What is blood type and Rh factor?
Each blood group has its own individual characteristics
It is believed that previously there was only one blood type. But since the beginning of the migration of mankind and the conquest of new lands, others began to appear. They did not attach much importance to the indicators.
But after careful study, it was found that each type has its own characteristics and is incompatible with certain groups. Experts began to take into account the identity of the blood when carrying out transfusions and surgical interventions. Today every person knows this information.
Blood group is a special set of properties of red blood cells. It is impossible to determine a person’s identity based on changes and characteristics of the plasma composition. But thanks to knowledge of the identity of the blood, it is possible to establish a connection between the donor and the recipient during transfusion, which is important during transfusion and transplantation.
Determination of blood identity occurs based on the results of a laboratory test, depending on the type of red blood cells.
Their cell membrane may contain a large number of combinations of protein compounds controlled by chromosome No. 9. They do not change under the influence of numerous internal and external factors throughout a person’s life.
Depending on the possible combinations, 4 blood groups have been identified. The third in medicine is designated as B or III. Along with information about blood affiliation, the Rh factor is also indicated. This is the ability of red blood cells to stick together. There are only two of them: negative and positive. The first type is found in only 15% of the population.
How and where can you find them?
The third negative blood group is much less common than the first and second
To establish the Rh factor group, blood is drawn and laboratory testing of the resulting material is carried out. During the analysis, the presence of specific antibodies is compared.
Laboratory research can be carried out in several ways:
- Express method. The tube containing the blood sample is not heated. They use a special universal serum suitable for all types.
- Gelatin method. Blood and gelatin solution are mixed in equal proportions.
- Alternative way. Petri dishes are used.
- With the help of papain. The method is carried out in extreme cases when it is necessary to determine the compatibility of blood during transfusion.
Establishment of blood identity and Rh factor is carried out immediately after the birth of the child. The result is entered into the medical record. The study can also be prescribed by the attending physician if necessary.
Why do you need to know your blood type and Rh factor?
Knowledge of blood identity may not always be required throughout life. But this information may be necessary in the following cases:
- Transfusion. May be required after injury accompanied by extensive hemorrhage.
- Carrying out planned and emergency surgery. In some cases, a transfusion may be required.
- During transplantation.
- Before planning a pregnancy. In order to exclude Rh conflict.
- During the period of control and observation of a pregnant woman, when the incompatibility of the blood of the father and mother is established.
- To identify the presence of hemolytic disease in infants. Blood is taken for analysis from a newborn 1-2 days after birth.
There are times when urgent transfusion or surgery is required. Knowing the identity of your blood and the Rh factor can save the life of not only the patient, but also another person.
Consequences of Rh conflict during pregnancy
When red blood cells break down, bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced in the liver, is released into the fetal blood. A large amount of bilirubin is toxic; it negatively affects the function of the child’s internal organs. This condition is called hemolytic disease of the fetus. Severe hemolytic disease leads to intrauterine fetal death.
Hemolytic disease develops quite rarely. Even if Rh conflict occurs, the fetus is well protected. The placenta retains most antibodies from the mother's bloodstream. Protection can be weakened by:
- chronic diseases of the mother;
- bad habits;
- placental abruption;
- severe toxicosis.
In a healthy pregnant woman, fetal red blood cells practically do not penetrate into her bloodstream. Therefore, antibodies are not produced. Puncture of the membranes to collect amniotic fluid for examination and puncture of the fetal umbilical cord increase the risk of mixing blood.
Hemolytic disease in a newborn child manifests itself in three forms.
- Edema is the most difficult option. Multiple edema, including intracavitary edema, is characteristic. The skin is pale, the internal organs are enlarged.
- Jaundice - the baby is born with yellow skin and the whites of the eyes. It proceeds relatively easily.
- Anemic - mild form. The baby is pale, lethargic, with poor appetite.
The complication most often occurs in the icteric form and is called kernicterus. This is damage to the cerebral cortex by toxic bilirubin.
Compatibility with other blood types
The theory of blood group compatibility appeared in the mid-20th century
Blood belonging to the third group and having negative Rh is considered rare and special, since it contains a special antigen to the A antibody. It will be compatible with any that does not contain antibodies to the B antigen.
Often, blood that is similar in all respects is used, but in emergency cases, when the procedure is urgently required and the necessary blood is not available, universal blood is used.
If the patient has a third negative group, the third and first ones can be transfused. Previously, it was believed that Rh was not of particular importance, and a negative one could be transfused both for the first type and for the second. But at the moment, only blood of the same type is used.
Characteristics of people with 3 negative blood
Blood type, according to experts, also influences the formation of a person’s character and personality. According to research results, it was found that people with third negative blood are romantic by nature. In relationships, they are most interested in the inner world of their partner.
They always complete all their tasks and try to get closer to the ideal. They demand the same from those around them. People with third negative blood will always come to the rescue. They are quite delicate and try not to offend others.
In work, people with 3 negative blood group and negative Rhesus make a compromise in exceptional cases. They demand from their subordinates that they perform their duties perfectly.
People with third negative blood are clean and love order not only in the workplace, but also in their home.
That is why they do not always manage to find their life partner. Some problems and disagreements may arise in the family, as they often require maintaining ideal order in the apartment. But the conflict is quickly resolved thanks to the diplomacy and gentle nature of people with a third negative blood type.
But a person’s upbringing, as well as his living conditions, also play a big role in the development of character. Such people do not conflict; in relationships they try to find a compromise and solve the problem that has arisen.
Recommendations for proper nutrition
Those with negative blood group 3 have a very good metabolism.
Blood belonging to a certain group also affects a person’s taste preferences. People with the third negative prefer dairy and fermented milk products. They can be consumed for breakfast, lunch and dinner, regardless of the fat content. The body easily absorbs and processes all substances. That is why such a diet does not cause obesity.
When there is a risk of Rh conflict
You should know that Rh incompatibility occurs in 75% of all cases when an Rh-negative woman becomes pregnant from an Rh-positive partner. In most episodes, difficulties do not arise if this is the first pregnancy. This happens due to the absence of Rh antibodies in the blood, because the body has not previously been in contact with Rh-positive blood, which means that Rh conflict does not develop. When the second child is conceived, antibodies already appear in significant quantities.
The entry of the embryo’s red blood cells into the circulatory system of the expectant mother activates “memory cells.” Therefore, during subsequent conceptions, a rapid attack of antibodies occurs on the Rh factor of the embryo, which can result in the following complications:
- miscarriage - 3-4% of all cases;
- ectopic conception - 1%;
- abortion - in 5-6 cases out of 100;
- premature birth - 10-15%.
The risk of Rhy incompatibility between spouses is important to take into account when planning conception. If you are the owner of Rh-negative blood, then you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- find out in advance the partner’s blood type and Rh;
- develop and maintain a proper diet;
- try to protect yourself from stress;
- take measures to strengthen the immune system to prevent a possible failure.
Blood group third negative
In the characteristics of this type of blood, one can highlight some features of character formation, taste preferences and compatibility. It is generally accepted that such people are individualists, prone to mood swings, which does not prevent them from being patient when necessary and being able to find a diplomatic approach to solving a problem. They are emotional and good at speaking. They find themselves in activities related to the public.
The third negative blood group in women affects their love of cleanliness. The house of such a housewife is always tidy and mess is not held in high esteem. Sometimes this character trait has a negative impact, since a woman demands that others maintain order, which not everyone can do. However, conflicts that arise on this basis are quickly smoothed out thanks to diplomacy.
The third negative blood group in men makes them leaders who are demanding in fulfilling their official duties at work. They rarely agree to compromise decisions in the field of their professional activities.
In people with blood group 3 and Rh negative, the characteristics of taste preferences are formed due to the nomadic lifestyle of their ancestors. The digestive system is adapted to any type of food; they find dairy products especially attractive. It is considered a huge plus that such people are not overweight and do not need long-term and frequent diets. The following will be useful for use in everyday nutrition:
- meat, excluding poultry and pork;
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- seafood;
- eggs.
Corn, margarine, certain oils and nuts should be avoided. Frequent use of fatty fish and meat will not have the best effect. It is advisable to avoid their presence in the diet. From drinks, exclude the consumption of carbonated water, rich in carbohydrates, and tomato juice.
Nutrition for blood group 3
Third blood group, Rh negative: diseases
Life of a nomadic type strengthened the immunity of the ancestors of people with blood group 3 and negative Rh. The characteristics of the immune forces of their body were so strengthened that they made it possible to survive severe epidemics and plague. But this does not make them completely invulnerable. There are a number of pathologies to which they are predisposed:
- in the postoperative period, their body is more susceptible to infections than others;
- Group 3 with negative Rh in girls contributes to the occurrence of complications after pregnancy;
- vulnerability to autoimmune diseases;
- predisposition to inflammatory processes of the respiratory system;
- joint diseases and the risk of osteochondrosis;
- vulnerable to depression and often experience symptoms of fatigue that become chronic.
If a person is faced with the acute question of transfusion, then it is necessary to take into account that for people with blood group III, donor biomaterial of the same group or I is suitable. The latter option is an alternative and requires additional compatibility analysis. Group B donor material is suitable for the same blood type or for group IV.
Attention! It is important to take into account the Rh factor of the donor and recipient, since Rh-positive blood cannot be given to people with an Rh-negative indicator.
Transfusion scheme by blood group
More on the topic “Immunological incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus”:
anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin - pros and cons
Immunological incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus. But now, in the first 24 hours after childbirth/abortion, the mother is given an injection of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin. Every maternity hospital now has it.
Umbilical cord puncture...
Immunological incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus. To study fetal blood, puncture of the umbilical cord vessels (cordocentesis) under ultrasound guidance is used. In China, it is forbidden to determine the gender of an unborn child.
Amniotic fluid puncture
Immunological incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus. The puncture site is chosen depending on the location of the placenta and the position of the fetus. Possible complications may include: increased uterine tone...
edema - the reason for hospitalization????
Immunological incompatibility of maternal and fetal blood
Taking into account that with hemolytic disease of the fetus, swelling of the placenta occurs, its thickening by 0.5 cm or more may indicate a possible disease of the fetus
Postmaturity and negative Rh factor
Immunological incompatibility of maternal and fetal blood
According to CTG data, in case of fetal suffering, there are clear signs of heart rhythm disturbances. It is important to maintain the first pregnancy in women with Rh-negative blood.
Negative Rh factor
Immunological incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus. Rhesus-conflict pregnancy: don’t panic! Rhesus - conflict during pregnancy, how to avoid problems.
Different Rh factor.
Immunological incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus. Rhesus-conflict pregnancy: don’t panic! Rhesus - conflict during pregnancy, how to avoid problems.
Rhesus conflict mothers
Immunological incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus. First pregnancy and Rhesus - a conflict. During pregnancy, immunological incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus may occur due to the Rh factor, less often according to the AB0 system and even less often according to some other...
KTG for oparina
Immunological incompatibility of maternal and fetal blood
According to CTG data, in case of fetal suffering, there are clear signs of heart rhythm disturbances. It is important to maintain the first pregnancy in women with Rh-negative blood.
Negative Rh and termination of pregnancy
It is believed that antibodies in the mother's blood begin to be produced when the baby's blood enters the mother's blood. this does not happen during a normal pregnancy; this is possible during childbirth, but not Immunological incompatibility of the blood of the mother and fetus.
Pregnancy in women with 3 negative blood group
Women with this type of blood usually do not have problems with conception: they can easily become pregnant and carry a baby to term. But planning a pregnancy should be taken with full responsibility, since some troubles are possible due to the negative Rh of the expectant mother in combination with the positive Rh of the father.
In this case, the baby may inherit the father’s Rh indicator, which will lead to an Rh conflict between the fetus and mother. The pregnant woman’s body will begin to produce antibodies that perceive the fetus forming in the womb as a hostile object that needs to be attacked. Under such circumstances, spontaneous abortion is possible.
Rh compatibility chart for parents
If the pregnancy is not terminated for natural reasons, and the woman manages to carry the child to term, there is a high probability of pathologies occurring in the baby’s body. They can manifest themselves in the form of problems with the visual and hearing systems, disorders in the functioning of the brain. The expectant mother and baby need constant monitoring. It is important to take a blood sample to determine the formation of antibodies.
Important! When antibodies are detected in the mother's blood, the situation becomes critical. To maintain pregnancy and reduce the risk of pathologies, a blood transfusion may be prescribed.
Intrauterine treatment of the fetus
- Plasmapheresis is a blood purification in which all toxic substances are removed from the mother’s blood plasma (the blood is distilled through a plasma filter and poured back in)
- Hemosorption – used to clean carbon filters that collect harmful substances
- A piece of the future father's skin is implanted into the mother's skin. This serves as a distraction for the immune system and helps reduce the attack of antibodies on the fetus.
- Desensitization
- Immunoglobulins
Planning pregnancy and 3 negative blood group
In women, the Rh characteristic affects the course of pregnancy and its outcome in the case when the girl is negative, and the guy who will become the father is positive. In this case, you need to see a doctor for advice.
Usually, the first pregnancy with such indicators passes without disturbances and risks for the expectant mother and child. Future pregnancies will require close monitoring by a gynecologist.
Rh conflict tends to occur in the last period of pregnancy. To avoid the development of such a scenario, doctors refer the young couple to undergo an Rh test. Based on the results obtained, the doctor will be able to draw conclusions.
If a woman who is Rh negative carries a child who is Rh positive, doctors will offer an anti-Rh globulin vaccine. A timely visit to the clinic for specialized help will give confidence in the successful development of pregnancy without subsequent complications.
The interesting video below will help you get an idea of the evolution of blood:
What are Rh antibodies and how do they affect the fetus?
Rh antibodies are compounds of a protein structure that are produced in the mother's body in response to the ingestion of Rh-positive red blood cells from the fetus (the expectant mother's immune system perceives these red blood cells as foreign). If Rh antibodies are detected in the mother's bloodstream, the obstetrician makes a diagnosis: Rh sensitization. This occurs with artificial or spontaneous termination of an uterine or ectopic pregnancy. Rh antibodies can also appear after the first birth if the born child is Rh positive (during childbirth, the baby’s blood enters the mother’s bloodstream, causing a corresponding reaction). Sensitization of the body of a Rh-negative woman is also possible through transfusions of Rh-incompatible blood (even if such transfusions were carried out in early childhood).
The process of immunization of a pregnant woman begins with the formation of Rh antigens in the red blood cells of the fetus. Since antigens of the Rh system are contained in the blood of the fetus from 7-8 weeks of pregnancy, in some cases early sensitization of the mother’s body is possible. However, in the vast majority of cases, the first pregnancy in a Rh-negative woman (in the absence of previous sensitization of the body) proceeds without complications. The risk of developing Rh sensitization increases with subsequent pregnancies, especially if the first pregnancy is terminated, bleeding during the first pregnancy, with manual separation of the placenta, and also if the birth is performed by caesarean section or is accompanied by significant blood loss. This is explained by the fact that with the listed complications, there is a high probability of a large number of Rh-positive red blood cells entering the maternal bloodstream and, as a consequence, the formation of a large number of Rh antibodies. In addition, during the first pregnancy, the immune system of the expectant mother encounters Rh-positive red blood cells of the fetus for the first time. Therefore, not so many antibodies are produced: approximately as much as is needed to destroy fetal red blood cells entering the mother’s blood. In addition, these antibodies belong to class M immunoglobulins, which are large in size and poorly penetrate through the placenta to the fetus. But after childbirth, “memory cells” remain in the woman’s body, which in subsequent pregnancies will be able to “organize” the rapid and powerful production of antibodies against the Rh factor. These will be antibodies of a different type - class G immunoglobulins, which are smaller in size than immunoglobulins M, and therefore penetrate the placenta more easily and are more aggressive. Therefore, the reaction of the female immune system to the Rh antigen of the fetus during the second and third pregnancy is much faster and more severe than during the first. Accordingly, the risk of fetal damage is higher.
According to medical literature, after the first pregnancy, immunization occurs in 10% of women. If a woman with Rh-negative blood avoids Rh immunization after her first pregnancy, then the next pregnancy with an Rh-positive fetus, the probability of immunization again is 10%.
Rh sensitization does not harm the health of the expectant mother, but it can pose a danger to the child. Once in the bloodstream of the fetus, Rh antibodies destroy its red blood cells, causing anemia (decreased hemoglobin), intoxication, and dysfunction of vital organs and systems. This condition is called hemolytic disease (hemolysis - destruction of red blood cells).
The breakdown of red blood cells leads to damage to the kidneys and brain of the fetus. As red blood cells are continuously destroyed, his liver and spleen try to speed up the production of new red blood cells, while increasing in size. In the end, they too fail. Severe oxygen starvation sets in, and a new round of severe disorders begins in the child’s body. In the most severe cases, this ends in intrauterine death at various stages of pregnancy; in milder cases, the Rh conflict manifests itself after birth as jaundice or anemia of the newborn. Most often, hemolytic disease quickly develops in a child after birth, which is facilitated by the entry of a large number of antibodies into the baby’s blood when the integrity of the placental vessels is disrupted.
Treatment of hemolytic disease is complex and complex; sometimes the baby requires a replacement blood transfusion. Doctors inject him with Rh-negative blood of his type and carry out resuscitation measures. This operation must be performed within 36 hours after the baby is born.
Characteristics of the characteristics of the third blood group
Each group has its own individual characteristics. These include power, media specifications, and compatibility. Let's look at each feature separately.
The character of people who have the third blood group is characterized by calmness, romanticism and a sensitive attitude towards others. They also require others to try to be clean, hardworking and cultured. They constantly act as a teacher in order to bring the work they and their interlocutor started to an ideal result. Their demands are quite high and therefore others seem to be a little boring and demanding.
Let's talk about the nutrition of the owners of group 3. These people constantly moved, so their stomach easily adapted to new conditions and diet. Third-graders can easily combine various foods and not feel discomfort in the stomach. Such nutrition does not make them fat and any complications are excluded. The third group with negative Rh has such advantages and nutritional privileges.
Products useful for them:
- any meat products;
- fish;
- various cereals;
- fermented milk products;
- eggs.
Undesirable vegetables:
- tomatoes;
- corn;
- pumpkin;
- olives.
Pork is also not recommended because it is fatty and contains a lot of unnecessary cholesterol.
It is much easier to find a donor for this blood group than for 4.
There are no negative indications for pregnancy in carriers of group 3. It proceeds quite calmly and effectively. It rarely happens that the nature of the blood of the father and mother is not suitable for conception. There are very few such cases. In the modern world, medicine has made great strides forward, so doctors can cope with any problem. The main thing is to apply on time and believe that everything will be fine.
Sometimes it happens that the Rhesus of mother and child is incompatible, but even in this case, our medicine has a special technique that helps to give birth to a healthy baby. You need to do everything on time and the doctor will help you carry the baby and give birth on time without any problems. The sooner a woman in labor contacts a gynecologist, the sooner she will be helped, otherwise a miscarriage may occur or the baby will die in the womb.
Descendants of nomads
The third blood group, according to various sources, is characteristic of 11 to 20 percent of the inhabitants of our planet. The characteristics of the type of this category of people consisted of centuries-old traditions and customs of ancient nomadic peoples. The third positive one, according to historians and geneticists, was formed about 10 thousand years ago. 3 negative group is much less common. Today, representatives of this type can be found in every corner of the world. It is believed that people with blood type B or III first appeared as a result of mass migrations, which were characteristic mainly of Asian peoples.
Due to extreme conditions, men and women of this type needed strong immunity and endurance to survive. Evolutionary development has given this ability to people with 3 positive blood group. They have a surprisingly efficient gastrointestinal tract, but are not resistant to rare viruses and can suffer from lactose intolerance.
If a blood transfusion is required and the recipient has a 3 or B negative blood group, donor biomaterial with a positive RH cannot be used.
People with blood type B tend to be open-minded and optimistic. They are not capricious when it comes to personal comfort indicators. For this category of the population, traveling on foot with a backpack through the impenetrable jungle is no worse than a comfortable flight to a prestigious resort. They value adventure and will take any chance to escape boredom and do something truly interesting.
Is it possible to prevent Rh conflict?
While planning a pregnancy, partners should have their blood tested. If it suddenly happens that parents turn out to be carriers of different Rhesus, this is not a disaster. It is necessary to take a blood test once before the 32nd week of pregnancy. The doctor will monitor the development of conflict between the blood of the baby and the mother based on the level of antibodies.
A qualified gynecologist will be able to prescribe the necessary treatment in a timely manner. Most often this is the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin, which binds and removes aggressive bodies from the mother’s body. The vaccine is administered immediately after the birth of the child and any interventions on the uterus - abortions, punctures, operations and other manipulations. Early obstetric care or exchange blood transfusion to the baby after birth is also practiced.
Gnomic.ru recommends Kholod Group
Repair of Indesit refrigerators at home - call a specialist
We professionally repair Indesit refrigerators + any other manufacturers. More than 5 years of experience. Free visit of a specialist and diagnostics!
Use promo code: Gnomic.ru
and get a guaranteed 10% discount
We work in Moscow and the region.
Call
Compatibility of men and women
Blood type 3 positive leaves its mark on a person’s character traits and behavior pattern. People belonging to this category combine courage, determination, emotionality and high intelligence. More than a third of such people independently move towards their goals and achieve success. They can honestly say: no one promoted me in this, I achieved everything myself. In love, they also take victories and defeats lightly. Men strive for intimacy, but do not perceive refusal as an insult, but prefer to remain friends.
In union with a woman like:
- They strive to search for new sensations; adherence to traditional national or religious values can save the relationship.
- Dominant in relationships. There is no place for boredom in such a marriage; a man is always ready to experiment.
- A clash of temperaments can either strengthen or destroy a relationship.
- The man plays a dominant role, but the family is a unified team.
Women of blood type 3, on the contrary, love flirting, but most often do not seek further acquaintance. Paired with a man like:
- An active union of two versatile personalities.
- A sensible and sensual couple who literally divides everything in half.
- A calm union that is not spoiled even by a rare physical connection.
Safety
In fact, the blood type number does not play as important a role in family planning as the Rh factor (RH). If a woman’s RH is positive and a man’s is negative, the expectant mother should be under close medical supervision throughout the entire pregnancy. In most cases, pregnancy proceeds without any complications or pathologies.
As a result, a healthy baby is born.
Both expectant parents should have laboratory tests done in advance to be prepared for any surprises that pregnancy may bring. What blood type a child will have can be calculated independently, but the result is not guaranteed. There is only a probability, which is calculated as a percentage.
- If parents have the first and third groups, then with a 50% probability the child will inherit the blood type of one of them.
- Parents with blood types 1 and 4 or 3 and 4 in 50% of cases give birth to children with blood type 3.
- In a union of two people with the second and third groups, the probability of getting a child of any of the 4 known types is 25%.
- Parents with 2 and 4 or 4 and 4 types of erythrocyte cells in 25% of cases have children with blood group B (3).
- Incredibly, if both parents have blood type B, then the chance of passing it on is only 75%. In other cases, children are born with the first group.
How is it inherited?
There are 4 types of blood group (first, second, third and fourth) and are inherited by the child from the mother and father, as is its Rh factor. To understand why Rh conflict may occur, you should delve a little deeper into genetics. All cells in the human body, with the exception of reproductive ones, have 2 chromosomes of dominant and recessive genes. When an egg is fertilized by a sperm, a new cell is formed with a unique set of chromosomes, which is responsible for the external and internal characteristics of the baby.
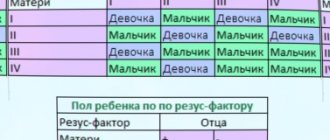
INTERESTING: what blood type will the child have: calculation using a special table
The table provides information about the child’s Rh factor depending on what Rh the father and mother have:
| Father mother | DD | Dd | dd |
| DD | + | + | + |
| Dd | + | +/- | +/- |
| dd | + | +/- | – |
Rh negative occurs in 100% of cases in babies whose parents are also Rh negative. With other combinations, any Rh factor is likely to appear. The gender of the parent is not important. The process is influenced exclusively by the dominant gene.
Rh conflict occurs if the mother is Rh negative and the fetus is Rh positive. Her body is not familiar with the baby's new cells. However, the problem occurs in less than half of all cases, since it requires the blood of the baby and the mother to mix, and this does not happen during pregnancy, because the placenta protects the fetus. A similar phenomenon is observed when:
- miscarriage;
- abortion;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- bleeding throughout the entire period of gestation.
For this reason, this phenomenon is unlikely during the first pregnancy. The risk increases with repeated conceptions.
Can a father and mother with positive Rh have a negative child?
Is it possible to give birth to a baby with Rh negative if mom and dad are Rh positive? This phenomenon is not considered a pathology or deviation and does not indicate the infidelity of the spouse.
Rhesus is passed on to the child with the father's genes. In a man, a pair of genes is responsible for positive Rh. It appears in two combinations:
- The first one is DD. Both genes are dominant. They occur in 45% of men with positive Rh. In this case, the baby is always born Rh-positive.
- The second is Dd. Rhesus heterozygosity allows the dominant gene to be transmitted to the fetus in half of the cases, which means that the probability of transmitting a recessive negative gene is 50%. The number of males with the Dd combination is about 55%. About a quarter of Rh-positive men have Rh-negative children. Rhesus conflict does not occur, even if the family has different parameters.
Can parents with negative Rh have a child with positive?
The opposite situation is often asked about by future parents planning to conceive a child. Is it possible for a man and woman who are Rh negative to have a baby who is Rh positive? For this, Rh combinations should be considered. Negative Rh is the combination dd, i.e. a combination of two recessive genes. In other words, neither the father nor the mother has a specific protein in their red blood cells, and there is nowhere for such an antigen to come from in the child. That is, he will have negative Rh blood.
Rh factor
Over the course of long studies, scientists have discovered that more than 80% of people have special antibodies in their blood. This is a special type of protein called agglutinogen. And only 20% of the world’s population does not have this protein in their blood. Thus, the Rh factor is an indicator of the presence of D antibodies in the body. Those who have it are Rh positive and vice versa.
These indicators are extremely important for any person throughout his life. This analysis is carried out at birth and further as necessary. This is especially important if an emergency blood infusion is necessary, because if a person is injected with biomaterial with a different Rh factor, a conflict may occur, which sometimes even leads to death.
Probability when carrying a fetus for the second time
During the second and subsequent pregnancies, the likelihood of Rh conflict increases significantly. This is explained by the fact that a Rh-negative woman has already developed an immune memory, which leads to increased formation of antibodies to the D antigen contained in the blood of her Rh-positive baby.
The second and any subsequent pregnancies, regardless of how they proceeded and how they ended, become a catalyst that triggers the production of antibodies in the mother’s body.
However, this does not mean at all that a woman who has given birth to one child can no longer become pregnant, since this will certainly lead to an Rh conflict. A woman just needs to be more careful and responsible about controlling antibodies.
And the first thing that is required is not to refuse an injection of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin when prescribed by the attending obstetrician-genecologist , if you plan to carry and give birth to your second baby healthy. This will allow the binding of foreign Rh-positive antigens and prevent the production of antibodies in the mother’s body, which significantly reduces the risk of complications during a subsequent pregnancy.
If antibodies were not produced during the first pregnancy, and immunoglobulin serum was administered on time, then when carrying a second baby, the probability of an Rh conflict will be equal to the same initial 10%.
Indicator conflict
What is Rh conflict? This is an incompatibility of blood parameters between a woman and her unborn baby. This phenomenon occurs only if the expectant mother has Rh minus and the baby’s biological father has Rh plus. However, a conflict arises only if the baby inherits the father’s characteristics. In such a situation, the development of a Rh conflict between mother and child is not unlikely.
What happens at this moment? When a baby develops its own circulatory system, its blood cells can enter the mother's bloodstream. At the same time, the woman’s immune system begins to perceive the child’s blood as an enemy. The immune system actively fights this enemy. Thus, the mother's blood cells begin to actively destroy the unborn baby. When the mother's antibodies enter the baby's blood through the placenta, they kill the baby's blood cells. As a result of this struggle, the baby may develop various dangerous pathologies.
This situation can also cause premature birth or miscarriage.
However, Rh conflict is observed in only 10% of all pregnancies with a negative Rhesus mother. In most cases, doctors manage to avoid dangerous consequences, and the child is born completely healthy. Negative blood type and pregnancy are not a ban today, but only a reason for more careful monitoring of a woman and her baby.
What is the danger when a conflict develops?
Rh conflict pregnancy - what is it?
In obstetrics, this concept is understood as any pregnancy accompanied by the production of antibodies directed against fetal cells. The Rh conflict itself develops in the same way as any other immunological reaction. It occurs due to the fact that a mother with a negative Rh factor and an unborn child who has a positive Rh factor exchange blood.
In this case, the mother’s immune system regards the presence of the fetus in her body as a foreign threat and begins to produce antibodies against it. For this to happen, it is enough that 35-50 ml of red blood cells from the blood of her future baby enter the woman’s body. However, even if there is incompatibility between the blood of the mother and child due to the Rh factor, the Rh conflict itself does not always arise.
For example, it happens that during such a pregnancy antibodies may not be produced at all, or there may be so few of them that they cannot cause serious harm to the health of the unborn baby.
There are a number of factors that increase the occurrence of Rh conflict during gestation. And not all of these reasons are associated with the blood of her unborn child entering a woman’s body.
- First pregnancy. With it, the risk of Rh conflict is 10-15%.
- A miscarriage increases this risk by 3-4%.
- Medical abortion - by 6%.
- Ectopic pregnancy - by 5-10%.
- Normal labor - by 10-15%.
- But if obstetric forceps were used during childbirth, the risk of Rh conflict increases by 33.7%.
The more “bloody” the obstetric intervention was, the greater the risk of immunization. The same thing happens if there was no bleeding, but the placental barrier was broken.
- With a cesarean section, this risk increases by 52.5%.
- With manual separation of the placenta - by 40.3%.
- Antepartum hemorrhage increases it by 30%.
- And with eclampsia, when the placental barrier is disrupted, the risk is 32.7%.
Rh conflict can be very dangerous during pregnancy, since antibodies seriously attack the fetus’s body and destroy its red blood cells. In case of Rh conflict, massive destruction of red blood cells is observed, which is why a large amount of bilirubin, which has pronounced toxic properties, is released into the blood.
As a result, all organs and tissues of the fetus are damaged, but the baby’s nervous system suffers especially severely; for example, the tissues of his brain soften, which can lead to mental retardation. The spleen and liver, the main purpose of which is to rid the body of bilirubin, do not cope with their function. And the massive death of red blood cells itself leads to the baby developing anemia and hypoxia.
All these three factors, launched together, lead to a serious complication - hemolytic disease of the fetus.
The consequences of complications - hemolytic disease of the fetus can be:
- Miscarriage.
- Intrauterine fetal death.
- Anemia.
- Problems with the functioning of the baby’s liver and spleen (for example, jaundice may develop).
- Congenital dropsy.
- Damages to the brain and nervous system.
As for the Rh-negative mother, who has become the unwitting culprit of all these troubles, the Rh conflict itself will most likely not affect her health in any way, even if the developing fetus suffers from this. serious pathologies.
Sometimes, but not always, with a Rh conflict, the expectant mother may develop preeclampsia, which is a truly serious complication.
Why can’t a mother’s pregnancy be terminated if she has a negative Rh?
Doctors do not recommend that women with Rh negative undergo abortions unless for medical reasons, but even then they advise them to think carefully before making such a decision. With each subsequent pregnancy, antibodies in a woman’s body are produced at an ever-increasing speed and in ever-larger quantities. And the possibility of a successful gestation of the fetus decreases significantly with each termination of pregnancy.
Rh factor
| Father | Mother | Child | Probability of conflict |
| Plus | Plus | 75% plus and 25% minus | No |
| Plus | Minus | 50% plus and 50% minus | 50% |
| Minus | Plus | 50% plus and 50% minus | No |
| Minus | Minus | 100% minus | No |
Rh-negative mother Rh-positive father = Rh-positive fetus Please note: no matter what group the mother has, Rh negative during pregnancy becomes a cause of conflict. In this case, the embryo inherits it from the father and brings the “new protein” into the body of the Rh-negative mother.
Her blood “does not recognize” this substance: there is no such protein in the body. Accordingly, the body begins to defend itself and produce antibodies. They penetrate the placenta into the baby's blood and attack his red blood cells. The fetus tries to defend itself: the spleen and liver begin to work hard, and they increase significantly in size. If a child has few red blood cells left, he develops anemia, or anemia.
Rh-negative women should monitor their body very carefully and listen to its signals. This attitude will help prevent:
- dropsy (fetal edema);
- anemia;
- miscarriage;
- disorders of the child’s brain, speech or hearing.
To protect the baby from these consequences, women with negative Rh during pregnancy must undergo all tests prescribed by the doctor on time.
If your chosen one and you have positive and negative Rh factors, respectively, this must be taken into account when planning a pregnancy. Often, Rh conflict does not appear during the first pregnancy, although the parents have different Rh factors. Whatever blood type the expectant mother has (Rh negative) during pregnancy, during the second birth the likelihood of conflict is very high, since her blood most likely already has antibodies.
Analysis
When attending a gynecologist's office, each woman is tested for Rh factor and blood type. This is necessary in order to take preventive measures in a timely manner if a woman suddenly has a negative blood type during pregnancy. In such situations, the woman’s sexual partner also needs to donate blood for testing.
It is worth noting that during the first pregnancy, the occurrence of a resus conflict between mother and child is quite rare. The thing is that the mother’s body has not yet developed antibodies and the child practically does not suffer. Subsequent pregnancies may become more complicated.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of conflict, namely:
- Past abortions.
- Risk of miscarriage.
- Difficult previous births.
- Infusion of blood with the opposite rhesus.
A negative Rh factor during pregnancy should be detected in a woman as early as possible. An expectant mother with this phenomenon must be registered with a special person. During the entire period of bearing the baby, she will have to take a blood test for antibodies. It is worth noting that in the case of a negative blood group in women during pregnancy, abortion is strictly contraindicated, especially if the husband is Rh positive. Termination of the first pregnancy can put an end to future motherhood.
Causes of the conflict
A woman with negative Rh and a man with positive Rh are able to conceive. If the mother’s Rh factor is positive and the father’s is negative, then the risk of developing a conflict is 50%. The parent's blood type during pregnancy affects the degree and speed of formation of possible pathologies.
It happens that the female body is not able to produce a sufficient amount of antibodies. The main reasons for the development of incompatibility are fertilization of the egg after abortion or miscarriage. In this case, the risk of developing a conflict increases several times. In a woman, the factor does not change during pregnancy and for the rest of her life, only the amount of antibodies produced by the body in the blood may increase.
A conflict can develop in a woman whose first pregnancy ended in a caesarean section. If during childbirth doctors separated the placenta manually, and the patient has a history of uterine bleeding, then the risk of Rp incompatibility is 50-60%. Women with a negative Rp factor should be especially attentive to their own health - mothers who have suffered the following pathologies while pregnant are at risk:
- acute respiratory viral infections;
- gestosis;
- cold.
Antibodies produced by the body do not disappear anywhere. Their number increases with each subsequent pregnancy. If the structural structure of the chorionic villi is disrupted, the mother’s immunity begins to produce antibodies at an accelerated rate.
To give birth or not
Many girls with a negative Rh factor are simply afraid to get pregnant and give birth to children. However, modern gynecologists insist that negative consequences can be avoided and a healthy child can be born. Yes, of course, there is a risk of Rh conflict, but these are isolated cases. Firstly, you shouldn’t worry when a man is negative and a woman is positive. In such couples, there are no problems with bearing a baby. If both partners have negative Rh, for example, the wife has the first negative blood type, and the husband has the third negative blood group, the pregnancy also proceeds without complications, because the child will inherit the same Rh as the parents.
However, the presence of a negative Rh factor only in a woman is not a reason to refuse the happiness of motherhood. Today, such women only need to more carefully follow all doctors’ recommendations and regularly donate blood to detect antibodies. Modern drugs make it possible to quickly cleanse the mother’s blood of harmful cells, and the child grows and develops normally.
Also in the arsenal of doctors today there are other methods to protect a child from the development of pathologies. This includes infusion of Rh negative blood into the baby and protecting the baby from biological exchange with the mother.
These measures are used in extreme cases, only when the baby is really in serious danger.
In some cases, pregnancy monitoring with a negative Rh factor must take place in a hospital. If you are scheduled for hospitalization, do not refuse under any circumstances. After all, your baby’s health depends on it.
Probability when expecting your first baby
The first pregnancy is considered relatively safe in terms of Rh conflict . The fact is that usually the placenta reliably protects the fetus from the effects of antibodies, and they themselves either do not have time to be formed, or, if they are produced, then in very small quantities. To put it simply, the mother’s body does not seem to notice the developing fetus, and therefore the production of antibodies does not occur until the child’s blood begins to mix with the woman’s blood.
During the normal course of pregnancy, this usually happens during childbirth.
The likelihood of a baby coming into contact with antibodies produced by the body of his Rh-negative mother is extremely low, although possible. In general, the occurrence of Rh conflict during the first pregnancy is not frequent and is approximately 10%.
The most mysterious group
Most of the debate among doctors is about the fourth negative blood group. Until recently, it was believed that blood group 4 with a negative Rh factor was incompatible with bearing a child. However, recent studies have proven that patients give birth to healthy babies. At the same time, an amazing fact was discovered: people with group IV can be transfused with any blood, the main thing is that the Rhesus matches.
The fourth blood group is the youngest. This means that it carries information about modern living conditions. It has been proven that people with this blood type are more resilient and can perfectly adapt to different living conditions. These facts indicate that women can successfully bear and give birth to children. All rumors about the danger of childbirth with 4 negative group are common myths and misconceptions.
Sources
- https://organserdce.com/diagnostika/analysis/3-otritsatelnaya-gruppa-krovi-harakteristika.html
- https://LechiSerdce.ru/analiz-krovi/10683-tretya-gruppa-krovi-otritsatelnyim.html
- https://kodkrovi.ru/gruppi-krovi/xarakter-nositelej-3-otricatelnoj-gruppy-krovi/
- https://krov.expert/gruppa-krovi/3.html
- https://krov.expert/gruppa-krovi/otritsatelnyj-rezus-faktor-u-zhenshhiny-pri-beremennosti.html