficial type of basal cell carcinoma is the most benign. This tumor looks like a pink spot with a rim raised above healthy tissue. Some people may confuse such a neoplasm with eczema, which does not have a rim, which distinguishes these formations from each other. Often, superficial basalioma is multiple in nature, almost does not grow into the depths of the tissue, and grows extremely slowly in width.
We recommend reading Osteoid osteoma - causes, types, treatment
The treatment chosen is the same, regardless of the form of cancer of the basal layer of the skin of the nose.
Stages
Due to the fact that the development of the tumor is not accompanied by metastasis, the staging is determined based on the depth of germination into the underlying tissues, their destruction and the width of the superficial lesion. Like other cancers, nasal basal cell carcinoma is divided into four stages:
- At the first stage, the tumor looks like a small elevation of pale pink color, or a red nodule ranging in size from one millimeter to a centimeter. At this stage, basal cell carcinoma does not yet extend beyond the dermis. In appearance, the formation can be similar to either a blister or an abrasion, depending on the type. After some time, liquid begins to ooze from the basalioma, and its surface becomes covered with a crust. If the crust is removed, the tumor bleeds. Stage one basal cell carcinoma does not cause pain or any discomfort.
- The second stage is characterized by the growth of the tumor through all layers of the skin, but the tumor does not yet reach the subcutaneous fat. At this stage, a single shiny node up to two centimeters in diameter is formed, through the surface of which capillaries are visible. Sometimes multiple lesions also occur, when the neoplasms begin to gradually merge, forming a lobular shiny plaque. In the center of such a formation, in the second stage, tissue begins to gradually deteriorate.
- Stage three basal cell carcinoma measures more than two centimeters and has already grown through all layers to the bone tissue. The tumor enlarges and becomes dense, the color of the tumor is rich, red, the vessels are dilated and clearly visible. The tumor often ulcerates. After some time, a rim appears around the formation, and later a full-fledged cushion. In the center of the basal cell carcinoma, tissue decomposes, forming an erosion or ulcer with a crust on top. Compression of nerve endings leads to loss of sensitivity in the area of basal cell carcinoma.
- During the fourth stage, a deep ulcer forms. At this stage, basal cell carcinoma can grow into the bone, extending into the head. The node with the ulcer is very dense, inelastic, immobile when stretched.
In the early stages, basal cell carcinoma in the nasal area responds well to treatment in various ways, of which there are many, so if a neoplasm occurs, it is necessary to visit a doctor as soon as possible.
Diagnostic features
If you have discovered such a formation, try not to delay visiting a doctor. First, he will conduct an external examination of the tumor. Moreover, it is also necessary to examine all visible mucous membranes and skin. The specialist will also examine all lymph nodes. Basalioma of the skin of the nose or other areas is examined using a magnifying glass.
In addition to the external examination, you will also have to undergo some tests. For example, a histological examination of the neoplasm is necessary. To do this, make a scraping and a smear-imprint. Naturally, a piece of the material taken must be sent for biopsy. In addition, the specialist must perform an ultrasound examination of the tumor. This diagnostic method helps to find out how deep the roots of the tumor have spread, as well as how much tissue will have to be removed due to surgery.
Features of traditional treatment
It should be noted that nasal skin basal cell carcinoma should be treated only under the supervision of an experienced specialist. However, there are a lot of folk recipes that will help you eliminate this unpleasant and dangerous pathology. Naturally, you should consult your oncologist. So, among the most effective means are the following:
1. Ointment made from celandine and burdock. In order to prepare it, you need to take a quarter cup of raw materials, pour hot pork fat into it and leave in the oven for two hours. At the same time, the fire should be low so that this mixture does not boil, but simmers. Next, you need to strain the product, pour it into a glass jar and leave it at room temperature for several days. Apply to the damaged area of skin three times a day.
2. Fresh juice or decoction of celandine. In the first case, you need to use an orange liquid. To prepare the decoction, brew finely chopped leaves of the plant (1 teaspoon per glass of boiling water). You need to take the substance 3 times a day (one-third of a glass). Please note that you will have to prepare such a decoction every day, as it quickly loses its healing properties.
3. To eliminate the tumor, you can use a golden mustache. To do this, apply a cotton swab moistened with plant juice to the affected area.
Traditional recipes (4 options)
Many folk remedies are suitable for treating basal cell carcinoma of the face. They should not be applied to bleeding plaques to prevent germs from entering.
Before using traditional recipes, you should consult with your doctor, as they can only be auxiliary methods of combating the problem.
Properties of carrots
The fresh vegetable is grated and applied to the neoplasm as a compress. Along with this, you should drink a glass of carrot juice at least 2 times a day.
Celandine to the rescue
The surface of the nodule is lubricated with the juice of the plant every day. Along with external use, celandine tincture is used internally.
To prepare it, you need to dry the flowers of the plant, pour boiling water over 1 spoon of plant material and take 50 ml per day.
Tobacco tincture
50 g of tobacco is poured into 1 glass of vodka, placed in the refrigerator for 14 days, the composition is shaken daily.
After 2 weeks, the infusion is filtered. A piece of cotton wool is soaked in the medicine, pressed against the plaque and secured with a band-aid. Treatment lasts 10 days.
Yeast Help
The product is diluted with warm water. After this, a piece of gauze is soaked in the solution and applied to the tumor for 2–3 hours. The procedure is repeated every day.
Complete treatment of the disease often guarantees complete healing. Self-therapy and traditional medicine without consultation with specialists can lead to serious negative consequences and complications. In general, the prognosis for patients is favorable.
Operation
Skin basal cell carcinoma, which must be treated comprehensively, can be removed using radical methods. For example, surgery. Naturally, everything here depends on the degree of neglect of the pathology and damage to soft and hard tissues. There are also contraindications to surgery: severe infection, intolerance to medications used for anesthesia, as well as poor general condition of the body.
It should be noted that surgical intervention is by far the most effective. However, it has a certain disadvantage: a long recovery period, as well as a poor aesthetic effect (presence of scars). It must be said that it is undesirable to perform such an operation on the face.
Excision of the tumor must be done within healthy skin, retreating from its edge by 1-2 cm. Next, a histological examination of the skin is carried out to exclude further spread of the pathology.
Stages of disease development
The disease is divided into five stages during its development:
- Stage zero is characterized by the formation of a cancer cell in the body, but without signs of nevus formation.
- At stage 1, a superficial spot up to 20 mm develops.
- At stage 2, the nevus begins to grow to 50 mm.
- Stage 3 is characterized by growth into the depths of the dermis and ulceration on the surface.
- Stage 4 is determined by the large size of the tumor, the presence of multiple ulcerations and destruction of the bone structure.
Also, doctors sometimes use another classification:
- The initial stage (t1n0m0) is similar in characteristics to the zero and first stages - this means that the tumor does not exceed 20 mm without the presence of ulcerations.
- Advanced stage (t2n0m0) – there are initial signs of ulceration formation, the dimensions do not exceed 50 mm.
- The terminal stage is characterized by large sizes and deep penetration into the skin.
Features of laser and radiation therapy
Basalioma of the skin of the nose, which in most cases cannot be treated with a scalpel, can be removed using more modern methods. For example, laser therapy has proven itself well, which allows you to get rid of tumors quickly and effectively, without leaving scars on the skin, and the recovery period is noticeably reduced.
It should be noted that the procedure is performed under sterile conditions, without the touch of the surgeon’s hands. And the likelihood of relapse after such an operation is extremely low. However, such removal will be most effective if the tumor is small in size. It should also be noted that this treatment is not indicated for everyone. For example, a laser cannot be used if the patient has other skin pathologies, chronic, cardiovascular, infectious diseases.
As for radiation therapy, it is also quite effective, but not everyone can tolerate it well. For example, the skin may react poorly to radiation. In addition, this method can provoke a lot of complications.
Treatment of primary basal cell carcinoma and relapse
Despite the fact that the disease is classified as malignant, the prognosis in most cases is favorable if the patient promptly seeks help from an oncologist. The treatment method is selected individually in accordance with the clinical picture (type and size of basal cell carcinoma). The age of the patient, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies, is also of great importance. Treatment methods for primary basal cell carcinoma and relapse may differ.
Surgical intervention and rehabilitation after surgery
The most common and fairly effective method of treating basal cell carcinoma is surgical removal of the tumor. If its size is small, the operation is performed under local anesthesia. The specialist performs the excision, affecting 5 mm of healthy tissue around the tumor, which significantly reduces the chances of relapse.
Often surgery is performed using a dermatoscope. Thanks to this equipment, the doctor sees the exact size of the tumor. This allows for proper removal.
Mohs microsurgery is a fairly effective method of treating basal cell carcinoma. The essence of the procedure is sequential cavity cutting of the tumor. The oncologist immediately examines the taken material under a microscope. If malignant cells are present in the tissues, the manipulation is repeated. The indication for such an operation is the initial stage of basal cell carcinoma with a high risk of relapse.
Surgery is the most effective way to treat basal cell carcinoma
After surgery there is a rehabilitation period.
- To reduce postoperative swelling, a cold compress is placed on the affected area.
- Over the next few days, a tight bandage is applied to the wound surface.
- Antiseptic treatment is carried out daily.
Depending on the type of operation and the extent of the lesion, the patient remains in the hospital from 5 to 10 days.
Unfortunately, surgical treatment methods have their contraindications. These include:
- diabetes;
- intolerance to anesthetics;
- inability to completely remove the tumor due to its special location (periorbital region, ears).
A fairly effective method for removing flat basal cell carcinoma at the initial stage is cryodestruction. Thanks to the use of liquid nitrogen, the procedure is quick and painless. However, the risk of relapse remains high.
The procedure for removing basal cell carcinoma with liquid nitrogen (Elena Malysheva about the treatment of basal cell carcinoma - video cryodestruction) leaves virtually no scars behind.
Laser removal of basal cell carcinoma
A popular method of treating basal cell carcinoma in the initial stages of its development is removal of the tumor using a laser. This technique began to be widely used relatively recently. It has a number of advantages, including:
- absence of blood during the intervention;
- complete sterility;
- good cosmetic effect;
- short rehabilitation period;
- non-contact (the tool does not come into contact with the skin).
Using a laser you can remove small basal cell carcinomas
The method is especially effective if the tumor is located in a hard-to-reach place (corner of the eye, ear). The body of the neoplasm is removed without damaging healthy tissue. The wound surface is immediately cauterized. The advantage is that the patient does not need to undergo special preparation before surgery. Removal can be performed on an outpatient basis with preliminary local anesthesia. If the affected area is not extensive, there is no need for hospitalization.
Radiation therapy
This technique is used independently or after surgery, if it was not possible to completely remove the malignant neoplasm or the oncologist suspects the development of a relapse.
Irradiation is harmful to both malignant and healthy cells, as it affects DNA. Therefore, when carrying out radiation therapy, there is always a risk of developing new cancer foci after a few years.
As a rule, close-focus radiation therapy is used for basal cell carcinoma. The number and frequency of procedures depend on the form of the disease and its stage. In most cases, one manipulation every three days for a month is enough. The treatment is painless. One session lasts 10–15 minutes.
Radiation therapy is another method of treating basal cell carcinoma.
Even with the right technique, there is a possible risk of complications. Often, burns or signs of radiation dermatitis appear in the area of exposure. The unpleasant consequences of treatment disappear after completion of the course of therapy.
To speed up the process of epidermal restoration, the doctor may prescribe corticosteroid ointments.
Throughout the treatment, the patient should avoid exposing the area to direct sunlight, as well as friction. It is recommended to apply sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15 to irradiated facial skin.
Photodynamic therapy
The technique shows high efficiency in removing small tumors. The essence of photodynamic therapy is the use of special drugs - photosensitizers. They are administered to the patient intravenously. Three days later, the tumor is irradiated using a laser. As a result, malignant cells are destroyed and basal cell carcinoma disappears.
The advantage of the technique is that healthy cells remain undamaged under the influence of the laser. Therefore, the rehabilitation process after treatment is significantly accelerated.
Drug therapy for basal cell carcinoma of the face
Treatment of skin cancer in the early stages can be carried out using the following groups of drugs:
- Medicines for chemotherapy (Fluorouracil, Gleevec, Radachlorin, Alkeran). In most cases, topical medications are used.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments. Good results are shown by drugs from the group of corticosteroids, such as Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone.
- Immunostimulating medications. Ipilimumab is often prescribed for skin cancer.
In most cases, drug therapy is carried out in combination with radical treatment (irradiation, surgical removal of the tumor, etc.).
Drugs used for basal cell carcinoma of the face - gallery
Gleevec is a drug for chemotherapy
Prednisolone - corticosteroid ointment
Ipilimumab is an immunostimulating drug
Alkeran is a local medication
Traditional methods of treating basal cell carcinoma
It is impossible to get rid of a malignant tumor using traditional medicine recipes alone. Moreover, any therapy without prior consultation with an oncologist can lead to serious complications (including death). However, some drugs show high effectiveness at the initial stage of the disease or help speed up the process of tissue restoration in the postoperative period.
Burdock root ointment
To prepare the remedy you need:
- Pour 100 g of raw material (burdock root) into 100 ml of water and cook for 20 minutes.
- Remove the root and add 10 ml of vegetable oil to the resulting decoction.
- Mix thoroughly and cook for another hour and a half over low heat.
The result is a viscous mass, which should be used to treat damaged areas twice a day.
It is also useful to lubricate the basalioma with freshly squeezed burdock root juice.
Carrot
The product is considered a real storehouse of vitamins. It is recommended to grate the carrots on a fine grater. The resulting pulp should be applied to the tumor for 10 minutes 4 times a day.
Celandine
A teaspoon of crushed leaves is poured into a glass of boiling water and simmered over low heat for 15 minutes. The finished product is taken orally, a tablespoon three times a day. The medicine should be stored in the refrigerator for no more than three days.
Herbal collection
To prepare the medicine you will need the following ingredients:
- 20 g birch buds;
- 20 g of meadow clover inflorescences;
- 20 g celandine;
- 20 g burdock;
- 1 tbsp. l. finely chopped onions;
- 150 g olive oil;
- 10 g pine resin.
- The onion is fried in vegetable oil until golden brown.
- Then the vegetable is removed, and the oil is mixed with resin and kept on low heat for a few more minutes.
- The herbal mixture is added to the composition, everything is thoroughly mixed and poured into a glass jar.
- Infuse the mixture throughout the day.
- Use to treat affected areas several times a day.
Plantain
Fresh leaves of the plant are used to treat basalioma. Initially, they are kneaded or rubbed to a pulp. The finished product is applied to the affected area and secured with a bandage. The compress should be kept until completely dry.
Folk remedies for basal cell carcinoma - gallery
A medicinal ointment is prepared from burdock root, which helps tissues heal faster.
Grated carrots should be applied to the affected area
Fresh plants are used to treat basal cell carcinoma.
A product for internal use is prepared using celandine.
Elena Malysheva about the treatment of basal cell carcinoma - video
Photodynamic treatment
Skin basalioma, the symptoms of which do not make themselves felt for a long time, can be eliminated with the help of special devices. For example, using the photodynamic method, which cures the disease in 92% of cases. However, this method cannot be used if the patient has increased sensitivity to light.
Tumors of different sizes, both single and multiple, can be eliminated in this way. Photodynamics not only kills the tumor itself, but also damages the blood vessels that feed it and promote its growth. In this case, healthy areas of tissue may be slightly damaged.
Signs of disease formation
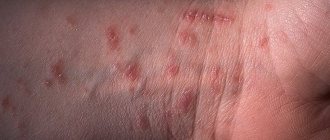
The first signs of basalioma are thin red veins on the nose
. When the initial stage of this disease lasts, basalioma looks like a tiny pink nodule on the skin, and at its edges there are slightly dilated vessels. This nodule is covered with a thin crust, which is often simply scratched off. But then it forms again.
A tiny sore on the skin can be mistaken for an abrasion or herpes. Therefore, this does not cause any fear in the patient and he is not going to treat the ulcer. But as this defect develops, it covers an increasingly large part of the face. Now along the edge of the wound you can see a dense protrusion resulting from small nodules that look very similar to pearls. Sometimes a flat spot may form on the skin, resembling a drop of mother-of-pearl, which protrudes just a little above the surface.
It happens that such a spot is completely mistaken for eczema. But basilioma differs from eczema precisely in its nodular edge, which eczema does not have. This type of neoplasm is said to be superficial, and it can be cured quite easily. When the disease is at the earliest stage, it does not manifest itself in any way: there is no desire to scratch, no severe pain.
But when the tumor begins to develop and bones and cartilage are damaged, the person begins to experience pain. This disease varies in forms. Some species are characterized by a rather sluggish development, while others are quite aggressive and can spread very rapidly. Typically, such a tumor will remain invisible on the skin for a long time, perhaps even five years. But you need to know that it develops not in width, but in the depth of the ulcer.
Yes, basal cell carcinomas really rarely allow metastases to develop, and yet it is better to start treatment as early as possible, because this disease can affect the facial nerve, and the consequence of this will be a violation of facial expressions.
When a malignant tumor forms on a skin area, it constantly increases in size. Sometimes basal cell carcinomas larger than 100 mm are recorded. Symptoms of the pathology in the early stages of formation are not pronounced - a small bubble of a pinkish-gray hue appears on the skin. On palpation, it feels like a dense formation covered with a crust on top.
The disease occurs in two forms - it can grow above the dermis or move inside. Plaques of different sizes gradually form above the skin. Pathologies developing inside can destroy bone structures.
Cryodestruction as one of the most effective treatment methods
Not too cheap, but a very good way to eliminate tumors is freezing. This procedure cannot be called completely painless, but it is quite effective and safe.
The procedure must be performed under local anesthesia. However, the entire operation lasts a few minutes and requires virtually no recovery period (except for a few days). You can use this method if you have basal cell carcinoma of the scalp or face. That is, on open areas of the body there will be practically no scars or cicatrices visible.
To carry out the procedure, a special apparatus and liquid nitrogen are used. This operation is paid, but it is done quickly. It is only advisable to choose a good specialist.
Complications, prognosis and prevention of the disease
If you have basal cell carcinoma of the face, folk remedies together with other treatment methods can give a good effect. However, it is best to try to avoid those factors that can cause the development of pathology. For example, you should not spend too much time in open sunlight, try not to come into contact with chemicals or radioactive substances. Try not to delay treatment of any skin lesions.
As for complications, it can be an infectious infection, which leads to severe inflammation, damage to large vessels, destruction of bone tissue, which then requires a long rehabilitation period.
As for the prognosis, in most cases it is favorable. Naturally, patients may experience relapses. However, keep in mind that if the tumor is already large or has grown into soft and hard tissues, then the operation to remove it will not be easy. Moreover, subsequently you will have to restore cartilage and skin. That is, it will be necessary to carry out additional plastic surgeries, and they are not so cheap.
In any case, a timely visit to the doctor will not only preserve your health, but also protect you from long-term rehabilitation. Be healthy!
Characteristics of the disease
Skin basal cell carcinoma (basal cell carcinoma) looks like open sores on the surface of the skin. Recently, it has been diagnosed in 80% of patients over 50 years of age. It is very rare in young people and children. Men are more susceptible to this disease than women.
The disease develops only on the dermis of any area of the skin. Usually located on areas of the nose, around the eye - in the area of the upper or lower eyelid, ear, forehead, scalp, temporal region. It is found on the cheek, on the skin of the neck, upper lip, on the shoulder, on the arm, in the back area. It is most often found on the face - up to 90% of all cases. In other cases, it is fixed on the leg or arm and body.
Basalioma is a malignant tumor. A neoplasm develops without the presence of a capsule and a specific membrane. Malignant cells immediately penetrate the tissue, causing the destruction of healthy structures. Germination occurs both in depth and in width, which is accompanied by expansion of the affected area.
The disease quickly penetrates deep into the skin layer, but increases in size only by 5 mm per year. Therefore, it is considered to be slowly progressive, which means that it can be easily cured. The difference between the pathology and others is the absence of metastasis to other areas of the skin. Because of this, doctors classify this pathology as borderline neoplasms - this means that the disease is benign and malignant at the same time.
Basalioma on the skin
The node is formed by a mutated cell from the basal layer of the dermis. Since the skin epithelium and basal layer are present on the skin, basal cell carcinoma can develop exclusively on the skin of the body. The tumor is not able to form on the tissues of internal organs with other areas.
Externally, the disease looks like a small spot, mole or nevus on the skin, gradually increasing in size. With the growth process, a small depression with an ulcer, covered with a crust, develops in the center. Under a layer of thin crust, an uneven surface with the presence of blood discharge is noticeable.
ICD-10 pathology code C44 “Other malignant neoplasms of the skin.”