Bartholin's gland abscess (abscess of the large vestibular or large gland of the vestibule) is an infectious and inflammatory disease in which a delimited cavity is formed in the gland tissue, filled with purulent contents.
Bartholin's glands are small paired glands of the vaginal vestibule, which are located at the base of the labia minora, their excretory ducts open on the inner surface of the labia minora. During palpation, sexual arousal and during sexual intercourse, a secretion is released through the ducts, providing sufficient lubrication of the female genital tract, preventing irritation of the mucous membranes.
According to statistics, abscess of the Bartholin gland is registered in approximately 2% of women, most often 20–40 years old. The disease does not develop in children, but is rarely observed in older women and adolescents.
Bartholin's gland abscess manifests itself as severe pain and swelling in the labia area
Timely treatment begins to avoid the development of complications, the prognosis is usually favorable.
Causes
An abscess is a complication of bartholinitis - inflammation of the vestibular gland; the inflammatory process can develop against the background of an existing cyst in the gland tissue. Infectious agents usually spread from primary foci located in the urethra, vagina, and rectum. Most often, the causative agent of infection comes from adjacent organs. In rare cases, hematogenous spread of infection from isolated foci is observed. The cause may also be sexual contact with an infected partner; the infection can also be transmitted through dirty hands, medical instruments, or by sharing towels.
Risk factors include:
- decreased immunity;
- hypothermia of the body;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- infectious diseases;
- frequent stress;
- presence of bad habits;
- excessive physical activity;
- use of certain medications (for example, long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs);
- injury (including during any medical procedures).
The pathological condition can occur due to congenital narrowness of the excretory canal, in which the release of secretions becomes difficult or completely blocked, a cyst is formed, against which an abscess can develop when an infection occurs.
There is a high risk of developing a Bartholin gland abscess in cases where a woman tries to independently treat infectious diseases of the genital tract and/or does not follow medical recommendations.
How to cure an inflamed Bartholin gland cyst without surgery
Treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor and is aimed at restoring the functioning of the gland, eliminating infection and relieving painful symptoms. Conservative treatment is prescribed for frequent relapses, as well as in the initial stage. Typically, treatment includes:
- antibiotics that eliminate the infectious pathogen (Doxycycline, Ceftriaxone);
- use of ointments (Vishnevsky, Ichthyol, Levomekol);
- antiseptic solutions for washing (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt);
- immunostimulants.
Usually, in addition to the main treatment, the doctor recommends physiotherapeutic procedures:
- UHF;
- magnetic therapy;
- infrared irradiation;
- warming procedures based on paraffin and ozokerite.
>Important! Can a cyst resolve on its own? In the early stages, if you follow the doctor's recommendations, the formation may resolve. However, if it is neglected, you should not expect a “miracle”; the cyst will not go away on its own, it only needs to be removed.
Classification
An abscess of the Bartholin gland can be true and false (the latter is most often noted), unilateral and bilateral, specific and nonspecific. We speak of specific when a pathogen is isolated that causes the development of specific infections (including sexually transmitted infections); nonspecific infectious agents can be staphylococci, streptococci, and E. coli.
There are true and false abscesses of the Bartholin gland:
- true - is a formed abscess, the parenchyma of the organ is affected;
- false - blockage of the gland duct with inflammation, but without purulent melting, without the spread of the pathological process to the parenchyma of the gland.
Cyst formation during pregnancy
A woman may develop a Bartholin gland cyst during pregnancy. If the neoplasm does not show signs of inflammation, it does not affect the course of pregnancy in any way. In this case, treatment of the cyst is postponed until the postpartum period. If the cyst is inflamed, then, according to indications, an operation is performed to remove the festering cyst.
Symptoms
The pathology is accompanied by pronounced local symptoms, as well as signs of intoxication of the body.
An abscess forms in the lower or middle third of the labia. On palpation, it has an elastic consistency and is not fused with adjacent anatomical structures. Upon palpation, a small amount of pus may be released.
There is a sharp pain in the labia area, the pain can radiate to other parts of the body, intensifies with physical activity, during bowel movements, and with palpation of the inguinal lymph nodes. There is pronounced swelling in the affected area, which may partially or completely block the entrance to the vagina, and hyperemia. There may be a sensation of a foreign body in the perineum.
The patient experiences weakness and fatigue, increased sweating, headache, chills, tachycardia, and increased body temperature to subfebrile levels. With a false abscess, the general condition does not suffer (one of the diagnostic signs).
As the pathological process progresses, the tumor usually breaks through and pus comes out. After this, symptoms usually subside.
What is bartholinitis
Bartholinitis is based on inflammation of the Bartholin gland, which is located in the area of the vestibule of the vagina. Most often, the pathological process is one-sided. The Bartholin gland secretes a clear liquid that provides an optimal degree of hydration of the mucous membrane and comfort for intimate contacts.
The peak incidence occurs at the age of 20-30 years. With highly contagious infections, the anterior genital tract, and a significant decrease in the activity of the immune system, bilateral forms of bartholinitis are observed.
Complications
In the absence of timely, properly selected treatment for the acute form of the disease and with reduced immunity, the pathology can become chronic. In the chronic course of the disease, periodic maturation and opening of the neoplasm is observed; during the period of remission, a dense, painless formation is formed in the thickness of the labia; a feeling of discomfort may be observed during sexual arousal and sexual intercourse. The affected area is gradually deformed due to cicatricial changes after the opening of abscesses, and secondary lymphadenitis develops.
A complication of the chronic variant of the pathology can be non-healing rectovaginal fistulas. If they are large enough, stool may be thrown into the vaginal lumen.
In the absence of adequate treatment, there is a risk of inflammation spreading to fatty tissue, the formation of phlegmon, and the entry of infectious agents into the bloodstream with the development of sepsis.
Bartholinitis and pregnancy
In pregnant women, the activity of the immune system decreases, which can provoke inflammation of the Bartholin gland. Sometimes it recurs early or late. Gynecologists treat bartholinitis during pregnancy. Professionals should be contacted immediately upon the appearance of colored lips and any discomfort.
Any infectious process can lead to miscarriage and other adverse consequences. It is prohibited to independently select medications that may have a teratogenic effect on the developing fetus. The gynecologist will select the necessary local remedies that will stop the inflammatory process and the spread of infection.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, first of all, a collection of complaints and anamnesis and a gynecological examination are required. Laboratory tests are prescribed (general blood count, bacteriological examination of secretions from the gland duct, tests for sexually transmitted infections). Ultrasound examination may be required to clarify the diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with boils of the labia, edema abscess, and malignant neoplasms. To exclude cancer, as well as in case of recurrent pathology, a biopsy may be necessary.
Treatment
Conservative treatment (drug therapy, physiotherapeutic techniques) can be effective only in the early stages of the pathological process. In other cases, treatment is combined - surgery with drug support.
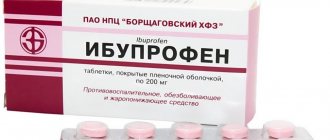
Non-surgical therapy is recommended to be carried out in a hospital; the patient can carry out post-operative treatment at home under the supervision of a doctor. Antibacterial and/or antifungal drugs are prescribed (if the abscess is of fungal etiology), anti-inflammatory drugs, and painkillers.
Abscess is treated primarily surgically
The choice of type of surgical intervention is selected depending on the existing symptoms, the general condition of the patient and a number of other factors, based on the opening of the Bartrolin gland abscess and removal of pus, followed by anti-infective treatment. Surgical treatment methods are presented in the table.
| Method | Description |
| Wide incision | Excision and emptying of the abscess |
| Incision with installation of a word catheter | Excision, installation of a catheter for 1.5-2 months in order to form an excretory channel for the outflow of secretions |
| Marsupialization | The abscess is opened, the cavity is washed, after which the walls of the capsule are sutured to the mucous membrane of the labia to form a duct |
| Bartholinectomy | Removal of the gland along with the abscess |
The operation can be performed either under local anesthesia (more often) or under general anesthesia. For 2-3 days after opening the Bartholin gland abscess, it is necessary to wash the postoperative wound with antiseptic solutions. In the postoperative period, you need to wear loose underwear made of natural fabrics; it is recommended to use panty liners. The patient should not use tampons during menstruation.
When using non-radical surgical methods to remove a tumor, relapses of the pathology are possible.
How you can help
The resulting Bartholin cyst requires surgery. But if the disease is at an early stage, it can be cured at home.
When starting to treat this disease at home, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Before each procedure, wash your hands with antibacterial soap;
- when processing items used in treatment, use Miramistin;
- use only a sterile bandage;
- Wash the hidden abscess with saline solution or treat it with peroxide.
Lotions
Lotions with the following remedies will help cure bartholinitis:
- Saline solution . To prepare, dissolve 3 level tablespoons of salt in 1 liter of warm boiled water. Soak a piece of gauze in the solution and apply to the problem area for 35-45 minutes. The procedure is repeated 3-6 times a day.
- Blackberry leaves. Mix 1 tablespoon each of blackberry leaves, yarrow, and nettle. Pour 1 liter of just boiled water, leave for 2-2.5 hours and filter. Lotions should be applied daily, preferably before bedtime. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes.
- St. John's wort. Pour 6 tablespoons of raw material into 1 liter of hot water, boil for 3 minutes, cool, filter. This remedy can also be used to treat an opened purulent cyst. The procedure is carried out every evening before bed. The lotion is left for 20-25 minutes.
Products for internal use
This disease can be treated using products for internal use prepared according to the following recipes:
- Knotweed and nettle . Mix nettle and knotweed (2 parts each), add 1 part each of horsetail, pickleweed and Icelandic moss. Pour boiling water over the herbs at the rate of 500 ml of water per 2 tablespoons of the mixture. Leave for 45 minutes, filter thoroughly. Take 1/3 cup of the decoction daily.
- Walnut. Grind 300 g of nuts in a blender, mix with 1 kg of honey, add 100 g of boiled garlic and 1 teaspoon of dill seeds. The drug is taken 1 tablespoon, 2-3 hours before meals. Daily consumption helps boost immunity.
- Aloe leaves. Pass 400 g of leaves through a meat grinder, add 800 g of honey, pour in 400 ml of dry red wine. Boil in a steam bath for 50-60 minutes, filter well. You need to take 1 tablespoon 30 minutes before your main meals.
Persons with allergies should avoid these medications. Otherwise, the clinical picture will only worsen.
Baths
Chronic female bartholinitis can be treated with baths. They add such funds
- Chamomile. Mix 6 tablespoons of chamomile with 2 teaspoons of mint and 4 tablespoons of immortelle inflorescences. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into 200 ml of just boiled water and keep in a steam bath for 15 minutes. Cool, filter. You need to take a chamomile bath every day 1.5 hours before bedtime.
- Sage. Mix 1 tablespoon of sage with the same amount of Icelandic moss and mint, add 2 cups of just boiled water. Leave for 40 minutes, cool to 25 degrees, strain. Take a sage bath 2-3 times a day.
- Calendula . Mix 4 tablespoons of calendula flowers with the same amount of chamomile, pour in 1 liter of cooled boiling water, simmer over low heat for 5 minutes, cool, filter. This remedy helps relieve hyperemia around the Bartholin gland. The procedure is carried out every other day. The duration of the course is 7 days.
- Potassium permanganate. Dissolve potassium permanganate powder, taken from the tip of a knife, in 10 ml of hot water. Separately, steep 2 tablespoons of eucalyptus leaves in 200 ml of boiling water for 40 minutes. Mix potassium permanganate with eucalyptus infusion. A bath with such a solution helps stop the inflammatory process. It should be done daily, 2-2.5 hours before bedtime.
The duration of the bath is from 15 to 25 minutes.
Tinctures
It is recommended to use tinctures prepared according to the following recipes:
- Aloe. Grind 300 g of aloe leaves in a meat grinder, add half a teaspoon of fresh honey and 10 drops of dry wine. Heat in a steam bath, achieve homogeneity, boil for 15 minutes. Cool, filter. Take no more than 4 times a day, 1 teaspoon before meals.
- Icelandic moss . Mix 100 g of moss, 20 g of nettle and 20 g of knotweed. Pour a liter of cooled boiling water, boil for 15 minutes, leave for 2 hours, filter. The product is taken 1 teaspoon, 3 times a day. Signs of the disease disappear after 7 days.
- Valerian roots. Grind the rhizomes, mix 40 g of raw materials with the same amount of Icelandic moss, add 40 g of immortelle flowers and pine shoots. Pour the collection with 800 ml of boiling water, keep in a steam bath for 20 minutes. Remove from heat, leave for 60 minutes, filter thoroughly. Take the medicine 1 teaspoon after meals.
Before using these folk remedies, you must ensure that there are no contraindications. They cannot be treated during pregnancy.
Other methods
Treatment involves douching, the use of ointments and suppositories.
- Douching with acidophilus helps relieve the condition . It is recommended to alternate this remedy with solutions of potassium permanganate and Chlorhexidine.
- Levomekol ointment, which combines healing and antimicrobial components, has a good therapeutic effect. It is able to stop the inflammatory process.
- If bartholinitis is aggravated by the development of a purulent abscess, it is recommended to use Vishnevsky ointment.
- A less “fragrant” analogue of this remedy is Ichthyol ointment.
- To restore the vaginal microflora, vaginal suppositories Acylact and Laktonorm are used.
In order to prevent the development of the disease, you must carefully observe genital hygiene. Regularly undergo preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
Prevention
To prevent the development of the pathological process, it is recommended:
- avoid promiscuity;
- use high-quality contraception;
- promptly treat diseases against which an abscess may develop;
- increase immunity;
- avoid physical overload;
- avoid stressful situations;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- avoid hypothermia;
- carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Acute bartholinitis
Acute bartholinitis has the most striking clinical manifestations. Causes severe pain, especially while walking. During an exacerbation, there are favorable conditions for the active reproduction of opportunistic microorganisms. Therefore, the inflammatory process often leads to purulent formal diseases.
The specialist prescribes antibacterial agents, drugs that relieve pain and restore the woman’s normal well-being. At an early stage, local cold is used to relieve the acute process, which is applied to the area of the external genitalia. The inflamed area is treated with antiseptics and ointments with ichthyol are applied.
The development of acute bartholinitis can be provoked by the following unfavorable factors and diseases:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- use of tight underwear, especially important natural ventilation of the skin;
- exacerbation of gynecological diseases, including thrush;
- damage to the genital mucosa, penetration of infectious pathogens from the rectum, vagina and urinary tract through small abrasions;
- hypothermia of the body;
- avitaminosis;
- severe stress;
- hormonal changes in the body.
Infectious pathogens penetrate the Bartholin gland, enter the bloodstream or through minor injuries to the external genitalia.
It is important to prevent the disease from becoming chronic. Prolonged course of the disease leads to the formation of abscesses requiring surgical interventions.