Medical Consultant Gastroenterology Erosive bulbitis: symptoms, diagnosis, prevention and treatment
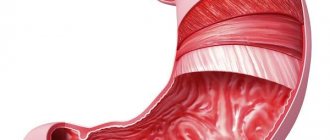
Erosive bulbitis is an inflammatory disease of the initial part of the duodenum, which is accompanied by the appearance of single or multiple erosions on the mucous membrane. The disease occurs with equal probability in men and women. This diagnosis is established exclusively after fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) and based on the patient’s complaints. Treatment necessarily requires adherence to diet and medication.
- What forms are there?
- Reasons for appearance
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Drug treatment
Proton pump inhibitors
- H2-histamine receptor blockers
- Antacids
- Angioprotectors
- Gastro- and duodenoprotectors
- Anti-Helicobacter therapy
Causes of follicular bulbitis
Let's consider the main factors that determine the development of the inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the duodenal bulb, into which the stomach opens with the ducts of the pancreas and gall bladder. These include:
- addiction to bad habits: smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages with any ethanol content;
- prolonged consumption of food high in fat, spicy seasonings, and cooked by frying;
- lack of a balanced nutritional diet and eating regimen;
- high frequency of stressful conditions;
- development of pathogenic microflora, including the appearance of helminths and lamblia in the patient’s body;
- abuse of strong coffee.
Prevention
In order to prevent disease and complications, you should adhere to the following rules:
- limit the consumption of spicy, fatty, fried foods, alcoholic beverages,
- do not take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and glucocorticosteroids for a long time,
- quit smoking,
- undergo preventive examinations by a gastroenterologist, especially if gastrointestinal diseases have already been noted.
When taking NSAIDs for a long time, doctors recommend using them in conjunction with PPIs.
With timely diagnosis and properly selected therapy, the disease does not pose a serious threat to the patient’s life. However, in advanced cases, treatment will be more labor-intensive, which requires patience on the part of the patient. You should not ignore the symptoms of the disease, but it is better to immediately make an appointment with a gastroenterologist and at the same time undergo an FGDS.
Features of the pathology
Follicular bulbitis of the stomach is a type of gastroduodenitis and is often a prerequisite for its development. Factors that negatively affect the mucous membrane of the duodenal bulb lead to impaired motility in this area of the digestive tract and an increase in the reaction of lymphoid tissue in this area of the intestine.
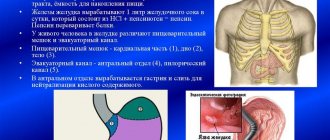
An increase in the amount of gastric juice produced, as well as a decrease in the protective functions of the bicarbonate layer, enhances the aggressive effect of HCl in this area of the digestive tract and the growth of lymphoid follicles. This leads to the appearance of neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the bulb in the form of white bubbles and nodules up to 3 mm in diameter. They indicate the development of follicular bulbitis.
The essence of the disease
Erosive bulbitis is a lesion of the bulbar part of the duodenum, which is characterized by the formation of superficial lesions on the mucous membrane. The main symptom of this pathology is pain in the epigastrium. Dyspeptic symptoms and bleeding may also occur.
This disease is detected in 1-3% of people who have undergone gastroscopy due to pain in the upper abdomen. However, doctors claim that in reality this disease is more common. Bulbit is diagnosed with equal frequency in men and women. Moreover, the chronic form of the disease in most cases is present in people over 40 years of age.
Symptoms of pathology
An acute inflammatory process developing in the duodenal bulb is characterized by nonspecific symptoms, which complicate self-determination of the disease. The clinical picture of the disease does not differ significantly from the symptoms of a number of other diseases of the digestive tract.
Consultation with a gastroenterologist is a necessary measure for timely detection of pathology and treatment. The list of the most characteristic signs of follicular bulbitis includes:
- feeling of pain in the stomach several hours after eating;
- attacks of nausea;
- pain of varying intensity in the abdomen, navel and right hypochondrium;
- rare manifestations of vomiting;
- a feeling of bitterness and metallic taste in the mouth;
- the appearance of problems with bowel movements;
- belching with bile;
- deterioration of health, accompanied by general weakness, headaches.
Types of bulbite
The disease is classified depending on the course and forms of its manifestation. There are two types - acute and chronic. With timely treatment, the disease is cured completely and without consequences. Neglect of the disease leads to a chronic course. Forms of bulbitis are also distinguished according to the severity of the course, depending on the site of localization of the inflammatory process.
- Moderate gurgling. The pathology is characterized by dull pain and a feeling of heaviness after eating. The pathology causes nausea, vomiting, and frequent belching.
- Superficial bulbitis. The inflammatory process affects only the mucous membrane. As a result of inflammation, pain and swelling appear, and it is difficult for digestive juices to enter the duodenum. The condition leads to stagnation of bile and a lack of enzymes required for digestion. Superficial bulbitis has two forms - acute and chronic. The acute form is infectious in nature, the chronic form is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission.
- Catarrhal bulbitis. This type of disease is a severe phase that occurs as a result of neglect of superficial bulbitis. Expansion of capillaries on the surface of the mucosa, impaired intestinal motility, reflux, and the release of large amounts of mucus are observed. This type has a seasonal exacerbation. May be asymptomatic. Becomes pronounced as a result of eating spicy foods, stress or drinking alcohol.
- Erosive bulbitis. With this type, deep damage to the bulb tissue occurs. The inflammatory process is observed up to the muscle layer. Erosion is caused by Helicobacter in combination with gastritis. With chronic erosive bulbitis, the patient experiences discomfort after eating, and aching pain appears at night. On palpation, severe pain appears. With erosive-hemorrhagic bulbitis, traces of blood appear in the stool. Neglect of the disease can lead to the formation of ulcers.
- Focal bulbitis is characterized by the spread of the inflammatory process. Foci of inflammation can form both towards the intestines and towards the stomach. This type of disease often manifests itself as a result of hormonal imbalances. Exacerbations are often caused by vitamin deficiency, prolonged fasting, and strict diets.
- Atrophic bulbitis. This species is characterized by the appearance of sour belching, which appears after eating. The patient is worried about heaviness in the abdomen, rumbling, and abnormal stool.
- Follicular bulbitis. This type of bulbitis develops as a result of inflammation of the lymphatic vessels. Small nodular formations – follicles – appear on the inner surface of the duodenal bulb. The causative agents of the infection are helminths and Giardia. Follicular bulbitis responds well to treatment.
Currently reading: The main manifestations of focal bulbitis and methods of treating the disease
Diagnosis of the disease
Timely seeking medical help from a gastroenterologist allows you to prevent the development of complications, eliminate the problem as soon as possible, and alleviate the patient’s condition. To identify follicular bulbitis, a clinical diagnosis is prescribed. The main methods for identifying an acute inflammatory process in the duodenal bulb include:
- palpation of the patient’s abdomen, which makes it possible to determine the level of pain;
- radiography aimed at identifying disturbances in intestinal motility and determining the volume of the duodenal bulb;
- duodenoscopy is an effective diagnostic method for identifying the level of inflammation, tissue swelling, hyperemia, bleeding of the initial part of the small intestine, as well as detecting erosive damage to the integrity of its mucous membrane;
- pH-metry, designed to determine the level of acidity of gastric juice and the influence of smoking, food intake and other natural factors on this indicator;
- electrogastroenterography, which makes it possible to determine disturbances in the functioning of the hollow muscular organ of the gastrointestinal tract and the initial part of the small intestine;
- antroduodenal manometry to assess the dynamics of pressure in the stomach during contractions of its walls.
The choice of diagnostic measures is carried out by the attending physician, who, after receiving the results, draws up a complete clinical picture of the pathology, including its type, severity, and causes of development.
Symptoms
Erosive bulbitis has very characteristic symptoms. These include the following:
- pain in the epigastric region, which appears 2 hours after eating or at night;
- heartburn;
- constipation;
- sour or bitter belching;
- nausea and vomiting with bile;
- bloating;
- feeling of fullness in the abdominal cavity.
Pain that occurs in the epigastrium can radiate to the navel and left hypochondrium. They usually disappear completely or decrease after eating or drinking milk. Vomiting also reduces discomfort.
Features of the treatment of follicular bulbitis
Elimination of pathology in the initial part of the small intestine involves treatment at home using medications, dietary nutrition and the use of recipes from traditional healers, the effectiveness of which has been tested by many years of practice.
A timely solution to the problem of follicular gastric bulbitis eliminates the risk of deterioration of the patient’s condition, as well as the development of serious complications and irreparable consequences. Therapy for the emerging pathology is reminiscent of methods for solving the problem of duodenitis. The initiation of drug therapy is determined by the attending physician, who, based on the results of clinical diagnosis, prescribes medications. Their list includes:
- medicines to reduce the concentration of hydrochloric acid in digestive juice: Almagel, Phosphalugel, Gastal, Rennie, Gaviscon;
- drugs to reduce the aggressiveness of the fluid produced by the gastric glands: Ranitidine, Omeprazole;
- anthelmintics: Levamisole, Suramin;
- sedative pharmaceuticals that provide the opportunity to reduce stress on the gastrointestinal tract: tincture of motherwort, valerian.
Herbal treatment
It is better to use herbs to treat follicular bulbitis after consultation with a gastroenterologist. Here are some of them:
- Take 50 ml of freshly squeezed juice from plantain leaves. Mix with 5 teaspoons of honey. Drink 1 tablespoon 3 times a day, before meals (diet food).
- Drink 70 ml carrot juice 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
- Prepare an infusion of St. John's wort (pour 2 tablespoons of dry herb with a glass of boiling water), drink 50 ml after meals.
- Decoctions of calendula and chamomile (2 tablespoons pour 250 ml of water).
If you follow your doctor’s recommendations and monitor your diet, you can get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of the disease as quickly as possible and maintain the results for a long time.
Diet and traditional medicine recipes in the fight against follicular bulbitis
A strict regimen of dietary intake plays an important role in eliminating acute inflammation of the duodenal bulb. Acceptable methods of food processing include stewing or cooking in a double boiler or oven.
Eating large amounts of coarse fiber, smoked meats, spicy and fried foods is strictly prohibited when treating follicular gastric bulbitis. After a month of following a strict diet, it is allowed to expand the menu with the introduction of new products.
Among the recipes of traditional healers, the use of which is permitted only after the recommendations of a gastroenterologist, it should be noted:
- a mixture of 45 ml of freshly prepared juice from plantain leaves and 5 tsp. honey, which is recommended to be consumed 1 tbsp. l., at least three times a day before taking dietary meals;
- carrot juice, which has a healing effect on the mucous membrane of the duodenal bulb, is taken in an amount of 60–70 ml three times a day half an hour before meals.
- St. John's wort infusion prepared from 2 tbsp. l. its inflorescences and a glass of boiling water (infuse for one hour), it is recommended to use 50 ml after meals.
Decoctions based on calendula and chamomile also have an anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect on the mucous membrane of all organs of the digestive tract, including the duodenal bulb.
Timely treatment, taking into account the recommendations and prescriptions of a gastroenterologist, provides the opportunity to obtain a lasting positive result, relieve pain, as well as normalize the functioning of the duodenal bulb and eliminate the re-development of follicular bulbitis.
1zhkt.ru
Reasons for appearance
The disease can develop independently (primarily) or be a consequence of another pathological process (secondary) and be symptomatic.
The most common primary factor is infection with Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter pylori is a microorganism that primarily affects the stomach and duodenum, causing inflammation in these organs and the formation of erosions, and subsequently ulcers.
Initially, the microbe is localized in the stomach, where it causes increased secretion of hydrochloric acid. Its excess has a damaging effect on the internal walls of the organ. The acidic contents of the stomach can enter the duodenum, where an alkaline environment predominates. The intestinal mucosa is not adapted to such changes, and therefore its integrity is violated. In addition, the pathogen is able to independently move into the duodenal bulb, where it multiplies and causes damage.
The following conditions are also considered to be the cause of the development of the disease:
- Uncontrolled and prolonged use of certain medications. Most often these are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Analgin, Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Diclofenac) and glucocorticosteroid hormonal drugs (Prednisolone, Dexamethosone). Medicines of these groups inhibit the formation of mucus in the stomach and duodenum, which is the main barrier to the irritant.
- Pathologies of the respiratory, cardiovascular, urinary, endocrine systems and liver.
- Impaired blood supply to the organ.
- Crohn's disease and bowel cancer.
- Burns.
- Postoperative period
The presence of the following risk factors in a patient also contributes to the appearance:
- Frequent stressful situations.
- Alcohol consumption.
- Smoking.
- Irregular diet with a predominance of spicy, fatty and fried foods.
- Exposure to harmful substances (vapors of fatty acids and alkalis, fluorine compounds, etc.)
Chronic erosions often appear after 40–50 years.
Mechanism of bulb inflammation
Digestion is disrupted due to the stomach secreting too much acid. The acidic lump of food enters the bulb. Bile and pancreatic juice also come here. Stagnation of the caustic mixture occurs, as a result of which the mucous membrane of the duodenal bulb is affected. When examining such a patient on FGDS, white bubbles with a diameter of up to 3 mm will be visible.
Stagnation can also be associated with helminths or giardia. Modern research has proven that Helicobacter does not have any effect on this problem of the gastrointestinal tract. With an infectious lesion of the bulb, FGDS reveals a special picture: the mucosa is dotted with small nodules of the lymphatic system. These are both single and group follicles, the diameter of which is 2-3 millimeters.
Follicular bulbitis is often the initial stage of gastroduodenitis - adjacent inflammation of the stomach and duodenum.
Diet
Like any other pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, erosive bulbitis requires a change in diet. If you are ill, you should follow these recommendations:
| Authorized for use | Need to limit |
|
|
Causes of the disease and its symptoms
Factors that provoke inflammation of the duodenal bulb are the following:
- reduced immunity;
- eating large amounts of fried, fatty, spicy food;
- smoking;
- drinking large amounts of alcohol;
- non-compliance with diet;
- emotional overstrain.
When the disease occurs, the following symptoms will be observed:
- pain in the epigastric region, occurring on an empty stomach, sometimes at night, radiating to the navel and back;
- due to stagnation of the food bolus, gastric juice refluxes into the esophagus, resulting in heartburn;
- a bitter taste, sometimes a metallic taste;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting, bringing relief.
Concomitant symptoms of follicular bulbitis are headaches, dizziness, and disturbances in intestinal motility, manifesting themselves as both constipation and diarrhea. As a result of intoxication of the body due to stagnation of food, as well as due to toxins of helminthic infestations, if the lesion is infectious in nature, increased fatigue, pain and trembling in the muscles occur.
Symptoms of erosive bulbitis
You need to know not only what erosive bulbitis is, but also what symptoms are characteristic of it. Erosion of the mucosa over time causes vascular damage and bleeding. In such patients, the character of the stool changes.
It becomes dark and runny due to clotted blood. This condition is called melena.
In severe cases, erosive bulbitis of the duodenum is manifested by vomiting like coffee grounds.
Other common symptoms of the disease are:
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- decreased appetite;
- bitter belching.
With bulbitis, heartburn may occur. It manifests itself as a burning sensation in the chest. Heartburn is a sign of increased acidity.
Damage to the stomach and ampulla of the duodenum is possible due to foodborne toxic infection.
In this case, secondary inflammation develops. In such patients, body temperature often rises.
Follicular bulbitis in pediatrics
In pediatric practice, it is more difficult to diagnose this disease, since in children it is almost asymptomatic at the initial stage. The causes of occurrence are practically no different from follicular bulbitis in adults, with the difference that in children the disease develops faster.
If such symptoms appear, it is better not to delay visiting a gastroenterologist. This will make it possible to diagnose the disease in time and prevent possible complications or the disease becoming chronic.
Patient examination:
- Palpation of the abdomen to identify the location of pain.
- R-graph of the intestine with barium to identify disorders in intestinal motility, describe the size of the duodenal bulb.
- Duodenoscopy is the most effective examination method that allows you to diagnose other gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Measuring the level of stomach acidity , as well as studying the effects of food, smoking, and other reasons on the intensity of secretion and concentration of gastric juice.
- Electrogastroenterography - helps to find pathology in the smooth muscles of the stomach and duodenum.
- Androduodenal manometry allows you to assess the pressure created in the stomach when its walls are compressed.
The choice of such manipulations is determined by a gastroenterologist, and after receiving the results and taking into account the severity of the disease, he prescribes treatment.
Treatment of follicular bulbitis
In the initial stages of this disease, patients are treated at home. Medicines and diet are used for this. Traditional medicine recipes and herbal medicine, proven over the years, also make a positive contribution:
- So that the mucous membrane of the duodenal bulb can recover, drugs are used that reduce the concentration of HCl in gastric juice, astringent and enveloping: Almagel, Gastal, Phosphalugel, Rennie. Physiotherapy, infusions and teas from medicinal herbs (chamomile, plantain, St. John's wort, Irish moss), and propolis medicines have a positive effect.
- Drugs that reduce the production of gastric juice are advisable: Ranitidine, Omeprazole.
- There is no need to take antibiotics for this disease. Antihelminthic (anthelmintic) agents are indicated: Suramin, Levamisole. It is also useful to know herbs that have an antiparasitic effect - tansy, cloves, and wormwood.
- Sedatives: tincture of valerian, motherwort to relieve stress, which also negatively affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Specifics of traditional and folk therapy
During treatment, you should adhere to a strict therapeutic diet. Meals should be fractional, the frequency of eating in small portions is five to six times a day. It is important that food does not irritate the mucous membrane of the duodenum and stomach. Therefore, too hot or cold food is strictly prohibited.
In many cases, the pathology begins to manifest itself against the background of the development of worms, Giardia, so careful deworming is carried out. This type of therapy lasts quite a long time, since the intestines contain not only adult worms, but also larvae and eggs. Treatment uses medications and alternative therapies.
Among the folk remedies for helminthic infestations, tinctures and herbal decoctions based on cloves, wormwood, and tansy are actively used. To prepare the medicine, you need to pour a glass of boiling water over a spoonful of herbal tea. Leave for twenty minutes. Take the prepared tincture three times a day on an empty stomach. It is forbidden to give this medicine to children, pregnant and lactating women.
To speed up the process of restoration of damaged mucous membranes, flaxseed decoction, rosehip-based jelly or oatmeal are used. With their help, you can relieve heavy stress on the intestines and increase immunity. Can be used in the treatment of children.
To prepare the tincture, use the following recipe: take equal proportions of wormwood flowers, oak and buckthorn bark, tansy, pour boiling water in a thermos, leave to infuse overnight. Filter and consume before breakfast. The finished herbal infusion has a laxative effect, so it cleanses the gastrointestinal tract well of various parasites.
Follicular bulbitis requires timely treatment. Do not self-medicate. If you detect manifestations of bulbitis, contact a gastroenterologist.
Diet for follicular bulbitis
The diet, as with gastritis, is strict. Up to 14 days - first table, pastel mode, eliminate physical activity. Then - move on to the fifth table, but eating fried and smoked foods is not recommended for several more months.
Strict adherence to diet instructions is the key to recovery from this disease. It is allowed to eat stewed, boiled or baked food.
It is not recommended to consume large amounts of food rich in fiber, as well as fried, smoked, spicy foods. You need to stick to the diet for at least a month to achieve a positive effect.
gastritam.net
Main causes of the disease
Follicular bulbitis of the stomach is an inflammatory disease, which is characterized by damage to the duodenal bulb. In most cases, patients experience severe pain localized in the epigastric region of the stomach, as well as signs of dyspeptic disorder. The main diagnostic method is fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy.
This manipulation allows for a visual assessment of the condition of the duodenal mucosa. The goal of treatment is to eliminate the provoking factors of pathology and improve the regenerative functions of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract.
Follicular bulbitis manifests itself due to the harmful influence of predisposing factors that are in the fight against local immunity.
The main factors that can provoke the occurrence of bulbitis:
- frequent stressful situations;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- improper and unbalanced diet;
- a large amount of fatty, fried, smoked and spicy foods in the diet;
- gastritis caused by Helicobacter pylori.
The noted factors provoke damage to the mucous membrane, inhibit its recovery processes, which leads to an inflammatory process, manifested by a serious clinical picture.
Interesting read: papillitis of the stomach and how it differs from follicular bulbitis of the stomach.
Diagnostics
A comprehensive examination is required to make a diagnosis. The patient is asked about symptoms, dietary habits and lifestyle, and a chart of previous complaints is studied. An examination is carried out, the abdominal cavity is palpated. The doctor assesses tension in the abdominal muscles and the presence of pain.
X-rays of the duodenum help identify structural abnormalities, spasms and tumors.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) determines changes in the appearance of the mucous membrane: swelling, redness, severity of the capillary network and the presence of defects. It is possible to prescribe an ultrasound examination and fibroesophagoduodenoscopy.
Laboratory diagnostics are carried out:
- The level of pH - acidity is measured, which allows us to draw a conclusion about the type of gastritis.
- The contents of the duodenum are analyzed for the presence of infection if a bacterial or parasitic lesion is suspected.
- A blood and stool test reveals the inflammatory process, the causative agent of intestinal infection.
If necessary, enzyme immunoassay and PCR diagnostics for Helicobacter pylori are performed. Identified polyps are subjected to histological examination.
Classification of bulbitis and its symptoms
There are several subtypes of follicular bulbitis. A typical classification is based on the duration of the symptoms of bulbitis, as well as a kind of cyclicity. There are acute and chronic bulbitis, characterized by periods of remission and exacerbation.
According to the clinical picture, the pathology is divided into the following subtypes:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- gastritis mimicking;
- pancreatitis;
- mixed type.
The disease can occur at any age. The main symptom of bulbitis with follicles is pain, which has varying intensity. The pain is concentrated in the upper abdomen. Characteristic features of pain during inflammation of the bulb: it can spread throughout the entire back, the greatest strength manifests itself at night and on an empty stomach, the acute nature of the sensations generally predominates.
By taking medications designed to reduce the increased acidity of gastric juice, you may notice that the pain subsides and becomes spastic. In such a situation, the cause of pain is improper motor function of the duodenal bulb. With this failure, food is retained in the initial part of the intestine, as a result of which symptoms of dyspeptic syndrome appear.
Signs of follicular bulbitis:
- paroxysmal intense nausea;
- upset stool, alternating constipation with diarrhea;
- sour belching with food particles;
- feeling of discomfort, heaviness and fullness in the stomach.
In most cases, vomiting brings relief, as it helps empty the stomach and duodenal bulb. Follicular bulbitis occurs against the background of severe disruptions in the nervous autonomic system. In turn, this is manifested by weak tremor of the limbs, acute tachycardia, weakness, and bouts of cold. Basically, this clinical picture is observed in children. If you find the listed symptoms, you must consult a doctor to get diagnosed and begin rational treatment for this disease. It is important to start therapy in a timely manner, since the pathology can progress and provoke a number of complications.
vashzhkt.com
Erosive gastric bulbitis - what is it?
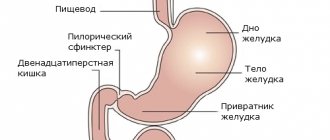
The disease is an inflammation of the duodenal bulb, the section located closest to the stomach. In addition, the bile ducts may also be affected. The pathology occurs in acute and chronic forms and is characterized by the appearance of bleeding erosions on the mucous membrane.
The appearance of defects is provoked by an increased level of acidity of digestive juice, which is usually associated with Helicobacter pylori infection and chronic gastritis.
In the normal state, food is alkalized in the bulb, mixed with bile and enzymes, and the bolus of food moves into the lower intestines.
In the case when the bulbar part of the duodenum fails to neutralize the increased acidity of the gastric environment, the walls of the organ become inflamed and cease to cope with their functions, undigested food stagnates, aggravating the inflammatory process. With the appearance of wounds on the mucous membrane, superficial bulbitis becomes erosive.
In addition to pH imbalance, the causes of pathology may include:
- violation of healthy eating rules: irregular meals, overeating, abuse of fast food, soda, strong coffee, fried and spicy foods, alcohol;
- smoking;
- general decrease in the body's defenses;
- pathogenic activity of bacteria and parasites (giardia, roundworm, helminths);
- intestinal infection (salmonellosis, dysentery); Crohn's disease;
- hereditary predisposition;
- individual characteristics of the body associated with high mobility of the duodenum. The intestine, bending, forms additional loops in which undigested food accumulates, which provides a breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms;
- inflammatory process due to foreign bodies entering the digestive tract;
- food poisoning;
- chemical and thermal burns, injuries to the gastrointestinal tract;
- long-term treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and hormonal drugs;
- long-term stress.
Classification of the disease
There are several forms of pathology:
- erosive-focal - isolated foci of affected areas are observed on the mucous membrane of the bulb;
- catarrhal-erosive, in which the inflammatory process affects the cells of the upper layer of the epithelium;
- erosive-ulcerative - the defects become deeper, the muscle layer of the internal organs is affected;
- erosive-hemorrhagic - blood vessels are damaged, that is, inflammation affects even deeper layers;
- confluent erosive, when individual foci merge, the mucous membrane becomes covered with a filmy coating.
There is no specific “risk” age for developing this disease. It affects both men and women equally.
Causes and symptoms
Simply the presence of parasites in the body is not enough to cause follicular bulbitis. The impetus for the development of the disease can be the following reasons:
- decreased immunity;
- violation of the diet and a large amount of salty and spicy food;
- dysfunction of digestion in the intestines and stomach.
Follicular bulbitis occurs due to an ambiguous reaction of the lymphatic system to lamblia and helminths. If there are parasites in the lymphatic vessels, a large number of bubbles form on the walls of the gastrointestinal tract between the stomach and duodenum. These blisters become very sensitive to the waste products of parasites and, without the necessary treatment, can develop into peptic ulcers.
The symptoms of follicular bulbitis are similar not only to the symptoms of other types of bulbitis, but also to many other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. It is necessary to contact a gastroenterologist if:
- Pain appears in the solar plexus area, which can radiate to the navel, back or ribs. The pain is aching and intermittent and can appear with a long absence of food, often on an empty stomach.
- After each meal, there is a reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. This condition is accompanied by heartburn or unpleasant belching.
- A person feels bitterness in the mouth. The reason for the bitterness and unpleasant odor is not due to belching and heartburn, but because due to the follicles, food is retained in the forebrain and due to stagnation a characteristic odor appears.
- When eating a large amount of food, severe pain occurs in the stomach area or just below. The pain may go away after vomiting. Often meals are accompanied by an unpleasant feeling of nausea.
If these symptoms frequently recur or are persistent, it is necessary to promptly begin treatment for follicular bulbitis, which is successful in most cases.
Causes
As already mentioned, the main cause of all our ailments, including bulbitis, is poor nutrition. To this reason you can add bad habits - alcohol and tobacco abuse.
Strong drugs also often contribute to the destruction of the mucous membrane. Poisoning or injury - all this in different combinations can cause or provoke the development of erosive gastritis.
Genetics also does not come in last place and plays a role. That is, you can consider yourself a member of a risk group if one of your relatives has already suffered from similar diseases.
However, the root cause of the development of bulbitis, just like ulcers and gastritis, is the spread of a special type of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori. Many methods of treating bulbitis are aimed at combating it. And the factors that provoke the development of this bacterium are already listed above.
So, to summarize, the reasons can be structured as follows (they will be valid for all gastrointestinal diseases):
- Violation of the rules of nutrition in a gross form, excess in food and, in contrast, self-torture diets in which the stomach tries to digest itself, frequent consumption of fatty foods and a love of fast food, carbonated water, hot sauces.
- Stress and depression.
- Dormant or active infection in the gastrointestinal tract, expressed in the presence of the same Helicobacter pylori or helminths or Giardia.
- Genetic inheritance.
- Weak immunity.
Of course, most often the cause will not be individual factors, but a combination of any of the listed factors.
Treatment methods
Traditional treatment of follicular bulbitis is carried out in three directions:
- Strict diet. During the treatment of follicular bulbitis, it is necessary to eat food that minimally irritates the intestinal mucosa. Very hot and cold foods, spicy and salty foods are prohibited. It is best to eat foods that are quickly digested and absorbed: pureed soups, boiled meat and fish. Coarse fiber is also prohibited for complete treatment, so it is better to limit the consumption of bread, fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Drug treatment. The main cause of follicular bulbitis is parasites. When treating inflammation, it is mandatory to get rid of lamblia and helminths. Getting rid of parasites, or deworming, takes quite a long time. This is due to the fact that it is necessary to remove not only the parasites themselves from the body, but also their eggs and larvae.
- No antibiotics. For follicular bulbitis, antibiotics should not be used as medicine. They will not help cope with the cause of the disease - intestinal parasites. At the same time, antibiotics can significantly worsen the condition of the human immune system, which is responsible for “protection” against parasitic infection.
For follicular bulbitis, you can use traditional medicine treatment methods, but only after consultation with your doctor.
Basically, with this disease, folk remedies are used to combat parasitic infestation. An effective remedy in the fight against Giardia and helminths is a combination of three herbs: tansy, cloves and wormwood. 1 tbsp. a mixture of these herbs in equal proportions is poured into a glass of boiling water and left until cool (room temperature). The decoction should be drunk in several doses throughout the day. The decoction of these herbs has some side effects, so it should not be used by pregnant and lactating women, as well as children under 12 years of age.
A decoction based on oak bark helps fight and accelerates the elimination of helminth waste products from the body. To do this, the bark is mixed with buckthorn bark, tansy and wormwood. The mixture is poured with boiling water and then cooked for 5-10 minutes. After cooling, the broth must be strained. To improve the effect, brewed herbs can be left in a thermos overnight and consumed in the morning. Every morning you need to take at least half a glass of fresh broth.
After eliminating the parasitic infection, it is important to restore the normal functioning of the intestinal mucosa. Violation of its integrity is of particular concern in children, who cannot always follow a diet and maintain a normal diet. To improve digestion, in this case, decoctions based on flax seeds, rice or jelly, made from rose hips with minimal addition of sugar, are used.
mygastro.ru
Drug treatment
As mentioned above, the main provoking factor for the development of erosions is irritation of the mucous membrane of the duodenum with contents coming from the stomach. The fundamental goal is to reduce acid secretion and stimulate mucosal healing by improving blood circulation in it.
This can be achieved using the following groups of drugs:
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs).
- H2-histamine receptor blockers.
- Antacids.
- Angioprotectors.
- Gastro- and duodenoprotectors.
If the disease has developed against the background of an existing pathology, it is imperative to treat the underlying disease that led to the development of erosive bulbitis.
Proton pump inhibitors
Under normal conditions, the formation of hydrochloric acid requires the entry of acidic hydrogen ions (H+) into the lumen of the stomach. They penetrate there through special channels located in the parietal cells of the mucous membrane.
Drugs in this group disable these acid ion transporters, which leads to a decrease in acidity. In the practice of doctors, the following tools are most often used:
- Omeprazole.
- Omez.
- Pulset.
- Pantoprazole.
- Rabeprazole.
H2-histamine receptor blockers
Histamine, acting on receptors specific to it in the stomach, causes an increase in acid secretion. Medicines “close” the receptors, which is why the histamine molecule cannot have its effect. This group of medications includes the following drugs:
- Ranitidine.
- Kvamatel.
- Famotidine.
- Roxatidine
Antacids
Modern drugs contain aluminum or magnesium bases, which, when interacting with an acid, cause its neutralization. The most commonly used medications are:
- Almagel.
- Maalox.
- Gastal
The drugs are recommended to be taken as symptomatic relief, and not for regular use.
Baking soda acts as an antacid. However, after taking it, carbon dioxide is formed, which “swells” the stomach and causes an even greater increase in secretion and deterioration of the condition.
Angioprotectors
Due to the fact that the development of erosions is significantly influenced by impaired microcirculation, some doctors recommend the use of drugs that protect blood vessels. The main one is Trental. It improves oxygen delivery to tissues, has an antioxidant effect and stimulates improved blood supply to affected tissues. The drug does not affect acid formation in the stomach and the destruction of H. pylori.
Gastro- and duodenoprotectors
For all forms of erosive bulbitis, doctors often prescribe such medications. The most commonly used are Sucralfate and De-nol. The drugs stimulate the production of mucus, which protects damaged areas of the organ from the aggressive effects of acidic foods.
De-nol additionally has anti-Helicobacter activity.
Anti-Helicobacter therapy
If the patient has a confirmed infection with Helicobacter pylori, the doctor’s tactics change and treatment is used aimed at destroying the microorganism. For this purpose, eradication therapy regimens have been developed.
The two main ones most commonly used are:
- PPI + Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin. Treatment course 7 days
- Similar to the previous one + De-nol. Duration of therapy is 14 days.
Treatment regimens are selected by the doctor individually.