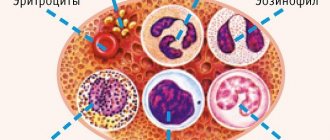
What is ESR
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a blood test that allows you to find out how quickly the blood is divided into its components - plasma and red blood cells. Blood cells are heavier than plasma and leukocytes, so under the influence of gravity they separate and settle to the bottom of the container. The time of this settling is measured by analysis.
During a blood test for ESR, the blood is divided into separate fractions
When a person is healthy, the membranes of his red blood cells are negatively charged, as a result of which they repel each other - as is known from physics, differently charged particles attract, and particles with the same charge sign repel. The disease changes blood parameters, because of this, red blood cells either combine into groups, which reduces their settling time, or change their properties, which slows down the speed of their descent to the bottom. In any case, deviation of the ESR parameter from normal values in any direction allows one to suspect the appearance of some problems in the body.
Video: ESR - what your blood tells you
Why is it important to monitor ESR in the blood during pregnancy?
Red blood cells are red blood particles whose main task is to supply oxygen to body tissues and remove carbon dioxide from them. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate shows the characteristics of the movement of red blood cells in the blood. With a low ESR value, the fetus may lack oxygen, which puts it at risk of developing hypoxia. A value higher than normal may mean a change in the parameters and composition of the blood as a result of inflammatory processes or destructive changes in the body. In any case, discrepancies with the norm are a signal for increased care and additional health checks.
- At the beginning of pregnancy, the female body undergoes serious changes - in particular, blood volume increases, as another constantly growing organism is added, more oxygen is required.
- In the second trimester, the active development of the child begins - basic tissues are laid, organs are formed. This requires a large amount of resources from the mother's body, which is why the ESR continues to rise.
- At the last stage of pregnancy, the baby already takes up a lot of space in the mother’s womb, squeezing her organs, which means that the load on the woman’s body increases. In addition, childbirth is approaching, so the composition of the blood changes somewhat to prevent heavy blood loss during childbirth. All this also leads to an increase in ESR.
If at any stage of pregnancy the body cannot fulfill the required goals, the development of the fetus will go wrong, which can lead to various negative consequences. Therefore, it is very important to monitor the condition of the expectant mother’s body throughout the entire pregnancy, including changes in the ESR value. If there are deviations from the norm, you should consult your doctor.
Ways to clarify the diagnosis
A change in ESR does not always indicate a pathological process. Each organism is individual and a slight increase or decrease may be a variant of the norm.
To clarify the possible cause and nature of the disease, the pregnant woman is prescribed:
- Blood for leukocytes. With inflammation and some oncological processes, there will be an increased level of leukocytes.
- C-reactive protein. It is a marker of inflammation. Reactive protein is always elevated in acute or aggravated chronic processes. CRP never increases with endocrine disorders or cancer.
- Urine examination. The presence of protein, white blood cells, mucus or pus in urine indicates a kidney or bladder infection.
- Biochemistry. Studying the composition of plasma makes it possible to assess the nature of metabolic processes.
- Vaginal smear. Checking vaginal discharge can reveal: inflammatory processes, sexual diseases and some types of infections.
- Ultrasound. Hardware diagnostics are necessary to assess the condition of the abdominal organs.
We recommend: The importance of the TSH hormone in pregnant women and the norm by trimester
If necessary, the gynecologist refers the pregnant woman for a consultation with an endocrinologist, oncologist or immunologist.
Until the cause of the deviations is determined, one should not panic. Nervous experiences will negatively affect the child and worsen laboratory parameters. A woman should remember that modern medicine has reached a high level and if the disease is detected in a timely manner, she has the opportunity to give birth to a healthy child.
What analysis allows you to measure ESR
The list of standard tests, both for health problems and for preventive examinations, includes a general blood test. It gives an idea of the composition of blood and its properties, and includes information on the following indicators:
- hemoglobin, red blood cells, reticulocytes;
- leukocytes and their varieties;
- ESR.
To measure the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, one of two test options is performed, depending on the equipment available in the laboratory and the qualifications of doctors:
- according to Panchenkov (diagnosis of capillary blood);
- according to Westergren (diagnosis of venous blood).
According to Panchenkov’s method, the ESR parameter is measured using some chemical additives, in particular sodium citrate - it acts as an angicoagulant, that is, it inhibits blood clotting. After the blood from the finger enters the test tube, a solution of the chemicals required for the analysis is added to it. The container with this mixture is placed vertically and left in this position for an hour so that the blood is separated into its components. After the specified time, the height of the transparent part of the “column” of liquid is measured - that is, the plasma from which all the red blood cells have sunk to the bottom. This value is used as an indicator of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
According to the Panchenkov method, blood is taken from a finger for analysis.
When performing a test using the Westergren method, similar steps are performed, but the blood is taken from a vein. To measure ESR, a more accurate and detailed scale of 200 divisions is used, in contrast to the scale of 100 divisions used according to the Panchenkov method. This method is considered more accurate and reliable, as well as less susceptible to the influence of various external factors.
The Westergren method is a standard method for determining ESR, known since 1921
Why is Westergren's erythrocyte sedimentation rate tested?
As a rule, Westergren ESR is performed together with other blood tests. This method is included in the list of general clinical blood tests. It allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of the drug intervention or help in the early diagnosis of diseases of various etiologies.
The most common diseases that affect ESR levels in the blood:
- Sepsis,
- Abscesses of various etiologies,
- Autoimmune diseases,
- Arthritis,
- Myalgia of various origins.
It should be noted that an increase or decrease in ESR levels is not an independent disease, but a sign indicating the occurrence of pathological processes in the body. To find out the exact reason for the change in the rate of sedimentation of blood cells, additional diagnostic measures will be required. In some cases, ESR returns to normal without drug or invasive intervention.
Norms of ESR in the blood by trimester of pregnancy
For each period of gestation there is a specific ESR rate, since the tasks facing the expectant mother’s body differ depending on the period. To check whether the ESR indicator corresponds to the period of pregnancy, the examination schedule includes three blood donations at 12, 21 and 30 weeks. The ESR norms can be visually presented in the form of a table of the dependence of the ESR value on the trimester.
Table of ESR indicator by trimester of pregnancy
| Outside of pregnancy | 1st trimester | 2nd trimester | 3rd trimester | Before birth | Postpartum period | |
| Norms of ESR indicators, mm/h | 2–15 | 13–23 | 25–30 | 35–40 | 45–50 | 30–35 |
The norm is considered to be a decrease in ESR to the value for non-pregnant women one and a half to two months after birth. If this does not happen, then it is necessary to conduct an additional examination, as this may indicate the presence of a source of inflammation or other health problems in the young mother.
Some deviations in one direction or another are not critical; they can be caused by the individual characteristics, weight or age of the woman or non-dangerous chronic diseases. If you know the reason, tell your doctor about it. Some medications can also interfere with the test result. In case of incorrect analysis, namely:
- not on an empty stomach;
- day or evening;
- after physical activity;
- under stress;
the ESR value may rise above normal. In addition, there may also be inaccuracies when measuring the parameter. Therefore, if the value deviates from the norm, it is advisable to retake the test, preferably in another laboratory, and consult a doctor with the results of the retest. Based on these data, the doctor can refer the woman to undergo other tests and, based on the totality of all the results, prescribe treatment, if necessary. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate.
During pregnancy, like all women in this condition, I donated blood. Once again, at an appointment with a gynecologist, it turned out that my ESR indicator was greatly underestimated - while the norm at this period was 25 mm/hour, I had 10. At the same time, all other parameters were normal, and I felt extremely well excellent. The doctor suggested not to worry ahead of time, but to retake the blood, since one can never rule out errors when measuring or taking a test, especially if there are no other symptoms of disorder in the body. Repeated analysis showed complete compliance with the norm.
Reasons for deviations
Fluctuations in laboratory parameters depend on the individual characteristics of the body, nutrition, and emotional background. Blood clotting plays an important role. If a deviation from the norm is detected, the doctor may recommend other types of studies to exclude the possibility of developing a pathological process.
Excess
The most common cause of increased ESR during pregnancy is anemia. Normally, red blood cells repel each other, interacting like charged particles. This affects their settling rate. The fewer there are, the less interaction, the faster the subsidence. There are types of anemia when the number of red blood cells remains at the same level, but they lose their properties. This also leads to rapid settlement.
Important information: Normal ESR levels in the blood of children by age (table)
Exceeding the ESR may mean an increase in the level of leukocytes or abnormalities in protein composition.
The reasons for the increased value may be:
- Inflammatory process in the pelvic organs or digestive system. The red cell sedimentation rate can be affected by any inflammation, even caries.
- Kidney pathologies. The presence of pathogenic microorganisms and a focus of inflammation always entails changes in biochemical parameters. During pregnancy in the 2nd trimester, the load on a woman’s internal organs begins to increase, incl. kidneys Pyelonephritis with bacteriuria may develop. Therefore, if the ESR is abnormal during pregnancy, concern arises about the possibility of manifestations of dysfunction of the urinary system.
- Colds.
- Viral, infectious processes.
- Autoimmune diseases of various etiologies, incl. nephrotic syndrome and allergies.
- Rheumatism.
- Fungal infections, parasites.
- Malignant pathologies.
An increase in the indicator may indicate blood thinning, the presence of bleeding (not only visible, but also hidden).
Often ESR is increased in the second trimester and in later stages due to increasing load on the legs, which affects the condition of the veins. Developing varicose veins affect the biochemical indicator.
Accelerated erythrocyte subsidence does not always indicate the presence of a dangerous pathology. Even if the indicator increases above 50 mm/hour, you cannot draw conclusions on your own. If the number increased moderately in the second trimester and in the last months, this is considered normal. A sharp jump is sometimes observed before childbirth. Unreasonable worries can negatively affect your well-being and aggravate the situation. The diagnosis is confirmed or refuted by the results of additional tests.
If the indicator goes off scale, being at the level of 85 or 90 mm/hour, first eliminate the laboratory error in the calculations. If the value is confirmed by repeat testing, the causative disease is identified.
Important information: Table of norms for segmented and band neutrophils in children by age
Decline
Poor health may be accompanied by a decrease in ESR in pregnant women. More often this happens in the early stages due to taking various medications and an unbalanced diet. However, in this case there is a possibility of a number of pathologies:
- Sickle cell anemia. This is a hereditary pathology characterized by a violation of the structure of hemoglobin.
- Developmental muscle dystrophy, called myodystrophy.
- Polycythemia. The disease is associated with excessive synthesis of elements of the myeloid lineage, which is responsible for the formation of red blood cells.
ESR may fall below normal during pregnancy in the third trimester if the water-salt balance is disturbed. The indicator depends on the emotional state and decreases with stress and neurosis.
Deviation of the ESR parameter from the norm
To get an unambiguous answer about the reasons for deviations of the ESR parameter from the norm, the expectant mother needs, as prescribed by a doctor, to undergo an additional comprehensive examination, which will reveal all the information about her condition.
Reasons for deviations
An ESR value that is higher than normal during pregnancy may indicate the following problems in the body:
- anemia;
- increased blood viscosity (due to insufficient fluid intake);
- placental abruption and risk of bleeding;
- inflammation, infection (including intrauterine);
- diseases of a rheumatological nature - systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatism, temporal arteritis;
- renal dysfunction - pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, development of nephrotic syndrome;
- helminthic infestation;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- varicose veins
A low ESR value may indicate any of the following health problems for the expectant mother:
- liver dysfunction;
- insufficiency of metabolic processes;
- poor nutrition;
- stressful situations, frequent neuroses;
- hematopoietic disorder;
- autoimmune processes.
Symptoms of deviations
There are quite a lot of diseases and health problems that cause ESR to deviate from the norm, and each of them has its own symptoms, so it is difficult to combine them into one group. The only thing they all have in common is a noticeable deterioration in their health. That is why at the first signs of the disease - weakness, lethargy, pain, fever - you need to consult your doctor.
Any signs of deterioration in the health of a pregnant woman are a reason to consult your doctor
It is worth remembering that many diseases do not give clinical manifestations and can only be detected by test results or during a doctor’s examination. Therefore, you should be as careful as possible when taking tests and not skip them without good reason.
Treatment
Since a deviation of ESR from the norm is only a diagnostic sign of the presence of a disease, it is impossible and pointless to influence the ESR value itself; it is necessary to treat the original source of the deviation, which additional diagnostics will help identify. Each disease is treated in a specific way, so there is no general treatment.
Some reasons for deviation of ESR from the norm are quite simple to correct. These include those changes in the body of a pregnant woman that do not affect internal organs, but are the body’s reaction to changes due to pregnancy or due to improper actions of the expectant mother:
- If the increase in ESR is caused by anemia, then, on the recommendation of a doctor, a pregnant woman should introduce more iron-rich foods into her diet - apples, buckwheat, liver - and if this does not help, the gynecologist will prescribe iron-containing drugs.
- If the ESR increases due to varicose veins, you need to undergo examination by a phlebologist, after which the doctor will most likely prescribe medications aimed at maintaining and strengthening blood vessels, which will reduce the manifestation of varicose veins.
- Worm infestations can be treated with gentle anti-worm medications. The drug should only be prescribed by a doctor, since many drugs are toxic and prohibited for use during pregnancy.
- Poor diet, frequent stress, lack of fluid intake - these reasons are also quite easy to eliminate after consulting a doctor. If the ESR deviation was caused only by them, then after some time the blood test will return to normal.
- If a high ESR value was caused by an infection in the body, then it must be eliminated. Much depends on the source of infection. For example, caries can be cured without any problems, but a common cold must be treated under the supervision of a doctor, since not all medications and methods are allowed for pregnant women.
For more serious reasons related to diseases of internal organs, tumors, problems with pregnancy itself, it is necessary to contact the appropriate doctors. With timely and correct treatment, the disease can be cured or at least its consequences for the woman and her child can be eliminated.