The mechanism of development of chronic sinusitis
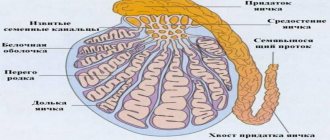
The facial bones of the skull have air sinuses (pockets), the so-called sinuses, which communicate with the nasal cavity through the anastomosis. Closest to the nasal passages are the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses, whose task is to warm, disinfect and humidify the inhaled air.
The surface of the sinuses is covered with mucous epithelium; underneath there is loose tissue and capillaries involved in many processes. For various reasons, the outer membranes can become inflamed and block the anastomosis, blocking the outflow of nasal secretions from the sinus. Stagnation of mucus in the “pockets” of the nose provokes the development of an acute inflammatory process - sinusitis, which doctors, in general, can call sinusitis.
In the acute form of the pathology, it is mainly the mucous epithelium of the sinuses that becomes inflamed; this process has pronounced symptoms and lasts no more than 3–4 weeks. In the absence of treatment or interruption of the course of antibiotic therapy, the disease can become chronic, characterized by periods of remission alternating with exacerbation of the pathology. Sinusitis is considered chronic if its duration exceeds 6–8 months.
In chronic sinusitis, not only the upper layer of the epithelium, but also the submucosal tissue and the bone walls of the sinus can become inflamed.
The development of the chronic form of the disease is always preceded by acute sinusitis
Laboratory research
For reliable diagnosis, doctors practice laboratory tests.
- A general blood test determines the sedimentation rate of ESR.
- In some cases, a test for the level of reactive protein is prescribed. It shows the development of acute sinusitis.
- If the doctor suspects a dysfunction of the immune system, a test for immunoglobulins and HIV infection is recommended.
- Cytological analysis of secretions from the nasal passages determines the cellular composition of the mucous masses. The study helps determine the origin of the pathological process and shows the source of inflammation.
- A study with the strange name Sweat test diagnoses cystic fibrosis, which should be eliminated to avoid the development of complications.
Without special education and medical practice, it is prohibited to draw conclusions about the severity and form of the disease. Often, self-diagnosis at home based on severe symptoms does not lead to the expected results during treatment.
Classification
Depending on the prevalence of inflammation, chronic sinusitis can be unilateral or bilateral. Most often, a unilateral form of the disease is diagnosed.
With bilateral sinusitis, the symptoms are more pronounced and the disease progresses with accelerated force
Depending on the cause of inflammation of the sinuses, sinusitis is classified as:
- infectious - when infected with viruses, fungi, bacteria;
- allergic - develops with allergic rhinitis, hay fever;
- vasomotor - when there is a violation of the innervation (regulation of the work of the brain) of the capillaries as a result of neurovegetative disorders, taking medications.
The morphological classification of sinusitis involves the identification of its forms depending on the pathological changes in the sinus mucosa.
- Exudative form:
- catarrhal - the mucous membrane of the sinuses is edematous;
- serous - the discharge is mucous, non-purulent;
- purulent - the presence of thick yellow exudate with the subsequent development of sclerotization (replacement with connective tissue) of the epithelium.
- Productive form:
- polypous - the formation of polyps on a thin stalk, formed from mutated epithelial tissue;
- parietal-hyperplastic - proliferation of the outer layer of the mucous membrane, as a result of which the lumen of the sinus closes;
- cystic - occurs when the secretory gland is blocked, as a result of which mucus accumulates in it and forms a cyst with a thick secretion inside and an epithelial membrane.
- Alternative form:
- cholesteatoma - the formation of a tumor, which contains dead epithelial cells and decay products, as well as cholesterol crystals;
- caseous - necrotization of the tissue of the sinus mucosa, in which a white coating forms on the surface;
- necrotic - death of soft tissue, which over time spreads to bone tissue and leads to abscesses and meningitis;
- atrophic - pathological changes in which the mucous membrane becomes thinner.
- Mixed form:
- purulent polyposis - the formation of polyps is accompanied by copious discharge of purulent exudate;
- serous-catarrhal - this form is characterized by signs of severe nasal congestion caused by swelling of the sinus mucosa and discharge of serous exudate.
Pathological changes in the sinus mucosa, if left untreated, rapidly progress, which leads to the progression of the disease from an exudative form to more serious ones that require surgical intervention.
Chronic sinusitis occurs as a complication of the acute form of the disease. There is a classification for it, highlighting the routes of penetration of the pathogen. This:
- rhinogenic - through the nasal passages;
- hematogenous - the infection penetrates the sinuses along with the blood flow;
- odontogenic - when infection penetrates through the root of a diseased tooth;
- traumatic - with injuries to the skull, soft tissues of the face, in which swelling occurs in the mucous membrane.
Classification of chronic sinusitis according to B. S. Preobrazhensky is considered the most reliable
Treatment with folk remedies
Comprehensive treatment of sinusitis is the key to a positive result in eliminating inflammation. Widespread methods of therapy are inhalation with a special nebulizer apparatus and thermal sessions. For inhalations, decoctions of medicinal herbs, saline solutions, and essential oils are used. With their help, mucus is able to liquefy and drain in a timely manner, without causing purulent accumulations in the sinuses.
It is possible to get rid of inflammation without surgery by lubricating the nasal passages with essential oils. Most often I use sea buckthorn oil and a mixture of rose hips. The products not only eliminate inflammatory processes in affected areas, but have an antiseptic effect and strengthen the protective immune system. It is advised to use essential products carefully so as not to provoke allergic reactions. It is better to conduct a test before use and confidently continue therapy without the risk of unwanted manifestations.
Causes of development and conditions for exacerbation of the disease
The formation of chronic sinusitis is preceded by an acute form of the disease, the main pathogens of which are viruses, staphylococcus, streptococcus or fungi. Less commonly, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses occurs against the background of allergic reactions occurring in the body, or after injury to the soft tissues of the face.
Factors contributing to the transition of the disease from acute to chronic form are varied:
- improper treatment of acute sinusitis or lack thereof;
- reducing the course of antibiotics after the main symptoms disappear;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract, such as tonsillitis, adenoids in children, vasomotor and allergic rhinitis;
- the presence of structural pathologies - curvature of the nasal septum, polyps, ridges and spines;
- unfavorable living or working conditions - dusty rooms, tobacco smoke, harmful fumes, polluted air;
- decreased local immunity after suffering a serious illness, treatment with antibiotics, or with chronic diseases of the endocrine system;
- poor dental condition, for example, caries, pulpitis, granuloma on the upper jaw (in such cases, odontogenic sinusitis is diagnosed);
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- bad habits.
One of the common causes of odontogenic sinusitis is a violation of the bone septum between the diseased tooth and the sinus, the integrity of which can be disrupted during the treatment of molars and premolars of the upper jaw
Symptoms and signs of sinusitis in adults
Chronic sinusitis can last from 6 months or longer, worsening with episodes of colds, hypothermia and other factors that reduce the body's resistance. Due to the vagueness of the manifestations, the pathology in the early stages is often confused with a common runny nose, and when it passes into a productive form, with vasomotor rhinitis.
Signs of chronic sinusitis in remission are:
- a feeling of a lump or dryness in the throat in the morning, due to the flow of exudate into the larynx;
- bad breath;
- periodic nasal discharge, which can be thin and clear or thick and purulent;
- impaired sense of smell or its complete loss during a bilateral inflammatory process;
- frequent headaches localized in the temples;
- aching pain in the teeth, spreading across the upper jaw;
- a feeling of fullness in the nose, aggravated by pressure in the eye socket when tilting the head;
- redness or peeling of the skin between the upper lip and nose;
- increased fatigue, decreased memory, sleep disturbances caused by lack of oxygen.
When the disease worsens, symptoms appear as follows:
- increase in body temperature within 37–37.5 °C;
- signs of intoxication of the body - weakness, headaches, body aches;
- the occurrence of conjunctivitis or swelling of the eyelids;
- change in voice timbre, nasality;
- pain radiating to the cheek, eye socket, ear or temple, aggravated by sneezing, blowing the nose, coughing.
With the exudative form of sinusitis, during the period of exacerbation, the discharge becomes more abundant and does not stop with traditional treatment of the runny nose, and with a fungal infection, it can have a yellow, brown or red tint, as well as a foul odor.
How to treat sinusitis at home with antiseptics
Quite often, first aid for sinusitis involves taking antiseptics. Such effective drugs help to quickly remove all thick pus and improve breathing through the nose. There are several common antiseptic medications that can be used to cure a runny nose.
Chlorophyllipt
The disease can be cured with the help of the drug Chlorophyllipt. It is most often used in the treatment of bacterial forms of the disease, as the medicine has antibacterial properties. Also, the use of Chlorophyllipt helps remove purulent accumulation from the sinuses.
Before using this effective remedy, you must prepare a special solution. To do this, you will have to mix 10 ml of the drug in 55 ml of water and drink 20 drops three times a day before meals. If the dosage is determined incorrectly, an allergic reaction may occur.
Furacilin
Some people fight a runny nose with the help of Furacilin. This drug will destroy all bacteria in the nasal cavity and remove all mucous accumulations that are in it. Experts do not always recommend using Furacilin when treating a runny nose, as it has many side effects. These may include nausea, appetite problems, rashes, vomiting and headaches. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a doctor before using it.
During treatment, the product is used daily, twice a day. Furacilin should be used no longer than 5-6 days.
Miramistin
Also, accumulated fluid in the nose is removed with the help of Miramistin. Thanks to its antiseptic effect, the product effectively fights germs and bacteria that cause a runny nose. In addition, Miramistin activates immune cells and strengthens human immunity.
The drug is sold in the form of ointment and drops. If you use ointment for sinusitis, you will have to lubricate the inflamed nasal cavity with Miramistin once a day. Many experts do not advise treating a runny nose with ointments, as they are not very effective. Therefore, it is better to use Miramistin in the form of drops during treatment. When using them, 2-3 drops of the product should be instilled into each nostril daily.
How to recognize the disease in children
A chronic form of sinusitis can develop in children over 3 years of age if they are exposed to frequent respiratory diseases and have overgrowth of adenoid tissue. When the symptoms are erased, the disease cannot be recognized immediately. To prevent complications in the form of meningitis, sepsis, otitis, asthma, parents should pay attention to the following signs indicating chronic sinusitis:
- nasal congestion is manifested by heavy breathing, the child’s mouth is often slightly open, the baby sniffles in his sleep;
- an unreasonable cough after sleep that does not recur during the day;
- unpleasant, putrid odor from the mouth caused by mucus running down the nasopharynx;
- lacrimation;
- change in voice timbre;
- the child often complains of a headache;
- decreased activity and appetite in the baby.
If a child has at least two of the listed symptoms, you should consult a doctor for additional examination.
In children under three years of age, the maxillary sinuses, like other sinuses, are not yet fully formed, so the risk of developing sinusitis at this age is minimal
Features of the disease during pregnancy and breastfeeding
In the early stages of pregnancy, during the formation of the fetus, the chorion, which is the precursor of the placenta, produces active substances that suppress the woman’s immunity. This is necessary so that immune cells that recognize and neutralize foreign genes do not provoke fetal rejection.
In the future, with the active growth of the baby in the womb, there is a high probability of depletion of useful nutrients (nutrients), which also affects the state of the immune system. During this period, a woman is especially susceptible to various colds, and since treatment with medications is not available, there is a high probability of complications and the development of sinusitis.
The danger of sinusitis in both acute and chronic forms is that if nasal breathing is impaired, a lack of oxygen occurs, which can lead to fetal hypoxia. No less dangerous is the spread of infection through the bloodstream, which will lead to infection of the baby with the ensuing consequences.
For the treatment of chronic sinusitis during pregnancy, drug therapy, including antibiotics and sometimes corticosteroids, is not applicable. Only in extreme cases can a doctor prescribe local antibiotics, and if necessary, perform a sinus puncture.
The safest method is to rinse the sinuses with a Yamic catheter followed by sanitization with antiseptic solutions
If the disease occurs during breastfeeding, the treatment method is selected individually depending on the stage of neglect of the pathology and changes in the mucosa. In case of purulent forms of sinusitis, breastfeeding should be interrupted or the baby should be temporarily switched to formula while maintaining lactation by pumping while taking antibiotics.
Surgical treatment is indicated for productive forms of sinusitis. In this case, the child is transferred to formula for a short period of the operation and recovery of the mother.
Surgical intervention
How and with what to treat sinusitis is determined by the attending doctor. If the case is severe, a consultation is held to make the correct and competent decision on therapy. Surgical intervention is inevitable in the following cases:
- Conservative treatment did not bring the required positive results.
- With secondary manifestations of pathology with chronic suppuration in the nasal sinuses.
- Diagnosis of intracranial diseases, the formation of which is directly related to sinusitis.
- Chronic inflammation of a closed form.
- When an infection migrates to nearby human organs.
There are contraindications for surgical operations. The doctor is obliged to study the patient’s condition and be sure that the body will tolerate the surgical method of treatment. You cannot operate in the presence of endocrine diseases or pathologies of the hematopoietic system.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
The diagnosis of chronic sinusitis is established on the basis of the clinical picture (patient complaints, history of chronic inflammatory diseases), as well as physical and instrumental examination.
- During an instrumental examination of the patient, the doctor can use a rhinoscope or endoscope, which helps to detect pathological changes in the tissues of the nasal passages, the presence of polyps, a curvature of the nasal septum, and hypertrophy of the mucosa in the anastomosis area.
- If there is nasal discharge, a bacterial culture is performed to determine the causative agent of the disease.
- If unilateral chronic sinusitis is suspected, diaphanoscopy can be used - transillumination of the sinuses using a Hering light bulb inserted into the oral cavity. In the absence of pathology, normal transillumination of the sinuses is noted, and the patient feels the light source with both eyes. Inflammation in one of the sinuses becomes an obstacle to the path of the beam, which is expressed in the darkening of the corresponding half of the face, and the pupil does not sense the light source.
- To establish a more accurate diagnosis and determine morphological changes, contrast radiography is used . This method allows you to see in photographs taken in different projections of the skull, darkening of the mucous membrane of the sinuses, as well as the presence of exudate, polyps and other neoplasms. In case of pathology of the sinuses, darkening is noted on the radiograph due to the delay of rays by a medium denser than air.
- MRI is used to determine the location and size of tumors.
- CT (computed tomography) allows you to determine the degree of destruction of bone tissue and nearby structures of the facial skeleton.
Chronic sinusitis is differentiated from trigeminal neuralgia, inflammation of the alveolar process of the upper jaw, periostitis of the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus and some immune diseases.
Computed tomography is the optimal diagnostic method indicated for children under 14 years of age
Diagnostics
Sinusitis in the picture
Diagnosing sinusitis is often not difficult, since the course of the disease can be recognized even by the existing signs. The treating doctor can make a diagnosis based on an examination and interview with the patient.
If there is a suspicion of purulent sinusitis, then an additional X-ray examination of the maxillary sinuses is performed, thanks to which the presence of pus can be determined. With a chronic course, diagnosing the presence of the disease is much more difficult. Additionally, a computed tomography scan of the maxillary sinuses may be required to identify a foreign object, polyps, cysts and many other changes. You can see the changes that occur in the nasal cavity during sinusitis in the video.
How to cure chronic sinusitis
Comprehensive treatment of chronic sinusitis begins with eliminating the root causes and factors in the development of the pathology, that is, with dental treatment, removal of polyps, strengthening the immune system, and correcting abnormalities in the structure of the nose. In parallel with this, measures are taken aimed at reducing inflammatory reactions in the mucous membrane, eliminating bacterial or fungal infections in cases of its presence.
Exudative forms of chronic sinusitis can be cured with conservative methods, including medication and physical therapy, while for productive and alternative forms of the disease, surgical intervention is indicated. When eliminating pathology surgically, medications are also used as a way to eliminate infection and suppress the inflammatory process. After the operation, a course of physiotherapy is prescribed, which is necessary to regenerate the mucosa and restore the functionality of the sinuses.
Drug therapy: nasal drops, antibiotics and other drugs
The treatment regimen depends on the manifestations of the pathology, the form and stage of development of the disease (remission, exacerbation). The doctor may prescribe the following groups of medications:
- Antibiotics. Antibiotic therapy is carried out only after confirmation of the purulent form of the disease. Targeted drugs are prescribed after receiving the culture results. Before this, broad-spectrum antibiotics of the penicillin group are prescribed: Amoxicillin, Augmentin. If an allergic reaction to penicillins develops, drugs from the macrolide and azalide group are prescribed: Azithromycin, Sumamed, Clarithromycin. The course of treatment is selected individually and can last from 10 days to 3 weeks.
- Antihistamines are prescribed simultaneously with antibiotics to relieve swelling in the catarrhal form of sinusitis, as well as if the disease occurs due to allergies. Fenspiride is most often prescribed. L-Cet, Tavegil, Claritin are suitable for treating children.
- Decongestants - drugs with pronounced vasoconstrictor properties are used to improve the outflow of exudate from the sinuses. Drugs such as Otrivin, Naphthyzin, Nazivin are used a few minutes before using the sinus lavage with a YAMIK catheter or the “cuckoo” method.
- Antiseptic solutions Chlorhexidine, furatsilin, Miramistin are used to cleanse the sinuses during puncture and use of the YAMIK catheter.
- Local glucocorticoids are used for allergic etiology of sinusitis, as well as if there are polyps in the nose. Most often, drugs are prescribed in the form of a spray, for example, Nazeral, Beconase, Nasobek. This group of drugs is not used in the treatment of chronic sinusitis in pregnant women.
- Moisturizing solutions and sprays based on sodium chloride are used to cleanse the nasal passages of accumulated mucus and dried crusts. Irrigations help restore the mucous membrane and have a moisturizing effect.
Physiotherapeutic methods
Treatment of sinusitis will be effective with complex therapy, which involves the combined use of medications and physiotherapeutic methods:
- Electrophoresis using medications, including enzyme preparations, is prescribed to reduce the severity of inflammatory processes in the sinuses.
- Inhalations with antiseptic solutions, antibiotics and glucocorticosteroids are indicated for the exudative form of the disease. This method of administering drugs allows you to avoid their side effects, as well as deliver solutions sprayed into a fine mist directly to the inflamed tissues.
- Ultrasound treatment allows you to activate metabolic processes in mucosal tissues and accelerate their regeneration.
- Diadynamic pulse currents are indicated for purulent sinusitis. This procedure can reduce inflammation and restore the drainage functions of the sinuses. In addition, it has an analgesic effect.
A course of electromagnetic wave procedures is prescribed to improve sinus drainage and relieve swelling
Sinus rinsing without punctures
Until recently, puncture was considered the only way to wash inflamed sinuses and administer medications into them. This procedure involves puncturing the sinus, which can lead to complications and is not always painless. Today, if sinus drainage is necessary, the “cuckoo” technique and the Yamik sinus catheter are used.
Proetz flushing, popularly called “cuckoo”, involves the movement of liquid under the influence of vacuum. Using a catheter, an antiseptic solution is poured into one nostril, and the liquid with pus is drained from the other nostril using an electric suction. When performing lavage, the patient lies on the couch with his head thrown back, and to prevent the liquid from entering the throat, it is necessary to constantly pronounce the drawn-out sound “ku”, which is why the method got its name.
This technique is used to treat chronic exudative sinusitis in pregnant women.
The flushing procedure using a Yamik sinus catheter is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. The device is made of flexible latex and has a tube with channels inside and small air chambers at the ends. After its introduction into the nasal cavity, air is pumped into the chambers, inflating them, blocking the passage into the nasopharynx and the exit to the outside, thereby creating a sealed space. A syringe is inserted into the catheter and negative pressure is created, which causes pus to be evacuated from the sinus on its own.
The next step is to inject the drug into the sinus, which is pumped into the nasal cavity with another syringe. Due to the negative pressure created, fluid is drawn in through the anastomosis.
Such procedures are contraindicated for children under 5 years of age, as well as for patients with nosebleeds and productive forms of sinusitis.
Treatment of sinusitis with Yamik-catheter without punctures - video
Diet for chronic sinusitis
The diet for chronic sinusitis is based on excluding from the diet those foods that contribute to increased mucus production, fluid accumulation, and intoxication of the body. At the same time, it is recommended to consume foods that can restore the lack of vitamins and microelements, as well as strengthen local immunity.
Prohibited items include:
- Dairy, as it promotes mucus production. The exception is fermented milk products, which restore intestinal microflora. This leads to strengthening of the immune system, which is very important when taking antibiotics.
- Caffeine, rich broths, and offal contain purines, which support inflammatory processes.
- Products containing large amounts of salt, which retain water in the body and cause swelling.
- Alcoholic drinks, since their consumption leads to dehydration of the mucous membrane, which is undesirable for sinusitis.
- Products that enhance mucus production in the body:
- gelatin;
- aspic;
- seaweed;
- corn;
- baked goods;
- white sugar;
- fat meat.
If you are prone to allergies, you should avoid substances that can cause an attack and aggravate the situation.
Products recommended for sinusitis:
- Freshly squeezed fruit and vegetable juices saturate the body with essential microelements and strengthen the immune system.
- Fresh pineapples contain bromelain, a plant enzyme that helps reduce inflammation in the mucous membranes.
- Garlic is rich in essential oils that accelerate blood circulation, which leads to improved metabolic processes in tissues and the elimination of congestion.
- Green tea is a source of antioxidants; for sinusitis, such a drink not only tones, but also reduces intoxication of the body.
When treating a chronic form of the disease using traditional methods, it is recommended to eat raw horseradish. However, such diet therapy can harm the stomach or cause high blood pressure.
Products that can and are useful to eat for sinusitis - photo gallery
Before consuming fresh juice, you should consult a gastroenterologist
Pineapple is useful for sinusitis, but is contraindicated in case of increased acidity of gastric juice
Garlic is suitable for both treatment and prevention of sinusitis
Fresh horseradish contains phytocindes - a powerful weapon in the fight against microbes
Green tea will be doubly tastier and healthier if you add ginger root, lemon and honey to it.
The most effective folk methods against chronic sinusitis
Traditional medicine methods are used as adjuncts against the background of traditional therapy. They:
- relieve swelling;
- promote the evacuation of exudate from the sinuses;
- improve metabolic processes in tissues;
- eliminate pathogenic microorganisms.
Among the most popular traditional medicine recipes used for chronic sinusitis are the following:
- Cyclamen root. It contains saponins - substances that cause increased secretion of mucus, as a result of which the swelling of the tissues disappears, and the exudate is thinned, which facilitates its better evacuation from the sinuses. To prepare drops with cyclamen juice, the root of the plant is grated and squeezed through cheesecloth. The resulting liquid is diluted with a solution of furatsilin 1 to 4 and one drop is instilled into the nostril on the side of which inflammation is observed. The procedure is repeated three times a day for a week. Contraindications are pregnancy and lactation.
- A rinse solution with calendula eliminates inflammation and clears dried mucus from the nose. To prepare it, you can use an alcohol tincture of calendula, purchased at a pharmacy or made at home. One teaspoon of calendula tincture is diluted with a glass of still mineral alkaline water and a teaspoon of salt is added. After making sure that the salt has completely dissolved, the solution is poured into the nostrils using a syringe without a nozzle or a special teapot with a long spout, convenient for nasal rinsing. Such procedures should be carried out twice a day.
- Compresses with Kalanchoe. Cotton compresses with aloe or Kalanchoe juice relieve inflammation and promote mucosal regeneration. To prepare this remedy, the cut leaf of the plant is wrapped in parchment and left in the refrigerator for 8–12 hours. Then it is twisted through a meat grinder, the resulting pulp is mixed with peach oil. Moisten cotton swabs with the prepared product and insert them one by one into the nostrils. The duration of the manipulation is 10–15 minutes.
- Propolis cakes are indicated for catarrhal sinusitis. Thermal procedures are contraindicated in the purulent form of the disease, as well as in the formation of cysts and polyps . To prepare the compress, you need to melt beeswax in a water bath, adding propolis to it in a ratio of 3 to 1. After the mass has cooled to a temperature of 40 ° C, you should form cakes from the wax and apply them from the side of the maxillary sinuses, covering the surface with cellophane and warm with a scarf to keep warm longer. This procedure helps accelerate metabolic processes and eliminates intoxication in tissues.
Before carrying out any thermal procedures, you should definitely consult an otolaryngologist, since in some cases they can cause a worsening of the condition and the development of complications.
Home remedies for chronic sinusitis - photo gallery
Calendula is an excellent antiseptic, which is used in folk medicine to disinfect and relieve inflammation.
Kalanchoe has the property of drawing out pus and restoring mucous membranes
Cyclamen juice may cause burning and sneezing. When using drops for the first time, you should reduce the concentration of juice by half
Beeswax with propolis relieves swelling and has an analgesic effect
Homeopathy
The healing properties of homeopathy are based on the properties of some natural components to influence processes in the body. True homeopathic remedies contain small doses of active substances, which, when the concentration increases, can, on the contrary, cause symptoms of the disease. Thus, homeopathic medicines act on the principle of vaccination, training the immune system in relation to a specific disease. For chronic sinusitis, medications are selected individually by homeopathic doctors.
In regular pharmacies you can purchase drugs called homeopathic, due to the natural components they contain. They are often prescribed to children and women during lactation. The most popular are Sinuforte and Cinnabistin tablets, which eliminate symptoms and improve the patient’s well-being.
Surgical intervention
Indications for surgery are:
- productive forms of chronic sinusitis;
- fungal infection in the sinuses;
- lack of a positive reaction to conservative therapy carried out for three weeks.
Puncture or puncture
This method is used for both diagnosis and treatment. A puncture with a Kulikovsky needle is performed under local anesthesia. It is done at the top point of the arch of the lower nasal passage.
After the puncture, the doctor attaches a syringe, which draws out the contents of the sinus and injects the drug into the cavity. If necessary, a catheter is inserted into the puncture area, through which drainage and medication are subsequently administered.
Endoscopic surgery
Surgery using an endoscope allows you to minimize tissue trauma, since you do not need to open the sinus wall to perform various manipulations. The endoscope, like a surgical instrument (laser, scalpel, forceps), is inserted through a natural opening, after which the necessary actions are performed - removal of polyps, fungal mycetoma, restoration of patency of the anastomosis. An image enlarged several times is displayed on the monitor, which allows the surgeon to operate purposefully - to remove pathological tissues without affecting healthy ones.
Colwell-Luke operation
This manipulation is carried out through the dissection of the fossa located above the gum line, as a result of which the surgeon gains access to the cavity to cleanse it of pus or excise tumors. The operation is performed both under local anesthesia and general anesthesia.
Endoscopic surgery can reduce the rehabilitation period by half
Treatment of the disease
There is a unified system for classifying diseases - ICD-10. It is designed for the convenience of doctors and allows doctors to quickly obtain data on diseases. Every 10 years, the World Health Organization checks the document from the database and the accuracy of the information provided in it. Thus, chronic sinusitis has a code according to ICD-10 – J32. Depending on the pathogen and the general condition of the patient, doctors choose the method of therapy.
Attention! It is quite difficult to achieve complete relief from chronic sinusitis! However, complex measures can quickly eliminate symptoms and eliminate inflammation.
How to treat chronic sinusitis without surgery
Treatment in adults involves clearing infected sinuses of bacteria and mucus. A distinction is made between drug therapy and treatment without antibiotics.
Vasoconstrictor drops will help get rid of numerous nasal discharge and eliminate swelling. But the dosage prescribed by the doctor should be strictly followed. Otherwise, there is a risk of the body becoming accustomed to the medicine.
Chronic odontogenic sinusitis resolves quickly. It is only necessary to perform sanitation of the oral cavity. Elimination of the source of infection is the main method of treating chronic odontogenic sinusitis.
It is important to know! If the cause of sinusitis is an allergy, the doctor will prescribe antihistamines. Sometimes a hormonal medicine is prescribed - Nasonex.
Treatment with antibiotics
Antibiotics are used to stop the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. They eliminate the cause of sinusitis. Fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, penicillins, and macrolides are prescribed. Antibiotics have the main effect, but local antiseptic sprays are additionally used.
Most often, patients are prescribed the following antibiotics:
- Macropen;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Augmentin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Cefazolin.
New generation antibacterial drugs - Azithromycin, Cefix - help to recover in a short time.
As for topical medications, vasoconstrictors (Galazolin, Xymelin, Rinorus, Tizin) and antibacterial (Isofra, Polydexa) drops and sprays are used in the treatment of sinusitis.
During exacerbation
Drug therapy in the acute period involves the use of drugs that reduce swelling of the mucous membrane and promote the removal of mucus. If purulent discharge is present, only antibiotics will help. They can be in tablets, injections or drops.
A common method is to pierce the sinuses using a special needle. After the manipulation, rinse with antiseptics and introduce an antibacterial drug into the cavity. These are the most effective measures that eliminate headaches and other symptoms of acute sinusitis.
A good alternative to a puncture is the painless procedure of installing a catheter. It is performed under local anesthesia and does not require additional actions in the form of a puncture.
Important! Auxiliary treatment consists of taking general strengthening drugs, a complex of vitamins, and immunomodulators.
Remission
During the period of remission, the disease cannot be ignored. Pathogens should be completely eliminated. Otherwise, after some time, sinusitis will worsen.
Outside of an exacerbation, antibiotics are usually not used; local therapy is used. Rinsing the nose with medicinal solutions reduces discomfort and suppresses the active proliferation of microbes.
Surgery
Sinusitis can be cured without surgery. But if conservative treatment does not bring the desired results, surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
Indications for surgery are the following:
- tissue proliferation in the paranasal sinuses;
- the presence of foreign bodies, fistulas between the sinus and the oral cavity;
- inability to perform a puncture;
- infection of formations.
Know! Surgery will not help prevent relapses. Recurrent sinusitis is possible.
The preferred method of correction is endoscopic surgery using general anesthesia.
Physiotherapy
Various physiotherapeutic procedures are used in the treatment of sinusitis. The choice depends on the form of the disease - acute or chronic, the stage and severity of the process.
Prescribed:
- electrotherapy;
- laser treatment;
- therapy with ultra-high frequency currents;
- medicinal inhalations.
They use special magnetic therapy devices, nebulizers, and universal physiotherapeutic devices.
Treatment with folk remedies
Many patients believe that homeopathy therapy is an effective treatment. Of course, additional actions will not hurt if you use them with the permission of your doctor and in moderation.
Treatment with folk remedies involves rinsing the nasopharynx with sea water, as well as herbal decoctions and oils:
- propolis oil;
- Kalanchoe juice;
- celandine and aloe juice;
- oil from thuja cones and needles;
- cyclamen juice.
Let's look at the most popular recipes.
Sea salt
For effective treatment, it is necessary to regularly rinse the sinuses. For this procedure, you can prepare the following solution: 1 tsp. Dissolve sea salt in 0.5 liters of warm water.
Cyclamen
To prepare this product, you will need to squeeze the juice from the grated cyclamen root. Dilute with Furacilin solution in a ratio of 1:4. Place the resulting drops into the affected nostril 3 times a day for 3 weeks.
Attention! Doctors recommend using herbal decoctions and mixtures at home only after consulting an otolaryngologist!
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
In the treatment of chronic sinusitis, the prognosis is conditionally favorable. The result depends on well-chosen therapy and the stage of the disease at which the patient sought medical help. In exudative forms of chronic sinusitis, drug treatment and adherence to the rules of prevention make it possible to transfer the disease to the stage of long-term remission.
Productive forms of sinusitis require surgery, the result of which depends on the skill of the surgeon. After its implementation using any of the methods described above, complications are possible in the form of:
- violations of the innervation of the upper jaw;
- blurred vision;
- fistula formation;
- secondary infection of the cavity.
If left untreated, complications may occur such as:
- meningitis;
- sepsis;
- osteomyelitis of the upper jaw;
- inflammation of the optic nerve;
- phlegmon of the orbit of the eye.
Treatment
Since sinusitis threatens with quite dangerous complications, it is imperative to carry out competent, timely treatment, which can be conservative or surgical. Conservative therapy implies:
- taking medications;
- traditional methods;
- physiotherapy.
Treatment of sinusitis in adults at home involves the use of complex therapy. The treatment plan should be drawn up exclusively by a doctor, since incorrectly administered therapy can lead to complications and the disease becoming chronic. You can learn more about how sinusitis therapy is carried out by watching the video.