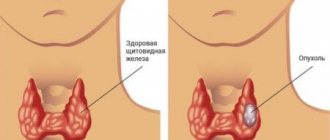
Thyroid adenoma is a disease caused by a benign tumor process. The encapsulated fibrous neoplasm is clearly defined and in most cases has a characteristic round or oval shape. When detecting such a tumor, doctors most often recommend its removal, since the fibrous capsule can grow, causing compression of adjacent tissues and threatening malignant degeneration.
What is a thyroid adenoma
As part of the endocrine system, the thyroid gland regulates the functioning of organs and vital systems through the production of hormones, which include thyroxine and triiodothyronine. A decrease in the level of thyroid hormones leads to hormonal imbalance, disruption of the cardiovascular system, and is also an indirect cause of a number of gastrointestinal diseases.
According to ICD-10, the international classification of diseases, the group of formations of the thyroid gland that provoke the development of its dysfunction includes:
- cysts are small-volume neoplasms filled with colloidal contents;
- nodes are focal neoplasms delimited from neighboring structures by a dense shell of a fibrous capsule;
- adenoma is a benign tumor prone to slow progress and malignancy.
An adenoma is a nodular neoplasm located in the thickness of the thyroid gland and consisting of histologically altered cells.
This diagnosis is made based on microscopic examination of tissue taken from the node during a biopsy.
Causes
The exact reasons for the appearance and progression of a benign tumor in the thyroid gland have not been established. Doctors identify supposed negative factors that increase the risk of developing a tumor process:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Hormonal changes in the body (age-related or occurring as a result of a concomitant disease).
- Long stay in environmentally unfavorable regions.
- Chemical intoxication (in hazardous industries or in domestic conditions).
- Uncontrolled therapy with iodine-containing drugs.
The combination of these factors can cause pathological activity of the anterior pituitary gland, which is responsible for the production of thyrotropin.
Additional risk factors include disorders of the autonomic nervous system. An adenoma caused by a malfunction of the pituitary gland rarely grows to a large size. When hyperproduction of thyrotropin is compensated by thyroid hormones, spontaneous regression of the tumor may occur.
Symptoms
The signs of an adenoma localized in the thyroid gland are mixed. In the early stages, the patient does not experience discomfort, so a benign neoplasm is most often discovered by chance, during a routine examination by an endocrinologist.
Chronic thyroiditis of the thyroid gland: what is it?
In women aged 40 years and older, thyroid tumors are detected much more often than in men, so mature patients should pay special attention to the primary manifestations of this pathology, including:
- Mental instability, inadequate reactions to habitual stimuli, and some women tend to attribute them to manifestations typical during menstruation.
- Increased sweating with altered heart rate.
- Decreased performance, attacks of weakness and apathy.
- Sudden weight loss unexplained by a reduced-calorie diet or other targeted interventions.
- Pathological sensitivity to elevated temperatures.
The appearance of such signs in children and adolescents is a reason to undergo a full examination by an endocrinologist, since the progress of the disease can lead to delayed physical development, memory impairment, and in girls, a negative impact on the development of the reproductive system.
Diagnostics
To determine the optimal therapeutic tactics, the endocrinologist will need the results of the following studies:
- Blood test (general and thyroid hormone tests). In the latter case, blood is drawn from a vein, before which hormone replacement therapy and vitamin therapy are temporarily canceled if the complex includes iodine.
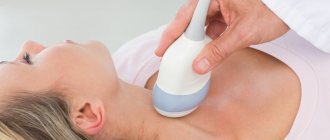
- Ultrasonography. During the examination, the doctor determines the exact size of the left and right lobes of the thyroid gland, as well as the volume of the tumor and its location. On ultrasound, the adenoma looks like a fibrous capsule, inside of which there is a toxic node.
- Cytology. The puncture, which is carried out using a thin needle, will allow tissue to be collected from the right and left lobes of the organ with a minimum of discomfort. In the presence of small nodes, cytological examination is carried out under ultrasound control. Studying the biopsy cells under a microscope provides the doctor with information about the etiology of the tumor process and makes it possible to exclude malignant degeneration of the tumor cells.
Additional diagnostic methods include computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the thyroid gland. These types of studies are prescribed in case of an atypical location of the organ or in cases where ultrasound diagnostics turned out to be insufficiently informative. Contrast diagnostic procedures are used extremely rarely, since they require the introduction of solutions, the use of which is undesirable in cases of damage to thyroid tissue.
Diagnostic procedures
In making a diagnosis and determining the form of thyroid adenoma, both laboratory and instrumental studies are used. The most popular and priority is ultrasound. It allows you to determine the size of the thyroid gland, the number, and location of the nodes. The next important examination is radioisotope scanning. Depending on how the node absorbs radioiodine, the level of activity of the adenoma is determined.
It is important to check your thyroid hormone levels, especially if you are at risk of developing a toxic type of tumor. It is characterized by the following results of hormone studies:
- serum TSH level is reduced;
- T3 level – elevated or close to the upper limit;
- T4 level – increased or approaching the maximum permissible threshold.
A non-functioning adenoma does not affect hormones - their amount does not exceed the norm.
Next, a biochemical analysis is carried out. With its help, impaired glucose tolerance and hypolipidemia are determined. The final stage of the examination to accurately confirm the diagnosis and determine the morphology of the thyroid adenoma is a fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the node. Then the cellular composition of the tumor is studied. A biopsy is the most accurate examination of tumors. 80% of such studies help determine the type of tumor: benign or malignant.
Types of adenoma
For a doctor drawing up a treatment plan, an important task is to determine the type of adenoma. In endocrinology, it is customary to distinguish the following forms of the disease:
- toxic (Plummer's disease), occurs against the background of hormonal disorders;
- follicular, accompanied by the proliferation of follicles around the affected node;
- papillary, occurs with the formation of multiple cysts filled with brownish contents;
- an adenoma formed by Hürthle cells is an oncocytic tumor, initially benign, but susceptible to malignancy and early metastasis.
Classification
Depending on the morphological structure, follicular, papillary, oxyphilic, functioning, clear cell and other types of thyroid adenoma are distinguished. The source of tumor development is the A- and B-follicular cells of the thyroid gland.
- Follicular adenomas are rounded encapsulated nodes, dense elastic consistency, with sufficient mobility. Among euthyroid nodular formations of the gland, they account for 15-20%. Follicular formations also include varieties such as colloid (or macrofollicular), microfollicular, fetal, trabecular (or embryonic) adenoma of the thyroid gland.
- Papillary adenomas have a cystic structure; Inside the cysts, papillary growths are detected, surrounded by a brownish liquid.
- Functioning (toxic) tumors are accompanied by the development of Plummer's disease - excessive production of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), which suppress the secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone by the pituitary gland. Clinically manifested by signs of hyperthyroidism.
- Adenoma developing from B cells (oxyphilic adenoma from Hürthle-Askanasi cells, Langhans tumor, oncocytic adenoma) has the most aggressive course and in 10-35% of cases turns out to be malignant upon histological examination.
Treatment of thyroid adenoma
Treatment without surgery in the event of a benign tumor of the thyroid gland is possible only in cases where the adenoma was identified at the initial stage of development and was provoked by hormonal changes in the body.
Most often, conservative plans are implemented when adenoma is detected in children. If treatment is carried out using conservative methods, a patient of any age should regularly visit an endocrinologist to monitor the dynamics of the proliferation of altered tissues.
Drug therapy is indicated:
- during pregnancy with a confirmed diagnosis of colloid adenoma;
- in preparation for surgery to control the growth of toxic adenoma.
In addition to removing the affected thyroid nodule, thyreostatic therapy is carried out as part of the treatment of a benign tumor. Taking Carbimazole, Propicil, Thiamazole is recommended if an imbalance of thyroid hormones is detected as a result of laboratory diagnostics. Thanks to hormonal therapy, the concentration of hormones in the blood decreases, due to which tumor growth slows down. The goal of the hormonal course is to prevent the growth of a thyroid tumor and relieve the symptoms of the disease.
Elderly patients are prescribed radioactive iodine preparations. Using this method, based on the ability of a toxic type adenoma to absorb radioactive iodine compounds, it is possible to achieve destruction of the internal structures of the tumor and its final disintegration.
Treatment with radioactive iodine is prescribed if there are contraindications to surgery, which often occur in elderly patients. An alternative treatment option for a benign thyroid tumor in this case may be injection therapy, which involves the injection of ethanol into the node in a volume of 1 to 8 ml. Repeated injections cause destruction of the tumor due to cauterization of cells with a pathological internal structure.
Throughout the course of treatment, the patient is provided with mental peace, a diet with a high protein content is introduced, and exposure to the open sun must be avoided.
Treatment with folk remedies
To prepare the patient for surgery, the attending physician may recommend correcting the condition of the thyroid gland using herbal medicines that inhibit the activity of the organ due to an indirect effect on the pituitary gland.
Treatment with traditional medicine is not effective in isolation from other therapeutic methods. Before starting herbal medicine, it is recommended to discuss the advisability of using the selected herbal tea or herbal medicine with your doctor.
Removal
Operations recommended for tumor processes in the thyroid gland are carried out in several formats:
- Enucleation is a gentle operation during which the tumor capsule is removed.
- Hemithyroidectomy is resection of part of the thyroid gland (the lobe in which the tumor is found).
- Subtotal resection - excision of both lobes of the thyroid gland (a section weighing up to 6 g is left).
- Thyroidectomy is a radical operation, after which the patient needs lifelong hormonal therapy.
How does adenoma appear and progress?
The disease originates from a small node in the thyroid gland, which has a smooth surface. It is characterized by clear outlines. It is rare to see the formation of multiple nodes, even scattered throughout the organ. Often this disease is accompanied by the formation of a goiter. As soon as the first manifestations of the disease are detected, you need to consult a doctor and begin treatment. After all, this disease can be a precursor to a more serious and difficult to reversible problem - thyroid cancer.
Thyroid adenoma does not impede its work. An exception is Plummer's disease, which is accompanied by a clinical picture of hyperthyroidism.
Adenoma can manifest itself as follows:
- significant weight loss;
- extremely poor health in hot weather;
- feeling of anxiety and uncharacteristic irritability;
- profuse sweating;
- tachycardia (increased heart rate) in the absence of physical and emotional stress;
- weakness and fatigue, which had not previously been observed in the patient.
Increased blood pressure, digestive disorders, and fever may also occur. Particular attention should be paid if these symptoms occur in women, since this phenomenon most often occurs in them.
If the patient is already elderly and does not seek treatment in a timely manner, the development of this disease is accompanied by heart problems - rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath. The skin of such patients is always moist and the limbs are hot. In this case, the color of the skin does not change. Rarely, changes in the eyes occur - exophthalmos, shine in the eyes. Changes in the condition of the mucous membrane of the eyes, no dryness.
Based on their structure, there are several different types of endocrine gland adenoma in clinical practice.
Follicular adenoma of the thyroid gland most often occurs in young patients. This type of tumor received this name because it begins to develop in follicular cells. This species is divided into subspecies:
- fetal;
- colloidal;
- simple;
- trabecular.
To find out which type it is, you need to know the type of cells inside the tumor.
Follicular adenoma has a dense structure, a smooth surface, and takes on a spherical shape. Any laryngeal movements can dislodge the capsule. 10% of cases of development of this tumor lead to cancerous formations, adenocarcinomas. In the remaining 90%, the tumor is benign. However, the difficulty of follicular adenoma is that it is very difficult to identify in the initial stages. For this type of tumor, the release of hormones is uncharacteristic, which is why its development goes unnoticed.
Follicular adenoma has signs at an early stage:
- increased sweating;
- weight loss;
- weakness;
- drowsiness.
When symptoms appear, not all patients turn to an endocrinologist. As a rule, they go to see a specialist only when the tumor begins to compress the esophagus, larynx and respiratory tract, thereby depriving the patient of a comfortable life.
Toxic thyroid adenoma, also called Plummer syndrome, is characterized by the appearance of nodular formations that produce an excess amount of hormones. Toxic adenoma occurs in one or more nodes. According to statistics, it is small in size - round or oval. Easily determined by palpation. Such a tumor is sensitive to the iodine content in the blood: the greater its amount, the larger the adenoma, and this leads to an increase in the production of the pituitary hormone.
The tactics of combating a tumor depend on its size: up to 20 mm, treatment is carried out mainly with medication. A size greater than 20mm forces one to resort to surgery. When adenoma capsules are scattered over the entire surface of the thyroid gland and their number is large, doctors decide to remove the gland.
The emergence of so-called thyrotoxic thyroid adenoma sometimes occurs in existing non-toxic nodes.
Papillary adenoma of the thyroid gland is a cyst-shaped tumor containing dark fluid inside. It spreads in the form of papillary growths that attach to the inner walls of the thyroid gland.
Oncocytic adenoma of the thyroid gland, or otherwise Hürthle adenoma, is common among young women 20-30 years old who have developed AIT, inflammation of the thyroid gland. The pathology is often hidden and occurs with thyroiditis - a decrease in thyroid function.
The oncocytic form is often mistaken for cancer because of its appearance—a yellow-brown tumor composed of several different cell types. Sometimes hemorrhages can be found near such a pathology.
An atypical adenoma of the thyroid gland is a neoplasm, which is a cluster of various cells: follicular, proliferating, which in structure can have several shapes: round, oval, oblong, and even spindle-shaped. Here, the cell nuclei are hyperchromatic; compared to the nucleus, the size of the cytoplasm is much smaller.
If malignant cells were detected during microscopy, this is a signal that the neoplasm has turned into a malignant course.
Oxyphilic thyroid adenoma consists of oncocytes. The cells of such a tumor reach large sizes, and the neoplasm itself does not contain colloid. This is the most aggressive formation, since more often than other types it degenerates into malignant formations.
Most neoplasms in the thyroid gland are benign. These can be dense round formations or fluid-filled cysts. There are both cases with single nodes and multiple spread over the surface of the organ. Education rarely becomes malignant. However, to eliminate all risks, you need to be regularly monitored and examined by an endocrinologist.
Diet for adenoma
During the treatment of adenoma and as part of the prevention of thyroid disease, doctors recommend following a balanced diet, giving preference to foods with a high iodine content.
The daily diet should contain a lot of protein foods of plant origin, fresh fruits and vegetables, with the exception of those that cause fermentation and gas formation.
Daily consumption of the following foods and dishes will help to avoid iodine deficiency, which contributes to the development of thyroid pathologies, and at the same time normalize the activity of the gastrointestinal tract, which often suffers from organ dysfunction:
- seafood, sea fish;
- buckwheat and millet porridge;
- beet;
- nuts and legumes;
- dried fruits.
Forecast
If the adenoma was detected at an early stage of development, it can be completely cured using conservative methods. The younger the age of the patient who is diagnosed with this disease, the more effective drug treatment will be.
The prognosis for life with adenoma directly depends on how timely and adequate the therapeutic course was. Provided that surgical treatment is timely, sufficient in scope, and followed by supporting adequate hormonal therapy, the likelihood of adenoma recurrence is extremely low. Prognosis worsens when a tumor is detected in adulthood (after 40 years).
If the adenoma is not treated, over time the benign tumor can develop into thyroid cancer.
About folk remedies
Surgery today is the main method of treatment for thyroid adenoma; treatment with folk remedies is auxiliary and additional. They can be used during preparation for surgery or after consultation for inactive adenoma. Aggressive neoplasms affect not only the thyroid gland, but also other internal organs and can lead to irreversible consequences that are dangerous to the health and life of the patient; alternative therapy is not indicated for them.
We recommend reading Meningioma of the brain - causes, types, diagnosis, treatment
Treatment of thyroid adenoma with folk remedies involves the use of herbal infusions and herbal components to reduce hormonal blood levels. Among the effective ones are the following recipes:
- Take 50 g of fresh Veselka mushroom in the egg stage, pour in 200 g of vodka and leave in a dark place for 14 days. The initial dose is 1 tsp. on an empty stomach, if the reaction is neutral, take 1 tbsp. l. three times a day, washed down with a raw egg or a spoonful of honey. Requires 3 courses of treatment for 30 days with breaks between them for 14 days.
- You need to take a collection of 3 parts of common horehound, 2 parts of field mint, 1 part of cocklebur, 2 parts of agrimony, 2 parts of common blackhead, 1 part of medicinal clover and 3 parts of red hawthorn. Chop all the herbs and mix well, then take 1 tbsp. l. collection, pour 200 ml of boiling water and steam for a quarter of an hour. Let it sit for half an hour, then strain, and add water to the strained broth to the original volume. Take a third of a glass half an hour before meals three times a day.
Prevention
Prevention of benign thyroid tumors involves eliminating or minimizing the influence of risk factors that negatively affect the functioning of this organ. If there is a genetic predisposition to endocrine disorders, patients are recommended to:
- regularly visit an endocrinologist and undergo a comprehensive examination of the thyroid gland;
- At least once a year, do a biochemical blood test to determine the content of hormones produced by the thyroid gland;
- eat properly, including iodine-containing foods in your daily diet;
- compensate for the lack of iodine by taking special medications recommended by the endocrinologist.
Patients who are not at risk should undergo preventive examinations with an endocrinologist after 40 years of age.
This will prevent the development of thyroid cancer, into which a benign tumor can transform in the later stages of development.
Clinical picture: what you need to pay attention to
Important! Like parathyroid adenoma, benign thyroid tumor is a widespread disease in women over 40 years of age. Men get it 3-4 times less often.
The first signs of the disease, as a rule, are absent: the small size of the nodule allows it to remain undetected for a long time. Hormonal imbalances also do not always occur.
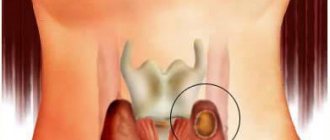
Over time, the mechanical signs of adenoma come to the fore. A person may notice a round formation on the neck with clear, smooth contours and a dense consistency - an adenomatous nodule of the thyroid gland.
During this period, it is important to consult a doctor as early as possible for timely diagnosis and treatment of the pathology, since the progression of tumor growth leads to the following symptoms:
- feeling of a foreign body in the throat;
- shortness of breath, suffocation;
- swallowing disorders caused by compression of the growing tumor of the esophagus.
The terminal stage of the disease is adenomatous goiter of the thyroid gland. This pathology is characterized by significant growth of tumor formation and almost complete atrophy of healthy tissues of the endocrine organ. The contours of an adenoma are easily determined on the skin of the neck with the naked eye (pictured below).
The adenoma has reached significant size
In Plummer's disease (functioning adenoma), the main manifestations of the pathology are quickly joined by symptoms of hyperthyroidism:
- a sharp decrease in body weight, regardless of the nature of nutrition;
- nervousness, irritability, increased anxiety;
- sleep disturbance (insomnia, shallow sleep filled with nightmares);
- intolerance to high temperatures, heat;
- tachycardia - rapid heartbeat;
- sweating - the skin is hot and moist to the touch.