The result of a decrease in intestinal tone and a failure of its normal functioning is discomfort, disruption of the digestion process and constant constipation. Intestinal atony is the main cause of this condition, and implies a decrease or complete cessation of peristalsis of the hollow walls of the small or large intestine. What role does peristalsis play for the human body and what it is is a little-known concept, especially for people who do not specialize in medical matters.
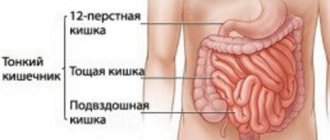
Peristalsis is the process of contraction of the muscles of the hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract, ensuring the movement of the food contained in them to the exit. Violation of peristalsis and the norms of contraction of the intestinal muscles lead to atony, disharmony in the gastrointestinal tract, and an increase in the time interval between bowel movements.
The prospect of weak muscle function threatens the appearance of frequent and painful constipation, which without proper treatment over time turns into a chronic condition.
Atonic constipation can be an alarming signal, a symptom of other disorders and diseases of the body, so a visit to a gastroenterologist for examination is advisable.
Timely and comprehensive therapy for atony, including taking medications, following a diet and aiming to restore and improve peristalsis, leads to positive dynamics and a beneficial effect in the treatment of gastrointestinal pathology such as intestinal atony.
Causes
Various factors can lead to the development of intestinal atony. Possible reasons that provoke a weakening of colonic motility:
- insufficient physical activity (physical inactivity);
- unbalanced diet;
- medicines;
- chronic diseases of the digestive tract;
- congenital pathologies of intestinal development;
- neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature;
- surgical operations in the abdominal cavity.
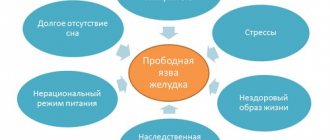
Some of the common reasons for decreased tone of the digestive organs are: poor diet and insufficient physical activity. A sedentary lifestyle and lack of adequate physical activity reduces the strength and number of peristaltic movements in the colon. Atony can be triggered by an unbalanced diet, when high-calorie carbohydrates predominate and there is not enough dietary fiber (fiber) in the diet. In some cases, chronic stress and psycho-emotional stress can cause the development of this disease.
Antispasmodics, antidepressants, narcotic analgesics, antiulcer drugs, sorbents, and antacids lead to a decrease in peristalsis. The tone of intestinal smooth muscles can decrease with endocrine pathology, congenital defects in the development of the digestive system, oncology, after surgical interventions, and during menopause.
Often, intestinal atony is diagnosed in late pregnancy (in the third trimester). It occurs due to mechanical compression of the colon by the uterus or increased synthesis of female hormones. One of the actions of progesterone is to relax the smooth muscles of internal organs.
If you can eliminate the causes of intestinal atony, the chances of achieving a full recovery increase significantly.
Physiotherapy
Exercise should become a habit every day. Swimming, cycling (exercise machine), morning exercises and walking in the fresh air are best. You can spend at least 3-4 hours in the fresh air every day. It is recommended to combine a walk with performing simple physical exercises to strengthen overall muscle tone.
Along with taking medications, the doctor prescribes physiotherapy: electrophoresis, a complex of exercise therapy, paraffin for the abdominal cavity and a contrast shower. A set of procedures will speed up recovery and have an effective effect on the intestines. Doctors strongly recommend going on vacation to a village or a sanatorium that specializes in diseases of the digestive tract. Psychologists advise practicing meditation and self-hypnosis to avoid stressful situations as much as possible. A sick person must give up bad habits. You should pay attention to your health status and symptoms of diseases in a timely manner. The earlier the disease is detected, the easier it is to treat.
Clinical picture
Intestinal atony is characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations. The severity of the symptoms of the disease depends on the severity of the pathological disorders and the severity of the decrease in motor function of the colon. Patients complain of constant constipation and digestive problems. Evacuations occur less than 3 times a week. This leads to a change in the structure of stool, which becomes too dry and hard. The act of defecation can be uncomfortable, even painful. Rare bowel movements are a defining diagnostic criterion.
There is the appearance of belching, nausea, intense pain in the abdominal area, and an imperative urge to defecate. Severe atony can result in intestinal obstruction. I am worried about a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, flatulence (increased gas formation). This condition affects the patient’s well-being. There is weakness, decreased performance, and increased fatigue. Due to malabsorption of nutrients, hypovitaminosis and anemia often develop.
What is gastric atony
Gastric atony is a sustained relaxation of the muscles of this organ, loss of tone in its walls. At the moment when a person begins to consume food, the stomach relaxes, but when the chewed mass enters it, the walls contract, and the food is, as it were, covered on all sides by the muscles. This function is called peristalsis; if under the influence of any reasons it is inhibited, then food stagnates and is ineffectively digested. It is easy to understand that such a phenomenon causes discomfort and problems in the operation of the system as a whole.
Specialist Note: There is a disease called hypotension, and it has similar symptoms and development mechanisms. Its essence lies in a decrease in the activity of peristalsis, which complicates the processes of digestion of food masses. Atony, in turn, is a relaxation of muscles of a stable nature, that is, it is a more advanced and complex problem in gastroenterology.
Gastric atony
Diagnostics
Intestinal atony may be suspected during the clinical examination of the patient. In addition to standard tests (blood, urine, stool, and helminth tests), it is recommended to conduct additional laboratory and instrumental research methods. To assess intestinal motility, radiography using a contrast agent (for example, barium sulfate) is prescribed. To exclude an organic cause for the development of atony, resort to:
- ultrasound examination;
- irrigoscopy;
- colonoscopy;
- biopsy with further histological examination.
Photo: ALPA PROD / Shutterstock.com
In severe doubtful cases, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may be used.
Types of disease
According to the mechanism of onset and further development of the disease, colon dyskinesia is divided into:
- primary form - an independent disease affecting the large intestine;
- secondary form - a complication that appears against the background of existing diseases, affecting the organs of the digestive tract.
According to the clinical form of manifestation:
- constipation - most acts of defecation occur with the release of dense stool, followed by short-term diarrhea;
- diarrhea - most of the bowel movements occur with loose stools. In this case, sharp, short-term pain in the abdomen is felt, which goes away after bowel movement;
- mixed form - defecation is accompanied by general weakness, bloating, nausea, and in rare cases vomiting. In this case, the act of defecation ends with constipation or diarrhea in more than 25% of cases.
Dyskinesia is a disease of the large intestine that affects only the lower, final part of the digestive tract. It is responsible for the absorption of water and the formation of feces.
Treatment
In accordance with clinical recommendations, treatment of intestinal atony should be comprehensive, individual, and consistent. The therapeutic course includes the following:
- diets;
- necessary medications;
- resonant electrical stimulation;
- physiotherapy.
It is recommended to follow a diet that will enhance intestinal motility. The patient should receive a balanced diet that ensures normalization of metabolism and restoration of the functioning of all organs of the digestive system. The diet includes foods/meals that contain a high amount of dietary fiber (fiber).
Drug therapy involves the use of medications that can improve intestinal tone and motility. This group includes prokinetics and anticholinesterase drugs. Choleretic drugs have an irritating effect on the intestinal walls. To relieve constipation, it is recommended to use laxatives.
The technology of resonant electrical stimulation is considered an innovative method for treating intestinal atony. Makes it possible to cope with the disease without using medications or surgery. To achieve a therapeutic effect, the individual frequency of the electric current pulse is calculated. As clinical practice shows, recovery occurs in 95% of cases. On average, you can restore the functioning of the digestive tract in 5 sessions.
Intestinal hypotension
A disease, the symptom of which is a slowdown in emptying the body and impaired digestion, is called intestinal hypotension. During normal functioning of the digestive organ, the interval between emptying should not exceed 48 hours. The main symptom of hypotension is frequent and prolonged constipation. This disease can be localized in the small or large intestine. Hypotension is most often observed in older people, bringing particular discomfort to their lives. The disease develops against the background of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and as an independent disease. Hypotension is a delicate problem, so a person is in no hurry to see a doctor. However, this disease should not be ignored to avoid complications.
Basic drugs
To normalize colon motility, digestion and the general condition of the patient, various medications are used. The therapeutic course is prescribed by the attending physician, taking into account the nature and severity of the pathology. Medicines for the treatment of intestinal atony:
| Pharmacological group | Name of drugs |
| Prokinetics | Domperidone, Itomed |
| Anticholinesterase | Ipigrix |
| Laxatives | Regulax, Guttalax, Pokilax, Slabexin, Piconorm |
| Choleretic | Holosan |
| Vitamin and mineral complexes | Vitrum Plus, Vitaton, Alphabet, Supradin |
Prokinetics
Domperidone, which is considered a dopamine receptor antagonist, can be prescribed as a prokinetic agent. The drug not only normalizes the motor function of the digestive tract, enhancing peristaltic contractions, but also has an antiemetic effect. In addition to intestinal atony, it is prescribed for nausea, vomiting, heartburn, gastroesophageal reflux, belching, a feeling of bloating, and flatulence.
Photo: LM99 / Shutterstock.com
Domperidone is not used if the patient suffers from:
- allergy to medication components;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- intestinal obstruction;
- prolactinoma (benign tumor of the pituitary gland).
Contraindicated for children under five years of age. Restricted for use in cases of severe impairment of the kidneys or liver, pregnancy, or breastfeeding. The advisability of using Domperidone for the treatment of intestinal atony in pregnant women can only be determined by the attending physician, taking into account the expected benefits and potential risks. Possible side effects:
- disorders of the digestive system (spasm of smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, feeling of dry mouth, loss of appetite);
- headaches, fatigue, fatigue, emotionality, frequent mood swings;
- allergic reaction (rashes, hives, swelling, eczema);
- feeling of heartbeat;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- frequent urination.
The full list of side effects is indicated in the official instructions for use of the drug. If adverse events occur during the treatment of intestinal atony, the prokinetic agent is discontinued and a new drug is prescribed. Concomitant use with anticholinergic drugs weakens the effect of Domperidone. Antimycotic agents and macrolides increase its concentration in the blood, so you need to be extremely careful when using them in combination. In pharmacy chains you can also find similar medications with the active ingredient domperidone: Motilak, Motonium, Domstal, Motinorm, Domet, Motogastrik.
A good stimulator of intestinal motility is Itomed with the active component itopride. It can be used for the treatment of chronic gastritis, dyspeptic disorders, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, and anorexia. The drug should not be used if you are allergic to the active ingredients of the drug, pregnant, breastfeeding, obstruction, bleeding or perforation of the gastrointestinal tract. Contraindicated in children under 16 years of age.
Typically, patients with intestinal atony tolerate Itomed quite well, but sometimes adverse reactions may occur (headaches, irritability, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, sleep problems, urticaria, rashes, Quincke's edema). Itomed helps accelerate the absorption of other medications. The prokinetic effect does not change under the influence of drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice. The effect of Itomed is enhanced when combined with anticholinesterase drugs. The course of treatment is prescribed by the attending physician, taking into account the cause, severity and nature of the course of intestinal atony.
Anticholinesterase drugs
The therapeutic course for problems with intestinal motility may include anticholinesterase drugs. Ipigrix is a classic representative of this group of drugs. The active component responsible for the pharmacological action of the drug is ipidacrine. Stimulates neuromuscular transmission, restores impulse transmission along nerve fibers, enhances the contractility of smooth muscles of internal organs, including the intestines.
Ipigrix is actively used in neurological practice. Treatment of intestinal atony with anticholinesterase drugs should be under the supervision of a physician. The duration of the therapeutic course is 10-20 days. In childhood, it can be prescribed starting from the age of 12. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, Ipigrix for intestinal atony is contraindicated. Ipidacrine has a tonic effect on the uterus, which can trigger the development of premature birth in a woman. Not prescribed for allergies to the composition of the drug, epileptic seizures, extrapyramidal disorders, angina pectoris, slow heart rate (bradycardia), intestinal obstruction, peptic ulcer in the acute stage.
Laxatives
Treatment of constipation associated with impaired intestinal motor function requires the prescription of laxatives. One of the popular drugs in this group is Regulax. Begins to act eight hours after application. Acting on intestinal receptors, it enhances motor function and ensures rapid emptying of the intestinal tract. Regulax is contraindicated in patients with:
- hypersensitivity to the components of the laxative;
- intestinal obstruction;
- pain in the abdomen of an unknown nature;
- strangulated hernia;
- acute inflammatory pathology of the abdominal cavity (for example, with appendicitis, ulcerative colitis, peritonitis);
- uterine bleeding;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- pronounced loss of water and electrolytes.
Drugs with a laxative effect should be used for intestinal atony in accordance with the instructions. If taken incorrectly, you may experience side effects (abdominal cramps, flatulence, nausea, vomiting, allergic reaction, etc.). The drug is used for no more than 14 days. Guttalax, Pokilax, Slabexin, Piconorm are analogues of Regulax.
Saline laxatives are not used to treat chronic constipation.
How to treat intestinal atony in an adult
Therapy for intestinal atony should be comprehensive and consist not only of drug treatment, but also nutritional adjustments with accompanying special exercises.
Treatment with medications involves the use of cleansing, laxatives or enemas, which increase the tone of the muscles of the intestinal wall and improve its peristalsis.
For intestinal atony, the following drugs are used:
- "Espumizan" - prevents intestinal bloating by reducing the amount of gases formed.
- "Metoclopramide" (in the form of tablets or injections) - has an antiemetic effect and increases intestinal motility.
- "Pancreatin" and its analogues. This enzyme agent helps improve food digestion.
- "Amiridin". This medicine helps improve the transmission of neuromuscular impulses, which enhance the contractile function of the intestine. It can only be used under medical supervision.
- "Regulax" - a natural preparation based on senna helps remove feces from the intestines and acts as a mild laxative.
- “Proserin”. This remedy increases gastrointestinal motility, promotes optimal transmission of nerve impulses and stabilizes neuromuscular conduction. Used only in hospital settings.
Drug treatment of the small intestine for atony begins with the use of prokinetics to increase tone and improve intestinal motility. Cholinesterase inhibitors have these properties. Cholagogues are also included in the treatment.
Laxatives are used only in the initial stages of treatment to normalize the defecation reflex, which has been impaired. There are several types of laxatives, which differ in their mechanism of action. Secretory drugs of synthetic or plant origin are usually used.
The principle of their operation is based on reducing the absorption of water in the intestines, diluting stool and irritating the chemoreceptors of the mucous membrane. These include the following products: preparations of rhubarb root, senna leaves, castor oil, sodium picosulfate, Bisacodyl and others. The main disadvantage of this group of drugs is considered to be the loss of water with regular use, the occurrence of addiction and pain.
Another group of such drugs are osmotic agents. This includes lactulose, a non-absorbable disaccharide, and high molecular weight polymers that retain water. They increase the osmotic pressure of feces, thereby stimulating the secretion of water into the intestinal lumen. Fecal masses become thinner, their dryness decreases, which means that the speed of their movement increases.
The third group of drugs are those whose action is based on an increase in the volume of feces (seaweed, plantain seeds, bran, calcium polycarbophil and others). These are natural laxatives suitable for frequent use. They have no side effects, and their use is more comfortable for the intestines.
Products that facilitate the movement of feces through a lubricating effect are also used: liquid paraffin, almond or olive oil. According to indications, intestinal cleansing is done: subaqueous baths or colon hydrotherapy.
Diet for intestinal atony
When dieting, they refuse high-calorie and refined foods and increase the diet of foods that contain dietary fiber and fiber (low content leads to atony). To eliminate constipation, fermented milk drinks, fruits and vegetables are included in the menu; it is also useful to eat pumpkin, oranges, boiled beets, carrots, peaches, herbs, and bran bread.
It is recommended to drink vegetable oil (1 tablespoon) at night. You can take a few tablespoons every day before going to bed. spoons of wheat bran, they help cleanse the intestines.
Natural laxatives are also recommended:
- plums;
- prunes;
- dried apricots
| Prohibited for use | Approved for consumption |
| fruits that have an astringent effect - pomegranates, quince, blueberries, pears, dogwood, bird cherry | fermented milk products - kefir, yogurt, yogurt |
| vegetables that cause excessive gas formation and irritation of the mucous membranes - cabbage, mushrooms, legumes, radishes, radishes, onions, garlic | porridge from buckwheat, millet, barley groats, pasta |
| rich broths | lingonberries, oranges, peaches |
| rice, legumes (peas, beans) | stale bread |
| mushrooms | lean boiled meat and fish |
| flour and confectionery products, chocolate, other sweets | low-fat broths, vegetable soups |
| smoked, salted, spicy, fried foods, lard | vegetable stew of carrots, tomatoes, zucchini and herbs, seaweed, pumpkin |
| strong coffee and tea | fruit and green teas, infusions of medicinal herbs, compotes, juices, kvass |
It is recommended to drink a sufficient amount of liquid per day (about 2 liters), this will help to better cleanse the intestines. Before breakfast, it is recommended to drink still mineral water (1 glass), which will enhance intestinal peristalsis.
The food you eat should be properly thermally processed - baked, steamed, boiled or stewed. Fried dishes are excluded from the menu. Prepared food should be eaten warm so as not to irritate the stomach. Eat at least 5 times a day in small portions, following a regimen, and it is recommended to combine the diet with walks and gymnastics.
Therapy of intestinal atony with folk remedies
A home remedy for eliminating constipation and normalizing digestion is to consume vegetable oil three times a day, one tbsp. spoon.
Herbal treatment is very popular.
Buckthorn infusion. Take 2 tbsp. spoons of buckthorn bark, brew with boiling water (200 ml) and leave for two hours. Drink the infusion twice a day, 1/3 cup.
A decoction of the string. Pour cold water (0.5 l) 2 tbsp. spoons of dry string and bring to a boil, leave under the lid for half an hour. Take 200 ml twice a day.
A decoction of flax seeds. 1 tbsp. Brew a spoonful of flaxseed with boiling water (200 ml), bring to a boil. Wrap the broth and leave for 1 hour. Drink 2 times a day, 3 tbsp. spoons.
A mixture of honey and aloe. Aloe leaves are cleaned and crushed. Heat 1.5 cups of honey in a saucepan, no higher than 40°C. Mix honey and leaves and leave for 24 hours. Take the product 1 tbsp. spoon one hour before breakfast.
Treatment with leaf tea. Green tea (large leaf) is used for therapy. Tea leaves are ground in a coffee grinder and taken 0.5 dessert spoon before meals 4 times a day.
Tincture of calamus and rhubarb. Calamus and gentian leaves, rhubarb root, taken in equal parts, are crushed and poured in a ratio of 1:10 with alcohol. Infuse for 2 weeks in a dark place. Drink the tincture twice a day, 1 teaspoon before meals.
Burdock decoction. It is effective for persistent constipation. 2 tbsp. spoons of crushed leaves pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave overnight. Take 1 glass of the decoction in the morning and evening before meals.
Tea with oregano. Take 1 tbsp. spoon of oregano, brew with boiling water (1 glass) and leave for a quarter of an hour. You should drink a cup of tea in the morning before meals and in the evening. This tea improves bowel function, relieves spasms and calms the nerves.
Before using folk remedies, it is recommended to consult a doctor and use them under his supervision.
Therapeutic exercise for intestinal atony
The level of physical activity is of great importance for intestinal atony. This is very important for patients who have been on bed rest for a long time due to illness (stroke, myocardial infarction, spinal injuries, severe head injury), as well as for those who are obese due to physical inactivity.
General strengthening physical exercises are important in the treatment of intestinal atony. They are aimed at strengthening the abdominal and pelvic floor muscles.
A set of therapeutic exercises combined with proper breathing and self-massage of the abdomen will help get rid of atonic constipation and increase intestinal peristalsis. Exercises should be performed at a calm pace, with a gradually accelerating range of movements. The duration of each lesson is 20-30 minutes.
These simple exercises need to be performed 10-12 times:
- Lying on your back with your legs raised, perform the “bicycle” exercise. This strengthens the muscles of the thighs and abdominals, accelerates blood flow in the abdominal cavity;
- lying on your back, legs bent at the knees, clasped with your arms and pressed tightly to your stomach. Freeze in this position for a few seconds, return to the starting position;
- standing on your knees with emphasis on your elbows and palms, straighten your arms, squatting on your buttocks, right and left in turn. Exercise helps to enhance peristaltic contractions of the intestines and the release of gases;
- kneeling, straighten and stretch your legs back alternately, arching your back. This strengthens the muscles of the buttocks and back and promotes blood flow from the pelvic organs.
These exercises can be combined well with self-massage of the abdomen. Abdominal massage involves the use of two main techniques:
- deep hand massage of the abdominal muscles from the right inguinal fold upward. Having reached the navel, they descend to the left side of the groin, continuing to massage the stomach;
- massage the lower abdomen, grasping the folds of skin with both hands, right and left, moving them up and down - the right hand moves down, and the left hand moves up and vice versa.
Video on the topic:
Nutrition
For treatment of intestinal atony to be effective, you should eat right. Products and dishes that contain sugars, organic acids, dietary fiber, and coarse fiber will help strengthen the motor function of the digestive tract. It is recommended to expand your diet with syrups, jam, honey, salted fish, smoked meats, pickled vegetables, fermented milk products, kvass, bran, legumes, nuts, cereals (pearl barley, buckwheat, oatmeal, barley), mushrooms, and fresh fruits. With reduced intestinal motor function and a tendency to constipation, some foods should be excluded from the diet (strong tea, jelly, slimy soups, white bread, fatty and flour dishes, mayonnaise).
Photo: ronstik / Shutterstock.com
Cold meals (below 16 degrees Celsius), which should be consumed on an empty stomach, will help improve intestinal motility. For example, okroshka, aspic, ice cream. Drinks that contain carbon dioxide enhance motor skills. Sour cream, cream, egg yolk, and vegetable oil have a similar effect. Some products contain several components that stimulate intestinal motility. Sauerkraut contains table salt, fiber, organic acids, etc.
Indicative menu for intestinal atony:
| Eating | Products/dishes |
| Breakfast | Fresh vegetable salad, cottage cheese, oatmeal, buckwheat with milk, weak tea |
| Lunch | Fresh pear, apple or sliced fruit |
| Dinner | Okroshka, beetroot soup, borscht, boiled lean meat with stewed cabbage or beets, barley porridge with gravy, compote, weak tea |
| Afternoon snack | A glass of kefir or yogurt |
| Dinner | Stuffed cabbage rolls, meatballs, buckwheat, pilaf, vegetable stew, weak tea |
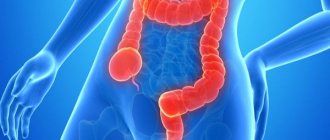
Symptoms of damage in diseases of the large intestine
The large intestine is the final part of the digestive tract.
Its functions include “refinement” of the absorption of substances useful to the body (proteins, vitamins, microelements, liquids), the formation and retention of feces, timely cleaning and emptying. Colon diseases are associated with disruption of these tasks. Signs indicate an inflammatory process, impaired motility (movement of feces), and a mechanical obstruction. Often, symptoms of diseases of the large intestine are formed due to disruption of the innervation or blood supply to certain areas.
Unlike diseases of the small intestine, there is no weight loss, vitamin deficiencies and no symptoms of impaired mineral absorption. Main features:
- bowel dysfunction in the form of diarrhea or constipation;
- the appearance of copious mucus and blood in the stool;
- pain syndrome - characterized by pain along the intestine in the lateral sections, intensified during defecation, after drinking milk, foods rich in fiber, has a dull aching character, relieved after stool;
- increased gas formation, bloating, rumbling;
- For patients, pronounced signs of neurasthenia are typical (dependence of mood on stool, irritability, insomnia). With prolonged constipation, mental state disorders are possible: depression, tearfulness.
All lesions can be divided into:
- diseases of the large intestine of a functional nature - reversible, do not have a specific organic pathology;
- organic intestinal diseases, accompanied by anatomical and physiological changes.
Functional diseases of the colon have several synonyms: dyskinesia, irritable colon, neurogenic colitis. All of them are united by one feature - the absence of organic changes.
The causes of functional disorders are most often associated with disruption of nervous regulation under stress. Less commonly, they are the consequences of previous intestinal infections, low physical activity, and overeating. Disruption of the normal nervous regulation of intestinal functions causes 2 consequences:
- Symptoms of hypertonicity are accelerated motor skills, increased secretion of mucus and water. As a result, diarrhea and cramping pain along the intestines occur.
- Signs of hypotonicity are fecal retention, dry mucous membranes, which leads to prolonged atonic constipation, dull pain in the abdomen.
Since such patients do not have any changes in the tests, and examination of the intestine does not show any abnormalities in the wall, treatment is carried out with the help of neurological drugs, physical therapy, physiotherapy, and folk herbal remedies.
Ulcerative colitis - the disease is most often localized in the rectum, but can spread to the entire large intestine. The reason is currently unclear. More data on hereditary defects. Ulcers form on the mucous membrane. The pain is localized in the left half of the abdomen. Blood is found in the stool.
Crohn's disease is a disease of the large and small intestines that affects the stomach and esophagus. The etiology is unclear. Characteristic symptoms: persistent diarrhea, weight loss, dehydration, high fever, damage to joints and eyes. There are deep ulcers in the intestines that can form fistulas in the pelvic organs, and the lymph nodes are enlarged.
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the process of the large intestine associated with blocking of the outlet with feces and swelling. This disease of the colon is manifested by pain in the right side of the abdomen, fever with chills, and vomiting. Urgent surgical assistance is required. Since the inflamed appendix quickly turns into gangrene, ruptures, causing peritonitis.
Colon diseases do not end with inflammation and ulceration. These changes are considered as provoking factors for the degeneration of mucosal cells into tumor cells (benign or malignant).
Polyps are a type of benign tumor. They are formed from overgrown epithelium. 80% of polyps are associated with villous epithelium. There may be no clinical manifestations. A polyp is detected during a routine examination or intestinal bleeding. The most studied causes: heredity, overeating animal foods, atonic constipation. It is important that every fifth polyp degenerates into a cancerous tumor. Therefore, it is better to remove it surgically in a timely manner.
The tumor can grow outward and not cause disturbances in the passage of feces for a long time. With the internal direction of growth, a narrowing of the intestinal lumen is observed, which serves as a mechanical obstacle to the motor function of the intestine. The “favorite” place for development is the rectum. This creates favorable conditions for diagnosis. Symptoms of colon disease usually manifest themselves as pain with a significant tumor size and bleeding from damaged vessels. Treatment is only surgical in combination with the use of cytostatics and radiation therapy.
Diverticula are saccular single or multiple formations formed in places where the wall is thinned during constipation in older people. Manifested by common symptoms of colon diseases. Can cause partial or complete intestinal obstruction.
There are diseases of the colon that depend on impaired blood supply.
Ischemic colitis is typical for older people with widespread atherosclerosis of intestinal vessels.
Hemorrhoids are excruciating pain in the anal area due to inflammation of the venous ring of blood vessels.
Colon diseases require early diagnosis using laboratory tests and visual inspection of the rectum . The effect of treatment depends on the identified stage of the lesion.
Prognosis and prevention
With functional disorders of intestinal motility, the prognosis is often quite favorable. By prescribing the optimal therapeutic course, in most cases it is possible to achieve recovery. If intestinal atony is caused by an organic pathology (for example, a malignant neoplasm, adhesive disease, congenital defect, severe somatic diseases), and the cause cannot be eliminated, the prognosis will be less favorable. Some patients require surgical treatment, the outcome of which is quite difficult to predict, since it depends on many factors.
A rational, balanced diet and sufficient physical activity will help prevent the development of colon atony. Regular clinical examinations make it possible to promptly identify pathology that can provoke a decrease in peristalsis.
Symptoms
There are two main forms of gastric atony based on the complexity of the situation and the degree of innervation disturbance - mild (which is called hypotension) and severe form (obstruction). Depending on the specific form, the patient may experience different symptoms.
Light form
In mild cases, the main complaint of patients is a feeling of heaviness after meals and constant constipation. Emptying occurs rarely, once every few days, while the volume of excreted feces is insignificant, they are dense and dry in consistency. An important sign is the absence of the normal feeling of relief after bowel movements.
Severe form
A severe form of the disease requires urgent treatment at the hospital. In its acute form, it manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- the feeling of fullness in the stomach does not go away over time;
- there is a feeling of fullness and severe heaviness;
- the pain is dull but intense;
- hiccups, belching;
- vomiting in copious amounts.
With chronic severe obstruction, the patient experiences rapid satiety, a sharp loss of appetite even at the beginning of eating, and a feeling of nausea. An obvious deterioration in well-being usually appears as a result of eating fatty foods or after drinking large amounts of water or drinks. The pain is dull, bursting in nature.