The action and effectiveness of Formetin in diabetes
Formetine is a hypoglycemic drug, that is, a medicine whose action is aimed at lowering the patient’s blood sugar level. The active substance of the drug, after entering the human body, slows down the process of formation in the liver of organic compounds that serve as sources of energy. These include:
- free amino acids;
- glycerol;
- glucose, which is quickly processed without having time to accumulate.
Almost immediately after taking the drug, the active component is absorbed in the diabetic’s stomach. After two and a half hours, the concentration of the active substance in the patient’s blood reaches its peak. Then Formetin is safely excreted along with urine.
Formetine is an effective drug prescribed for type 2 diabetes.
As a result of taking the medicine, the body's sensitivity to insulin increases, and the patient's condition and weight are normalized.
Note! The indication for taking the medication is overweight and obesity in type 2 diabetes. Formetine is not used as an effective means for weight loss. In advanced cases, a combination of medication and insulin therapy is required.
Signs of diabetes - video
Interaction with other drugs
The simultaneous use of iodine-containing radiocontrast agents is contraindicated. In this case, the risk of developing renal failure, excessive accumulation of the drug, and lactic acidosis increases.
Taking the medication in parallel with sulfonylurea derivatives, NSAIDs, Acarbose, and Insulin may enhance the hypoglycemic effect.
A decrease in hypoglycemic effect occurs when used together with:
- glucocorticosteroids;
- thyroid hormones;
- loop diuretics;
- phenothiazine derivatives;
- sympathomimetics.
In rare cases, simultaneous use with Indomethacin (suppositories) can cause metabolic acidosis.
Alcohol compatibility
Compatibility with alcoholic beverages or alcohol-containing medications is negative. Acute alcohol poisoning, especially in the setting of a low-calorie diet or liver damage, is associated with an increased likelihood of developing lactic acidosis.
Traditional forms of release and composition of the drug
The drug is available in the form:
- Round white tablets of a flattened shape, marked with a chamfer and a score. The dosage of the active ingredient, metformin, is 500 mg. The medicine is sold in quantities of 30, 60, 100 tablets in cardboard packaging with blisters of 10 pcs. Among the excipients:
- magnesium stearate;
- povidone;
- sodium croscarmellose.
Formetine comes in the form of round white tablets.
- In the form of round, biconvex white tablets. The concentration of metformin is 850 mg. The package contains 30, 60 or 100 pcs. The auxiliary components are the same.
In the first case, the cost of the medicine in Russia varies from 50 to 100 rubles, in the second - from 100 to 300 rubles.
How to take Metformin hydrochloride?
Before or after food?
Time to take the drug: with or after food.
For diabetes
The dose for adults for the first time is from 500 to 850 mg twice or three times a day. After 2 weeks, the dosage is revised in accordance with blood glucose measurements. Gradually increasing the daily dose allows you to avoid unwanted side effects associated with the digestive system. The daily dosage should not exceed 3000 mg in 3 divided doses.
The daily dosage for children over 10 years of age and adolescents is 500-850 mg per dose. After 2 weeks, the daily dose of the drug is revised in accordance with the level of glucose in the blood. The daily dose in pediatrics, divided into 2-3 doses, should not exceed 2000 mg in total.
Before prescribing the drug to elderly patients, as well as during treatment, regular testing of renal function is recommended. In persons with moderate stage renal failure (creatinine clearance 45-59 ml/min or GFR 45-59 ml/min), the use of the drug is allowed (daily dosage 500-850 once) in the absence of an increased risk of developing lactic acidosis. The daily dose does not exceed 1000 mg and is divided into 2 doses. Renal function testing is mandatory at least every 6 months.
For weight loss
The initial dose as a weight loss drug is 500 mg once a day with a gradual increase in dose by 500 mg weekly. The recommended daily dose should not exceed 2000 mg. The course of treatment is 3 weeks with breaks of about 1-2 months. In the presence of pronounced side effects, the daily dose is halved.
The other side of the coin, or side effects
Formetine therapy may cause the following side effects:
- skin rashes;
- “metallic” taste in the mouth;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- pain in the abdominal cavity;
- flatulence.
Such symptoms are more often encountered at the very beginning of the course; you can alleviate your well-being with the help of antispasmodics and antacids - drugs for acid-related gastrointestinal ailments.
Long-term treatment with Formetin can provoke the development of:
- hypovitaminosis B12,
- lactic acidosis - accumulation of lactic acid in tissues and blood;
- hypoglycemia - low blood glucose;
- anemia.
Contraindications to taking the drug are:
- kidney and liver dysfunction;
- diabetic ketoacidosis - a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism;
- state of diabetic coma (precoma);
- infectious diseases (chronic, acute) that can lead to kidney dysfunction or tissue hypoxia (heart failure, shock, myocardial infarction, kidney infection);
- insulin therapy necessary to restore the body after injury or surgery;
- chronic alcoholism or state of alcohol poisoning;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the product;
- periods of pregnancy and lactation;
- children under 10 years of age;
- hypocaloric diet;
- acidosis is an acid-base imbalance in the body.
Important! Experts do not recommend using the product two days before and after x-ray and radioisotope procedures, which involve the use of iodine-containing reagents.
People over 60 years of age and patients engaged in heavy physical labor should use Formetin with caution, because taking the medication can provoke lactic acidosis - an increased level of lactic acid in the blood.
The dosage of Formetin is prescribed exclusively by a specialist.
An overdose of the drug is fraught with the development of lactic acidosis. Without timely medical care, the disease can lead to death. Early signs of a dangerous condition include:
- general malaise;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- pain in the abdomen and muscles;
- low body temperature;
- dizziness.
Contraindications
- allergy to the active substance or any auxiliary component;
- conditions that increase the risk of lactic acidosis, including impaired renal function with creatinine more than 150 µmol/l, chronic liver and lung diseases;
- renal failure with creatinine clearance <45 ml/min. or GFR <45 ml/min/1.73 m²;
- liver failure;
- diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetic coma;
- acute congestive heart failure (but harmless in chronic heart failure);
- acute phase of myocardial infarction;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- acute alcohol poisoning.
- period before surgical operations (2 days), X-ray contrast studies.
Carefully
- children from 10 to 12 years old;
- elderly people (after 65 years);
- persons who are engaged in heavy physical labor, which increases the risk of lactic acidosis.
Instructions for use
The dosage of Formetine is determined by the doctor and depends on the patient’s health condition and the severity of the disease.
The instructions for use of the medicine suggest average initial doses of the drug. The adjustment can be made only after 15 days after the start of the course and passing a control blood test for glucose levels. After completion of therapy, the doctor prescribes a maintenance dose of the drug.
For diabetics with metabolic disorders, reduced dosages of Formetine are recommended.
The tablets should be taken after meals. In order to prevent the development of side effects, the prescribed dosage can be divided in half and the medication can be used twice a day.
When taking Formetin, you need to regularly monitor your blood sugar levels.
Overdose of Metformin hydrochloride
Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, tachycardia, drowsiness, and rarely hypo- or hyperglycemia. The most dangerous complication requiring immediate hospitalization is lactic acidosis, characterized by symptoms of intoxication and impaired consciousness. The administration of sodium bicarbonate is indicated; if it is ineffective, hemodialysis is required. Fatalities have been recorded after an intentional overdose of more than 63 g.
Alternative to Formetin
The table below shows the most common analogues of Formetin, which for one reason or another can replace the drug.
The doctor gives preference to a specific medicine based on the specifics of the clinical case. For example, Glucophage can be used not only for monotherapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus, but also in combination with other medications. Taking Siofor is contraindicated in type 1 diabetes. In this case, the drug should be replaced with one of its analogues. When treating a teenager, it is better to give preference to drugs such as Gliformin, Clucophage or Bagomet. Metformin will be the most gentle on your wallet.
How to replace the drug - table
| Bagomet | Glucophage | Gliformin | Siofor 1000 | Metformin | |
| Active ingredient | metformin | metformin | metformin | metformin | metformin |
| Release form | capsule-shaped round tablets | round or oval film-coated tablets | round white tablets | oblong white tablets | white round tablets in film |
| Contraindications |
|
|
|
|
|
| Age restrictions | up to 10 years | up to 10 years | up to 10 years | up to 18 years old | up to 15 years |
| Price (depending on dosage) | 220–520 rubles | 170–350 rubles | 120–350 rubles | 240–450 rubles | 100–250 rubles |
Analogs
The pharmaceutical industry produces medications similar in composition and effects to Formetine. Analogues of the drug are:
- Bagomet. The medicine is a long-acting tablet, the active substance of which is metformin. Bagomet has a hypoglycemic effect, its use helps stabilize or reduce body weight. Used in complex therapy of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
- Glucophage. The active substance is metformin hydrochloride. Glucophage is available in the form of tablets for oral administration. The drug helps lower blood glucose levels without causing hypoglycemia. During use, patients experience moderate weight loss. Glucophage is prescribed for type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Gliformin. The medicine has a hypoglycemic effect. Available by prescription in tablet form. Prescribed for diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2. Its use helps patients with these diseases maintain or lose weight.
- Metformin. The tablets are classified as biguanides; they help inhibit the process of gluconeogenesis in the liver, reduce the absorption of glucose, and enhance its utilization. Prescribed, according to the instructions, to normalize the weight of patients suffering from type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Siofor. A hypoglycemic drug produced in tablet form. The medication has an antidiabetic effect, inhibits glucose absorption, and increases the sensitivity of peripheral tissues to insulin. The use of Siofor has a positive effect on lipid metabolism and the coagulation system. According to the instructions, it is prescribed for type 2 diabetes mellitus, if the patient is obese.
- Metformin hydrochloride. Water-soluble powder with crystalline structure. The substance reduces the production of glucose by the liver, slows down its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, stimulates glycogen synthesis, affects lipid metabolism, reducing the concentration of cholesterol, lipoproteins, and triglycerides. The use of the product helps to reduce or stabilize weight. According to the instructions, it is used for type 2 diabetes in obese patients.
- Sophamet. The drug belongs to hypoglycemic drugs intended for oral use. According to the instructions, Sophamet is able to suppress gluconeogenesis, fat oxidation, and the formation of free fatty acids. During therapy, a moderate decrease or stabilization of the patient's weight occurs. Prescribed in the absence of effectiveness from diets and physical activity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Novoformin. A drug available in tablet form. Novoformin has a hypoglycemic effect and reduces glucose levels in the body. The use of the drug helps stabilize or moderately reduce weight in type 2 diabetes in obese patients.
pharmachologic effect
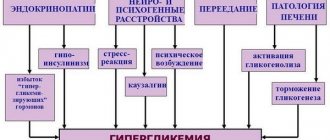
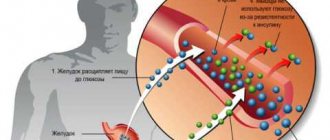
The active substance metformin, found in Formetin tablets, has a slowing effect on the process of gluconeogenesis that occurs in the liver. In addition, this is also accompanied by a decrease in the amount of glycogen. The active component makes it difficult to absorb glucose from the intestines and increases the removal of sugar from the circulatory system. In turn, the tissue's back reaction to insulin increases, which is characterized by inaction on its production by the endocrine part of the pancreas by B cells, bypassing the hypoglycemic reaction.
Formetin tablets significantly reduce the amount of “bad” cholesterol and triglycerides. At the same time, the number of high-density lipoproteins increases by 20-30%. Thus, this medication can provide real help to people suffering from excess weight when diets cease to be effective. This effect is due to a strong decrease in appetite and oxygen-free oxidation of glucose. In addition, in this case there is a decrease in the process of activation of tissue plasminogen due to the effect on its inhibitor.
The pharmacokinetics of the drug "Formetin" begins with the absorption of metformin in the gastrointestinal tract. Its maximum concentration in the blood is observed 2.5 hours after administration. Moreover, the degree of absorption of the usual dose reaches an average of 50-60%. This high level of absorption is due to the fact that this indicator is directly influenced by the connection of the active component with proteins in the plasma. But with metformin, this interaction is completely absent.
Deposition of the active substance occurs in muscle tissue, liver, kidneys and salivary glands. And drainage is carried out through the kidneys. The period of reducing the concentration of the active component by 2 times is from 1.5 hours to 4.5 hours.