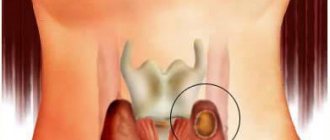
Cystic formations are cavities filled with liquid secretion. They belong to benign tumors. A breast cyst forms in the ducts of the breast. The doctor prescribes a comprehensive treatment, including medications and folk remedies. The choice of drugs and methods of therapy is influenced by the form of the disease and the reasons that led to hormonal imbalance.
Breast cyst - what is it?
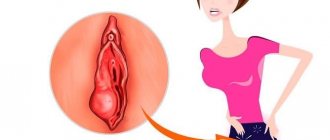
A cyst is a pathological formation, which can be multiple or single, and consists of a wall and liquid contents inside. Breast cysts form in the ducts and have the following characteristics:
- In the thickness of the mammary gland, a cyst is a cavity, a capsule, which is filled with non-inflammatory fluid.
- Before the formation of a cyst, the mammary duct of the gland expands, and then secretion accumulates in it and a fibrous capsule is formed. Sometimes a cyst can form in the terminal sections of the ducts, so in the future it becomes isolated and loses connection with the duct.
- The fluid that accumulates in the cyst varies in color; it can be yellow, dark green, or brown, which depends on its composition and how long the cyst has existed. Often the contents include dense particles that calcify, forming lumps of lime - this is not dangerous, but indicates that the cyst has existed for a long time.
- If the cyst formed a long time ago, then its capsule is denser; if recently, then it has thin walls.
- The woman does not experience any symptoms for a long time.
- Over time, suppuration and inflammation of the cavity may occur.
- Breast cysts often occur together with other dishormonal pathologies of the female reproductive system.
- Sufficiently large cysts can change the shape of the breast.
- A breast cyst can be of different shapes - irregular, round, oval. The size of cysts can range from a few millimeters to 5 cm and even more.
- A typical cyst usually has smooth and even inner walls, but an atypical breast cyst may have growths on the walls that penetrate into the cavity of the capsule; this creates difficulties in treatment, since when puncturing a multi-chamber cyst, it is not possible to aspirate the entire contents of all chambers.
- If there are many cysts - this is called polycystic mammary glands, then they can merge, transforming into multi-chamber clusters. In these cases, cystic tissue can affect over half of the entire breast.
- Cysts can be on one breast or on both mammary glands.
- Most often, the cyst capsule contains benign cells, however, it can also contain malignant ones.
- Breast cysts are quite common, especially in women without children aged 35-60 years.
- A sign of fibrocystic mastopathy is the formation of a breast cyst.
- Sometimes a fatty cyst may appear in the breast; its occurrence is not associated with secretory tissue, but the formation occurs due to the filling of the sebaceous gland of the skin with secretions. If a fat-containing cyst reaches a large size, it can become inflamed, but usually does not cause discomfort, does not bother during lactation and does not form a malignant tumor, so it is not treated surgically. Fatty cysts are best diagnosed with mammography.
Causes of breast cyst development
Medicine sees the main cause of breast cysts in changes in the hormonal balance in a woman’s body, for example:
1. Every 3rd woman with mastopathy develops cysts. In the case when, during the formation of a cyst, the fluid leaves through the duct, an enlarged, deformed duct remains instead. And if the cavity is filled with a viscous secretion, the growth of the cyst progresses.
2. It is believed that the risk group includes nulliparous women after 30 years of age.
3. Excessive production of estrogen, when the production of other hormones is suppressed, increases the risk of developing a cyst. Some sources of information claim that a disorder of hormonal regulation can be caused by taking hormonal contraceptives without a preliminary analysis of the individual hormonal status of a woman. Other authors believe that hormonal contraceptives themselves do not have a significant effect on the formation of cysts. However, their use for more than 5 years increases the risk of developing cancer and other processes in the mammary gland.
4. Hormone replacement therapy, which is often prescribed to menopausal women, should also be taken seriously because these medications affect breast tissue. Often, after taking hormones, a woman’s appearance of new tissue and cell growth are stimulated, and it is not known how these neoplasms will behave in the future in the breast tissue. Therefore, in the case of hormone replacement therapy, X-ray monitoring should be carried out every six months, since such changes may not be noticeable on ultrasound.
5. Also, according to many doctors, the root cause of the growth of breast cysts is the psycho-emotional state of a woman, which, as a rule, affects everything, the general condition of the body, the stability of hormonal levels, and metabolism. It is stressful situations that cause hormonal imbalance - quarrels, troubles and job changes, grievances, dissatisfaction with oneself - and immediately the mammary glands swell and swell. Therefore, women with mastopathy are often prescribed sedatives - valerian, motherwort - in order to stabilize the emotional state and not disrupt the production of hormones.
6. Metabolism and nutrition affect the development of breast cysts. Nutrition determines a woman’s metabolism and weight. Even a 2-kilogram weight gain can affect the mammary glands, since adipose tissue contains estrogens. Excessive obesity and metabolic disorders lead to hormonal imbalance.
7. Provoking factors for the development of cysts are mastopathy, thyroid diseases, ovarian dysfunction, inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages and the uterus itself - endometritis and salpingitis (see inflammation of the appendages - symptoms and treatment). Abortion (consequences) is a powerful hormonal stress for the body, which leads to an imbalance of all systems and organs in a woman’s body.
8. Also, osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine plays an important role in the development of breast cysts.
9. Many scientists suggest that there is a connection between the formation of cysts and dysfunction of the gallbladder and biliary tract.
Many people are interested in the question: If there are cysts in other organs, is it possible for them to appear in the mammary gland? There is no connection with cysts in the kidneys, liver, or ovaries with breast cysts.
Many women, having heard the diagnosis of a breast cyst, mean that this is an oncological disease and that they will be left without breasts. Surgical intervention is indicated if the cyst is large, causes serious concern, and there is really no other way out.
Classification
There are several types of cysts in the mammary gland. They differ in the nature of their course, localization, and each of the tumors requires individual treatment.
Solitary
It is formed in the form of a capsule, has different color, but not thick contents. This single formation develops in one of the glands; a cyst of the left breast is more often diagnosed. Shows a minimum of signs at a small size. Discomfort is felt when the walls of the tumor grow and the adjacent ducts are compressed.
Fibrous
The tissue is capable of rapid growth and degeneration, which increases the risk of developing cancer. The connecting partitions form several cavities in which the substance accumulates. The contents of such a cyst in the mammary gland can be released from the nipples.
Atypical
This type of formation does not form walls during development, which leads to the growth of its elements inside the gland. More often it is localized in the dilated duct, periodically becomes inflamed and increases in size. If an atypical cyst in the chest hurts quite strongly, this may indicate the development of small papillomas or cancer cells.
Multi-chamber
Multiple small capsules and cysts form in the gland, which gradually merge. There can be many compounds; the contents in each compartment differ in composition. Complex formations often affect the shape of the breasts, making them disproportionate.
Fat
The reason for the appearance of a fat capsule is clogging of the sebaceous glands. This functional disorder is associated with pregnancy and lactation. A benign cavity contains milky inclusions inside. The separated dead lipids are processed into an oily liquid.
Symptoms of a breast cyst
Small breast cysts may not bother a woman at all, and the patient can only learn about their existence after a thorough self-diagnosis, or after visiting a mammologist. And if the cyst is medium or large in size, then a woman may feel a sensation of some kind of compaction and slight pain in the formation before menstruation. As the cyst grows, it puts pressure on the tissue around it, causing discomfort.
- With a large breast cyst, symptoms can be characterized by a burning sensation, soreness of the place where it is located, nagging pain, and unevenness when palpating the tissue near the cyst.
- The cyst is sometimes accompanied by discharge from the nipple, in which case it can be assumed that it communicates with a duct (see discharge from the mammary glands).
- A small cyst makes itself felt only in the periods before menstruation, while large cysts bother you constantly and do not depend on the menstrual cycle.
- The huge size of the cyst creates a noticeable deformation of the gland, even the color of the skin changes, it becomes reddish, and over time, bluish.
- If the size of the cyst is not large, then it does not threaten the patient’s life or reduce the quality of life.
- However, with giant cysts and with the addition of an infection, with inflammation and suppuration of the breast cyst, the woman experiences noticeable discomfort.
- If inflammation develops in the cyst, high body temperature, redness of the mammary gland occurs, and the lymph nodes in the armpits become enlarged.
- It is very rare, but there are clinical cases when a cyst degenerates into a cancerous tumor. And the presence of fibrocystic mastopathy in a woman increases the risk of breast cancer.
What sizes do they come in?
- Small formations (about 0.5 cm) are considered safe. Their formation is not accompanied by any symptoms. Usually discovered during a routine examination or mammography. This is the so-called norm for cyst formation.
- Medium-sized seals (from 1 to 3 cm) cause some discomfort. The woman begins to experience pain. This is due to the fact that the tissues grow, increase in size and begin to put pressure on the milk ducts. During this period, girls usually consult a doctor for advice.
- With a size of 3-4 cm, the cyst is clearly visible. The girl can feel the tumor on her own. Such seals are considered quite large.
A size of 4 cm falls into the category of very large. Cysts usually do not grow to this size. If hormonal therapy fails to stop cell growth, the seal is removed. Resection is subject to formations from 3 cm in diameter.- Five-centimeter cysts are considered gigantic. The risk of rupture is very high. These cysts are immediately removed and their cells are sent for cytological examination. This size can be achieved if a woman persistently ignored signs of a tumor and did not consult a doctor. Or if the cells began to actively divide, and unusually rapid growth occurred (in this case, there is a high probability of cancer).
- Formations larger than 5 cm are rare. Typically, such neoplasms rupture, the internal fluid spreads into the tissues, the walls of the cyst stick together and can resolve on their own. This happens rarely (about 2% of cases). In place of a burst cyst, a new one most often forms. Also, when a rupture occurs, sepsis (blood poisoning) can occur. If it is not eliminated immediately, it can even lead to death.
Large
Large neoplasms are usually classified as lumps larger than 3 cm. As a rule, they are under constant monitoring. If the tumor was discovered when the size was already large, the doctor will refer you for puncture (cell collection) and cytology (determination of cancer cells). If the result is negative (if there is no cancer), resection (removal) of the cyst will be performed.
Large formations are visible to the naked eye. New growths from 3 cm visually change the outline of the mammary gland. The breasts become asymmetrical, uneven, “with lumps.”
Neoplasms larger than 5 cm pose a serious danger to a woman’s life.
Little ones
Small cysts include neoplasms from 0.1 to 1 cm. Such seals are not removed. Controlled with drugs containing hormones.
Seals up to 15 mm do not pose any threat to humans. Usually detected on ultrasound. Their treatment involves prescribing medications that will help them resolve or prevent their growth in the tissue.
Seals from 1 cm are under constant monitoring. An ultrasound of the mammary glands is performed twice a year to monitor the size. If growth is slow, then the patient is prescribed medications.
Small tumors are usually easier to treat. Their walls are formed from a thin layer of cells that easily dissolves.
Seals that reach 2 cm are considered small, but are already on the verge of medium. They are monitored three or four times a year. To prevent growth, hormonal drugs are prescribed.
If the tumor is not growing, then there is nothing to worry about.
If even slow growth is observed, it is better to send the cells for cytological examination.
Diagnosis of a cyst
Even when examined by a mammologist by palpation, the doctor can identify a cyst if it is of medium size, while small cysts can be determined using ultrasound and mammography. Using ultrasound, you can determine whether there are intracystic formations in its cavity, and mammography can provide detailed information about the shape, size, and exact number of cysts. Ultrasound allows you to distinguish a fibroadenoma from a cyst.
Also, in difficult cases, the doctor may refer you for an MRI of the breast; however, this diagnosis is used everywhere as the safest and does not have a negative effect on the body. But the consequences of the influence of a magnetic field on the body have not yet been precisely studied. According to physicists, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging affects the entire body in a negative way.
Therefore, before agreeing to such a diagnosis, you should establish a clear need for it. If this is not important, then it is better to refuse unnecessary stress on your body.
If papillomas are found in the cyst, then a biopsy can be taken for examination under the control of an ultrasound sensor. Such material is subsequently sent for histological examination if the number of epithelial cells is high, therefore, this is a suspicion of breast cancer. The same conclusion may follow if the aspirate is brown or brown in color.
What is the maximum size for removal?
There is no maximum size for deletion. Resection can be performed on both small (up to 20 mm) and large tumors.
For large tumors, a puncture is performed. A small amount of fluid is removed and sent for cytological examination. If the neoplasm is benign, resection is performed with removal of adjacent tissue. If there is a suspicion of a malignant tumor, the entire mammary gland is removed.
The maximum size can be anything. If the tumor has not yet ruptured, then resection surgery can be performed. The main problem when removing giant tumors is the risk of tumor rupture during surgery.
If lumps appear in the chest, you should consult a doctor. Regardless of the size of the cyst, you should not self-medicate. A competent mammologist will select the most gentle regimen for recovery.
Treatment of breast cyst
If a woman is diagnosed with a breast cyst, she should undergo a thorough examination for hormonal status, be examined by a gynecologist, and in no case self-medicate.
Is it possible to massage the mammary gland?
The mammary gland has very delicate tissues and it is impossible to perform an intense massage of the breast in order to squeeze out fluid through the nipple, it is very dangerous, the mammary gland should not be touched again, let alone intensively massaged. Under no circumstances should this be done. Try not to injure the mammary glands with underwear, try to prevent bruises, treat the skin on your chest with care, as you age, you can lubricate it with olive oil, this will make it more elastic and not so dry. It’s a completely different matter if a woman has given birth and her breasts are filled with milk 2-3 days after birth, this is an exception when massaging is simply necessary to avoid stagnation and lactation mastitis.
The cyst can resolve on its own, does it need to be treated?
Spontaneous resorption of a cyst is an extremely rare occurrence, so you should not start the process and treat small cysts conservatively, and for 1.5 cm cysts, a puncture is indicated to collect the contents, then ozone or air is introduced into the cavity to smooth out the walls. This procedure will help establish the diagnosis and prevent relapse.
What conservative or alternative treatment for breast cysts can be carried out?
Only a doctor can prescribe treatment for a breast cyst after a thorough diagnosis or after surgery - these are various dietary supplements, homeopathic drugs, herbal medicine, herbal preparations:
- Particularly popular are preparations with extracts from seaweed containing iodine compounds, as well as dietary supplements with extracts from broccoli and cauliflower.
- There are a lot of different herbal mixtures that are specially selected so that they have a positive effect on the liver and metabolic processes, and increase resistance to stress.
- As for compresses at the beginning of the inflammatory process, the best decongestant, absorbable and anti-inflammatory are cabbage leaves and alcohol compresses. Again, this is used only after diagnosis and prescription by a doctor.
No self-medication for breast cysts should be performed
Why? Any treatment with herbs or compresses is unacceptable without the exact instructions of a doctor, who must monitor the condition of the woman’s cysts over time. Self-treatment is unacceptable, because without establishing an accurate diagnosis, establishing whether there are any formations, determining whether they are benign or malignant, you cannot experiment with your health.
Oncological tension has increased significantly in recent years, and what is benign today may turn into an oncological process tomorrow. Self-medication can speed up this process and lead to the saddest thing.
If the cyst begins to grow, then under ultrasound control, treatment of the breast cyst is carried out using drainage - a fine-needle puncture, in which the capsule is punctured and the contents are aspirated, followed by the introduction of ozone or air into the cavity. This method is used only for single-chamber cysts without a malignant process or existing intraductal papilloma. After such treatment, annual or semi-annual monitoring by a mammologist is necessary for timely detection of relapse. If during the procedure the contents were completely removed, and histology did not reveal cells prone to growth, and according to ultrasound data, fluid was also not detected, then in 80% of cases the walls of the cyst will shrink and there will be no relapse. However, in case of fluid retention, its accumulation will continue and the procedure is repeated.
In some clinics, after collecting fluid, ethyl alcohol, rather than ozone, is injected into the cyst cavity; this is not a safe method, since it often leads to tissue necrosis. And if you are faced with such aspiration, ask what is injected into the cavity after aspiration; even the introduction of air is better than alcohol.
Simple cysts in most cases do not require surgical intervention, but if there is parietal growth, then puncture is necessary to exclude oncology. If benign neoplasms are detected, the cyst and neoplasm are removed within 30 minutes under local anesthesia by vacuum biopsy. But, if it is a malignant neoplasm, then this is a different situation and the woman is sent for oncology treatment.
In cases where repeated dehydration of the cyst with the introduction of ozone does not produce results, it continues to recur, and no malignant cells are detected, only in this case the cyst is removed in the same way described above.
How safe are such operations?
- If a woman is worried that she may be left without breasts, there is no need to worry - even very large cysts can be treated in some way without removing the breast.
- Any doctor strives to preserve the beauty of the mammary glands, so incisions and any consequences of surgical intervention remain invisible.
- According to statistics, from 1 to 4% of cases, malignant neoplasms still develop inside the cyst. Therefore, it is worthwhile to be examined in a timely manner, carry out the prescribed treatment and trust your doctor.
- The scar after sectoral resection remains for life, and if a woman wants to give birth to a child, tissue truncation can affect lactation, since some ducts will be destroyed, which can lead to stagnation of milk. Therefore, if a woman is young and plans to give birth, then it is better to exclude interventions on the glands.
The main causes of the disease
Medicine identifies several causes that can lead to the appearance of polycystic disease. At the same time, the provoking factors of single and multiple cysts have their own individual characteristics.
Experts believe that the development of the disease is provoked by a disturbance in the exchange between the following hormones:
- Progesterone (deficiency).
- Testosterone (excess).
- Estrogen (fluctuations in different directions).
In recent years, the number of episodes of polycystic disease has increased several times, and the disease is diagnosed not only in adult women, but even in teenage girls.
| Single seal | Multi-chamber seal |
| Thyroid diseases. Ovarian diseases. Inflammation of the genitourinary organs. Disturbances in endocrine and hormonal structures. | Hormone imbalance. Genetic predisposition to benign lumps. Inflammatory diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems. Abnormalities in the thyroid and adrenal glands. Diabetes. Obesity. Mastopathy. No pregnancy before age 30. Repeated abortions. Taking a very hot shower. Frequent visits to the solarium or sunbathing. Chronic depression and stress. Ignorant or long-term use of hormonal drugs, including contraceptives. Mechanical chest injuries. Operations on the mammary glands. Unfavorable environment or harmful working conditions. |