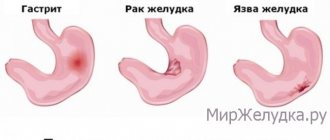
Stomach ulcers are diagnosed in almost 10 people out of 100. Pathological changes in the mucous membrane are accompanied by various complications, so you need to know the signs of a stomach ulcer and the first symptoms.
Related articles:
Diet for stomach ulcers Treating stomach ulcers at home: the best recipes Perforated gastric ulcer: symptoms and treatment of the disease Treatment of stomach ulcers using traditional methods We treat stomach and duodenal ulcers with medications
Signs of peptic ulcer
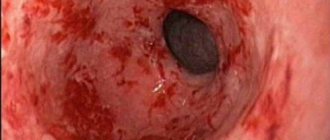
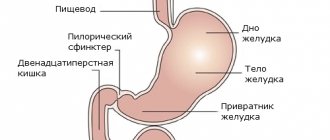
Gastric ulcer is a pathological change in the gastrointestinal tract, which is characterized by the formation of small defects in the mucous membrane of the organ. The cause of the disease is the negative effects of hydrochloric acid, pepsin, bile, and Helicobacter pylori infection. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and hormone-based drugs can cause peptic ulcers.
Important! Peptic ulcer disease is an irreversible pathology; scars form in places where defects appear.
A stomach ulcer does not always occur against the background of severe pain; the manifestations may be mild. The clinical picture is influenced by the location of the ulcer, its size, age and general indicators of human health.
But most often the ulcer is accompanied by severe pain in the stomach area, sometimes it radiates to the left side of the chest and lower back.
Signs of a stomach ulcer:
- The first symptoms occur at the initial stage, characterized by sudden attacks of pain in the navel area, which intensifies on an empty stomach or at night. During an attack, it is difficult for a person to move; he strives to take a comfortable position in order to alleviate the pain. The condition is aggravated by a decrease in blood pressure, the face becomes pale, the lips acquire a bluish tint, and the person constantly feels hot. On palpation there is a sharp pain.
- In the second stage, the pain subsides and may disappear completely. But at the same time, the person’s temperature rises, the mouth feels constantly dry, the pulse quickens, and gas formation increases. At this stage, constipation may appear and gas accumulates near the diaphragm on the right side.
- The third stage is perforation of the ulcer, mixed peritonitis develops within 12 hours. At this stage, the disease has a clear clinical picture - there are signs of severe intoxication, a general deterioration in health, and urgent hospitalization is required.
At the initial stage of development, an ulcer can be confused with other diseases. If you experience frequent attacks of heartburn and nausea, constipation or diarrhea, you should undergo a full medical examination. The development of a peptic ulcer may be indicated by sour belching, the presence of blood in the stool, and stomach pain before and after eating. With pathology of the gastric mucosa, the lips constantly dry out and cracks appear in the corners of the mouth.
Ulcers are often diagnosed in children, especially young people during puberty. The signs of peptic ulcer disease are the same for children and adults.
Important! Peptic ulcer disease is characterized by cyclical pain attacks, most often exacerbation occurs in spring and autumn.
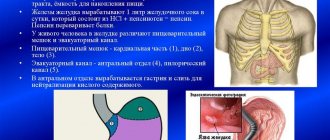
A stomach ulcer is formed when there is an imbalance between the aggressive factors of gastric juice - hydrochloric acid and enzymes - and the protective properties of the mucous membrane - renewal of the epithelium (surface of the gastric mucosa), mucus production, adequate blood supply, production of prostaglandin hormones.
The role of aggressiveness of gastric juice in the formation of ulcers depends on gastric secretion, which, according to I. P. Pavlov [12], goes through three phases:
- The first phase - reflex - is caused by irritation of the branches of the vagus nerve and activates the gastric glands, which produce gastric juice. This occurs reflexively in response to the smell or sight of food when it enters the stomach.
- The second phase - hormonal - depends on the entry into the blood of the hormone gastrin, which is produced by the mucous membrane of the antrum (outlet) of the stomach and the initial part of the duodenum when they are irritated by food masses or inflammatory processes.
- The third phase - intestinal - depends on the entry of the hormone enterokinase into the blood. This hormone is produced in the small intestine when a bolus of food enters it.
An adult produces one and a half liters of gastric juice per day, with 80% of the juice produced in the first phase of gastric secretion, 15% in the second and 5% in the third. If disrupted, these phases can change significantly. For example, during inflammation in the antrum of the stomach, too much of the hormone gastrin is released, which is why gastric juice is produced in excess “idle”. This increases inflammation and leads to the appearance of ulcerative defects in the wall of the stomach or duodenum [3][8].
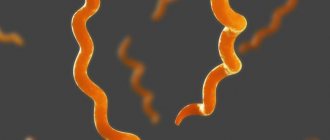
A large role in ulcer formation is played by H. Pylori , which acts in two ways: on the one hand, bacteria attach to cells, produce toxins and cause inflammation, which makes the mucous membrane more sensitive to aggressive factors; on the other hand, they produce certain substances, which causes stomach cells to produce excess hydrochloric acid.
With prolonged uncontrolled use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the protection of the gastric mucosa is impaired. At the same time, the aggressiveness of the gastric juice increases, due to which the cells of the mucous membrane are damaged and die, after which an ulcer gradually forms.
Chronic overwork and prolonged stress weaken general immunity and cellular defense, and through the neurohumoral mechanism increase the acidity of gastric juice. This upsets the balance between the factors of aggression and defense, which leads to the appearance of “stress” ulcers, which were first described back in 1983 by Dr. J. Svan [11].
A number of diseases are accompanied by persistently increased hyperproduction of hydrochloric acid, due to which the compensating capabilities of the stomach tissues are depleted and multiple ulcers appear.
A separate role is given to predisposing factors. For example, the effect of nicotine when consuming tobacco leads to spasm of blood vessels throughout the body, including the vessels of the wall of the stomach and duodenum, disrupting blood circulation in them. Because of this, the mucous membrane experiences oxygen starvation, metabolic processes in it deteriorate, which leads to a weakening of tissue protection and creates the preconditions for ulcer formation.
Stages of ulcer formation
Stomach ulcers rarely occur in a completely healthy person. Its appearance is preceded by a number of pathological changes.
Initially, due to an imbalance between the factors of aggression and defense, a banal chronic inflammation of the stomach appears - chronic gastritis. This condition can last for years, and its manifestations range from the absence of any complaints to pain in the upper abdomen and digestive disorders. Chronic gastritis occurs with periods of exacerbation, often in spring and autumn.
Without treatment, against the background of the same negative factors, increased aggressiveness of gastric juice and depletion of the protective properties of the mucous membrane, its cells begin to actively die, which leads to the appearance of surface defects - erosions. The body fights these processes by filling eroded areas with fibrin - a kind of “painting foam”. But when this resource is exhausted, aggressive gastric juice begins to affect the deep layers of the wall of the stomach and duodenum that remain unprotected, thus forming an ulcerative defect.
The gradual deepening and widening of the ulcer can lead to damage to the muscles of the gastric wall and erosion of the walls of large vessels, which causes gastrointestinal bleeding. Or the ulcer can “grow” through the gastric wall, which will lead to the spilling of stomach contents into the abdominal cavity [3][4][8][9].
Signs of exacerbation of a stomach ulcer
Gastric ulcers can worsen at any time, most often this occurs when the immune system is weakened. Or due to non-compliance with diet, alcohol abuse, smoking, excessive physical activity.
The duration of the exacerbation period is 4-12 weeks. After proper treatment, provided that all the doctor’s recommendations are followed, the period of remission can last several years.
Signs of exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease:
- pain of a dull, cutting or stabbing nature, which is localized in the central upper abdomen, can radiate under the ribs on the left side;
- pain occurs 30–60 minutes after eating and stops after emptying the stomach;
- when the integrity of the mucous membrane is damaged, acidic gastric juice enters the lower esophagus, which leads to heartburn;
- nausea and vomiting – after vomiting a person feels better;
- increased gastric acidity leads to constipation, sour and musty belching.
Attacks of pain after eating lead to the fact that a person begins to eat less - weakness and sudden loss of body weight occur.
Special symptoms of stomach ulcers in men
Men are more prone to the appearance of ulcers, since the causes of the disease are male in nature:
- smoking;
- nervous experiences (stress);
- frequent drinking of alcohol.
According to experts, high stomach ulcers (greater curvature) are more common in middle-aged men.
Note! Male nature is less suspicious, and therefore the disease, which is mild or asymptomatic, manages to progress to stages 3-4 without treatment, and even develop into a malignant tumor.
The main symptoms of a high ulcer (greater curvature) in men are as follows:
- It worsens when the climate (season) changes;
- Aching pain in the abdominal area, alternating with sharp tingling, when favorable conditions arise: climate, food intake;
- Frequent heartburn, nausea, belching;
- As the ulcer progresses, it can cause bloody “acid vomiting,” as well as bloody diarrhea and constipation.
Symptoms of early stage stomach ulcers in men usually include:
- poor appetite;
- vomiting and nausea;
- discomfort in physical well-being;
- sudden weight loss;
- fatigue, weakness;
- abdominal pain several hours after eating.
Signs of a perforated stomach ulcer
An acute complication of peptic ulcer disease is perforation, characterized by severe pain that quickly covers the entire abdomen and high fever.
With a perforated ulcer, bleeding may begin in the stomach, the stool becomes black with an admixture of blood, the vomit becomes dark brown, and blood impurities also appear in it. All these symptoms are extremely dangerous to human life and health. Urgent medical attention is required.
Bleeding is the most dangerous complication of perforation of an ulcer. Due to severe blood loss, anemia, tachycardia, and hypotension may occur. The patient experiences severe weakness, nausea, the body becomes covered in cold and sticky sweat, and fainting is possible.
Perforation of an ulcer has 3 stages of development:
- chemical peritonitis - lasts 3-6 hours, all signs of exacerbation of peptic ulcer appear, pronounced protrusion of the muscles of the anterior wall of the peritoneum is observed;
- bacterial peritonitis - develops 6 hours after perforation, symptoms become less acute, the process of intoxication begins, intestinal paralysis;
- the third period is the most dangerous, occurs 12 hours after the appearance of the first signs, is characterized by severe intoxication - uncontrollable vomiting occurs, dehydration occurs, systolic pressure drops, and the temperature rises sharply.
In the third stage of development, a person becomes indifferent and may not respond to external stimuli. The volume of the abdomen noticeably increases due to the large accumulation of gas. The kidneys begin to work worse - the amount of urine gradually decreases, and over time, urination stops completely.
A tale about a witch whom we invite to ourselves
Waking up in the middle of the night from pain and heartburn, Semyon Semyonovich for some reason imagined an old woman with a stick, hunched over, and certainly with a wart on her nose, which had cast a spell on him.
- Who are you? - he asked, swallowing in hopes of ridding himself of the sensation. - Baba Yaga?
- No, honey! - the hag answered brightly. - I am your Ulcer!
- What do you want from me?!
“I’ll tell you this in detail now,” the witch promised, sitting down on a chair and preening herself. - I settled in your stomach, and now this is my patrimony. All your excesses, food at the wrong time, smoking and twitchy nerves opened the way for me. And my faithful servants, bacteria called Helicobacter, help me defeat you...
The sea is up to your knees. You spit on the fact that you eat whatever you like and not regularly, and life shakes you up every now and then, provoking the release of adrenaline. Some people even like it when they “tickle in the pit of the stomach,” and we don’t have time to think about the consequences of constant stress.
But the “old witch” follows you with silent steps, waiting to pounce - and not let go for as long as possible.
Treatment methods
Gastric ulcer is a chronic disease that requires constant maintenance therapy in combination with proper nutrition. Treatment begins with a thorough diagnosis, since the symptoms of ulcers, gastritis and other diseases of the digestive system are largely similar.
Therapy for stomach ulcers consists of several components - drug treatment, surgery, diet, and traditional recipes.
Medicines
To destroy Helicobacter bacteria, antibiotics of the following groups are used:
- macrolides – Erythromycin, Clarithromycin;
- antibacterial agents of the penicillin group - Amoxicillin;
- nitroimidazoles – Metronidazole.
Important! You can learn about the treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers here.
To reduce the acidity of gastric juice, Omeprazole, Ranitidine, Almagel, Maalox are used. De-nol is an effective drug that not only has an astringent effect, but also destroys Helibacter infection.
Solcoseryl is used for intravenous injections - the drug promotes the rapid restoration of the epithelium on the surface of the stomach.
Important! In therapy, 3–4 components are used simultaneously; the doctor selects them individually. Duration of treatment – 2 weeks.
Diet
A diet for ulcers involves a complete abstinence from alcohol, strong coffee, and all unhealthy, hot and cold foods. You should not eat foods that are designed to increase appetite - onions, garlic, radishes.
You can only eat steamed and boiled food in a liquid or pureed state. You should eat 5-6 times a day, drink 250 ml of milk for breakfast every day, eat cereal, prepare dishes from seasonal vegetables, non-acidic fruits and berries.
Surgery is necessary when the ulcer is perforated - otherwise the cells may degenerate into neoplasms that are similar to malignant tumors.
Important! How to treat stomach ulcers at home? Read our article.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods can be used only during periods of remission of peptic ulcer disease. Juice therapy helps cope with stomach ulcers. Healthy juices - cabbage, potato, blackcurrant, birch, sea buckthorn.
Important! Find out more about treating ulcers with folk remedies on our website.
Honey will help reduce the manifestation of peptic ulcers. Mix 300 ml of liquid honey with 300 g of chopped walnuts and unsalted butter. Place the mixture in a fireproof dish and bake in the oven for 20 minutes at 100 degrees. Take 15 g of medication three times a day 30 minutes before meals, do not drink it.
Stomach ulcers are an incurable disease, so they are easier to prevent. Stress, alcohol and smoking, junk food, and poor diet have a negative impact on the functioning of the digestive system. The diet should contain a minimum amount of foods that irritate the gastric mucosa and increase acidity. Hands should be washed frequently and thoroughly to avoid Helicobacter pylori infection entering the body.
Symptoms of stomach ulcers at an early stage in children
The cause of the disease in children is considered to be infection with Helicobacter bacteria. This bacterium is found in the body of 90% of the entire population of the planet in a latent form.
It is activated during periods of weakening of the body, together with other factors it begins to actively destroy the structure of the mucous membrane of the stomach and digestive organs.
Experts usually include the following as the main symptoms of peptic ulcer disease in children:
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements necessary for a growing body;
- frequent nervous experiences, stress;
- improper diet and nutrition;
- infection with pathogenic bacteria due to ignoring hygiene rules (unwashed hands, unwashed toys, etc.).
During the period of exacerbation of ulcers in children, the following picture is observed:
- Symptoms of stomach ulcers in the early stages in children are less pronounced and latent compared to the adult form;
- There is a healthy appetite, or even increased;
- Hypovitaminosis and moderate intoxication;
- Heartburn, stabbing/cutting pain in the abdominal/subcostal/back region, absence of nausea and vomiting.
Signs vary depending on the stage, extent and location of the ulcer.
A young body responds well to treatment and is less at risk of complications : bleeding, perforation and penetration (penetration into other organs).
The course of therapy is recommended to be carried out every six months to a year, or during periods of exacerbation.
Experts consider typical symptoms of ulcer formation in children to be:
- vomiting coffee grounds;
- black stool that looks like tar;
- drop in blood pressure and deterioration of the patient's condition.