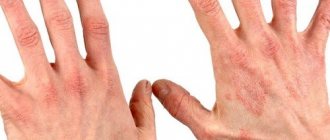
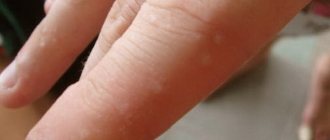
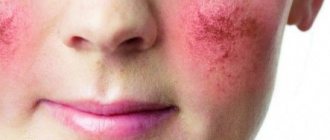
Inflammatory allergic formations on the skin, caused by allergies or toxicosis, are referred to in medicine as atopic dermatitis or eczema. This disease occurs in children of different age categories.
Atopic dermatitis can be either congenital or acquired. The underlying factor is heredity, as a result of which children suffer from the disease from the first year. Depending on age, the disease is divided into the following forms:
- Infant, which includes children aged 0 to 3 years.
- Children's room, which includes children from 3 to 7 years of age.
- Teenage: children from 7 to 16 years old.
The disease often occurs in children under one year of age, but by the age of five, the signs of the disease decrease. After the age of 10 years, the disease is much less common. It is difficult to treat atopic dermatitis in children, since the disease is caused by a chronic symptom and is associated with other types of diseases.
Causes of the disease
Atopic dermatitis in a child is formed through genetic similarity to allergies and other types of adverse factors. Signs of hypersensitivity in parents lead to an 80% risk of developing eczema in their children.
Even if one of the parents in the family has a tendency to allergic formations, the child’s risk of developing eczema will be about 50%.
The main reasons that contribute to the formation of atopic dermatitis in children include the following symptoms:
- Food allergies. The main cause of childhood eczema is food allergy, which is provoked by a woman’s improper diet during pregnancy, as well as by the mother during breastfeeding. If a mother overfeeds her child or, on the contrary, transfers him to artificial nutrition, then this comes down to the development of negative consequences.
- If an exacerbation occurs during pregnancy. During the period of bearing a child, the expectant mother exposes the fetus to various negative factors, which include: chronic illnesses, infectious diseases.
- Pre-existing illnesses. Diseases that are precursors to atopic dermatitis include:
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- gastritis;
- worms;
- enterocolitis.
- Other allergens. Irritants such as household chemicals, contact allergens, medications and other types of allergens have no less negative impact on the development of atopic dermatitis in children.
The presence of pets increases the risk of atopic dermatitis in a child by 90%. No less significant factors in the formation of atopic dermatitis are stress or psycho-emotional stress, unfavorable environment and parental smoking, as well as changes in weather conditions.
Occurrence of the disease
The term “atopy” includes any genetically determined predisposition to allergic diseases or a combination thereof. They appear when exposed to certain external stimuli. Chronic atopic dermatitis also belongs to this group. The disease has an alternative name - atopic eczema syndrome.
If both parents suffer from this disease, then their child has an 80% chance of also being infected. When only one is sick (either the mother or the father), then this is observed in 56% of children. At the same time, pathologies of the respiratory organs of an allergic nature increase this value to 60%.
Set of violations
Some experts believe that a predisposition to allergic reactions is caused by a combination of different genetic disorders. Some aspects are scientifically proven - this may be influenced by natural insufficiency of the digestive system. Impaired intestinal motility leads to improper breakdown of food. The work of the excretory system is hampered; due to damage to the epidermis, autoantigens and autosensitization are formed.
The following happens:
- those food components that are not only useless, but also harmful to the body are absorbed;
- antigens with toxins are formed and accumulated;
- the functioning of receptors is disrupted in the central and peripheral nervous systems;
- the functions of the immune and endocrine systems decline;
- with the development of autoaggression, autoantibodies are produced;
- Immunoglobulins are formed, which lead to the development of delayed or immediate atopic irritation.
As people get older, the role of nutritional factors in the development of atopy weakens. Affected skin becomes not a consequence, but an independent pathological process that takes on a chronic form. Not only does the dependence on food antigens disappear, but the body’s response mechanisms to external stimuli also change.
In the future, anatomical dermatitis manifests itself under the influence of such factors:
- air fragrances, household dust and chemicals used for sanitary purposes are household irritants;
- cosmetics, soaps and perfumes are chemical allergens;
- wool or synthetics with a coarse structure, other fleecy fabric - physical irritants;
- bacteria, viruses and fungi.
Immune mechanism
Sometimes the skin has too little of the structural protein filaggrin. The congenital absence of this element has a detrimental effect on the body, because it is necessary to interact with keratins and reduce the level of lipid synthesis. In such a situation, the epidermal barrier cannot form correctly; many substances - and among them there are pathogens and allergens - easily penetrate through it. Filaggrin deficiency also causes excessive production of immunoglobulins, which are associated with immediate allergic reactions.
In almost half of the cases, the disease is observed in adults as a result of late manifestation of pathology caused by a combination of genetic abnormalities. For other patients, there are two options:
- A disease that has continued since childhood.
- The disease has passed from a latent latent form, in which there are no clinical symptoms, into an open variation.
The patient may experience a relapse. Re-development is sometimes caused by genetic reasons, but more often by provoking factors:
- excessively dry air;
- environmental problems in the place of permanent residence;
- disturbances in endocrine and metabolic processes;
- weakened immunity;
- infection with acute infectious diseases;
- inflammation of foci of chronic infection;
- heavy shift work;
- severe or prolonged stress;
- long-term stress on the psyche;
- long-term insomnia and other sleep disorders.
Sometimes a severe exacerbation occurs simply because the patient tries to independently cure chronic atopic dermatitis, while resorting to traditional medicine. Most recipes for homemade decoctions and tinctures contain medicinal plants, which themselves can be allergens.
For proper treatment, several factors need to be taken into account:
- stage of disease development;
- degree of damage;
- patient's age;
- features of predisposition to allergic reactions.
Only the attending physician can do this. Homemade remedies pose another threat. Despite the anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects, the ingredients of the tinctures are not cleared of unnecessary accompanying elements. Some of them contain tanning and drying substances, although the patient needs, on the contrary, moisturizing ones. The patient should also take into account possible individual intolerance.
When preparing products yourself, it is impossible to remove natural animal fats and unrefined vegetable oils. They close the pores in the skin, which creates the possibility of infection with subsequent suppuration and the occurrence of an inflammatory process.
The factor of a combination of genetic disorders and a malfunction of the immune mechanism are the two main theories about the causes of atopic dermatitis. Doctors suggest the existence of other primary factors, but a full version has not yet been formed.
Symptoms
The fundamental symptoms of atopic dermatitis include the following manifestations:
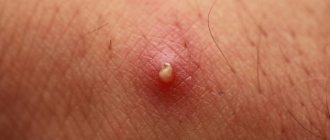
- the appearance of an allergic rash;
- dry skin;
- formation of a skin rash on the body in the folds;
- the occurrence of itching.
If two or three signs are diagnosed, then the disease can be considered proven. Symptoms of eczema enable parents to identify signs of the disease in advance and go to the hospital. Let's look at the symptoms of the disease in children in different age categories.
Clinical manifestations of skin disease
All dermatitis combines inflammation processes on the skin of a different nature. They are often accompanied by a deterioration in the person’s general condition.
Atopic dermatitis is a non-infectious skin disorder. Adults suffer more severely from the disease than children. The first symptoms appear already in childhood. There is another, more common, name for the disease - “diathesis”.
Conventionally, the development of symptoms can be divided into three stages:
- Infant. Symptoms are localized mainly on the face. “Birth crusts” appear in the parietal region.
- Children's room. The disease becomes seasonal. The symptoms are most pronounced in winter and autumn. The localization area is expanding: rashes, rashes and redness are visible on the neck, shins, elbows, and under the knees.
- Adult. Dermatitis takes on an eczema-like or lichen-like form. Areas of localization grow and appear on the chest, back, hands, and buttocks.
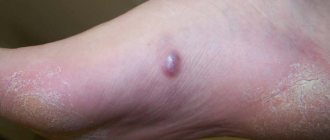
Contact dermatitis. Signs appear almost instantly, with a clearly limited affected area. Burning and itching of the skin are the causes of its redness, the formation of blisters, the development of necrosis, and cyanosis of the tissues.
The severity of the manifestations is directly related to the duration and strength of the impact. In severe cases of the disease, the body temperature rises.
It has two stages of manifestation: chronic and acute. If the acute form appears immediately after interaction with the allergen and disappears after its elimination, then the chronic form develops slowly. Its symptoms appear only after sufficiently long and repeated exposure.
Perioral dermatitis is always localized on the face. Main symptoms: redness, peeling of the skin, itching, burning, cracking of the skin, pain; in severe cases, swelling, pustules or nodular rashes appear.
Allergic dermatitis: signs of the disease appear after exposure to an allergen and are expressed in skin redness, sneezing and itching, the development of swelling, and the formation of blisters. Symptoms may appear several days after irritation. Often this dermatitis turns into eczema.
The symptoms of cold dermatitis resemble allergic dermatosis. Always accompanied by a runny nose, redness, burning and itching of the skin, and conjunctivitis. Cases of asthma appearing when inhaling cold air have been recorded. Locations are uncovered areas: face, neck, ears, hands.
Symptoms of drug-induced dermatitis appear everywhere and include redness, burning, and itching. You often feel full, and a symptom of “lack of air” may appear.
You need to treat your body very carefully. If changes appear in its functioning, or at least one of the symptoms of the disease appears, you should seek medical help to avoid complications.
Infant form
Atopic dermatitis in children in infancy begins with the formation of red spots on the body of the infant. Such spots appear mainly on the child’s face, in the cheeks and forehead. Based on these signs, you can immediately determine that the child is developing a disease.
The nature of the course of dermatitis in the infant form is predominantly of the acute type. Swelling forms on the skin, and the surface layer opens with a crust. Dermatitis can also be localized on the following parts of the body, such as the buttocks, legs, head, arms and legs.
Age periods
The nature of the course and combination of symptoms, the predominant forms vary depending on the age of the patient. Each age period has its own characteristics, which are distinguished in the phases of disease development:
- The first infant phase covers the age from 0 to 3 years (infancy and early childhood);
- The second or childhood phase covers the age from 3 to 10 years (preschoolers, primary schoolchildren, teenagers)
- Third or adult - from 10 and older (puberty and adults).
This classification takes into account clinical manifestations characteristic of a particular age. This includes features of the localization of lesions and the relationship of certain skin manifestations.
In children
Infantile dermatitis covers two phases: infant and childhood. The first manifestations begin at the infant stage (7-8 weeks). The localization of the rash is mainly the face area. Usually the cheeks and forehead are affected. The skin of the buttocks is susceptible to rashes, as well as the extensor surfaces - the area under the knees, elbows, forearms.
In this phase, inflamed areas with a weeping rash predominate. The facial skin is affected by bright spots of erythema with a high degree of swelling (papules, vesicles) which are accompanied by severe itching. Remission is partial (areas of skin on the folds remain affected). An exacerbation can be triggered by food irritants and is accompanied by symptoms of food allergy.
| Manifestations on the skin of a child |
In the childhood phase, inflammation is less exudative and often becomes chronic. During this phase, the natural color of the skin changes (pigmentation of the eyelids), and spots form. Signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia may appear. This phase is characterized by a wavy nature of the manifestations, which are bright red swollen spots merging into solid foci. The scratches get wet, become crusty, and there is a risk of infection. Usually the skin on the folds of the arms and legs, hands and feet, chest, and neck is affected. Seasonal exacerbations of dermatitis are characteristic.
After reaching 8-10 years of age, 50% of patients experience recovery. For the rest, the disease continues, moving into phase 3 (adult phase).
In adults
Atopic dermatitis in adults covers the third phase. These are patients over 10 years of age (puberty and adults). At this time, the disease manifests itself as rashes in the scalp, forehead, and perioral area. The neck is often affected, then the rash spreads to the forearms and wrists. Severe forms may be accompanied by diffuse (total) skin lesions. Rashes appear in the form of redness, flaky areas, infiltration, cracks. The affected areas are fixed and rarely change location. During remissions, the skin is partially or completely cleared, excluding the popliteal and elbow folds. By the age of 30, remission often develops with preservation of skin sensitivity.
Children's uniform
Atopic dermatitis in children under 12 years of age manifests itself primarily in the area of skin folds, such as the elbows and knees. The disease manifests itself in the form of red spots on the skin, as well as papules, which cause unpleasant pain.
The shape of the skin changes, it becomes dry, peeling and even lichenification occur. This is a sign in which a certain pattern is formed on the skin, causing signs of itching. Atopic face in a child is the main sign of the disease, which manifests itself in the form of changes in skin color, increased pigmentation in the area around the eyes, and an additional fold appears around the eyelid. Cracks appear on the skin, which is especially pronounced in the area of the back of the surfaces of the hands and fingers.
If at the age of up to three years the disease is called diathesis, then from the age of three it turns into the natural form of atopic dermatitis. Often symptoms of the disease appear on the back of the ears, as well as on the neck and parotid area. Such symptoms of the disease often continue until the child reaches puberty.
Teenage form
Atopic dermatitis in infants is significantly different from the disease in adolescence. From the age of 12 years, the disease is predominantly permanent. Skin changes occur in the face, neck, chest, back, arms and legs. The skin becomes dry, signs of lichenification form on it, as well as scratch marks. Cracks in the skin appear on the hands and feet.
In quite rare cases, an exacerbation of the disease can be detected, which manifests itself with signs of redness of the skin. If a bacterium joins dermatitis, the disease begins to regenerate and spread throughout the body. This form of the disease is less treatable and requires a special approach, which includes the use of antibiotics.
A teenager with dermatitis often complains of itching, which only gets worse over time. Such symptoms should definitely give parents a reason to take their child to the hospital for examination. If you identify the disease at an early stage, then curing it is much easier than dealing with acute dermatitis in children.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing, it is very important to comply with the basic diagnostic criteria, which include a description of the complete clinical picture of a given disease and the compliance of all symptoms. It is also important to know if any family members have allergies. A blood test is taken to rule out other dermatological diseases.
During the diagnostic process, they usually try to determine the exact allergen that caused the disease. This is done with the help of special tests from an allergist, the most common allergens are checked: pollen, pet hair and many others.
Important! The specific allergen that caused the disease cannot always be identified.
Stages of the disease
The disease atopic dermatitis is serious, which depends on the stage of its progression. In medicine, dermatitis in children is divided into four main stages, which are characterized by the following symptoms:
- Initial stage. This stage is characterized by the development of exudative-catarrhal symptoms in children. The initial stage is characterized by the following symptoms: swelling of the skin, hyperemia, peeling and redness. It is possible to return a child from this stage to his former life, but this will require active treatment and adherence to a hypoallergenic diet. If the disease is not treated, this is especially important for infants and infants, then the disease gradually progresses to the next stage - severe.
- The pronounced stage is due to the transition of the disease to the chronic or acute phase. The chronic phase is characterized by the sequential formation of skin rashes. The acute phase is characterized by the formation of crusts and scales on the skin.
- Remission stage. This stage is caused by a decrease in symptoms or their complete disappearance. The duration of the remission stage can last indefinitely: from several weeks to 2-3 years.
- Clinical recovery. The stage is determined by the absence of underlying symptoms for 3 to 7 years. This stage depends mainly on the severity of the disease and its form.
Each stage has its own signs, which can be distinguished by an experienced doctor. It is important to remember that atopic dermatitis in infants has a more pronounced degree of manifestation than in adolescence. This is due to the baby’s immature immune system.
General symptoms of dermatitis
Dermatitis looks completely different depending on the form of the disease. But there are also general symptoms that are similar for all types of disease. These include:
- rash. The location, size and type of rash differ. However, with any type of dermatitis it will be present. And often it is by the nature of the rash that a preliminary diagnosis can be made.
- itching The intensity of this symptom can vary and depends on how much the nerve endings in the skin are irritated. Severe itching is observed with allergic dermatitis.
- redness. Characteristic of acute forms of dermatitis, it can be focal and diffuse. peeling. Often occurs in chronic forms of dermatitis, if there is excessive dryness of the skin.
- weeping (exudation). It also occurs during the chronic course of the disease, as well as in the absence of proper treatment. May be accompanied by the appearance of crusts and plaques.
Possible complications
Complications of the disease atopic dermatitis arise due to the lack of adequate treatment for the disease. But besides this, complications can be caused as a result of physical impact on the affected areas of the skin. This may be scratching the skin, which itch periodically or constantly. If the integrity of the skin is violated, this will lead to a negative consequence in the form of penetration of various types of infection into the upper layers of the epidermis. Let's consider the main possible complications of atopic epidermis.
- Virus infection. Regardless of the stage, form and nature of the disease, children diagnosed with diathesis are susceptible to skin damage from viral infections. The most common causes of viral complications include herpes, warts and other negative skin manifestations.
- Bacterial damage. Particular attention is paid to a complication called pyoderma when affected by staphylococci. In most cases, the pronounced stage is caused by the appearance of Staphylococcus aureus strains on the skin.
- Fungal infection. Present as a complication of dermatitis in 5% of cases. With a fungal complication, hair, nails, and skin folds are affected. In children, fungal parasites often affect the mucous membranes of the mouth and eyes. The main causative agents of fungal infections are yeast-like fungi.
Consequences and complications of atopic dermatitis in children
The most dangerous thing is when a child begins to scratch the itchy area. This can lead to the formation of small wounds, which, in turn, become infected with fungus and other microorganisms, which can lead to a secondary infection (pyoderma). It is usually treated with antibiotics. All this affects both the skin and the child’s health. It is increasingly difficult for him to fall asleep, as a result he does not get enough sleep, and any body movements, bathing or clothing lead to uncomfortable sensations.
Often, fungi, viruses and bacteria can “attack” the baby immediately, as a result he will develop a purulent inflammatory process and a “cold”. With timely treatment and proper preventive measures, such difficulties can be avoided.
Methods of treating the disease
Atopic dermatitis must be treated immediately to avoid unpleasant consequences in the form of complications. Severe forms of the disease are treated with corticosteroid-based medications. Products that help moisturize and soften the skin are used at any stage of the disease. The main goals of treating the disease are:
- change in the direction of the disease;
- decrease in the severity of the disease;
- control of the disease throughout the entire period.
The treatment of the disease is based on two methods: medicinal and non-medicinal. The medicinal type of treatment is due to the use of various medications, the prescription of which depends on the age of the child, as well as the stage and form of the disease. Drug treatment includes both external agents and drugs for systemic action.
Non-drug treatment is based on measures that are aimed at eliminating the effects of negative factors. These factors include the causes of the disease, such as food allergies, previous diseases and other allergens. Let's look at the main types of medications that are used to treat the disease.
- Antihistamines. To treat diathesis, 2nd and 3rd generation drugs are used, such as Cetrin, Zyrtec and Erius. Used to reduce allergy reactions. They are addictive, so frequent use should be avoided.
- Antibiotics. Antibiotics are used after diagnosing the presence of bacteria in the body. Such drugs are used mainly for external treatment. The main drugs include: Erythromycin and Rondomycin.
- Vitamins and herbal medicines. Taking vitamins speeds up the healing process. Particular attention is paid to vitamins such as B15 and B6. Taking them helps speed up the process of restoration of many functions in the body.
- Antiviral and antifungal agents. Creams and ointments, such as Clotrimazole and Namacitin, are also used to treat the disease.
- Antiseptics in the form of peroxide and chlorhexidine.
- Medicinal ointments: Levomikol and Bepanten.
- Immunostimulants, which are prescribed in case of acute signs of illness.
Equal attention should be paid to diet in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. If atopic dermatitis practically does not occur in adults, then in children it is a common occurrence. Diet for atopic dermatitis plays a fundamental role, especially for infants. If there are signs of illness, you should immediately exclude from your diet the consumption of foods that contain allergens. In the first year of a child's life, a nursing mother must exclude from the diet: cereals, eggs, cow's milk, citrus fruits, nuts and honey. Even if you introduce any new product into food, you should definitely do it gradually, monitoring the reaction of the baby’s body.
Features of atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis in adults and children is considered a local manifestation of malfunctions in the immune system. It is not difficult to understand what dermatitis looks like from a photo, but the main manifestation of the disease in any age group is considered to be severe itching of the skin. In the treatment of this disease, the focus is on an integrated approach, the goal of which is to normalize the basic functions of the immune system. That is why treatment is most often carried out using immunomodulators - drugs of the immunotropic group.
Atopic dermatitis in a child usually appears after eating foods containing cow's milk protein, for example, formulas based on it, citrus fruits, eggs, strawberries, strawberries, oatmeal and other types of cereals. Less commonly, dermatitis in infants occurs when wearing clothes that have been washed using powder.
Atopic dermatitis in young children and adults is a genetically determined, chronic inflammation of the skin that is of allergic origin. Symptoms of atopic dermatitis can occur under the influence of one or more factors:
- with contact allergies while wearing clothes;
- when allergens enter the body with food - food allergy;
- respiratory (dust, pollen, etc.) – respiratory or respiratory allergies.
Important! Sometimes it is simply not possible to identify a specific allergen.
Atopic dermatitis in children usually manifests itself in infancy. The onset of the disease occurs in the second or third month of life. Often the disease goes away completely by the fourth year of life, but sometimes it can become chronic and remain forever. In newborns, symptoms of the disease appear no earlier than the second month of life.
The risk of this disease is much higher if there is a predisposition to various allergic reactions, which is inherited. Also, atopic allergic dermatitis can appear in a baby if the mother during pregnancy (especially in the last trimester) was fond of eating allergenic foods, for example, strawberries, chocolate, citrus fruits.
Composition and instructions for use of Sebozol shampoo
It is important to understand that atopic allergy is not a skin disease, although it manifests itself in the form of skin rashes. The disease is a manifestation of the immaturity of the infant’s gastrointestinal tract and internal problems in the human body. Atopy in children has the following development mechanism:
- First, a substance enters the body that cannot be absorbed, neutralized by the liver, digested in the intestines, or excreted through the lungs or kidneys;
- Due to some transformation, this substance acquires the qualities of an antigen, that is, a substance foreign to a given organism;
- As a result, the child’s body begins to produce antibodies to neutralize it;
- The rash in atopic dermatitis appears when an antigen-antibody complex forms.
Also, the causes of the disease may be due to the fact that the pregnant woman consumed, inhaled, ate or otherwise came into contact with potential allergens, for example, eating a lot of chocolate. As a result, cocoa protein triggered the production of antibodies in the child. In the future, when the grown-up baby eats chocolate, he will definitely develop a rash.
Traditional methods of treatment
Treatment of atopic dermatitis is also carried out using traditional methods. The main methods of treatment are the following:
- Treatment with birch buds. You need to take a glass of birch buds, then fill it with water and boil for 15 minutes. The strained broth should be used to wipe the damaged areas of the skin.
- Oak bark. Prepare an infusion from 100 g of oak bark, which can be used to lubricate damaged areas of the skin. This infusion has a softening and calming effect.
- St. John's wort. Use St. John's wort juice, which must be placed in a water bath and wait until its volume is reduced by half. Add 1 spoon of butter to it. The resulting ointment should be used as an antiseptic.
The traditional method of treating atopic dermatitis in children is quite effective, but it is used in combination with the main treatment and only after the doctor’s permission.
Causes of AD in children
The cause of atopic dermatitis in children can be an allergic reaction to certain foods or allergens that can enter the body through the respiratory tract.
Dust, dry food for aquarium fish, air fresheners, wool, insecticides, and washing powder on clothes can also be to blame. With constant contact, the skin becomes vulnerable and more sensitive. This can lead to atopic dermatitis. By scratching wounds, a child can introduce bacterial infections.
The likelihood of atopic dermatitis in children
As we wrote earlier, atopic dermatitis is a chronic disease that occurs either as an allergic reaction or there is a genetic predisposition to it:
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in children
Treatment for AD depends on the child's symptoms, age, and overall health. It is impossible to completely get rid of atopic dermatitis. The goal of treatment is to reduce itching and inflammation. During treatment, it is important to increase skin moisture and prevent infection. Therefore, young mothers often ask the question: “What to apply to atopic dermatitis to ensure moisture in the baby’s skin”?
Treatment for atopic dermatitis includes:
- Hypoallergenic diet and treatment and prophylactic regimen. According to the results of the study, doctors found that in 93% of cases, 8 foods are responsible for food allergies: eggs, peanuts, milk, soy, tree nuts, fish, crustaceans, wheat.
- External therapy (use of creams and ointments);
- Drug therapy;
- Getting rid of external allergens;
- Systemically trim your child's nails to prevent scratching, which can cause skin irritation and infection.
What cream can be applied to a child with atopic dermatitis?
The most popular treatments are corticosteroid creams and ointments. They have a strong anti-inflammatory effect, moisturize the skin well, and help relieve itching and swelling.
Antihistamines are used before bed to relieve itching and improve your baby's sleep. Antihistamines are usually prescribed in drops or tablets.
Calcineurin inhibitor creams and ointments are applied to the skin and also help relieve itching and swelling.
Of the medications that are taken orally, the best ones are vitamins, which boost the immune system and thus help it recover and fight illness. We have collected information and reviews about creams and ointments for atopic dermatitis.
Let's take a closer look at the main areas of treatment for an atopic child and what creams and ointments (their names and characteristics) can be used for an atopic child during treatment.
Dermatological care
If atopic eczema/dermatitis flares up, use skin soothing products to relieve skin irritation and help your child tolerate the itching.
The advantage of ointments is that they contain a large amount of fat, they ensure deep penetration of the active substances into the skin. The advantage of creams is that they are softer in structure. They contain oils and water, which are absorbed into the skin much faster and moisturize it. Due to the rapid absorption of the cream, there is no oily sheen on the skin.
Hormonal agents
When you hear about hormonal treatments, what comes to mind first? Most likely, it is something harmful and can lead to significant changes in the body. In fact, hormones are internal substances that are secreted by the endocrine glands. They help the body function healthily when our immune system lacks something.
According to Dr. Evgeny Komarovsky, hormonal creams for atopic dermatitis do not pose a risk to the child’s health if they are used wisely and for a short time. The hormone can have a negative effect only when it enters the bloodstream (transmitted intravenously) for several days in a row during long-term treatment. To avoid negative reactions, pharmacologists have developed a different treatment method. Ointments and creams applied to the affected skin area effectively act on it and do not enter the bloodstream.
The advantage of hormonal drugs is their fast (almost instantaneous) response. They can really help the baby with wound healing and give both him and the rest of the household the opportunity to sleep. The ointments themselves do not harm the baby, but help him eliminate itching and rashes.
Topical steroids have a local effect (in a specific area of the skin) and do not enter the bloodstream. There are no age restrictions on the use of hormonal drugs.
It is not recommended to use hormonal products on the face, around the eyes, chest, neck, genitals, folds and mucous membranes. However, pimecrolimus-based drugs can be used on sensitive skin to relieve severe itching of the skin.
The products are divided into types according to their effectiveness on the body:
- Weak
- Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone. - Medium
- Afloderm, Lokoid, Flucinar. - Strong
- Celestoderm, Elokom, Flixotide. - Very strong
- Dermovate.
Effective hormonal agents for atopic dermatitis
Non-hormonal creams for atopic dermatitis
Hormonal ointments and creams should be alternated with non-hormonal ones. Non-hormonal agents also have anti-inflammatory and healing properties. They also relieve swelling and redness, stop itching and burning.
This type of ointment helps to moisturize the skin and remove dead skin cells.
Of the non-hormonal drugs, the most popular are:
- Skin Cap. The cream has an anti-inflammatory effect, with antibacterial and antifungal effects. The remedy eliminates signs of skin damage, helps get rid of redness, swelling, dry rashes, peeling and itching. The cream effectively acts against microorganisms that are located on the surface and in the deep layers of the skin. However, the cream is not recommended for use up to one year.
- Protopic. The ointment is used in the treatment of moderate and severe atopic dermatitis in children from two years to sixteen. Accordingly, the use of ointment by pregnant and nursing mothers is prohibited. Treatment with ointment lasts until the manifestations of atopic dermatitis completely disappear.
- Desitin. A combined drug with anti-inflammatory properties, protects the skin from skin inflammation and prevents the occurrence of diaper dermatitis. Ointment for atopic dermatitis for children forms a protective coating on the skin and mucous membranes. The product can be used in infants immediately when the first symptoms and redness appear.
- Wundehil. The ointment consists of a combination of biologically active substances that provide anti-inflammatory and healing effects. The ointment quickly relieves pain, heals wounds and irritation, and protects against further infection of wounds. It is based on propolis extract, tincture of Japanese sophora and other plants. Can be used on infants and during pregnancy.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines stabilize mast cells, which are responsible for adaptive immunity and are responsible for the body's allergic reactions. Antihistamines are considered sedatives, that is, calming. Doctors recommend the use of sedative antihistamines in patients with significant sleep disturbances caused by severe itching. They relieve itching and swelling in skin manifestations, especially in atopic syndrome, which manifests itself through asthma and rhinitis.
With daily use of antihistamines, there is a risk of developing the body's addiction to them. This often happens with first-generation drugs, such as: Suprastin, Tavegil, Fenkarol, Diazolin. We recommend changing these medications every 5-7 days. It should be remembered that first generation antihistamines are contraindicated for people who lead an active lifestyle: schoolchildren, drivers, athletes. The drugs cause decreased concentration and impaired motor coordination.
Some of the most popular antihistamine creams and ointments are:
- Fenistil-gel ointment.
The product has antiallergic and antipruritic effects. Gel with local anesthetic properties and cools the skin upon application. Thanks to its soft consistency, the gel penetrates deep into the skin and has a calming effect. The maximum effect occurs after 1-4 hours. - Cream Gistan.
Based on extracts of medicinal herbs with the addition of an antihistamine. Used for skin rashes, urticaria, atopic dermatitis. The cream is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as in children under two years of age.
Immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressive drugs are used to suppress the body's immune response. Why is this necessary? This is necessary in order to suppress allergic reactions or autoimmune processes.
Immunosuppressants help stop the cycle of scabies or itching and soothe affected skin, and also reduce the risk of skin infection. The most commonly used drugs are oral immunosuppressive drugs. However, among them, dermatologists recommend Elidel
cream for atopic dermatitis in children.
The cream also has an anti-inflammatory effect and helps reduce itching and swelling of the skin. Allowed to be applied to the skin of children from three months for six weeks. If corticosteroids are contraindicated for your child, the doctor will most likely prescribe Elidel. According to reviews, Elidel cream is excellent for children with atopic dermatitis at an early age.
Due to its soft structure, the cream can be applied to the skin of the face, scalp, folds and groin parts of the body.
Dermato-cosmetological products
Local peeling, dryness after washing and increased skin sensitivity are standard symptoms that almost every person at any age has encountered. There are many factors: temperature changes, water hardness, poor nutrition, dust, environment, stress, etc. As we have already written, atopic dermatitis cannot be cured, but it can be suppressed. To do this, it is enough to maintain the moisture and cleanliness of the skin in a stable condition and with the help of properly selected cosmetics.
Many companies have already repurposed themselves and are creating cosmetic products (lotions, gels, oils, ointments and creams) specifically to eliminate the symptoms of atopic dermatitis. In this block we will look at companies that create cosmetics for atopics:
- Sesderma. A Spanish brand that has been producing a series of dermocosmetics since 1989. The company produces various creams for problem skin, and a separate Atopises line is dedicated to the care of atopic skin. The series includes emollients (products that soften and moisturize the skin). The products are based on cosmetics based on jojoba, shea butter, aloe, urea and lipid complex.
- Uriage. The French company produces a series of therapeutic dermatocosmetics for atopic dermatitis. The basis of cosmetics includes: thermal water, shea butter, omega fatty acids. Uriage also produces a Cu-Zn range that is suitable for the treatment of weeping atopic dermatitis
- Bioderma. A series of cosmetics from a French pharmacological company helps maintain normal skin condition. Some products contain zinc to combat dermatitis, while cleansers and light creams contain citric acid to help even out skin tone.
- Weleda. German cosmetology company that produces natural cosmetics. All creams and other skin care products produced by the company are also recommended for baby skin care. All the company's products only support therapy for atopics. They are not worth treating the disease separately.
- La Roche-Posay. The French dermatological company includes special microelements in its cosmetics. These microelements help heal and restore the skin. The atopic line includes various oils, as well as zinc, copper and manganese. One of the company's useful products is bath oil, which softens water.
- Eucerin. A company that produces innovative cosmetic skin care products. The AtopiControl cosmetics series includes products that soothe and moisturize the skin. The range of the series includes shower oils, washing gels, lotions and creams.
Means to prevent dry skin of atopic baby
In addition to special cosmetics for intensive skin care, it is recommended to use regular baby cream for atopic dermatitis in a child. It prevents dry skin and the appearance of symptoms of atopic dermatitis. Atopic cream for children is also suitable for the prevention of AD.
Baby creams
There are four types of baby cream:
- Classic baby cream perfectly moisturizes, nourishes and softens baby's skin. The cream is an excellent preventative.
- Protective baby cream protects the baby's delicate skin from the sun, wind, and frost.
- Anti-inflammatory baby cream contains anti-inflammatory and healing ingredients that help relieve redness and prevent diaper rash.
- A baby cream special for diapers helps against diaper rash and skin irritation. It should be applied to clean and dry skin every time you change a diaper.
The Emolium series of baby skin care products has a large number of useful components. According to reviews from young mothers, Emolium cream perfectly helps to moisturize and nourish the baby’s skin.
Moisturizers for atopic dermatitis
In addition to moisturizing, the skin needs to be nourished. Locobase healing cream has these properties.
for atopic dermatitis
.
It makes the skin soft and elastic, and also helps to build a protective barrier for the epidermis to reduce the number of relapses. The cream contains no dyes or flavors, which allows it to be used for children.
Another good moisturizer is Ruzam +
. The cream perfectly refreshes the skin, prevents feathering and stops the development of allergies. Atopic dermatitis and its treatment with cream are inseparable from each other.
It is recommended that you take any medications in consultation with your doctor, and then begin treatment. We strongly recommend that you consult your physician before using any product. Finally, let us briefly consider what folk remedies help with childhood atopic dermatitis.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is an excellent complement to the main treatment for atopic dermatitis, but not the main method of treatment.
Children are recommended to take baths with added starch
according to the ratio of 1 large spoon per 1 liter of water. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes. Then, it is recommended to wet the affected areas of the skin with a flannel diaper. Do not bathe your atopic child in herbal remedies, as they may increase irritation. It is better to consult a doctor first.
In addition to starch, you can take baths with birch bud tinctures
. To prepare the tincture, you need to pour boiling water over a tablespoon of birch buds and leave to infuse for 1-2 hours. Then, strain the tincture through cheesecloth and add to the bathing water.
You can also use grated
potatoes.
It is necessary to peel and grate the potatoes. Place the resulting porridge in gauze and apply to the problem area.
Ointment with St. John's wort is perfect
with local manifestations of atopic dermatitis. It is enough to mix 4 tablespoons of squeezed St. John's wort juice with melted goose fat. Apply the mixture to the affected areas twice a day.
Prevention
Prevention is the main means of treatment. To prevent the development of the disease in a child, preference should be given to the following recommendations:
- eliminate allergens from food;
- control air humidity and room temperature;
- eliminate all possible sources of dust and allergens;
- remove areas of mold formation;
- use exclusively cotton clothing;
- eliminate smoking in the house where there is a child;
- relieve the child from stress and anxiety;
- do not rub the skin at the slightest sign of itching;
- avoid excessive stress in childhood.
It is important to work with your child and teach him the right way of life, which will help him strengthen his immune system and always remain healthy and vigorous.