Duodenal ulcer: causes
Duodenal ulcer is an inflammatory disease that has a chronic course and recurrent nature. The mucous and submucosal layer of the intestinal wall is affected with the formation of a defect - an ulcer, the bottom of which is located in the muscular layer of the intestine. The following protective factors are present within the intestine:
- rich blood supply, providing adequate nutrition to mucosal cells and their rapid restoration in case of damage;
- alkaline reaction of the environment, neutralizing hydrochloric acid of the stomach;
- the ability to form protective mucus to destroy or become immune to bacterial agents.
Factors of aggression include:
- acidic environment of gastric juice;
- increased gastric motility;
- intensive synthesis of digestive enzymes.
When the activity of protective factors weakens, and aggressive factors, on the contrary, increase, there is a high risk of ulcers. The disease can be caused not by a single cause, but by a combination of several. Here are the main ones that are possible:
- an infectious inflammatory process caused by certain types of Helicobacter Pylori bacteria;
- chronic stress, frequent nervous strains (due to vascular spasms, blood circulation and nutrition of the cells of the duodenal mucosa are disrupted);
- genetic factors (hereditary predisposition to the disease);
- Irrational regime and diet: long periods of hunger, overload of the digestive system at one meal, “fast food”, abuse of aggressive foods (fried, fatty, smoked, canned foods);
- frequent alcoholism;
- smoking abuse, especially on an empty stomach;
- various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Rural residents are less susceptible to the disease than urban residents - in the city there is a more stressful pace of life and a less healthy diet. The highest incidence rate is observed in adults aged 30–45 years. Ulcers are more common in men than in women.
Types and stages of the disease
The classification of duodenal ulcers is quite diverse and depends on many factors.
By time of occurrence : acute (diagnosed for the first time) and chronic.
According to the nature (phase) of the course: relapse (exacerbation of a chronic ulcer) and remission (when symptoms subside, the process is not exacerbation, there are no complaints
By severity:
- latent (no symptoms, disease does not progress);
- mild (rare periods of relapse, occurring once every 2-3 years);
- average (relapses occur every year at least 1-2 times);
- severe (exacerbations recur 3 or more times a year).
Duodenal ulcers are classified by size (from several millimeters to several centimeters, especially large ones are called giant), as well as by the presence of complications:
- bleeding - destruction of the vessel occurs;
- perforation - all layers of the stomach or duodenum are destroyed;
- penetration - occurs when, due to perforation, the process spreads to neighboring organs, more often to the pancreas;
- stenosis - narrowing of the intestine due to scar formation against the background of an inflammatory process.
Each condition will have its own clinical picture and different treatment tactics, but all patients with a complicated ulcer are considered severe and require emergency medical care.
Symptoms of duodenal ulcer
Below are the main signs of ulcers characteristic of the disease. They can help you suspect a disease and seek medical help, examination and treatment as soon as possible.
- Pain. Localized (located) in the epigastric region (upper, “epigastric” region of the abdomen). They can radiate to the area of the right hypochondrium, to the lower back. They occur approximately an hour after a meal or snack, often at night or early in the morning (“hunger pain”).
- Heartburn. Occurs in 30% of cases of the disease. It is caused by inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the intestine and stomach, as well as a violation of their motility. As a result, the acidic contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus.
- Nausea, vomiting. They don't happen that often. Vomiting may include food or stomach contents. After vomiting, relief occurs and nausea disappears.
- Appetite disorders. More often they manifest themselves as an increase in it, but there is also an aversion to food and a fear of it associated with the occurrence of pain.
- Stool disorders. More often there is a tendency to weaken, the stool is mushy, but sometimes there may be constipation.
- Flatulence. Increased amount of intestinal gases, bloating due to disruption of food digestion.
Peptic ulcer of the duodenum is characterized by a cyclical course: periods of exacerbation of symptoms are replaced by periods of remission (calmness of the process). An exacerbation lasts from several days to 1.5 - 2 months. Remissions can be short or long. During the lull of the disease, patients feel absolutely healthy even without following a diet or medical recommendations. The disease worsens most often in the spring and autumn periods.
Folk recipes
Treating duodenal ulcers at home is a long process. In addition to medications, patients are recommended to use folk remedies. Herbal remedies, honey, aloe, sea buckthorn oil, and mineral water help fight the disease.
Products with sea buckthorn oil
The disease is treated with agents that can envelop the mucous membranes, tighten ulcerative formations on them, and regenerate damaged cells and tissues. Sea buckthorn oil has these properties. The medicine heals damage to the mucous membranes. To suppress the disease, pure malo or its combination with other natural remedies is used.
Recipes revealing how to treat duodenal ulcers with sea buckthorn oil:
- Before breakfast, drink 1 teaspoon of oil on an empty stomach. After taking the medicine, spend 1 hour in bed, periodically changing body position. Therapy is carried out daily until 200 ml of oil is drunk. At the beginning of treatment, heartburn sometimes appears. Tea soda dissolved in water (0.5 teaspoon per glass of liquid with a temperature not exceeding 60 °C) helps relieve the discomfort.
- Recurrence of the disease is prevented by consuming a mixture of oil (1 teaspoon) and honey (1 tablespoon) once a day. They are treated with the drug for a whole year. With daily use of the medicine, symptoms of the disease do not appear.
- To get rid of duodenal ulcer, make a mixture of a 2% solution of baking soda and oil. For one dose, prepare a mixture of 50 ml of soda solution and 1 teaspoon of sea buckthorn oil. Drink the product for 30 days.
Traditional preparations with aloe
Aloe heals ulcers and erosions that occur on the intestinal mucosa. The juice of the plant enhances the effect of the components used in mixture with it and accelerates healing.
The following preparations are prepared based on aloe:
- Combine aloe, honey and butter in equal parts. The mixture is consumed 3 times a day. First, drink 1 tablespoon of homemade medicine, then eat. Honey inhibits the development of bacteria, oil, protecting the mucous membrane with a film, eliminates pain, aloe heals ulcerations .
- From a three-year-old aloe plant, the leaves are cut off and crushed. To 150 g of aloe add 50 g of honey and butter, pour in 10 ml of Cahors. Place in a water bath and heat until the components dissolve. Take 1 tablespoon three times a day on an empty stomach, washed down with milk or soda solution. After 30 minutes they eat. Treatment lasts 30 days. A repeat course is carried out after 10 days.
- Healers have created an effective method that explains how to treat ulcers of the duodenum and bulb. Before breakfast, drink 1 raw egg. Maintain a five-minute interval, eat 1 teaspoon of honey. Then, after a 5-minute break, take a small piece of aloe and eat the pulp. Complete the procedure by taking 1 teaspoon of sea buckthorn oil. Have breakfast 30 minutes later.
Recipes with honey
It is useful to use honey for duodenal ulcers; it improves the functioning of the digestive organs, has an anti-inflammatory effect, relieves heartburn and irritation, nourishes the mucous membranes, and promotes the healing of ulcers.
Treatment of duodenal ulcers is carried out using the following recipes:
- Add 35 g of honey to 250 ml of warm water. Stir until dissolved and drink. Food is taken after 1.5 hours, provided that the acidity of gastric juice is increased. When acidity is low, drink the mixture 10 minutes before meals. Treatment lasts for 2 months. During the treatment period, sweets are completely removed from the menu. If heartburn occurs, it can be neutralized by drinking 125 ml of milk.
- Prepare a mixture from 500 g of honey, 500 ml of olive oil and freshly squeezed juice of 2 lemons. The mixture is made in a glass bottle, capped, and stored in the refrigerator. Before drinking the medicine, shake it up. Drink 1 tablespoon 3 times a day before meals. The interval between taking the medicine and food is half an hour. The pain syndrome subsides on the 5th day. Take the medicine again after a month. Treatment of duodenal ulcers according to this recipe is carried out twice a year: at the end of autumn and at the beginning of spring.
- Combine 500 g of honey and butter. Add 200 g of powder obtained from walnut partitions. The mixture is mixed, consumed on an empty stomach before breakfast, 4 teaspoons.
Herbal infusions
You can treat duodenal ulcers with folk remedies using herbs. Symptoms of the disease will disappear if you take decoctions of the following medicinal plants:
- A collection is prepared from elecampane, licorice, chamomile, calendula, yarrow, marshmallow and blueberry flowers. Measure out 2 teaspoons of each herb. Pour the mixture into 1 liter of boiling water. To infuse, leave for 1 hour. Drink ½ glass three times a day. The interval between taking the decoction and eating is 30 minutes. A home remedy is indicated for the treatment of ulcers with high acidity of gastric juice.
- For low acidity, prepare a collection of aralia, chamomile, St. John's wort, dandelion root, calendula, wormwood, mint, plantain, calamus, and sage. Mix 2 teaspoons of raw materials. Add 1 liter of boiling water to the prepared mixture. Let the mixture stand for 1 hour. Use 125 ml. Food is taken after 30 minutes.
- To 20 g of mint add 10 g of fennel and caraway seeds. The collection is poured into ½ liter of boiling water. Leave to infuse for 30 minutes. The decoction is used for ulcers, which are accompanied by indigestion, intestinal cramps, and bloating.
Mineral water
After the disease transitions from an acute state to the remission stage, patients are recommended to drink non-carbonated alkaline mineral water . The following mineral water is suitable for treatment:
- Borjomi;
- Essentuki No. 4;
- Slavyanovskaya;
- Berezovskaya;
- Smirnovskaya No. 1;
- Jermuk.
Drink healing waters three times a day, 200 ml. If acidity is high, drink warm water, taking small sips. A glass is drunk within 7 minutes and eaten after 30 minutes. Drinking water is allowed 1.5–2 hours after eating.
If the goal is to relieve heartburn, drink water slowly, in small doses (no more than 50 ml) with an interval of 20 minutes.
Before treatment, mineral water is heated to 40°C in order to release gases that provoke increased secretory function.
If secretion is reduced, drink cool water before meals. An interval of 30 minutes is maintained between the treatment procedure and food intake.
If an exacerbation occurs when drinking water, reduce the dose, frequency of administration, or interrupt treatment for 1–2 days. If individual side effects occur, consult a doctor or stop treatment.
The pathology quickly recedes and does not produce side effects if treatment with folk remedies is combined with drug therapy, physiotherapy, diet, and drinking mineral waters. Recovery is accelerated by quitting alcohol and smoking. The risk of relapse is minimized if the patient eliminates provoking factors, strengthens the immune system, and increases stress resistance.
Complications of the disease
Duodenal ulcer disease is dangerous because if left untreated, life-threatening complications can occur.
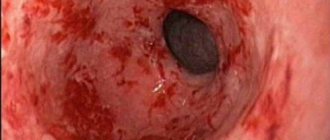
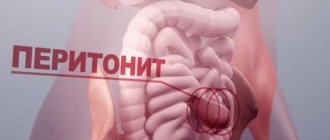
Perforated ulcer - the formation of a perforation (through hole) in the wall of the duodenum. In this case, blood from damaged vessels, as well as the contents of the intestine, leak into the peritoneal cavity, as a result of which peritonitis can develop.
Perforation of the ulcer is accompanied by a characteristic sharp “dagger” pain. The intensity of the pain forces the patient to take a forced lying position on his back or side with his legs brought to his stomach. At the same time, the patient’s stomach is hard – “board-shaped”, the skin is very pale, any movement causes pain. Sometimes an imaginary improvement occurs, but it can cost a person his life. In case of a perforated ulcer, emergency surgery is necessary.
Ulcer penetration. A type of perforation of an ulcer, but not into the abdominal cavity, but into an organ located adjacent to the duodenum. Most often - in the pancreas. During penetration, pain is also characteristic, but the intensity of the pain is less, and the abdomen does not become board-shaped. However, this condition requires urgent hospitalization.
Internal bleeding. As the ulcer grows, more and more tissues are involved in the inflammatory process and destruction, including the walls of blood vessels. Therefore, bleeding may occur from damaged vessels. If the blood loss is small, the clinical picture will be as follows: tarry or dark pasty stools and “coffee grounds” vomit (vomit in color and consistency resembles ground coffee). With massive blood loss, symptoms of shock will be observed: pale skin, cold sticky sweat, progressive weakness, dizziness, panic, loss of consciousness. This situation requires emergency medical attention.
Cicatricial duodenal stenosis. With frequent exacerbations and extensive ulcerative defects, healed areas of the intestine can become deformed, narrowing the intestinal lumen. This will interfere with the normal movement of food, cause vomiting and lead to distension of the stomach. As a result, the functioning of the entire body is disrupted. Cicatricial stenosis requires a surgical solution to the problem.
Malignization, or malignancy of the ulcer. Sometimes a cancerous tumor forms at the site of ulceration, requiring observation and treatment by an oncologist.
Drug therapy
Treatment of duodenal ulcer is carried out using the following medications:
- Pain syndrome is relieved using medications that inhibit the production of gastric juice: Omez, Gastrozol, Bioprazol.
- Products that form a protective film on the intestinal walls are used: Almagel, Maalox.
- To destroy bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed: Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin, Metronidazole. If the therapy has not achieved its goals, a new ulcer treatment regimen is drawn up, which includes other antibacterial drugs: Omeprazole, De-Nol, Ranitidine, Tetracycline.
- To stimulate intestinal motility, the following are prescribed: Trimedat, Cerucal, Motilium.
- Therapy includes analgesics, antispasmodics, multivitamins, sedatives, and antidepressants.
Exacerbated and chronic ulcers are treated using conservative methods from 2 weeks to 1.5 months . The duration of treatment is influenced by the patient’s condition and the size of the lesions. Treatment regimens are selected only by a doctor.
In case of exacerbation, a strict therapeutic diet is followed - table No. 1. When remission occurs, variety is added to the diet. But in both cases, they adhere to fractional meals, take only gentle food, exclude fried, fatty, salty, smoked, and spicy foods. Products are boiled or steamed. Surgery is performed if an emergency situation arises caused by a serious complication: intestinal obstruction, peritonitis, bleeding.
Diagnostics
A local physician or gastroenterologist will be able to determine the presence of an ulcer using the following measures:
- careful collection of anamnesis (patient complaints, symptoms of the disease);
- palpation of the abdominal cavity;
- fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (better known as FGS);
- contrast radiography;
- laboratory tests (stool analysis for the presence of occult blood, clinical and biochemical blood tests);
- tests for the detection of Helicobacter Pylori;
- determination of the acidity level of gastric juice.
Treatment of duodenal ulcer
In order not to lead the disease to complications, after diagnosing a peptic ulcer, it is necessary to immediately begin thorough treatment. The exacerbation stage is treated in a hospital setting. During remission, the patient undergoes treatment at home, visiting a doctor on an outpatient basis. The treatment regimen is developed by the doctor based on an integrated approach. Drug therapy from the following groups of drugs is prescribed.
- Gastroprotectors are agents that protect the intestinal mucosa from hydrochloric acid of gastric juice; in addition, bismuth-based gastroprotectors inhibit the activity of Helicobacter Pylori bacteria (Sucralfate, De-Nol, Venter).
- Antisecretory agents - inhibit the production of gastric secretions, reduce the aggressive effect of gastric acid. This group includes proton pump inhibitors, H2 receptor blockers, anticholinergics (Omez, Famotidine, Gastrocepin).
- Antibacterial and antiprotozoal drugs - to inhibit the vital activity of Helicobacter Pylori (Amoxicillin, Metronidazole).
- Prokinetic agents are drugs that improve gastrointestinal motility and relieve nausea and vomiting (Metoclopramide, Motilium).
- Antacids - for symptomatic treatment of heartburn. They have an enveloping effect, neutralize hydrochloric acid in the stomach (Maalox, Phosphalugel).
- Analgesics, antispasmodics - to relieve pain and spasms (Spazmalgon, Drotaverine).
- Drugs that affect metabolic processes in tissues improve blood supply to the intestinal mucosa and, as a result, cell nutrition (Actovegin, Solcoseryl, B vitamins).
The course of treatment is selected based on the severity of the process, and also taking into account whether the patient has Helicobacter Pylori. After treatment, a thorough examination should be repeated. FGS is required for clarity of dynamics.
A set of measures to get rid of the disease
In addition to medicinal methods of treatment, duodenal ulcers in the early stages can be cured forever with both medications and the addition of traditional methods (after the doctor’s approval) and a complete change in lifestyle. Eliminating stress factors, changing your diet and having a healthy lifestyle always lead to improved well-being and recovery.
The choice of treatment method depends on the cause that caused erosive damage on the surface of the digestive organs. For bacterial infection, a course of antibiotics is recommended. To increase effectiveness, drugs from different groups are prescribed together. In conditions of increased acidity, antibacterial therapy is supplemented with antienzyme agents. In case of a stressful cause of the disease, the main component is sedatives and antidepressants with mandatory consultation with a psychotherapist. To accelerate the healing of damage to the surface of the digestive organs, it is recommended to supplement therapy with drugs with regenerating properties.
In case of a complicated course with intestinal perforation or bleeding, a duodenal ulcer can only be cured by surgical intervention. The postoperative period is spent in a hospital under the supervision of doctors. A multicomponent approach to treating the disease with dietary nutrition and improving the functioning of the nervous system is the basis for a successful recovery.
During an exacerbation of the disease, the patient must be in a hospital facility with bed rest for at least the first two weeks.
Antibiotic therapy
In cases of bacterial etiology of the disease, the basis of treatment is antibiotics. The following active ingredients of drugs are active against the cause of Helicobacter pylori peptic ulcer: metronidazole, azithromycin, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, josamycin.
Antibacterial therapy for the treatment of ulcers is prescribed in several regimens: two-component, three-component, four-component. After the full course, it is necessary to undergo a re-examination for the presence of Helicobacter pylori. In cases of unsatisfactory tests, the group of antibiotics is changed, combined and a second course is prescribed.
To prevent the development of dysbiosis while taking antibiotics, probiotics are prescribed to maintain normal intestinal microflora. Popular effective products: Linex, Hilak Forte, Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin, Bak Set.
In order to finally get rid of bacterial infection in case of peptic ulcer, the course of antibiotics must be completed completely, observing the dosage and regimen.
Medicines that interfere with secretion production
Mandatory components in the treatment regimen for peptic ulcers are agents that reduce or prevent the production of hydrogen chloride and disable histamine receptors and the proton pump. The choice of drugs depends on the etiology and the presence of contraindications. Multidirectional action accelerates the healing of damage and promotes rapid onset of relief. Antisecretory agents help suppress the production of aggressive gastric secretions, relieving inflammation.
Increased production of hydrogen chloride is detrimental to the surface of the digestive organs. High acidity disrupts the functioning of the stomach and corrodes the mucous membrane.
Preparations to protect the mucous membrane of the digestive organs
To relieve pain, heartburn and protect the inside of the stomach and duodenum, antacids and bismuth preparations are recommended.
Bismuth-based medications are harmful to Helicobacter pylori; they cover the inner surface of the digestive organs with a protective coating, protecting them from aggressive factors. Trade names of bismuth-based products: De-nol, Vikair.
Antacids eliminate excess hydrogen chloride, relieve inflammation, and protect the mucous membrane. For ease of use, dosage forms are produced in the form of lozenges that quickly dissolve and suspensions. Combined antacids not only relieve pain, but also eliminate bloating and flatulence.
Medicines to speed up healing
Minor damage to the mucous membrane heals on its own when taking enveloping agents. In cases of extensive ulcers or slow regeneration, agents are recommended to accelerate epithelization and repair of ulcers. Preparations based on protein-free blood of young calves have a minimum of contraindications and side effects. For peptic ulcers with this active ingredient, injections of Actovegin and Solcoseryl are prescribed. Methyluracil stimulates the restoration of damaged epithelium, but has more side effects and contraindications and is prescribed less frequently.
Relief of nausea and vomiting
Prokinetic agents help improve peristalsis, relieve attacks of nausea and eliminate the urge to vomit. Metoclopramide (another trade name Cerucal) disables the vomiting and nausea center in the brain. Prescribed in the form of tablets and injections (in cases where it is impossible to take the drug orally). Motilium promotes better peristalsis and relieves the creeping feeling of nausea. Trimedat relieves spasms, improves peristalsis in both diarrhea and constipation, and eliminates nausea.
Drugs to eliminate spasms
Spasmodic pain in peptic ulcers is relieved using approved drugs: No-shpa (Drotaverine), Duspatalin (Veremed, Dutan, Mebeverine, Sparex), Spasmol, Spazoverine. Drugs in this group relax the smooth muscles of the digestive tract and reduce its contractile functions. To relieve pain and spasms during peptic ulcer disease, only certain groups are allowed that do not affect the condition of the mucous membrane; non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prohibited.
Stabilization of the nervous system
Research into the causes of the disease suggests that it most often occurs against the background of nervous disorders. To improve the psychological state, doctors prescribe sedatives, antipsychotics, antipsychotics, and antidepressants. The choice of group depends on the nervous disorder and the patient's condition. All drugs in these categories are strictly prescribed by a doctor.
Physiotherapy
For peptic ulcers of the duodenum and stomach, especially during exacerbations, therapeutic procedures are indicated. The multidirectional effects of physiotherapy act on different causes of the disease.
During exposure to currents, spasms are relieved, blood supply is improved, and inflammation is eliminated. With an ultrasound procedure and electrophoresis with novocaine, excessive secretion formation is reduced and pain is relieved. After procedures with therapeutic mud, blood circulation becomes better and inflammation goes away. Microwave and heat therapy combats inflammation and pain.
Only the attending physician, after a full comprehensive examination, prescribes a category of physiotherapy in order to enhance the effect of drug treatment for duodenal ulcers.
Therapeutic diet therapy
Anyone who is diagnosed with a stomach or duodenal ulcer must understand that for a complete recovery it is necessary to change their lifestyle and eating habits, which led to this disease. An obligatory component of the complex of treatment of the disease is dietary nutrition, especially at first and during exacerbation.
The basis of therapeutic nutrition is the exclusion of foods that irritate the surface of the internal digestive organs.
The first two weeks of therapy are prohibited:
- alcohol;
- smoking;
- fried;
- seasoned with spices;
- pickled and salted;
- indigestible and rough food;
- carbonated drinks;
- rich broths.
Allowed:
- milk and dairy products;
- porridge;
- eggs;
- lean, easily digestible meat;
- light, lean vegetables;
- all food must be pre-boiled and chopped;
- the temperature of hot dishes is about 50, cold - 40;
- eat six times a day in small portions.
At the next stage, vegetables, fruits, and fruit juices are gradually introduced. In any case, every patient must understand that in order to cure a duodenal ulcer forever, it is necessary to change both the diet (do not eat junk food, fast food) and give up bad habits such as drinking alcohol and smoking. Switching to a healthy diet will prevent the recurrence of the disease and ensure comfortable well-being and digestion.
Traditional treatment recipes
Official medicine does not prohibit resorting to traditional methods. In home treatment, if you follow the doctor’s recommendations for taking medications, physiotherapy, and following a diet, taking natural remedies will increase the effectiveness of the entire complex.
All doctors agree that it is unlikely that duodenal ulcers can be cured forever using traditional medicine alone; without drug therapy, the course of the disease can only be alleviated.
To heal damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive system, sea buckthorn oil is taken 1-2 teaspoons after meals for ten to fourteen days.
Bee products help restore the mucous membrane, relieve inflammation and pain. Honey and propolis are used to treat peptic ulcers at home. Alcohol solutions are avoided to avoid irritation of the digestive organs. Mix honey with olive oil and drink a teaspoon half an hour before meals. Propolis is diluted with butter or vegetable oil and drunk before meals for at least a month.
An effective folk remedy is a decoction of flax seeds. The herbal remedy is infused in a water bath and drunk 50 ml before meals for two months.
Mumiyo or stone oil has multidirectional effects on duodenal ulcers:
- bactericidal against Helicobacter pylori;
- promotes rapid healing;
- strengthens the immune system;
- protects the gastric wall from aggressive environments;
- neutralizes high acidity.
Mumiyo is drunk in its pure form in tablets or diluted with milk and water. The duration of use depends on the severity of the symptoms. To enhance the therapeutic effect, alternate with freshly squeezed cucumber juice.
During illness, it is useful to include bananas in your diet. They have a calming effect on the mucous membrane, relieve inflammation, and normalize digestive processes. Due to the high content of potassium, magnesium and beneficial compounds, they improve the functioning of the nervous system.
Freshly squeezed juices from potatoes and cabbage restore the functioning of the digestive system and help in the treatment of ulcers. Take on an empty stomach two to three times a day.
Phytotherapy
To cure duodenal ulcer permanently, in addition to medication, both traditional medicine and herbal medicine are added.
Chamomile decoction is drunk to relieve inflammation, spasms and regulate peristalsis. Flowers help eliminate nervous disorders.
Yarrow has analgesic and healing properties. The herb is infused for five minutes in a water bath and taken on an empty stomach, half a glass in the morning and evening.
The collection of medicinal herbs has multidirectional effects: yarrow, chamomile, St. John's wort, mint, centaury. The components are taken in equal proportions and left in a water bath for half an hour. Take twice a day, half an hour before meals in the morning and evening.
Clover flowers help relieve symptoms of peptic ulcers. They are brewed with fireweed and drunk half a glass twice a day.
Before taking any medicinal herbs, you should consult your doctor.
Regulation of psychosomatics
Constant chronic stress, depression, and scrolling through negativity in the head do not always respond to treatment with sedatives and antidepressants. Working with a psychologist to identify the reasons that led to the disorder comes first. To improve the situation, you need to change your attitude towards people and situations that cause attacks of anger and stress. Every patient with a psychosomatic cause of duodenal ulcer must learn to easily and calmly assimilate and “digest” information from the outside world. Fear and lack of self-confidence, according to psychologists, lead to damage to the digestive organs. After normalization of the psychosomatic sphere, ulcer healing occurs quickly.
To cure a stomach or duodenal ulcer quickly and permanently, you must strictly adhere to the recommendations of a gastroenterologist for taking medications, physical therapy, combining this with normalizing your emotional state and traditional methods. A single-component approach gives unsatisfactory results, so doctors resort to complex therapy. To avoid the re-development of peptic ulcers, patients are advised to change their lifestyle, eating habits, normalize the functioning of the nervous system and all body systems, and consult a doctor promptly if any ailment occurs.
Nutrition for peptic ulcers
Food should be gentle on the gastrointestinal tract. Aggressive chemical, mechanical and thermal effects are excluded. Dishes are served warm (not cold or hot), and during an exacerbation - pureed and liquid. In the hospital, a special diet No. 1 is prescribed. Food intake is fractional, 5 - 6 times a day in small quantities.
Allowed are boiled dishes from lean meats and fish, meat soufflés, steamed fish balls, dairy products without acid, pureed vegetables and fruits without coarse fiber, boiled porridge, white, dried or yesterday’s bread, weak tea and coffee, with milk, rosehip decoction.
The following are strictly prohibited: spicy, salty, pickled, fried foods, canned food, smoked meats, mushrooms, strong tea and coffee, carbonated drinks, alcohol, fatty meats and fish, sour fruits, berries and juices.
With a serious approach to the question of how to treat peptic ulcer disease and how to be treated so as to feel in full health for a long time, you can achieve long-term stable remission of the disease. According to the controversial opinion of some doctors, a peptic ulcer can be cured forever only if it is caused by the bacteria Helicobacter Pylori. If there is a genetic factor, you can only achieve remission, the duration of which depends on the patient’s lifestyle and his attitude towards his health.