The high intensity of life in modern society has not had the best effect on the nutritional value of many people. This circumstance has led to the fact that digestive problems are already becoming a common chronic pathology of the digestive tract. And while patients suffering from such disorders try to relieve unpleasant symptoms with the help of advertised pharmacological drugs, dangerous diseases develop in their bodies, such as gangrenous cholecystitis.
Most often, people over 40 years of age, as well as those who are prone to excessive eating, suffer from symptoms of the acute form of this pathology. In older people, the disease occurs more often.
General description of the disease
The disease is long-term in nature, characterized by periods of attacks and remission. At the same time, the disease does not weaken, but constantly becomes more complicated, the number and size of the stones grows and begins to put more pressure on the bile ducts and bladder.
Among the entire population of the world, approximately 10% face such a pathology. At the same time, the majority of patients are mature patients aged 40-50 years. In rare cases, cholecystitis is diagnosed in children under 14 years of age. The main threat in the development of cholelithiasis is clogging of the neck of the gallbladder and ducts of the organ.
Cholelithiasis (chronic calculous cholecystitis): treatment
Attention!!! With such disorders, symptoms of jaundice develop, as well as exacerbation of biliary colic. In this case, the patient experiences severe, unbearable pain. It is important not to confuse the problem with hepatitis and promptly prescribe adequate therapy.
Diagnosis of gallbladder gangrene
It is impossible to diagnose gallbladder gangrene solely by external signs. To establish an accurate and correct diagnosis, a number of studies are required. First of all, we are talking about the following studies:
- A physical examination of the patient, during which the doctor, by palpation of the abdominal organs, assesses the degree of tension and irritation of the patient’s abdominal muscles, and also notes the presence of the Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom (a sharp increase in abdominal pain after pressing with the hand on the abdominal cavity).
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, which allows you to assess the condition of the gallbladder, hepatic and bile ducts, and determine the presence of stones.
- Laboratory blood tests, during which the number of leukocytes can be determined. With necrosis of gallbladder tissue and the inflammatory process, there is a significant increase in the number of leukocytes, the value of which can reach 18 thousand.
Types of calculous cholecystitis
Experts distinguish two forms of the disease – acute and chronic. Each type of cholecystitis can also have two types - acute-complicated and uncomplicated (smooth).
An acute complicated type of calculous cholecystitis is diagnosed in rare cases. This form can appear due to the prolonged course of cholelithiasis without the manifestation of any symptoms. In the acute complicated form, the calculus completely clogs the common duct of the gallbladder. Because of this, inflammation of the walls of the organ occurs, which causes severe pain.
Additionally, with this disease, dangerous bacteria and infections from adjacent organs penetrate into the cavity of the gallbladder. This phenomenon occurs due to disturbances in the antiseptic effects of bile. Gradually, under the influence of the violations that have occurred, the tissues of the walls of the gallbladder begin to thicken, then they are gradually destroyed (destroyed). Due to blockage of the bile duct, all the pus formed as a result of the inflammatory process accumulates in the cavity of the gallbladder. This condition provokes bile peritonitis.
Gallstones
The chronic form of cholelithiasis can also last a long time and manifest itself only during serious exacerbations. In this case, infections and bacteria play a secondary role. With this form of developing disease, the main factors are problems with the composition of bile secretion, due to which it begins to thicken and stagnate, causing irritation on the walls of the gallbladder. Pathological processes are triggered by poor nutrition, increased body weight, diabetes, diseases of the endocrine system and the presence of persistent harmful bacteria and dangerous infections in the body.
Attention!!! Patients who have been diagnosed with bile duct dyskinesia, persistent gastritis, and liver disease should check themselves more often for the possible formation of stones.
Video - Chronic cholecystitis and cholelithiasis
Why is it developing?
Hepatic bile consists mainly of cholesterol, phospholipids, bile salts, bile pigments and water. When metabolic processes are disrupted, the quantitative and qualitative composition of the secretion changes, its colloidal stability is disrupted, which leads to the precipitation of its components.
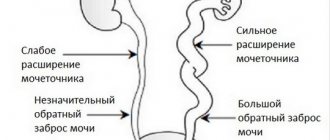
Stones form when bile stagnates, as the content of cholesterol and bilirubin increases 10-20 times. Dyskinesia of the bile ducts (smooth muscles do not contract), anatomical changes (the appearance of scars, adhesions), and congenital malformations of the gallbladder lead to stagnant processes.
The symptoms of stone disease depend on the number of stones, their size and location. In most cases, stones do not cause any symptoms because they do not reach large sizes and accumulate in an anatomical area where their movement is difficult.
While the stone is in the body of the bladder or its bottom, the person does not even suspect that the stone is carrying stones, but as soon as the stone with the flow of bile gets to the neck of the bladder or into the cystic duct, biliary colic appears. During the inflammatory process in the bladder, chronic cholecystitis develops, which in the acute stage can provoke stagnation of bile and the appearance of stones.
The movement of the stone can be caused by the consumption of fatty, hot, smoked, spicy foods, emotional or physical stress, an infectious process, or prolonged exposure to an inclined position. There are a number of factors that increase the risk of developing an acute form of the disease: female gender, obesity, age, family history of the disease, nutritional disorders.
Acute calculous cholecystitis develops due to blockage of the bile duct by a calculus
The risk of developing acute calculous cholecystitis in women increases due to an increase in estrogen concentrations, hormonal imbalances that occur during pregnancy and childbirth, and the use of hormonal contraceptives and synthetic estrogens.
Increased hormonal levels lead to a decrease in the contractility of the gallbladder and a decrease in the level of bile acids. With age, metabolic processes in the body slow down, the level of cholesterol in liver secretions increases, and the evacuation function of the bile ducts worsens, so the older a person gets, the higher the risk of calculus formation.
Obesity leads to accelerated synthesis of cholesterol and its release into bile, and following an inappropriate diet contributes to the deterioration of the functions of the bile ducts (a diet with reduced calories makes bile thicker). The likelihood of acute calculous cholecystitis increases if close relatives are diagnosed with a similar disease.
What is important here is not so much genetic predisposition as the same lifestyle and eating habits. An increased content of carbohydrates, fats, cholesterol in food, non-compliance with the diet, long-term parenteral nutrition, sudden weight loss due to fasting contribute to the formation of calculous cholecystitis.
Laparoscopic removal of gallstones
An important role in the development of the disease is given to a sedentary lifestyle, long-term hormone replacement therapy (taking estrogen), Crohn's disease, diabetes mellitus, and cirrhosis of the liver.
Obstruction of the bile duct leads to stagnation of liver secretions, and this provokes the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and damage to the gallbladder mucosa.
First, inflammation of the gallbladder is observed, which causes increased mucus production, then overstretching of the organ occurs due to the large amount of secretion formed, which causes even greater production of cytokines and destroys the walls of the bladder. As a result, the vessels of the bladder are compressed, cell necrosis occurs, and infection penetrates the organ. In severe cases of the disease, perforation of the gallbladder wall and release of bile into the abdominal cavity is possible.
There are several forms of acute cholecystitis:
- catarrhal (only the mucous membrane of the gallbladder is inflamed);
- phlegmonous (purulent exudate is present in the bladder);
- gangrenous (infection and inflammation cause necrotic changes in the organ);
- with perforation of the gallbladder;
- without gallbladder perforation.
Symptoms of various forms of the disease
Symptoms of calculous cholecystitis directly depend on the form of the disease. Thus, the chronic and acute forms of the disease have different manifestations.
Complicated-acute form of cholelithiasis
- unbearable cutting pain localized in the right side;
- pain radiates to the shoulder blade on the right side or the right shoulder;
- Such pain is provoked by eating disorders, depression, poor emotional state, and alcohol abuse;
- the patient notes attacks of nausea, which can turn into vomiting;
- cleansing the stomach does not reduce unpleasant symptoms;
- traces of bile secretion are noted in the vomit;
- body temperature increases, it reaches its highest values when pus accumulates in the cavity of the gallbladder;
- there is a significant drop in blood pressure;
- the patient notes a lot of cold sweating;
- Symptoms of icteric lesions gradually appear;
- urine and feces take on an unhealthy color.
Acute calculous cholecystitis
Chronic calculous cholecystitis
With this type of disease, the following characteristic symptoms are noted:
- prolonged pain of aching and dull nature;
- pain is localized in the area of the right hypochondrium;
- attacks are provoked three hours after eating food rich in fats and salt, as well as those that have undergone dangerous heat treatment in sunflower or butter;
- attacks may subside on their own, after partial digestion of harmful food;
- patients report attacks of nausea;
- some patients diagnose themselves with belching with a bitter aftertaste;
- if proper nutrition is too disrupted, severe vomiting with a large amount of bile will begin;
- there is no change in body temperature or blood pressure.
Types of cholecystitis
Attention!!! Moreover, with chronic cholecystitis, when the attacks subside, patients do not feel any discomfort and do not notice a significant deterioration in their general condition and decreased immunity.
How can it manifest itself?
With acute calculous cholecystitis, acute pain appears in the right hypochondrium and epigastrium. It radiates under the shoulder blade, into the neck, lower back, and shoulder girdle. An attack of colic can begin after drinking alcohol, physical stress, eating fatty or spicy foods, or after stress. The patient develops vomiting and low-grade fever.
With chronic calculous cholecystitis, the patient experiences bitterness in the mouth and nausea. Blockage of the bile duct by a stone causes obstructive jaundice, which also manifests itself in dark urine and discolored stool.
With phlegmonous, gangrenous forms, febrile temperature, severe intoxication, hypotension, severe pain and repeated vomiting appear. The patient’s blood pressure also drops sharply and weakness appears.
Diagnosis of the disease
If there is a suspicion of the development of calculous cholecystitis, urgent medical attention is required. Delay threatens the development of peritonitis, which is life-threatening for the patient. In most of these cases, urgent surgery will be required. The acute form of the disease is diagnosed by surgeons and eliminated by them.
If the disease is chronic, the diagnosis is made by a gastroenterologist. This is done in a regular clinic during a routine visit or during hospitalization during attacks of colic.
At the same time, in order to make an accurate diagnosis, the specialist is obliged to collect the patient’s complaints characteristic of the disease, check his general condition, and prescribe laboratory tests of the general type of blood and urine. Additionally, the level of pancreatic enzymes and its performance are measured. Liver tests and a coprogram, as the procedure for studying feces is called, will not be superfluous.
Final stage of chronic calculous cholecystitis
The preliminary diagnosis is confirmed by ultrasound examination of the gallbladder. If necessary, the patient is injected with contrast into the gallbladder to obtain clear X-ray images from cholecystography.
Attention!!! To study the properties of the formed stones and their possible danger, probing is prescribed. With this procedure, a laboratory technician captures part of the bile secretion and conducts a microscopic examination of it, this will help to choose a more accurate treatment plan.
Reasons for appearance
The formation of gallstones is associated with stagnation of bile, changes in its composition and the presence of an inflammatory component. As a result of errors in nutrition, infectious diseases, for example, hepatitis, diabetes, obesity, changes occur in the gallbladder. The bile thickens and stagnates, so the gallbladder becomes infected with various pathogenic organisms. Often the development of calculous cholecystitis is associated with acalculous cholecystitis, as a result of which the normal dynamics of gallbladder emptying are disrupted.
Treatment of calculous cholecystitis
Today, specialists use two methods to eliminate the resulting pathology - surgical intervention and traditional.
Acute form of manifestation of pathology
If calculous cholecystitis occurs in a patient for the first time, the attending physician uses drugs of an antibacterial, antispasmodic and analgesic nature. Toxic substances are removed from the body with special solutions. The patient is required to be prescribed a strict diet and recommendations are given to prevent recurrent attacks. In this form, therapy is carried out strictly within the walls of a medical institution, since independent therapy can lead to a life-threatening situation.
If all the adopted medicinal and gentle methods have not given any result, or the patient has already accumulated pus inside the gallbladder, the specialist, without any doubt, urgently removes the organ along with the stone fractions formed in it.
Laparoscopic and open surgery
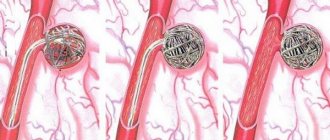
In most cases, surgeons try to perform surgery using laparoscopy, which is one of the most gentle invasive techniques. To remove the gallbladder, several punctures are made in the abdominal area with special small scalpels, strictly under constant monitoring of the monitor. If the patient has already developed peritonitis, only an open laparotomy is performed. Additionally, an inspection of the abdominal cavity is performed.
Chronic form of calculous cholecystitis
With this type of manifestation of the disease, the patient is prescribed a strict mandatory diet. He must completely remove from the diet foods that are rich in carbohydrates and fat. You should minimize the amount of salt, hot spices, and abstain from alcoholic beverages for life. In this case, the patient should significantly reduce sports and physical activity, lead as calm a lifestyle as possible, and avoid psycho-emotional shocks.
After the attack has been reduced and the pain has subsided a little, a litholytic course of treatment is carried out. For this purpose, medications are used that can break up stones in the gallbladder and its ducts. Such remedies include Ursosan and Litofalk . Additionally, you can take antispasmodic medications.
Attention!!! The chronic form of the disease, unlike the acute form, can be eliminated at home. Additionally, you can use traditional therapy methods for this, but it is important to consult with your doctor about the possibility of using them.
Video - How to prevent the formation of gallstones
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can make a final diagnosis based on laboratory and instrumental examinations. But before prescribing them, a specialist needs to conduct an objective examination:
- study the medical history and life history of the patient - to search for the causes of the disease, in particular, phlegmonous or calculous cholecystitis;
- perform a thorough survey and physical examination with mandatory palpation of the abdomen, measurement of blood pressure, pulse and temperature, as well as examination of the skin - this will provide the doctor with a complete picture of the first time of appearance, presence and intensity of symptoms.
Only after this is a laboratory examination carried out, which includes:
- general analysis and blood biochemistry;
- general urine analysis;
- coprogram.
But the most valuable is instrumental diagnostics, which involves performing:
- Ultrasound of the affected organ;
- radiography;
- EGDS is an endoscopic procedure for examining the internal surface of the gastrointestinal tract;
- ECG;
- CT and MRI - in cases where other instrumental diagnostic methods cannot detect pathology;
- multifractional duodenal intubation.
The acute condition is differentiated from acute appendicitis, peptic ulcer, cholelithiasis, pleurisy and myocardial infarction.
Features of drugs for the treatment of cholelithiasis
| A drug | Image | Description | Price |
| Ursosan | Dissolves stones, restores the mucous membrane of the stomach and gallbladder | 1000-1700 rubles | |
| Litofalk | It also helps dissolve stones in the bile ducts, relieves symptoms of hepatitis, improves the condition of the mucous membrane | 400-1500 rubles | |
| Drotaverine | Perfectly relieves spasms and reduces pain | 50-1000 rubles | |
| Librax | Belongs to the class of antispasmodics, which simultaneously improve the general condition of the patient. Allowed for use by children in urgent need | 800-1200 rubles | |
| Ospen | Has an antimicrobial effect, suppresses the production of pathogenic bacteria | 780 rubles | |
| Meratin | Relieves the inflammatory process, prevents the formation of pus and the development of peritonitis | 1550 rubles | |
| Mebeverine | Eliminates tissue spasm and pain, further improving overall well-being | 750-2500 rubles |
Attention!!! All described substances and drugs can be taken strictly after prior consultation with your doctor and determination of your individual dosage.
Treatment
After confirmation of the diagnosis, emergency hospitalization of the patient and immediate operation are necessary. Any delay can cause a complication such as rupture of the gallbladder, which entails the development of peritonitis, which, in turn, can cause the death of the patient.
The basis of surgical treatment is removal of the gallbladder - cholecystectomy. This operation is performed using several methods:
- laparoscopically – excision of the affected organ is performed using special instruments through several small incisions on the abdomen;
- laparotomy - removal of the gallbladder occurs through a large incision in the anterior abdominal wall.
In addition to surgery, patients are advised to take medications to relieve symptoms, as well as follow the rules of dietary table No. 5.
There is no specific prevention of the disease - it is only necessary to promptly eliminate conditions that can lead to gangrenous cholecystitis. With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable; with the development of peritonitis, there is a high risk of death.
Traditional methods of treating cholelithiasis
Horseradish roots
To prepare the product, thoroughly wash the horseradish fruits and cut off all wormy or rotten areas. Grate clean rhizomes onto a coarse grater. You should get at least one glass with a volume of 250 ml. After this, the mass is poured with one liter of boiling water and infused under a tight lid strictly in an enamel or glass container.
After this, strain the solution through a gauze bandage and place it in a cool place. Before use, the measured dose should be slightly warmed. It is necessary to take the medicine three times in doses of 50 g 10-15 minutes before the main meal. For taste, you can add a little sugar or its substitute.
Horseradish root for the treatment of chronic calculous cholecystitis
Plant juices
This is a rather labor-intensive recipe to prepare, but it gives good results, including during periods of exacerbation.
- In equal proportions of 500 ml, you need to take freshly squeezed agave juice, the plant must be at least 3 years old, beets, carrots and black radish.
- Having thoroughly mixed these ingredients, you should add to them the same amount of liquid honey, which can be melted in a water bath, as well as high-quality vodka.
- All ingredients are mixed together until smooth and poured into a three-liter glass jar.
- The jar should be closed with a strictly nylon lid and placed in an airtight bag.
- The container is buried in the ground with a neck for 14 days.
- After this, the infused liquid is poured into smaller containers and placed in the refrigerator. Care should be taken to ensure that the bottles are not exposed to direct sunlight.
- The dosage of the drug is 15 ml before each meal.
- The accumulated bile will begin to be released with the feces in the form of mucus.
- The course of treatment consists of consuming the entire tincture.
Regardless of how acute or severe the pain that appears in the abdominal cavity is, it is worth contacting a therapist first. He will help exclude some diagnoses and refer you to a specialist. At the same time, if the pain is acute and is not necessarily localized on the right side, you should urgently call an ambulance. The condition of peritonitis can manifest itself as pain in any location of the abdomen and abdominal cavity. Only timely treatment will help avoid death and return the patient to normal life. Study the most effective remedies for sinusitis at the link.
Treatment and surgery
Only correct diagnosis allows us to determine what could have preceded the patient’s serious condition. Based on this, the doctor selects the most effective course of treatment. The results of laboratory tests and methods of hardware-instrumental diagnosis of the gallbladder are used:
- echocardiogram;
- CT scan;
- ultrasonography;
- endoscopy of the intestines and stomach;
- radiography;
- duodenal multifraction probing of the bladder.
For the gangrenous form of cholecystitis, conservative treatment is ineffective, so the doctor prescribes surgical removal of the affected parts of the organ using one of two methods:
- Laparotomy is the surgical removal of a bladder or parts of it through an incision in the abdominal cavity.
- Laparoscopy – removal of damaged tissue through several small incisions.
To avoid complications after surgery for gangrenous cholecystitis, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed, and analgesics Ketalong and Spazmolgon are used to relieve pain.
The rehabilitation period after such a procedure depends on the patient’s physiology and the degree of development of the disease itself. The technique of the operation also influences. Usually the sutures are removed after 14-21 days if there are no complications or consequences.
Symptoms of the disease
One of the characteristic signs for the gangrenous form of cholecystitis is gangrene of the gallbladder, which is accompanied by inflammation of the peritoneum. At the same time, during a clinical examination, the following clinical symptoms of the disease are diagnosed:
- pain on the right side of the abdomen, which has an aching, cutting, pulling character. Symptoms may differ as the pathology develops; with severe pain, this sensation is transmitted to adjacent organs of the digestive tract and tissues of the entire cavity;
- an unreasonable sharp increase in temperature;
- increased heart rate;
- stable feeling of drowsiness;
- moderate to severe headaches;
- sudden change in mood - the patient, after a period of apathy, suddenly becomes energetic and excited;
- stool pathologies - sharply alternating constipation and diarrhea.
Simultaneously with the clinical manifestations of acute gangrenous cholecystitis, an increase in the volume of the entire abdomen appears, as well as yellowness of the visible mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes, and nose. Because of this symptom, the disease is sometimes called jaundice. The skin becomes pale during the development of the disease.
Prevention
No specific preventive measures have been developed for this disease. There are only general recommendations, including:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- body weight control;
- compliance with nutritional recommendations;
- taking medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- undergoing a preventive examination by a gastroenterologist twice a year.
Such measures will help prevent the formation of stones in the bile ducts.
Acute calculous cholecystitis without complications has a positive prognosis. In case of complications, as well as in elderly patients, the mortality rate from this disease is up to 60%.
Prevention of gallbladder gangrene in the postoperative period
In order to prevent complications after cholecystectomy, during the postoperative period patients are advised to diet and adhere to the prescribed regimen. Medicinal preventive measures include the use of choleretic drugs (Allohol, Hologon, Nikodin, Digestal, Flamin, etc.), which prevent stagnation of bile in the ducts.
In case of exacerbation and the appearance of postcholecystectomy syndrome after surgery, painkillers and analgesics are prescribed. During an exacerbation, the patient may be advised to undergo short-term fasting (no more than two days), during which only warm drinks are allowed in small portions (weak tea, juice diluted with water, rosehip decoction).
However, the main preventive measure in the postoperative period is diet No. 5, which provides for fractional meals, the inclusion of essential proteins, carbohydrates in the diet and the exclusion of harmful fats.
The main dishes for patients with gangrenous cholecystitis should be:
- vegetable and milk soups;
- boiled or steamed lean meats and fish;
- porridge made from oatmeal, rice and semolina;
- cottage cheese and fermented milk products;
- vegetables and fruits.
At the same time, the following should be excluded from the patient’s diet:
- fatty foods, including meat broths;
- fried foods;
- baked goods and baked goods;
- alcoholic drinks.
Patients are fed at least 5 times a day in small portions. The daily diet includes at least 2 liters of liquid.