Breast contusion is a closed injury. It is painful, dangerous with the prospect of complications, and requires increased attention. You can get injured everywhere: at home, in transport, while playing sports, due to an accident. The only correct tactic is to immediately consult a doctor. Initially, the woman needs to call an ambulance - specialists transport the patient to the emergency department. The doctor will prescribe an examination, and based on its results it will become clear what amount of intervention is required to normalize the condition.
Causes
Chest injuries can occur for many different reasons, but most often they occur as a result of road traffic accidents, conflict situations involving the use of physical force, or falls from great heights.
Depending on the cause, chest injuries can manifest in different ways. If a blow to the chest was caused by a moving object, the lung may be injured (without tissue rupture) or hemothorax may form. Such injuries may also be accompanied by rib fractures, which significantly complicates the situation. When the victim hits something hard, the lung may be damaged with swelling and bleeding, but the lung tissue remains intact. The heart muscle may also be damaged, which in itself is a very serious injury that requires immediate evaluation and treatment in a hospital.
With strong pressure on the chest, a strong outpouring of blood from the heart into the veins located in the upper chest, neck and head is possible, which in most cases leads to the death of the victim.
Diagnostic measures
The first thing a woman should do after an injury is to conduct an independent examination of the breast.
It is necessary to check each of the glands sequentially with your fingers, paying attention to compactions, areas of swelling, and asymmetrical areas. They also evaluate the appearance of the glands in the mirror, paying attention to the skin, nipple retraction, and the appearance of a venous pattern. If any abnormalities are detected, consult a doctor.
Chest contusion is mainly diagnosed using ultrasound. In this case, the doctor pays attention to the zonal decrease in echogenicity. If the patient comes rather late, and fibrin has already begun to form in the hematoma, hyperechoic zones may be detected.
Additionally, mammography is used. It is used to determine whether there are tumor changes in the gland tissues.
If necessary, MRI, CT, and ductography may be prescribed if the diagnosis needs to be clarified.
Classification
The classification of chest injuries depends on many factors. Injuries are distinguished by the presence or absence of combined injuries:
- isolated;
- combined (with bone fractures, organ injuries, TBI).
Also, chest injuries are classified according to the mechanism of occurrence:
- Concussions;
- Bruises;
- Squeezing;
- Fractures.
Anatomical disorders:
- With a violation of integrity;
- Without violating integrity.
Classification according to the presence or absence of organ damage:
- With damage to: lungs, heart, bronchi, esophagus, etc.
- Without damage.
Upon occurrence of complications:
- With complications - complications can be early (traumatic shock, pneumothorax, hemothorax) and late (purulent lung diseases, pleurisy).
- No complications.
Chest injuries are also divided depending on the nature of the damage to the lungs and heart:
- absence of respiratory failure;
- respiratory failure of the first, second and third degrees;
- absence of cardiovascular failure;
- cardiovascular failure of mild, moderate and severe severity.
When should you see a doctor?
After injury to the breast, it is important to conduct a self-examination, carefully palpating all its sectors and the armpit area. It is better to examine the breast in front of a mirror.
The reason for an immediate visit to a mammologist is:
- Uncharacteristic color of breast skin.
- Retraction of the nipple or skin into the gland.
- Change in the shade of the venous pattern.
- The presence of compaction and nodes in the structure of the breast.
First aid
With such injuries, first aid can play a very important role. If the injury is very serious, timely emergency assistance may even save the victim's life.
Closed injuries of mild and moderate severity are considered the simplest and respond well to treatment. To provide first aid for a bruise or compression of the chest, you must:
- Eliminate external factors influencing the formation of injury (if necessary);
- Provide the victim with the opportunity to breathe freely;
- Reduce pain using painkillers;
- Take the victim to the hospital or call an ambulance.
Open injuries are considered more complex when the integrity of soft tissues and mucous membranes is damaged. With this injury, severe hemorrhage, damage to internal organs and air flow to the pleural zone are observed. In the case of a severe open injury, the life of the victim depends on how quickly he is taken to the hospital.
In case of penetrating wounds of the chest, you must first close the hole that provides access to the pleural cavity. To do this, you can use a pressure bandage or medical plaster. After the hole is closed, the patient should be immediately taken to the hospital, where he will be given an accurate diagnosis and further treatment will be prescribed.
Treatment for each patient is selected individually, based on the nature of the injury, severity and risk of possible complications. For bruises, painkillers and, in some cases, antibiotics are prescribed. A few days after the injury occurs, the patient is prescribed physical therapy.
Regardless of the type of injury, the patient must undergo radiography and other diagnostic measures to determine the exact clinical picture and exclude the possibility of concomitant injuries.
Diagnostics
To find out the nature of the consequences of the injury and determine how much glandular tissue is affected by the pathological process, the woman is sent for tests.
Informative diagnostic methods:
- Laboratory testing of blood and urine. Allows you to detect the level of leukocytes and ESR (with active inflammatory processes, these indicators are increased). With a tumor, these criteria may remain unchanged, despite severe pain and swelling of the breast.
- Ultrasound of the breast. Basic research method. After laboratory tests, they immediately move on to this type of research, since from the entire diagnostic program, it provides a significant amount of information. Allows you to first understand the reason for the change in the shape of the mammary gland. If the swelling of the breast is associated with post-traumatic edema, during an ultrasound the doctor will determine the reduced echogenicity of the tissue. As the hematoma resolves, this indicator decreases. This does not happen with a tumor process.
- Radiothermometry. The temperature inside the glandular tissue and on the surface of the chest is determined. Electromagnetic radiation is detected in the microwave and infrared range. Receive information about the thermal activity of breast tissue from the outside and inside. Radiothermometry is an effective type of screening to exclude the development of a malignant neoplasm. The procedure also helps to monitor the effectiveness of the prescribed therapeutic program.
- Mammography. Thanks to the study, it is possible to confirm or refute the formation of a tumor. Typical post-traumatic changes are not characterized by the same signs as a neoplasm.
Complex radiation imaging methods are used in rare cases. Basically, when they cannot determine the cause of changes in breast parameters for a long time, if it is not possible to find out the nature of the tumor that has formed. Also, CT and MRI make it possible to determine the degree of blood supply to the breast, which is especially valuable on the eve of surgical interventions.
Fractures of the sternum and ribs
Typically, a fracture of the sternum is quite rare. The first sign of such an injury is pain, which gets worse when the victim takes deep breaths or coughs. Such a closed chest injury can only be treated in a medical facility, and during the therapy, painkillers and bed rest are prescribed.
There are the following types of rib fractures:
- tear-off.
- straight;
- indirect.
The most dangerous is an avulsion fracture - due to the displacement of bone fragments, the vessels and internal organs located inside the chest cavity can be severely damaged. When the intercostal vessels are injured, heavy bleeding occurs in the pleural cavity and hemothorax occurs. If a broken rib penetrates the lung tissue, and air from the lung begins to escape into the pleural cavity, a pneumothorax is formed. More often, rib fractures occur in adults, since in children the bones still have an elastic structure.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Chest injuries with rib fractures have the following symptoms:
- pain syndrome;
- impaired breathing;
- reduction of pain when sitting.
Treatment
To stop bleeding and maintain breathing, you need to take the necessary measures as quickly as possible.
If a simple rib fracture is observed, then bed rest is necessary.
The doctor prescribes medications so that the patient does not feel pain.
Applying heat is also helpful. In the case of more significant fractures, agents are often used to numb the nerves in the area between the ribs. It is possible to reduce pain. If it is difficult to breathe, a breathing tube is inserted into the victim.
If necessary, blood transfusions are given to compensate for blood loss.
To cope with lung injury, doctors take the necessary measures. To do this, a tube is inserted into the chest - it is possible to remove the air from the chest, the lungs expand. The introduction of saline solution for hemothorax helps prevent a state of shock.
Compressions, bruises and concussions
With mechanical compression of the chest, the injury is characterized by many factors:
- Breathing disorders;
- Development of suffocation;
- Sometimes complete loss of consciousness.
The skin in the neck and at the top of the sternum may swell and take on a bluish tint. Permanent loss of vision and hearing is possible, as hemorrhage occurs in the area of the eyeball and inner ear. In case of chest compression, the patient must be hospitalized, after which he must be in a semi-sitting position and completely at rest. The respiratory tract is also sanitized.
Bruises can be observed much less frequently than complete rib fractures; they are formed after a blow from a blunt object to the chest area, or after compression between two large blunt objects. Such a “blunt” injury is characterized by the occurrence of a hematoma and tolerable pain. Most often, in such situations there is no need to resort to special treatment, but sometimes, due to severe bruises, heavy bleeding can occur in the cavity and tissue of the chest, and be accompanied by damage to internal organs. In this case, the injury is considered severe and requires immediate hospitalization of the victim.
In the event of a chest concussion, the victim experiences a severe state of shock without any physical changes. The first signs of a concussion are heavy breathing with pain, rapid heartbeat and cold extremities. In case of such an injury, it is necessary to urgently take the victim to the hospital, ensure complete rest and inhale oxygen under pressure.
How to treat a chest contusion at home
If you have a bruise in the chest area, even if it seems minor to you, it is recommended that you first consult a doctor. If the bruise is mild, without complications or internal hematomas, you can treat it at home, strictly following the doctor’s recommendations. It should be remembered that a frivolous attitude towards even mild bruises of the sternum can lead to disastrous consequences. When treating a bruised sternum at home, you must follow the following recommendations:
- limit body movement;
- Apply cold compresses to the injury site for 1-2 days;
- use anti-inflammatory ointments;
- if the pain does not go away, but only intensifies, as well as in cases of a sharp deterioration in general health, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Medicines
When treating a chest contusion due to a fall, as in other cases, medications are prescribed based on the classification of the contusion and the severity of the consequences.
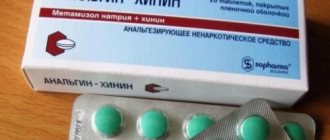
If there is no need for hospitalization, after consultation with a doctor, the use of painkillers (Analgin, Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Ketanov), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ointments (Finalgel, Ketonal, Diclofenacol, Nise gel, Fastum gel, Indomethacin) is allowed. If necessary, medications that relax the smooth muscles of the bronchi, expectorants (Bromhexine, Fluditek, Fluimucil) and other medications can be prescribed.
Folk remedies
Treatment at home can be carried out not only with the help of medications, but also with folk remedies. However, you should not completely abandon medications, especially if they are prescribed by a doctor. Treatment of the consequences of bruises in the chest area with folk remedies should be an addition to traditional therapy.
A well-proven and at the same time safe folk remedy for treating a bruised chest area are herbal tinctures with alcohol used for compresses on the affected area: compresses from St. John's wort, violet and burdock, oregano and coltsfoot and others. Such compresses have an analgesic effect and relieve swelling. Applying crushed plantain leaves to the site of injury will have a similar effect.
Proven means for accelerating the healing of hematomas are vinegar with honey and medicines based on bodyaga powder. As a pain reliever, you can use grated horseradish root (a compress on the bruised area) or cilantro tincture.
Open injuries
When victims have penetrating wounds, their condition depends on the presence or absence of associated injuries and hemopneumothorax. Hemothorax is formed due to heavy bleeding into the pleural zone, and pneumothorax due to the entry of air from the injured lungs. When the lung is damaged, the victim experiences hemoptysis, emphysema, and hemothorax. An accurate clinical picture can only be obtained after a chest x-ray.
Treatment of open trauma is carried out using surgical treatment. The patient must be hospitalized on the hospital premises, where an operation is performed, during which the wound is sutured. How strong the surgical intervention will be depends directly on the nature, location and severity of the damage.
Symptoms
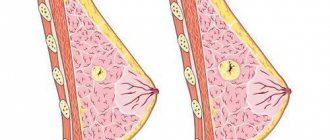
Symptoms characteristic of a breast bruise are similar to injuries to any other area. When examined by a doctor, a bruise or hematoma is determined. In this case, everything can be resolved successfully, or it can end in fat necrosis, which is accompanied by an increase in temperature, a change in the color of the affected area to black, and the discharge of pus from the nipples.
Due to the injury, the injured woman will complain of pain and swelling in the affected area. If the milk ducts have been affected, discharge from the nipple may be detected, which will be whitish or completely transparent.
Preventive actions
There is no specific prophylaxis to prevent bruises. The only thing that can be recommended is to avoid, if possible, contacts that could lead to trauma to the mammary glands.
These may include the following measures:
- refusal to move in complete darkness;
- careful adherence to traffic accident rules to prevent accidents;
- avoid forceful methods of conflict resolution;
- behave carefully in a crowd;
- Take precautions during outdoor games.
It is believed that measures to strengthen the skin will also be useful.