Why and who gets this disease?
Focal atrophic gastritis - what is it? This is a disease that occurs against the background of existing stomach damage. That is, the presence of chronic gastritis of any type is a risk factor for the occurrence of atrophy.
The focality of the process lies in partial damage to the glands. That is, atrophy does not develop in all cells at once, but only in a certain part of it. Therefore, this variant of gastritis is called focal. Those areas in which atrophy does not occur gradually increase in size. And it looks like areas of hyperplasia with alternating atrophy.
This occurs due to the fact that the body tries to compensate for the lack of function of the affected glands. Therefore, an imbalance in acid balance occurs.
The risk group for developing this disease includes:
- persons suffering from chronic gastritis without periodic treatment of exacerbations;
- lack of therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection;
- presence of bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol;
- excess body weight;
- presence of similar gastrointestinal diseases in the family.
The causes of the development of the disease include primarily the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection in the stomach. It is with its presence that most cases of atrophy are associated. Long-term infection causes constant inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane. Initially, superficial gastritis forms, then it becomes chronic. And at this stage it is very important to monitor the infection of the body.
It is necessary to undergo periodic examinations to determine the presence of infection in the stomach. If it is present, you should resort to treatment. If the cause is not eliminated in a timely manner, it will lead to the development of gland atrophy.
Gland atrophy is a condition in which cells are unable to perform their functions fully.
Another reason for the development of such a disease as focally atrophic gastritis is autoimmune processes. This means that the body’s own antibodies attack the cells of the stomach, which leads to the failure of their work. The reasons for the development of such autoimmune reactions are not fully understood.
Diet food
Diet is a necessary part of treatment for all types of gastritis. Depending on the goals of therapy, four types of diets have been developed:
- Diet No. 2 is considered basic. This diet involves adequate nutrition and stimulation of functional glands. With this diet, all dishes are boiled, stewed, baked. The diet allows various dishes: meat, fish, fermented milk, flour products, eggs, hard-boiled or scrambled eggs, vegetables and fruits are allowed - a total of 30 types of products are allowed;
- Severe pain syndrome requires the use of diet No. 1a, which is followed in the first days of the disease. Foods that stimulate stomach receptors are excluded from the diet. The diet consists of dishes in the form of liquid or puree, steamed, boiled, pureed. The basis of the diet is 9 dishes. If you are not lactose intolerant, you can use whole milk, cottage cheese, cream;
- When the symptoms of inflammation subside, diet No. 1 is prescribed. It is used to speed up the process of restoration of inflammation of the gastric mucosa. This diet helps restore normal functioning of the secretory and motor functions of the stomach. Extremely hot or cold foods are removed from the diet. Dishes containing a lot of fiber are not recommended. The list of permitted dishes consists of 11 items;
- In case of severe enteric syndrome, when there is intolerance to lactose and other products, diet No. 4 is prescribed. The purpose of this diet is to normalize the functioning of the stomach in order to relieve inflammation in its mucosa. Meals are split, and after the exacerbation is relieved, you can return to diet No. 2.
During an exacerbation of the disease in the first days, it is advisable not to eat anything at all, but only drink.
How does this disease manifest itself?
Atrophic focal gastritis manifests itself with local symptoms. These include:
- a constant feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating ;
- development of heartburn ;
- belching with sour contents;
- development of bad breath;
- nausea and vomiting due to errors in diet;
- digestive disorders such as dyspeptic disorders ( diarrhea and constipation ).
The first thing that worries patients is a feeling of heaviness and discomfort in the stomach. This feeling always occurs after eating and eating fatty and fried foods. Alcohol consumption is always accompanied by an exacerbation of gastritis.
The feeling of heaviness is localized in the stomach or the entire abdomen. After eating, such patients may develop constipation or, conversely, diarrhea. This is due to the fact that digestion in the stomach does not occur properly, which directly affects the functioning of the underlying sections.
Additionally, this is accompanied by a feeling of heartburn and belching of sour contents. Since this form of gastritis is accompanied by an imbalance in acidity, heartburn will always be present with this type of disease.
The development of bad breath indicates a severe course of the disease. This happens due to difficulty digesting food. Rather, the digestive processes slow down. Therefore, rotting of food products develops, which causes such a smell.
The development of nausea and vomiting occurs when the diet is violated and there is a strong error in the diet. Vomiting develops half an hour after eating.
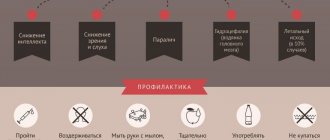
Disease prevention
Compliance with basic rules will reduce the risk of developing focal atrophy of the coolant:
- follow a therapeutic diet and lead a healthy lifestyle with proper rest and 8 hours of sleep;
- exclude the use of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products;
- avoid psychological and physical fatigue;
- You should undergo an annual examination by a gastroenterologist;
- it is necessary to lead an active, mobile lifestyle;
- Treatment of gastrointestinal diseases must be timely and complete.
Contacting a specialist and qualified treatment will help you avoid the dangerous consequences of the disease.
Drug therapy
Prescription of medications is carried out by a specialist doctor taking into account the diagnosis. If Helicobacter pylori infection is detected, eradication therapy . It involves the use of several antibiotic drugs in combination with general therapy. It includes the use of a number of antibiotics from the group of cephalosparins, aminoglycosides, and fluoroquinolones. If there is no effect, one medicine is replaced with another.
Gastroprotectors are prescribed to protect the gastric mucosa from acidity disorders. Preparations based on bismuth salts are used.
Substances are also used for replacement therapy. These are hydrochloric acid tablets and gastric juice. They are always used in the presence of gland atrophy. Thanks to them, the digestion processes in the stomach cavity are normalized.
Enveloping substances are used. It is recommended to resort to the prescription of antacids . Patients are always prescribed prokinetics . These are drugs that accelerate the evacuation of the food bolus from the stomach into the small intestine. Domperidone and other drugs based on it are used
To maintain enzyme activity when diagnosed with gastritis with focal mucosal atrophy, some patients are prescribed Mezim or Creon . They are necessary to facilitate the functioning of the pancreas.
Causes
There is no consensus among experts about the reasons that provoke the development of this disease. Among the factors contributing to the occurrence of atrophy of the gastric mucosa are the following:
- consumption of rough foods and insufficient chewing of food;
- carbonated drinks, coffee, alcohol;
- smoking;
- constant overeating;
- eating a large amount of hot, spicy and other foods with an aggressive taste;
- excessively hot or cold food;
- long-term use of medications;
- reflux (reflux of intestinal contents into the stomach).
All of these factors have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane, which over time leads to the occurrence of atrophic processes in it. [adsense1]
Useful video
Focal atrophic gastritis, the symptoms and treatment of which are clarified in this article, is a disease that should be treated under the supervision of a doctor. You can also learn useful information from this video.
Anesthesia
Severe painful attacks require the use of painkillers. But in this case, they do not resort to prescribing NSAIDs. For these purposes, only antispasmodic substances are used. They actively resort to Nosh-Pe or Drotaverine .
The course and duration of therapy is determined by the doctor.
Diagnostic measures
During the initial examination, a gastroenterologist takes an anamnesis of the disease, studies all the symptoms and prescribes treatment based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis.
Laboratory research:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- testing for antibodies and enzymes;
- blood testing and breath test for the presence of Helicobacter;
- ph-metry to determine the level of stomach acidity.
The following instrumental diagnostic methods are used:
- radiograph;
- endoscopy of the stomach to identify the lesion;
- fibrogastroduanoscopy, which allows you to determine the degree of ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum;
- biopsy and histology;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Based on all the tests, the doctor draws up a treatment regimen.
To avoid undesirable consequences, you should never begin to treat atrophic focal gastritis on your own.
Atrophic focal gastritis: diet
Diet for focal atrophic gastritis plays a major role in its therapy. In this case, it is divided into two options. During the period of exacerbation of the patient, a gentle diet is recommended. First of all, this is the exclusion of fatty and fried foods. Drinking alcohol and carbonated drinks is prohibited. It is advisable to quit smoking. It is recommended to remove sweets and fresh fruits and vegetables from the diet.
During the period of exacerbation, it is allowed to eat porridge prepared in milk with the addition of butter. During this period, all food must be boiled and finely chopped. It is recommended to drink more water.
When the exacerbation subsides, it is necessary to add various cereals to the diet. These can be buckwheat or millet cereals . It is recommended to eat more vegetables and fruits. But alcohol and carbonated drinks are also prohibited. Diet therapy for atrophic gastritis is aimed at irritating the glands. This is done to maintain the functioning of the remaining healthy areas of the gastric mucosa.
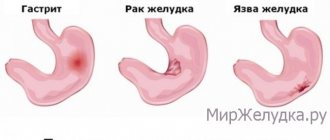
Gastritis with signs of malignancy
If the patient is not treated promptly, adenocarcinoma develops. In the early stages, gastritis with signs of malignancy is no different from simple inflammation. Symptoms such as changes in stool, epigastric discomfort, belching, nausea and vomiting are observed.
Specific signs appear only when surrounding tissues grow, the tumor is large and there are metastases.
With atrophic gastritis with malignancy in the later stages, symptoms of exhaustion and intoxication are pronounced. These include severe weakness, weight loss and low-grade fever. When the cardiac region is damaged, dysphagia occurs. Restoring the gastric mucosa in this case is difficult.
Forms of atrophic gastritis
According to the clinical course, atrophic gastritis is divided into acute and chronic. In addition, according to the location of the disease, the following types of disease are distinguished.
Focal
Chronic focal gastritis is characterized by the fact that on the gastric mucosa there is an alternation of areas with focal atrophy and hyperplasia of the epithelium and secretory cells. This is explained by the desire of healthy stomach tissue to compensate for the missing functions of the atrophied areas. In healthy areas, the secretory function of the glands increases, which leads to an imbalance in the acid balance in the stomach cavity. The pathological process is localized in the lower parts of the stomach.
Also called subatrophic gastritis. It is considered the initial stage of pathology.
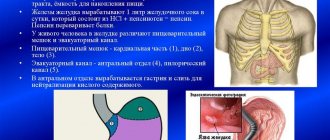
Antral
This clinical and pathological disease affects the stomach in the antrum. In this place, scar changes form on the surface of the mucous membrane. With such localization of the pathological process, the structure of the gastric outlet is damaged and the exit of food masses from the stomach becomes difficult.
With this disease, the acidity level of gastric juice increases. Symptoms resemble hyperacid erosive gastritis. Such mixed gastritis requires differentiation from a number of pathological conditions of the stomach.
What you need to know
The mucous membrane of the stomach is subject to the negative effects of external and internal factors.
“Forewarned is forearmed” - this famous phrase is perfectly suited to this situation. The fact is that often chronic focal gastritis can turn into a malignant form and lead to stomach cancer. The danger is that in the early stages, both oncological disease and focal gastritis manifest themselves with very similar symptoms, which significantly complicates differential diagnosis.
The cause of both antral and chronic focal gastritis is the bacteria Helicobacter pylori, but if in the first case we are talking mainly about the increased acidity of the gastric contents, then in the second case the acidity may be reduced.
There are also some age-related signs: young people usually have increased acidity, which is accompanied by symptoms such as heartburn, belching and nausea, but older people more often complain of pain in the epigastric region, diarrhea, an unpleasant taste in the mouth and a feeling of fullness in the stomach when small amount of food eaten.
Clinical manifestations
The symptoms of atrophic gastritis are characteristic and easily recognized.
- The first clinical manifestation of atrophic focal gastritis is a gradual decrease in appetite. There is a decrease in body weight.
- In the initial stages of the disease, the patient complains of pain in the epigastric region.
- A disease without pain is a sign of an atrophic process in the stomach.
- After some time, the patient begins to experience symptoms of digestive disorders. There is frequent nausea and vomiting.
- Patients complain of belching, heartburn, and rumbling in the stomach.
- Changes in metabolism lead to increased formation of gases in the abdomen and flatulence.
- Since the patient’s immunity is weakened, secondary infections and the development of diarrhea are possible.
Exchange disorders
After eating, a person has a feeling of heaviness in the stomach and a rotten smell in the mouth. The patient's appearance also deteriorates.
The skin becomes dull and pale. Hair becomes dull and falls out, nails crumble. This symptomatology is caused by vitamin deficiency and a decrease in blood hemoglobin.
General changes in the body
General signs of asthenia and intoxication are headache, decreased blood hemoglobin and blood pressure, dizziness.
When examining the patient's tongue, a thick whitish coating is discovered. In acute times, concomitant diseases of the digestive tract worsen - enteritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis. Local necrosis is dangerous. To avoid such a serious complication, seek medical help immediately if you experience symptoms.
Therapy
If such a serious disease is suspected in a patient, a laboratory instrumental examination is required. Based on the results of a comprehensive examination, doctors determine the causes of the disease and the stage of development, as well as the pathomorphological state of the mucous membrane.
Treatment of focal atrophic gastritis is long-term and complex, supervised by a doctor.
Principles of treatment
An unfavorable clinical diagnostic sign is the detection of areas of necrosis in the stomach. With this form of pathology, surgical intervention will be required.
If the disease is acute, treating focal gastritis at home is difficult. The patient requires hospitalization in the gastroenterology department. In addition to removing foci of necrosis, measures are taken to prevent atrophy of stomach tissue. This will require medication and a strict diet.
Eradication
Eradication is the elimination of the infectious pathogen of gastritis. The main cause of the disease is Helicobacter pylori. To cure the body of the pathogen, complex antimicrobial therapy is prescribed. Amoxicillin and metronidazole are often used. These antibiotics and antiprotozoal agents also kill other pathogenic microflora. Additionally, after a course of antibiotics, eubiotics, vitamins and immunomodulators are prescribed to restore intestinal flora.
Substitution treatment
Replacement therapy consists of normalizing the functions of the stomach and intestines and restoring metabolism. To treat focal gastritis, doctors recommend constantly taking medications that increase the secretion of hydrochloric acid and mucus.
If the patient has severe concomitant symptoms, medications that stimulate the secretion of gastric glands will be required. To restore the body's condition, mineral and vitamin deficiencies are replenished. To eliminate the deficiency of hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes in the stomach, the attending physician prescribes replacement treatment with the drugs Abomin and Pepsidil.
The question of how to treat focal atrophic gastritis is decided only by the attending doctor. To improve digestive processes, breakdown and absorption of nutrients in the intestines, the drugs Festal, Mezim, Creon, Pancreatin are prescribed.
Anesthesia
To relieve pain in a patient, myotropic antispasmodics such as drotaverine or noshpa, as well as anticholinergic drugs such as platyphylline, are prescribed.
Prescribing proton pump inhibitors or histamine receptor blockers in this case is inappropriate, since insufficient hydrochloric acid is already produced in the stomach.
Prevention
As with any other disease, it is important to know about preventive measures that are aimed at preventing the disease. Compliance with basic low-cost principles will help maintain health and the family budget. Women entering menopause should be especially responsible about their condition, because during this period they are most susceptible to various pathologies.
Prevention is based on adherence to the following principles:
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules (use of separate utensils, toothbrush).
- Timely eradication of Helicobacter in case of infection.
- Maintaining blood glucose levels at an acceptable level in diabetes mellitus.
- Taking hormone replacement therapy for thyroid pathologies.
- The use of multicomplexes of vitamins and minerals (with the obligatory intake of folic acid and cyanocobalamin).
- Rational nutritious nutrition.
- Elimination of stress, nervous and physical strain.
- Normalization of weight, with excess or lack of it.
- Avoiding excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages and smoking.
- Elimination of food poisoning (consuming only high-quality, fresh products that have undergone adequate culinary processing).
Inflammation of the stomach, accompanied by atrophic changes, occurs quite often in women. The clinical course is accompanied not only by gastric manifestations, but also by symptoms of concomitant anemia. Compliance with doctor's instructions, precise use of medications, supplemented with folk recipes can slow down the process of damage and prevent cancer complications.
Proper nutrition
To cure focal atrophic gastritis, follow a diet. If you eat foods that are not recommended for this disease, the results of treatment will be nullified.
- It is acceptable to eat vegetables and fruits on this diet.
- The meat should be boiled, not fatty or heavy.
- To ensure that vegetables are absorbed and maintain normal balance, they are boiled.
- For atrophic gastritis, fruits are only allowed to be ripe, fresh, washed and in no case sour.
- Ripe sweet berries and greens are useful.
- Food for gastritis should not contain heavy animal fats and carbohydrates. It is preferable to cook soups with vegetable broths, as well as chicken broth.
- Soft-boiled eggs, pasta, hard cheeses, and cereal porridge are allowed in the diet.
- You need to drink a lot of liquids. Non-acidic juices, mineral water, jelly, tea, compote are suitable.
If this dangerous disease is not treated, it can lead to the development of a malignant neoplasm. The sooner treatment is started, the better the prognosis.
Treatment methods for patients
For atrophic gastritis, treatment is pathogenetic, etiotropic and symptomatic. The main goals of therapy are the prevention of complications (malignancy) and improvement of digestion. It is impossible to completely cure patients. The following medications are required:
- astringent and enveloping drugs;
- gastroprotectors;
- corticosteroids;
- dopamine receptor blockers;
- prokinetics;
- enzymes;
- gastric juice substitutes;
- bismuth preparations;
- antibiotics.
The patient must adhere to a strict dosage of medications. The treatment regimen depends on the acidity of the stomach. For hypoacid gastritis, proton pump blockers and antacids are most often not prescribed. This chronic pathology of the stomach is an indication for the use of antibiotics. They are necessary when detecting Helicobacter pylori bacteria.
For the best effect, 2 or 3 drugs are prescribed at once. Protected penicillins, macrolides, tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins and nitroimidazoles have a detrimental effect on these microbes. The most commonly prescribed are Flemoxin, Amoxiclav, Azitrox and Metrogyl. Not everyone knows how atrophic gastritis is treated.
The treatment regimen includes medications that protect the mucous membrane. The drug De-Nol has proven itself to be excellent. It contains bismuth salts, which form a protective layer in the stomach. Enzymes (Festal, Panzinorm, Creon) are used to treat atrophic gastritis. They are needed for the normal breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
For vomiting and nausea, prokinetics are prescribed. They normalize the motor function of the stomach, facilitating the passage of chyme. You need to know not only how to restore the mucous membrane, but also how to increase the secretory activity of the organ. For this purpose, patients are recommended to drink decoctions of plantain, fennel and wormwood, as well as diluted lemon juice.
Rosehip decoction helps a lot.
In severe cases, the use of gastric juice is required. If there is moderately severe atrophic gastritis, then sea buckthorn oil can be used. Drug treatment is complemented by physiotherapy. Electrophoresis, magnetic therapy and electrotherapy help with gastritis. Relaxation in a sanatorium is recommended.
Important information: Symptoms and treatment of ulcerative gastritis
Description
In the name of the disease, a key role is played by “atrophy,” that is, starvation or exhaustion. In some areas of the stomach, the mucous membrane becomes excessively thin, which is why gastric juice, which is important for digestion, ceases to be produced.
The disease develops further, acidity increases. The pathogenic bacteria Helicobacter pylori begin to actively multiply on the mucous membrane. They secrete special mucus that covers the walls of the stomach and replaces gastric juice. The result is an imbalance of acidity, making digestion difficult.
At this stage, it is still possible to treat the disease with medication. If nothing is done, cancer cells actively spread in such an environment. Over time, oncology “takes over” the entire stomach and leads to irreversible consequences.
Classification
Focal gastritis is divided according to clinical signs into two forms - acute and chronic. Acute gastritis with focal atrophy makes itself felt within a few hours or days. It is painful, with pronounced symptoms.
The chronic form is more dangerous for the body because it does not “show” itself for a long time. Pain and symptoms are absent until the last moment. The destruction of tissues and mucous membranes occurs gradually but surely.
According to localization (site of inflammation), gastritis is of two types:
- atrophic or subatrophic;
- antral.
With the atrophic type, the pathological process occurs in the lower parts of the stomach. It is considered the initial stage of the disease.
Antral type means that the disease affects the stomach in the antrum - near the opening from which food masses come out. Scars appear on the mucous membrane, and going to the toilet brings discomfort. These changes are considered a serious stage of the disease and require immediate intervention.
Factors increasing acidity in chronic gastritis
The next exacerbation of the disease occurs when the concentration of hydrochloric acid in the digestive organ exceeds the norm (160 mmol/l), because alkaline components cannot neutralize it. An increase in acidity is provoked by external (exogenous) and internal (endogenous) factors.
External reasons include:
- smoking;
- frequent drinking of alcoholic beverages;
- long-term use of drugs aggressive to the epithelium;
- radiation;
- parasites and fungi.
In 85% of cases, gastritis develops due to the entry of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori into the digestive organ. Helicobacter is not afraid of an acidic environment, because produces an enzyme such as urease, which neutralizes the effect of hydrochloric acid. The neutral environment surrounding each bacterial cell makes it invulnerable, so colonies of microorganisms damage the mucous membrane, causing its inflammation.
Endogenous causes of increased gastric acidity include:
- hypovitaminosis;
- metabolic disease;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- chronic infections;
- decreased oxygen in the blood (hypoxemia);
- genetic predisposition to the disease.
In 5% of cases, relapse of the pathology occurs due to duodenogastric reflux, in which the contents of the duodenum (bile, pancreatic enzymes, salts) are thrown into the digestive organ and irritate its tissues.
The most common internal factor (10% of cases) of gastric inflammation is autoimmune processes.
Symptoms
Since focal atrophic gastritis affects a vital organ, many general signs of malaise occur. They are similar to signals about the development of various diseases, so only a doctor can accurately determine the cause of the symptoms after diagnosis.
Pain
In acute gastritis, pain appears periodically and noticeably. A dull pain occurs after every meal because the stomach stretches unnaturally. At night or when feeling hungry, the pain is aching. If you take painkillers, they only become quieter, but do not disappear.
With chronic atrophy, there are no acute pain sensations. The lesions are covered with bacterial fluid and therefore are not irritated. Discomfort becomes noticeable in the extreme stages, when malignant tumor cells are already growing.
Anemia
Digestive disorders affect the composition of the blood. It shows a deficiency of hemoglobin, B vitamins, and ascorbic acid. Such signs indicate the development of anemia.
It causes the following symptoms:
- the skin turns pale;
- hair falls out and nails break;
- weakness, drowsiness, and fatigue occur;
- migraines and frequent dizziness appear, up to loss of consciousness;
- immunity decreases.
Against the background of anemia, other diseases develop that are associated with a lack of the body's defenses. Without diagnosis, some therapists prescribe treatment for anemia and vitamin deficiency, although you need to “dig deeper,” because the reasons lie in the development of gastritis.
Dyspepsia
Focal atrophic gastritis is characterized by dyspepsia - digestive problems. These symptoms are most pronounced and are:
- constant heaviness in the stomach;
- frequent nausea, vomiting;
- increased salivation;
- constipation, periodically alternating with diarrhea;
- belching with a fetid odor of rotting breath;
- increased flatulence;
- noticeable white coating on the tongue;
- lack of appetite.
Advanced stages of atrophy lead to vomiting with the presence of undigested food debris, strange mucus, and blood. The patient stops eating properly, which causes him to suddenly lose weight. It even reaches the point of dystrophy - catastrophic lack of weight.
Development of anemic syndrome
If atrophic gastritis of the stomach is not treated, anemia develops. The main reason is a deficiency of iron, folic acid and cyanocobalamin in the body. The following symptoms appear:
- increasing weakness;
- decreased performance;
- fast fatiguability;
- mouth pain;
- burning tongue;
- paresthesia of the legs and arms;
- drowsiness;
- redness of the tongue;
- disappearance of papillae on the tongue;
- imbalance;
- clumsiness;
- defecation disorder;
- depression;
- convulsions;
- fragility and deformation of nail plates;
- increased hair loss;
- dizziness;
- feeling of heartbeat;
- pale skin;
- visual disturbances in the form of spots before the eyes;
- transient fainting;
- cold intolerance.
Important information: Is it possible to eat corn if you have gastritis?
Against the background of a lack of iron in the body, the development of glossitis, stomatitis and dysphagia is possible. All this makes work and daily activities difficult.
Causes
Modern medicine has not yet found an exact answer to the question “What is the main reason for the formation of atrophic focal gastritis?” But a number of additional reasons causing the disease are clear.
These include:
- poisoning;
- improper diet;
- abuse of spicy, salty, fatty foods;
- smoking, alcoholism, other bad habits;
- stress;
- heredity;
- disorders of the immune, endocrine, circulatory systems;
- inflammatory processes in the body;
- taking “aggressive” medications.
At risk are people leading a passive lifestyle, pensioners, drug addicts, and alcoholics. Hard physical or mental work, constant “eating” of a bad mood with sweets, parents suffering from chronic gastrointestinal diseases - these factors aggravate the situation.
Diagnostics
If gastritis of any type is suspected, a diagnosis is carried out. Without it, the doctor does not have the right to make such a diagnosis. Instrumental and laboratory tests are prescribed.
Instrumental diagnostics
Instrumental research includes methods that allow you to look at organs from the inside.
| Examination method | Description |
| Examination using an endoscope, which is inserted through the mouth into the esophagus. This way the doctor can identify foci of atrophy and areas of metaplasia on the mucosa. The “gut” also takes a sample of the mucous membrane (biopsy), a tissue sample to test for malignancy (biopsy), and gastric juice. | |
| This is an auxiliary method, thanks to which the size of the stomach, the appearance of the mucous membrane, and the presence of concomitant gastrointestinal ailments are determined. |
X-rays and computed tomography (CT) are not considered informative for patients with gastritis. A gastroenterologist may prescribe them as additional research methods, in addition to FGDS and ultrasound.
Laboratory diagnostics
For a more detailed diagnosis, special laboratory tests are required. These include a gastropanel - an advanced blood test that shows results for three indicators:
- pepsinogen content;
- presence of Helicobacter pylori;
- gastrin hormone levels.
The other main test is a biopsy, a sample taken during gastroendoscopy. It is checked for the degree of thinning of the mucosa (dystrophy).
Measurement of gastric acidity (pH), deficiency of microelements and vitamins, as well as other important details are shown by clinical tests of blood, feces and urine.
Only based on the results of all of the above tests, the attending physician draws up a treatment regimen.
How is diagnostics carried out?
To prescribe adequate treatment, a gastroenterologist must make the correct diagnosis. The patient is interviewed and an anamnesis is compiled based on complaints and examination and palpation. Additionally, general urine and blood tests are prescribed. The main diagnostic measure is short-term pH-metry of the gastrointestinal tract - a procedure aimed at measuring acidity. Based on the result obtained (high or low acidity), the doctor prescribes a suitable therapeutic diet.
To identify the microorganism Helicobacter pylori, a biopsy sample is used (direct method), but indirect signs (presence of antibodies in the blood) can also be indicated. After confirming the presence of bacteria, the attending physician administers antibacterial therapy.
In addition, for diagnostic purposes the following activities are carried out:
- endoscopic examination of the stomach;
- X-ray;
- immunological blood test;
- biopsy;
- fibrogastroduanoscopic examination.
Only an experienced specialist can recognize and treat atrophic gastritis based on a comprehensive examination. You should not self-medicate; at the first symptoms you should go to the hospital to avoid the development of negative, irreversible consequences.
Treatment
It is difficult to completely cure focal atrophic gastritis. The initial stages of the disease are treated with medications. In case of a critical exacerbation, the patient is hospitalized.
If there is a malignant tumor, in addition to drug therapy, surgical intervention (operation) is needed. Therapy must be complemented by a strict diet, otherwise the medications are useless.
Medication
Standard treatment of gastritis with medications takes place in the following stages:
- Eradication – destruction of Helicobacter pylori. Antifungal therapy is carried out using antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Metronidazole, Clotrimazole).
- Neutralization of acid. For this purpose, the drugs “Phosphalugel”, “Almagel” and the like are prescribed.
- Relief of pain with antispasmodics “No-shpa”, “Drotaverine”, etc.
- Elimination of digestive enzyme deficiency with drugs “Abomin”, “Pepsidil”, and others.
- Improved breakdown and absorption of nutrients. For this purpose, you need to take “Cerukal”, “Festal”, “Mezim”, “Pancreatin”, “Creon”.
If a deficiency of vitamins and microelements is detected, a vitamin-mineral complex like “Multi-Tabs” is also prescribed.
On a note! Despite the traditional list of medications, different medications are prescribed for each individual case. The above list is not considered the only correct one and may vary depending on individual symptoms and the patient’s intolerance to certain substances.
Folk remedies
It is impossible to cure atrophic focal gastritis on your own. But traditional medicine can serve as additional methods of therapy, unless the doctor thinks otherwise. Be sure to consult with him before trying traditional medicine on yourself.
Effectively reduce excess stomach acidity:
- potato and cabbage juice;
- decoction of mint, linden and chamomile;
- infusion of calamus, calendula flowers, and knotweed.
They drink 100 grams 2-3 times a day before meals for no more than 10 days in a row.
If you are worried about abdominal pain, a decoction of mint, cyanosis, watch, oregano, chamomile, and lemon balm would be appropriate. Infusions of licorice, marshmallow, flaxseed, and plantain leaves provide an enveloping and healing effect.
It is also worth drinking infusions of peony leaves, oregano, St. John's wort, and valerian roots. They have a beneficial effect on the nervous system: they calm, relax, and help the body cope with illness faster.
Diet
The diet for atrophic gastritis is strict and it is necessary to adhere to it for at least the first six months during and after treatment. But doctors do not advise patients to indulge in prohibited foods after this period and strongly recommend continuing to eat only healthy foods throughout their lives.
The diet includes the following:
- the meat should not be fatty or heavy, poultry and rabbit are allowed;
- you can have vegetables with a high level of fiber, as well as ripe, fresh, non-acidic fruits and berries;
- dairy products and eggs have a positive effect on the body;
- Pasta and various cereals are allowed.
Products must be boiled or steamed. They should be consumed warm, 5-6 times a day in small portions.
Even for a healthy person, it is important to drink plenty of fluids, preferably low in sugar and without gas. Mineral water, compote, tea, jelly, non-acidic juices, decoctions and infusions are suitable.
From your diet you will have to exclude spicy, salty, fried foods, alcohol, carbonated drinks, as well as smoked foods and store-bought foods with a high content of chemicals. It is advisable to quit smoking.
Patients with an acute form of atrophic gastritis are prescribed table No. 1, and during the period of remission - table No. 2 according to Pevzner.
Folk remedies
Traditionally, folk remedies are used to treat atrophic gastritis. The most effective recipes have a beneficial effect on the mucous membrane, and the mild effect of herbal remedies causes virtually no side effects.
Recipes such as:
- Mix a glass of fresh honey with half a liter of olive oil and the juice of 2 lemons. Store the mixture in a glass container in a cool and dark place. Drink 1 table. spoons, three times a day, 30 minutes before meals;
- take propolis tincture 30%, 20 drops, after diluting with water, 3 times a day for 21 days;
- mint leaf 1 table. Pour a glass of water over a spoon and heat over low heat for 10 minutes. Drink the strained broth at the table. spoon three times a day;
- take 1 table each of fennel and valerian rhizomes. spoon, mix 6 tablespoons of chamomile and 2 tablespoons of mint leaf. Take 2 tablespoons of the resulting mixture. spoons and pour a glass of boiling water. Drink a glass after the infusion has cooled and been strained;
- mix half a glass of honey and fresh aloe juice. Take a tablespoon before meals, 3 times;
- Take juice from sea buckthorn berries in a glass, with the addition of a teaspoon of honey, an hour before meals;
- if atrophic erosive gastritis is noted, treatment with sea buckthorn oil has a good effect. To do this, drink a table every day for a month on an empty stomach. a spoonful of butter.
Folk remedies should not be used as the only method of treatment. Only a comprehensive intake of medications and home recipes can have the desired positive effect.