Gouty arthropathy is a chronic disease that affects the joints and tissues around them. It occurs due to a violation of cell metabolism, due to too high levels of uric acid. As a result, sodium urate crystals accumulate in the joints, tissues around them, as well as in internal organs.
A person rarely feels this happening and notices the disease only when it takes on an acute form and suddenly attacks. After this, for a short period of time the joint swells and turns red (this mainly concerns the big toe, knees and ankle joint), it hurts, and the person may develop a fever.
Without treatment, gout can lead to heart disease, chronic inflammation of the joints, and pathologies in the functioning of the kidneys and blood vessels.
It can appear at any age, but most often men after forty and women after sixty suffer from this disease.
Causes and mechanisms of development of gout and gouty arthritis
- age (usually elderly);
- gender (usually male);
- eating habits (tendency to eat meat, alcoholic beverages);
- physical overload;
- hypothermia;
- kidney disease, in which the excretion of uric acid is impaired.
The basis of the disease is a violation of uric acid metabolism. An increase in the level of the latter may be due to its high production, low rate of elimination, or a combination of these two mechanisms.
At the beginning of the disease, uric acid salts accumulate in the body, then begin to be deposited in the tissues. Then the inflammatory process develops, initially acute. Over time, inflammation becomes chronic. Uric acid crystals are deposited in joints, tendons, blood vessels, and kidneys. As a result, gouty arthritis, nephropathy develop and nodules (gouty tophi) form.
There is primary and secondary gout, the latter is a manifestation of other diseases (psoriasis, leukemia, renal failure, etc.) or a consequence of taking medications (cytostatics, diuretics, etc.).
Complications arising from the disease
The course of the disease in the absence of therapy causes dangerous consequences. The transition from the acute stage to the chronic stage is one of the common complications. This stage is more difficult to treat; all joints and tissues of the body are involved in the process.
Excessive accumulation of uric acid in the joints causes the formation of gouty nodes - tophi. They are visible under the skin, white growths protrude under the skin, showing through in lumpy forms. If there is excessive accumulation, the node bursts, and a whitish substance with a cheesy consistency is visible in the open wound. These are excess urates that have settled in the form of crystals.
In the chronic form of gout, the affected joints lose mobility completely, and the joint capsule and bones are destroyed. Excess uric acid deposited in ligaments and tendons leads to their rupture during physical activity.
If the disorder is not treated, the accumulation of urate crystals causes complications associated with joints and internal organs. The disease often affects the kidneys. If they cannot cope with the removal of uric acid from the body, then this substance accumulates in them. In severe cases, kidney stones form, blocking the tubules. In this case we are talking about acute, chronic renal failure.
Complications make gouty arthritis a dangerous disease that, if left untreated, can lead to serious consequences.
Clinical manifestations of the disease
- Initial stage, without symptoms of the disease.
At this stage, the level of urate in the blood is increased, but there is no deposition in the joints and there is no arthritis; it can last up to 20 years.
- Acute gouty arthritis.
The disease begins with an acute attack of arthritis, most often the joint of the big toe is affected, less often the ankle, wrist, elbow, etc. The onset of the disease is so sudden and acute that the patient can clearly name the time when he fell ill. As a rule, an attack of acute pain develops against the background of complete health at night, possibly after overeating, drinking alcohol, or physical overload. The pain is accompanied by chills, increased body temperature, the joint becomes hot, swollen, sharply painful at the slightest touch, patients cannot find a position that will alleviate their condition. Typically unilateral joint damage. This attack lasts from 3 to 10 days and can go away without treatment.
In the first years of the disease, the interictal period is long. In most patients, arthritis recurs within the first year, but sometimes this period can last for years. As the disease progresses, the intervals between attacks decrease, and the duration of the attacks themselves increases.
- Chronic gouty arthritis and urate deposition.
It develops when the rate of urate formation exceeds the rate of their elimination and they begin to be deposited in tissues, forming so-called tophi (whitish deposits of crystals in the ears, in the area of affected joints, along the back surface of the elbows).
Periods of the disease
At the initial stage, no symptoms are detected. The analysis will show a large amount of uric acid. Diagnosis during this period is impossible. It's called latent.
The second stage is acutely relapsing. At this stage, a person realizes that he is sick. X-ray shows the lesion on the joints. The disease creeps up asymmetrically. Painful sensations of moderate intensity. The symptoms are complemented by a blue tint to the skin at the site of the lesion. The joint becomes larger in volume.
Gout is accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication. The patient feels chills, general malaise, and weakness. To establish the correct diagnosis, it is worth doing a blood test and an x-ray later. Gout at this stage is marked by attacks that periodically recede and come again. The presence of acid in the urine contributes to the further progression of the infection. When the treatment does not provide the desired result, the disease moves into the next stage – chronic.
X-rays show that at this stage, the formation of seals located on tissues and joints occurs.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of gouty arthritis is based on clinical manifestations, examination data by a specialist, as well as additional examination data. The level of uric acid in the blood increases to more than 0.42 mmol/l in men and more than 0.36 mmol/l in women. During an attack, signs of inflammation appear in the blood - ESR, leukocyte count, seromucoid, haptoglobin, and sialic acids increase. When examining the joint fluid, urate crystals are detected. On an x-ray, changes are detected at the stage of a chronic process in the joints. It is also possible to perform an ultrasound of the joint, which reveals signs characteristic of this pathology.
Therapy for this disease is aimed at relieving an acute attack of gout and its long-term treatment.
Treatment of an acute attack of gouty arthritis
The sore limb must be placed in an elevated position and provided with rest; during periods of severe inflammation, ice can be applied, and after the pain subsides, a warm compress can be applied. The patient needs to drink plenty of fluids up to 2.5 liters and strictly adhere to the diet. Medicines prescribed:
- colchicine (the most effective drug, prescribed as early as possible, discontinued a few days after the attack has subsided);
- anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, rheumoxicam, nimesulide, etc.), if there is no effect, hormonal drugs (prednisolone) can be prescribed;
- local treatment with the appointment of compresses of anti-inflammatory drugs and dimexide.
Long-term preventive treatment
- Lifestyle correction (fighting physical inactivity, proper organization of work and rest, losing weight, avoiding the consumption of alcoholic beverages).
- Diet.
Table No. 6 (offal, canned food, sorrel, legumes, chocolate, broths are excluded, the consumption of meat, fish, etc. is limited).
- Drug treatment with drugs that reduce the level of uric acid in the body (allopurinol, probenecid, sulfinpyrazone, allomaron, etc. are prescribed). This treatment is prescribed for high levels of uric acid (more than 0.48 mmol/l), frequent attacks (more than 3 during the year), chronic arthritis, the appearance of tophi, and kidney damage.
Basic principles of treatment:
- long-term treatment (years);
- cannot be started in the acute period;
- in the first days, colchicine or indomethacin and drinking plenty of fluids are prescribed to prevent attacks;
- it is necessary to clarify the type of uric acid metabolic disorder and, depending on this, select the necessary drug.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Treatment with physical factors is aimed at reducing pain, inflammation, correcting joint deformities, normalizing urate metabolism, reducing the duration and frequency of gout attacks.
In the acute period it is recommended:
- UV radiation of the joint in an erythemal dose;
- exposure to pulsed currents;
- high-frequency magnetic therapy (improves tissue nutrition, reduces inflammation);
- application of dimexide to the affected joint.
During the interictal period it is recommended:
- exposure to ultrasound on a sore joint (anti-inflammatory effect, destruction of uric acid crystals);
- phonophoresis with hydrocortisone (improves the removal of urate from the body);
- decimeter wave therapy on the area of the adrenal glands (activates the release of glucocorticoids into the blood, has an anti-inflammatory effect);
- balneotherapy (improves blood circulation and tissue nutrition, improves urate excretion), radon and iodine bromide baths are prescribed;
- drinking treatment with sodium bicarbonate mineral waters (by changing the pH of the blood, they inhibit the formation of urates and improve their excretion).
In conclusion, I would like to note that gout and gouty arthritis are pathologies that significantly disrupt the normal life of patients, leading to joint deformities and kidney failure. If the diagnosis is established in the early stages and the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, then with adequate treatment the quality of life increases and the progression of the disease slows down.
Specialists from the Kyiv Regional Clinical Hospital talk about gout and its treatment:
Read also: Arthritis of the joints
Rheumatologist Ilya Maslakov talks about gouty arthritis:
Measures for diagnosing gout
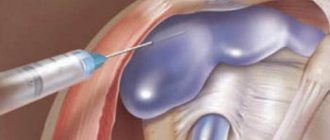
The main point of diagnosis is the detection of urine salt crystals in the synovial fluid. Take it for analysis, perhaps from any large-shaped joint, for example, the knee. Whether there is a lesion there or not is not important. You can take fluid for analysis during the period of exacerbation of the disease, at the stage of remission. For examination, the doctor can take the content of the tophi of another biological substance.
However, the confirmation of the diagnosis of “gout” is not the excess urea content, combined with the periodic inflammatory process of the joints of the big toes. Such symptoms are considered an indicator of changes in purine metabolism. Most people with this symptom do not experience gout.
If the illness lasts a long time, you need to undergo an x-ray. At the initial stage there are no signs of changes. Typical for gouty arthritis, they appear on x-rays. X-rays will show cartilage destruction, toe bone defects, and punctures.
When gout develops in the upper extremities, it is difficult to distinguish it from other diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Laboratory diagnosis is advisable. By doing a blood test, you can find:
- increase in ESR;
- neutrophilic leukocytosis;
- increased content of alpha-2 globulin, fibrinogen;
- manifestation of c-reactive protein.
These signs are detected during an attack and go away when it stops.
When gouty arthritis occurs, the characteristic diagnostic criteria are:
- hyperuricemia;
- the presence of gouty nodular formations, which are shown by x-ray;
- the presence of crystals of urine salts in the joint fluid, near the joint tissues;
- cases of acute arthritis, severe pain that began suddenly and suddenly went away after two days.
Severe pain
Is gout a disease of lovers of the good life?
No inflammatory joint disease is as closely tied to our lifestyle as gout. Moreover, this disease has the simplest and at the same time complex treatment. If it weren’t for the huge number of medical errors, the reason for which is ignoring some important components of a biochemical blood test, then treating gouty arthritis would not be difficult. In past centuries, gout was considered a sign of being chosen, since only noble nobles could eat well then.
Gouty arthritis: treatment and symptoms
Who is at risk of getting sick?
Today, gout is called a disease of obese people and lovers of good food. Mostly men suffer from it, and this is not without reason:
It is men who prefer red meat, smoked fish, alcohol, especially beer, which contains xanthine and guanosine in their diet - the breakdown products of these compounds are those same ill-fated purines, as a result of which uric acid is formed.
Elevated levels of uric acid in the blood are hyperuricemia
However, this does not mean that women do not suffer from gout: a woman’s advanced age is usually accompanied by hormonal disorders that can provoke gouty arthritis.
Added to this is physical inactivity, which sharply slows down metabolism - and uric acid accumulates in the blood
Factors contributing to the development of gout
Provoking factors for gout can also be:
- Taking diuretics in the treatment of hypertension
- Antitumor therapy
- Autoimmune diseases
- Kidney failure
- Glycogenosis
- Genetic predisposition
- Stress
The presence of ancestors in the direct line of people with gout does not mean the inevitability of the disease - all you need to do is monitor your lifestyle:
- Avoid overeating and unhealthy foods on the menu
- do not abuse alcohol
- avoid stress and exercise
How does gouty arthritis develop?
The bad thing is that uric acid is insoluble in water, alcohol, or ether. It is susceptible to dissolution in alkaline solutions, hot sulfuric acid and glycerin
What is constantly in the blood inevitably crystallizes, and then the process proceeds in stages:
- Uric acid precipitates as urate salts
- Urate salts begin to deposit on the cartilaginous hyaline surface
- The joint naturally reacts with inflammation sooner or later - this reactive response is called gouty arthritis
- Such an inflammatory reaction may not appear immediately - and gout does not manifest itself with any external signs and symptoms for a long time.
If the only symptom of gout is hyperuricemia, this stage of the disease is called latent.
The first manifestation of the disease manifests itself in the form of an attack - acute gouty arthritis begins
The first signs of the disease
- Acute gouty arthritis begins suddenly with an attack of severe, sometimes unbearable pain: the slightest touch to the affected area or attempts to move cause suffering
- The attack usually begins at night
- The affected joint swells, the skin over it becomes purplish-red and feels hot to the touch.
- In 90% of cases, one joint of the big toe is affected, but other joints can also become inflamed. The photo shows an example of gout of the toes:
- Less commonly affected are the joints of the hands, ankles, knees, elbows, and wrist joints.
- After three or four days the exacerbation goes away without a trace
- After some time the attack repeats again
The alternation of sudden attacks with temporary relief, the prolongation of each subsequent attack and the reduction of intervals between exacerbation phases are all signs of the development of gout.
Symptoms of chronic gouty arthritis
In the final stage, the pain practically does not recede - chronic gouty arthritis is diagnosed.
Symptoms of chronic gout appear:
- Complete destruction of hyaline cartilage
- Skin periarticular growths (tophi) In the photo - gouty tophi:
- The formation of so-called punches - cavities in the bone epiphyses
- Both the punches and subcutaneous tophi are filled with urate salts - this explains the whitish color of the skin over the nodes. When the tophi is opened or ruptured, a white mushy mass is found inside it. In the photo - gout with the tophi opened:
Tophi nodules form not only under the skin over the diseased joint, but also on the ears.
The development of urolithiasis and pyelonephritis are signs that gout is already severely advanced
Symptoms of female gout are milder:
- Acute attacks are rare
- Chronic aching pain, most often in the knee or ankle
- Formation of tophi and punctures occurs less frequently
Cause of medical errors
The symptoms of gout are often mistaken for arthrosis, especially when diagnosing the disease in women:
It’s not so bad if incorrect conservative treatment is carried out followed by incorrect recommendations for “collagen” nutrition - a diet with jellies and rich meat broths, which are killer for gout.
It is much worse when, having stated the complete destruction of the joint, would-be doctors offer expensive and absolutely useless endoprosthetics: uric acid urates after this operation are gladly taken for the remaining healthy joints.
Surgeons can, without hesitation, mistake gout for gangrene and, having opened the toe, later click their tongues in surprise: Eka, the process is progressing quickly! - so it went to the other finger...
All that was needed was to check the level of uric acid in the blood.
The most surprising thing is that even the existing analysis with an indicator of uric acid content that is twice as high does not really burden the minds of some “specialists”.
Another difficulty in diagnosing gouty disease is taking a biochemical analysis during an acute attack:
- During an exacerbation of gout, the concentration of urate crystals increases in the diseased joint, and the level of uric acid in the blood may be within normal limits
- To exclude medical error, you need to re-take the test in the intervals between attacks.
How to treat gouty arthritis
If treated correctly, gout can be completely cured.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment is carried out using the following drugs:
- During an acute attack, colchicine, a drug used specifically to treat gout, is used for three to seven days.
- It is also acceptable to take conventional NSAIDs: ibuprofen, indomethacin, movalis, nimesil, etc.
- Therapy is carried out over several months or even years to reduce the level of uric acid in the blood - allopurinol or Zeloric is used for this purpose.
- To remove urate salts along with urine, probenecid, etebenecid, sulfinpyrazone are used.
- In order to destroy existing monourate crystals, the drug uricozyme is prescribed
Read also: Arthritis disease
There are serious contraindications for probenecid and uricozyme group drugs:
- Nephropathy
- Kidney failure
- Serious kidney pathologies
Therefore, these drugs are not considered essential in the treatment of gout.
Diet is an important condition for curing gout
Any drug treatment will not bear fruit if the patient does not show will and does not moderate (literally) his appetite
Unfortunately, there are slaves of the stomach who, even on pain of death, are unable to give up their addictions. For such people, treating gout is very difficult: they are constantly (from attack to attack) forced to take allopurinol, which they manage to eat with juicy steaks and wash down with beer.
For other ascetics, in terms of nutrition, one course of medication is enough to cure the disease.
That is why treatment of gout is both easy and difficult - it all depends on the connection to a specific person.
The figure below shows a table with allowed and not recommended products:
Special diets for gout are at the end of the article.
Treatment of gout with folk remedies
Gout can be cured by removing uric acid from the body and always using a diet. If you don’t do this, no folk remedies will help.
Local treatment in the form of all kinds of lotions and compresses may relieve inflammation and pain, but will not exclude the possibility of further attacks, so we will not even consider it.
The exception is decoctions and tinctures taken orally to remove salts.
The following folk remedies may be of interest:
- Freshly squeezed black radish juice: Start drinking one teaspoon at a time, gradually increasing the dose to a tablespoon, and then to half a glass.
- You need to drink with caution, as the juice can cause hepatic colic and increased bile secretion: for pain on the right side, reduce the dosage
- avoid spicy and sour foods during treatment
- Pour a teaspoon of roots into a glass of boiling water and boil for 10 minutes in a water bath.
- Pour five grams of leaves into 300 g of boiling water and boil uncovered for five minutes.
- Rinse two tablespoons of rice and add water overnight in a half-liter jar
Video: How to treat gouty arthritis:
Treatment
Treatment consists not only of taking medications, but also of completely changing your lifestyle. This is a very important condition that significantly affects the patient's condition. To prevent the disease from developing further, it is recommended:
- eat as little seafood and meat as possible;
- increase your vitamin C intake;
- do not drink alcohol or consume fructose;
- body weight should be normal;
- drink as much fluid as possible;
- increase the amount of vegetables and dairy products in the diet;
- do not eat products made from wheat and yeast;
- regular gymnastics classes, etc.
If you follow all the doctor's recommendations, gout can be cured and you can maintain a normal, fulfilling lifestyle. If the disease is not started, it will not affect the duration and quality of life.
The exception is patients in whom gout develops simultaneously with diabetes, urolithiasis or arterial hypertension. Then the treatment is very difficult and can still lead to disability.
There are many traditional methods for treating this pathology, but it is better to use them only after consulting a doctor.
Gouty arthritis: forms of the disease and its treatment
Yulia Voinova
Rheumatologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Area of scientific interests: cardiovascular pathology in systemic connective tissue diseases, modern methods in the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid, psoriatic, gouty and other arthritis, reactive arthritis.
Author of a method and computer program for early diagnosis of heart failure in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, organizer and leader of schools for patients.
- This author does not have any more posts.
Before we dwell directly on the features of damage to the osteoarticular system in gout - gouty arthritis itself - it is necessary to define the disease itself. Gout is a chronic disease in which there is a deposition of urate crystals in various tissues of the body, which in their chemical structure are represented by crystals of monosodium urate and/or uric acid. According to the International Classification of Diseases, X Revision (ICD-10), gout and its accompanying gouty arthritis are classified as diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue. The most common clinical manifestation of this disease is “classic” acute gouty arthritis. The first attack (attack) is most often observed at the age of 40-50 years, although it can occur at any age. Men are most susceptible to this pathology.
Acute gouty arthritis
The most typical acute (sometimes even very acute) onset of the disease, often at night or in the early morning hours. There is very sudden, sharp and severe pain in the joints, usually the feet. The pain increases quite quickly, sometimes reaching unbearable intensity, the externally affected joint is swollen, the skin over the projection of the joint is hot and red. Active and passive movements in the joint are impossible or severely limited, the patient has difficulty walking. Pain in the affected area can be so intense that even in a calm state it causes unbearable suffering; even touching clothing causes aggravation of symptoms. In severe cases, the joint changes its configuration so much that a specialist sometimes thinks about a diffuse purulent lesion (phlegmon). As we indicated above, during the first attack of gouty arthritis, arthritis of the joints of the foot is observed, especially often damage to the joint of the big toe (monoarthritis - damage to only one joint) of the leg occurs, which is an undoubted indication of possible gout. Slightly less often, damage to the elbow, knee, wrist joints, hand joints, hip joints and other localizations is observed. Sometimes during an attack of acute gouty arthritis, severe general malaise is observed: increased body temperature, sweating. Also, in blood tests, increased ESR and leukocytes (leukocytosis) - nonspecific markers of inflammation - may attract attention.
Among the factors that provoke an attack of arthritis (triggers), the following are the most common:
- injury,
- increased physical activity,
- stress,
- violation of the diet (often an attack occurs after feasts),
- excessive alcohol consumption,
- infections,
- bleeding,
- surgical operations,
- taking certain medications (for example, diuretics, antitumor drugs, vitamin B12, heparin, etc.) and some other reasons.
Read also: Stiff fingers
Despite such an acute and sudden onset, arthritis with gout is also characterized by a very rapid “fading” of symptoms (even without treatment) within a few days. This feature should suggest the possibility of gouty arthritis. However, this feature of the disease is not a reason not to pay attention to such an insidious disease, since untreated gout is very variable in its clinical expression. Thus, in advanced cases, there is a gradual increase in arthritis attacks and/or a tendency towards a more prolonged course. In the most difficult cases, we see the most severe course of the disease with an almost complete absence of interictal (“light”) periods and the formation of so-called tophi - deposits of urate crystals.
Chronic gouty arthritis
This is essentially an already developed picture of the disease, characterized by the presence of various manifestations of this disease: tophi, chronic forms of joint damage, kidney damage resulting in urolithiasis (KD). The most typical localizations of tophi are as follows: joints of the hands, elbow and knee joints, joints of the feet, as well as in soft tissues - in the projection of tendons, ears. Tophi often do not cause pain and are often located near the most persistently affected joints. Sometimes tophi can spontaneously open, and thick, pasty, whitish or yellowish contents are released from the opened tophi. In severe cases, suppuration and ulceration of the tophi may occur. Sometimes numerous joints are involved in the pathological process, and the course of the disease begins to resemble rheumatoid arthritis, which requires a careful differential diagnosis. In severe cases of the disease and in advanced cases, there is severe, disabling damage to the joints with their persistent and severe deformation and dysfunction.