Diseases caused by a viral infection and having a number of characteristic symptoms are popularly called intestinal or stomach flu. In fact, such an acute pathology associated with damage to the intestinal mucosa is not, in fact, the flu. Diseases are provoked by ARVI viruses of the order Rotavirus or Reoviridae, which enter the human body along with water and food, as well as through household and airborne droplets.
In medicine, intestinal flu is called gastroenteritis or, in other words, rotavirus infection. So, why is such a pathology dangerous for the patient? How is the disease transmitted and how to treat it? And is it possible to avoid infection?
Routes of infection
Gastroenteritis is caused by a certain group of viruses (rotavirus) that enter the human body through the mucous membranes (epithelium) of the stomach, intestines and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The first symptoms of the disease usually appear within 1-2 days, but in some cases, deterioration in health becomes noticeable only on the 4-5th day. On average, the incubation period of the virus ranges from 12 hours to 5 days.
To protect yourself from infection, it is important to know in what ways you can catch the infection.
- Fecal-oral . In this case, the virus is transmitted to a healthy person from interaction with the feces or vomit of a patient (for example, when using a shared toilet). It is the main mechanism of transmission of the virus.
- Food. Eating low-quality or expired foods, raw tap water, unwashed vegetables or fruits can cause viruses to enter the body. To avoid this, you need to pay special attention to the quality of the food that ends up on the dinner table, wash your hands more often and observe the hygienic requirements for handling various categories of products.
All fruits and vegetables must be washed before eating
- Household . This method of infection occurs quite rarely, but it cannot be excluded. Lack of sufficient antiseptic treatment of the room in which the patient lives, poor cleaning can lead to the spread of the virus in the team or among family members.
- Airborne . You can become infected this way while communicating with a sick person. The risk increases if the patient opens their mouth wide, laughs, talks loudly, coughs or sneezes. In this case, a medical gauze bandage can provide relative safety.
Important! Washing your hands with hot water and antibacterial soap after using the restroom should be a mandatory rule for people of any age.
Can you get infected while swimming in a pool?
Rotaviruses are very resistant to environmental factors, including freezing and high temperatures. The virus is completely destroyed only after heating to 70-80 degrees, so it is quite difficult to fight it indoors. In public swimming pools and saunas, you can become infected with gastroenteritis if the establishment’s staff does not pay due attention to hygiene and treatment of the pool and high-risk areas (showers, steam rooms).
Important! The destruction of stomach flu viruses in water is achieved using disinfectants containing chlorine. At the same time, it is important to ensure that the concentration of chloride substances does not exceed permissible standards - otherwise, you can get serious poisoning if you accidentally swallow water.
Video - Rotavirus and its symptoms
Risk factor
Gastroenteritis occurs throughout the world, affecting people of all ages, races and backgrounds.
People who may be more susceptible to gastroenteritis include:
- Young children . Children in kindergartens or primary schools may be especially vulnerable because the child's immune system takes time to mature.
- Older adults . Adult immune systems tend to become less effective later in life. Older people in nursing homes, in particular, are vulnerable because their immune systems are weakened and they live in close contact with others who can transmit germs.
- Schoolchildren, parishioners or dormitory residents . Anywhere groups of people gather together in close quarters can be an environment for the transmission of intestinal infections.
- Anyone with a weakened immune system . If your resistance to infection is low—for example, if your immune system is compromised by HIV/AIDS, chemotherapy, or another medical condition—you may be especially at risk.
- Every gastrointestinal virus has a season when it is most active . For example, if you live in the Northern Hemisphere, you are more likely to have rotavirus or norovirus infections between October and April.
Symptoms and signs of pathology
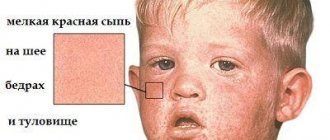
Symptoms of gastroenteritis begin with catarrhal phenomena - the patient begins to have a sore throat, cough, and rhinitis. This is what distinguishes gastroenteritis from other digestive disorders. After the number of viruses increases, dyspepsia occurs and signs of intestinal pathologies appear. The clinical picture in the acute period of the disease is as follows:
| Stage | Symptoms |
| Incubation | There are no symptoms. In rare cases, health deteriorates and a constant feeling of thirst appears. |
| Catarrhal period | Cough, sneezing, runny nose, nasal congestion. Symptoms resolve quickly (within 24-48 hours) |
| Acute period | Sore throat (when swallowing), redness of the tonsils, pain in the epigastric region, rumbling in the abdomen, loose loose stools, vomiting, fever, loss of strength |
| Recovery | Symptoms disappear, lethargy, drowsiness, and slight pain in the epigastrium may persist (rarely occurs) |
Stools with gastroenteritis are copious and frequent - up to 10 times a day. Feces may be yellow or gray in color and have a clay-like consistency. The smell is pungent, fetid.
Going to the toilet with gastroenteritis can reach up to 10 times a day
Important! If there is mucus or blood in your stool, it is important to report these symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately.
With excessive excretion of feces, dehydration may occur, so the patient must receive rehydration therapy and maintain a drinking regime.
Body temperature in adult patients most often fluctuates within subfebrile values (up to 37.2-37.5 degrees), but sometimes it can rise to high levels and reach 39 degrees and above. The degree of intoxication depends on the state of the patient’s immune system, the number of viruses and the degree of their activity (reproduction).
Only an infectious disease specialist should treat stomach flu. Self-treatment is unacceptable due to difficulties in diagnosing the pathology. The fact is that the symptoms of the disease are not typical, and their appearance may indicate other serious diseases: cholera, salmonellosis, etc. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination, as a result of which a decision will be made on the possibility of outpatient treatment.
Procedure for suspected rotavirus
How to treat rotavirus infection
To date, specific therapy for this pathology has not been developed. Treatment is symptomatic, aimed at eliminating dehydration, manifestations of intoxication and related disorders in the body.
First of all, the treatment of intestinal flu is directed towards rehydration. For this purpose, special saline solutions are used (for example, Regidron). To combat dehydration, you can also use a solution you make yourself. To do this, take 700 ml of boiled water or chamomile decoction, add 300 ml of raisin decoction, a little salt and soda, 8 tsp. Sahara.
To quickly eliminate intoxication, it is recommended to take sorbents. As a rule, activated carbon, Polysorb or Enterosgel are used. For severe diarrhea, which is combined with prolonged hyperthermia, Furazolidone or Enterofuril is prescribed. These antibiotics help fight possible secondary bacterial infection when infected with rotaviruses, and also effectively eliminate prolonged diarrhea. How to treat patients should be determined exclusively by the doctor, taking into account the etiology and severity of the disorders in the body.
To improve digestion, enzymes are prescribed, for example, Mezim, Creon or Pancreatin. They also prescribe medications that help restore intestinal microflora (Linex, Hilak-Forte, Bifiform). It is worth remembering that any medicine has side effects and can also provoke allergic reactions.
In the treatment of rotavirus infection, proper nutrition plays an important role. With intestinal flu in the acute period, there is a complete loss of appetite, so you can fast. The main goal is to drink enough fluid. It should be remembered that you should drink often, in small sips, so as not to aggravate vomiting.
Summer stomach flu
Listeriosis (stomach flu that occurs during hot weather during the summer months) is somewhat different from other forms of gastroenteritis. The carriers of the infection are the inhabitants of reservoirs and lakes, so the main route of infection is swimming in prohibited places. You can become infected with listeriosis after eating rotten or unwashed fruits, which are an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms.
Unlike winter gastroenteritis, listeriosis is almost always accompanied by high fever (above 39 degrees) and inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes. One of the first signs of the disease is conjunctivitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye. The patient's eye sclera turns red, and purulent contents appear in the corners of the eyes.
Important! With complicated listeriosis, the patient’s bronchopulmonary system, as well as the pancreas, may become inflamed, so treatment of this form of pathology almost always takes place in a hospital setting.
One of the first signs of listeriosis is conjunctivitis.
Take precautions when traveling
When you travel to other countries, you may get viral gastroenteritis (stomach flu) from contaminated food or water. You can reduce your risk of infection by following these helpful tips:
- Drink only well-sealed bottled or sparkling water.
- Avoid ice cubes because they may be made from contaminated water.
- Use bottled water to brush your teeth.
- Avoid raw foods - including peeled fruits, raw vegetables and salads - that have been touched by human hands.
- Avoid undercooked meat and fish.
Treatment of stomach flu
There is currently no specific treatment for gastroenteritis, so the patient is prescribed symptomatic therapy, combining dietary nutrition and medications. Complex treatment works in several directions:
- eliminates signs of intoxication;
- restores salt balance;
- stops vomiting and diarrhea;
- Helps prevent dehydration.
Stomach flu negatively affects the functioning of the heart and urinary system, so in some cases potassium supplements (for example, Panangin) and drugs to improve kidney function can be used.
The scheme for drug complex treatment of gastroenteritis is presented in the table below.
| Group of drugs | What is it used for? | What medications should I take? |
| Antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs | Reducing temperature, eliminating signs of intoxication, stopping inflammatory processes on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract | "Rinza", "Paracetamol", "Efferalgan", "Flyukoldex" |
| Antihistamines (histamine blockers) | Elimination of allergic reactions | "Ketotifen", "Tavegil", "Suprastin", "Loratadine" |
| Antitussives | Blocking cough receptors | "Bromhexine", "Tusuprex", "Bronholitin" |
| Multivitamin complexes | Strengthening protective reactions, improving well-being, preventing vitamin deficiency | "Alphabet", "Sanasol", "Complivit", "Duovit" |
| Antiviral drugs | Virus suppression | "Amiksin", "Arbidol", "Viferon", "Interferon", "Grippferon", "Remantadine" |
| Rehydration products | Restoring water-salt balance, normalizing kidney function, preventing dehydration | "Regidron" |
| Sorbents | Removing waste products of microorganisms, toxins and viruses, eliminating vomiting and diarrhea, cleansing the intestines | "Enterosgel", activated carbon, "Neosmectin" |
| Digestive enzymes | Improvement of digestive processes, elimination of dyspeptic symptoms | "Mezim Forte", "Creon 10000" |
After recovery, the patient is prescribed maintenance therapy using multivitamin or vitamin-mineral complexes, as well as medications containing probiotics and lactic bacteria, which include:
- "Linex";
- "Bifidumbacterin";
- "Acipol";
- "Normobact".
These drugs are needed to restore intestinal microflora
These drugs are needed to restore intestinal microflora, improve intestinal function, strengthen the immune system and normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diet for stomach flu
For any forms of gastroenteritis, the patient must follow a therapeutic diet that excludes fermented milk products and products based on milk protein. Dairy products are an excellent breeding ground for all types of pathogenic microorganisms, so consuming products containing milk sugar during treatment can increase the symptoms of the disease and lead to a deterioration in well-being.
Dairy products are prohibited for any form of gastroenteritis
It is advisable to eat pureed food in the first days of the disease - this will reduce the load on the digestive organs and intestines. If you don’t want to eat pureed meat, you need to grind it thoroughly, cutting it into small pieces or mincing it through a meat grinder.
Drinking should be plentiful and frequent. The patient is advised to drink warm tea with raspberries or lemon, compotes, juices (diluted with water), fruit drinks and other liquids with low sugar content.
After recovery, dairy products should be introduced into the diet gradually. It’s better to start with low-fat fermented milk drinks: kefir, fermented baked milk. Cheeses, milk porridges with butter, and fatty cottage cheese are included last on the menu.
Video - Stomach flu: causes and symptoms, treatment
Prevention of viral gastroenteritis
The best way to prevent the spread of intestinal infections is to follow these precautions:
- Get your child vaccinated . A vaccine against rotavirus gastroenteritis is available in some countries, including the United States. Given that the vaccine is given to children in the first year of life, it appears to be effective in preventing severe symptoms of the disease.
- Wash your hands thoroughly . And make sure your kids do it too. If your children are older, teach them to wash their hands, especially after using the toilet. It's best to use warm water and soap and scrub your hands vigorously for at least 20 seconds, making sure to wash around your cuticles, under your nails and in the creases of your hands. Then rinse thoroughly.
- Keep separate personal items around your home . Avoid sharing eating utensils, glasses and plates. Separate towels are provided in the bathroom.
- To keep distance . Avoid close contact with anyone who has the virus if possible.
- Disinfect hard surfaces . If anyone in your home has viral gastroenteritis, disinfect hard surfaces such as counters, faucets, and doorknobs with a mixture of 2 cups (0.47 liters) bleach to 1 gallon (3.8 liters) water.
- Check your child care center . Make sure the center has separate rooms for changing diapers and preparing or serving food. The room with the changing table should have a sink and a sanitary way to dispose of diapers.
When should you be concerned?
Like any other flu, rotavirus requires examination and appropriate treatment. In some cases, even inpatient monitoring is necessary. Only a qualified doctor can reduce the effects of severe dehydration and prevent further complications. Symptoms of exacerbation of the disease should serve as immediate signals to urgently call a doctor:
- vomiting that does not stop for more than a day;
- high temperature, which constantly stays in the range of 39-40 degrees;
- dark urine or light-colored stool with blood;
- muscle cramps;
- dizziness and heart palpitations.
comments powered by HyperComments
Diagnostics
Intestinal flu in adults with stable immunity manifests itself smoothly, in other categories of the population it is often similar to food poisoning, gastritis, dysbacteriosis and other diseases of the digestive tract.
Therefore, the diagnosis of rotavirus infection requires laboratory tests:
- general blood test to determine the level of leukocytes, ESR;
- general urine test to detect erythrocyturia, leukocyturia;
- PCR;
- passive hemagglutination;
- RIF - immunofluorescence reaction or Koons method;
- RSK - complement fixation reaction.
Other features of therapy
It is necessary to understand that all means of treatment are good and have a place if you resort to their help correctly and at the right time. Therefore, the full course of treatment should be comprehensive: medications should be taken in conjunction with the special diet described above and folk remedies to enhance the effect.
Unfortunately, any treatment is very often accompanied by a number of gross, even fatal mistakes. The most common mistake made by those who do experience stomach flu is the use of antibiotics in addition to the main course of medication. However, it is worth knowing that even though gastroenteritis is viral in nature, treating it with antibiotics is pointless and very dangerous. These drugs have a strong therapeutic effect, which greatly increases the load on the kidneys. Such a load, combined with weakened functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, can further affect the state of general health, as well as individual organs (for example, the functioning of the kidneys themselves, bladder, etc.).
Having encountered intestinal flu once, few people want to encounter it again. In order for such a meeting to be the only one for life or never take place at all, you must follow 4 very simple rules. They will not only prevent the manifestation of symptoms of abdominal flu and prevent its second coming, but will also act as a faithful guarantor for maintaining a normal gastrointestinal tract. So those 4 rules are...:
- regular personal hygiene;
- strengthening the maintenance of immunity;
- thorough water treatment and heat treatment of food products (especially of organic origin);
- drinking filtered and boiled water.
To achieve the fastest and most effective results, it is recommended to use the methods in combination: the main blow to the disease is dealt by specialized drugs, and folk remedies, together with diet, create a background favorable for rapid recovery.
Pathogen
Intestinal flu is caused by viruses that can multiply in the epithelial cells of the small intestine. The causes of infectious gastroenteritis are:
- Rotavirus;
- Norwalk viruses from the calicivirus family;
- Adenoviruses;
- Astroviruses;
- Toroviruses.
The source of infection is a sick person who releases pathogens into the external environment with feces and, in some cases, with droplets of saliva. They are transmitted to surrounding people through the fecal-oral route, that is, through contaminated food, through dirty hands and contaminated household items. In preschool institutions, household contact plays an important role: children become infected through toys, door handles, and pots contaminated with the pathogen.
Water transmission plays an important role; for example, rotavirus survives in cold water for months. Outbreaks of rotavirus gastroenteritis associated with the consumption of contaminated bottled water have been described.
What happens in the body during infection?
When rotavirus penetrates the body, within half an hour the pathogen can be detected in the cells of the small intestine. Due to the attack of the virus, the structure of the intestinal mucosa is disrupted. This in turn leads to disruption of the production of digestive enzymes responsible for the breakdown of complex sugars. Thus, unbroken carbohydrates accumulate in the small intestine, which attracts excess fluid, causing diarrhea or watery diarrhea.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine can also help avoid complications of stomach flu and treat the patient properly. If drug treatment is characterized by a narrow focus of drugs that are used strictly at a certain moment, then folk remedies form a generally favorable background for improving their effect and the ground for the most effective course of the full course of treatment.
Most of this is advice regarding nutrition. So:
- To avoid dehydration, you need to drink as much boiled water as possible, use various decoctions (chamomile, dill, marshmallow root - 100-200 ml every hour). In total, the daily volume should be at least 2 liters.
- To relieve intoxication, it is recommended to drink tea with ginger (half a glass up to 6 times a day), a drink with lemon and honey (up to 3-4 times a day), a fruit drink made from rose hips, chamomile and linden flowers (up to 6 times a day) , fruit drink made from currants, raspberries and cranberries with honey.
- Rice water can help cope with diarrhea. Cook a glass of rice in a liter of boiling water over low heat for 5 minutes. After this, the decoction should be filtered and taken 50 ml every 30 minutes.
A special diet occupies a special place. The following are foods that must be immediately excluded from the diet during treatment:
- fried and fatty foods;
- fermented milk products;
- pasteurized and freshly squeezed juices;
- carbonated drinks;
- sweet confectionery;
- bread.
Instead, daily frequent and divided into small portions are recommended:
- weak chicken broth;
- vegetable soups;
- cereals/porridges cooked in water (semolina, oatmeal, rice, buckwheat);
- boiled chicken eggs;
- dried fruits (dried apricots, raisins, figs);
- lean meats (boiled chicken and beef);
- stewed vegetables (except for radishes, beans, garlic and white cabbage, as they contain a large
- the amount of fiber, which contributes to excessive gas formation);
- dried loaf / crackers;
- tea with honey/raspberries, compotes.
You can return to your previous diet within a week after recovery. It is recommended to do this gradually, because... During the illness, the stomach has become accustomed to a different function and functions in a somewhat slower (incomplete) mode.