How to treat grade 2 deforming osteoarthritis of the knee?
Arthrosis of the knee, starting from stage II, is called deforming or osteoarthritis, and all because at this time pathological changes in the human joint take on visible shapes and sizes. If you take an x-ray, bone growths and narrowing of the joint cavity will be clearly visible. Typically, it is at this stage of deforming osteoarthritis that people pay attention to their deteriorating condition and visit a doctor for professional diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Degenerative-dystrophic processes in the cartilaginous and bone tissues of the joint, which little manifest themselves at an early stage, gradually intensify, transferring the disease to a new (II) level. This progression is facilitated by:
1. complete inaction during the development of arthrosis or untimely, incorrect treatment;
2. severe or regular knee injury;
3. the patient is overweight, due to which the load on the joint increases many times;
4. negative impact of professional activity (long-term sitting/standing);
5. menopause in women;
6. the presence of concomitant articular diseases or those associated with a disorder of the endocrine system, metabolic and circulatory disorders in the extremities.
Causes
Degenerative osteoarthritis of the right or left knee occurs due to disruption of the normal nutrition of cartilaginous structures and their subsequent degeneration. After the cartilage completely disappears, the functioning of the joint is disrupted, its mobility is lost, and growths called osteophytes form on the surfaces of the exposed articular bones.
The following negative factors can provoke knee damage:
- excessive physical stress on the lower extremities, for example, participation in strenuous sports or obesity;
- congenital pathologies of the structure of the musculoskeletal system;
- injuries, bruises, dislocations;
- age-related changes in the body that provoke deformation of joint tissues;
- metabolic disease;
- hormonal, endocrine disruptions;
- hypothermia;
- intoxication;
- avitaminosis;
- surgical operations on the knees, after which osteoarthritis of the knee occurs as a complication.
In order for the treatment of osteoarthritis to be effective, it is important to create an accurate picture of the pathogenesis and find out what factor was the impetus for the progression of the pathology.
Features of the disease
Osteoarthritis of the 2nd degree of the knee joint is the “golden mean” of pathology, in which effective treatment is still possible, but it is already more complex and lengthy than in the initial stage, and at the same time there is a high probability of it flowing into the most dangerous and severe phase III, often becoming the cause of permanent disability of a person. With the development of deforming osteoarthritis, the patient's cartilage tissue becomes thinner and loses its elasticity, and scattered foci of destruction appear in the area of the meniscus. Without stopping the disease at this stage, the condition worsens until the cartilage completely disappears and osteophytes form instead.
Osteoarthritis of the knee of the 2nd degree manifests itself clearly with a wide range of symptoms:
- pain is constantly present in and around the joint, noticeably intensifying after an overnight rest;
- touching the affected area is quite painful for the patient;
- while walking, a specific crunch or click is often heard;
- as a result of inflammation, the leg swells;
- movements are constrained, gait becomes unstable and slow.
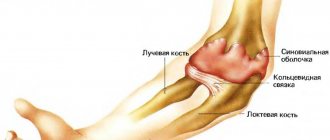
On an x-ray, you can notice not only deformation and thickening of the bone, but also osteophytic growths, a change in the joint space towards narrowing, as well as tissues adjacent to it.
Symptoms
There are three stages of the disease. Initially, DOA practically does not manifest itself; the patient experiences a slight crunch in the joints and mild pain after prolonged exercise. The bones are almost not deformed, maintaining their original shape.
Over time, the disease progresses, and the patient is diagnosed with grade 2 gonarthrosis.
Joint pain
It can be observed even at rest. The longest attacks occur after long walks or physical activity.
The most characteristic sign of the disease is pain in the knee joint
In order to get rid of the pain, a long rest is required, but as soon as you resume movements, the pain returns. The reason for this is the abrasion of the top layer of cartilage and exposure of the nerve endings. If a person rests for several hours, the joint membranes are restored.
Joint stiffness after sleep
This symptom occurs after waking up in the morning. In most cases, stiffness disappears within half an hour. If it lasts longer, this may indicate the development of an inflammatory process.
The cause of stiffness is a disruption in the production of glucosamine and chondroitin, components of natural intra-articular lubrication.
Clicking and cracking of joints
This symptom is observed already in the first degree of DOA, but with the development of the disease it worsens.
The crunching occurs not only when bending the limbs, but also when walking. The reason for this is damage to the articular surfaces, the formation of grooves and osteophytes.
Decreased range of motion
Trying to make the pain less intense, the patient strives to bend and straighten the limb as little as possible. After some time, the ligamentous apparatus adapts to the range of movements and the ligaments are shortened.
As a result, the range of movements is reduced, the person cannot fully straighten or bend the leg, and in some cases he begins to limp. It is possible to develop the joint, but for this you need to perform special exercises for a long time.
Increase in joint volume
The most common cause of this is synovitis, an inflammatory process occurring in the synovium. It may be accompanied by an accumulation of fluid in the joint cavity.
Also, swelling of the soft tissues, which occurs in the chronic form of the disease, can lead to enlargement of the joint. The cause of the pathology can also be the formation of osteophytes (spikes) along the edges of the articular surfaces.
What to do?
Treatment of grade II osteoarthritis is based primarily on taking the following medications:
- pain reliever;
- anti-inflammatory;
- restorative.
Among the analgesics, patients are recommended to take Paracetamol. It quickly relieves attacks of pain in joints and muscles, has virtually no side effects, and is suitable for long-term use. If the pain is so severe that it cannot be relieved with conventional painkillers, centrally acting analgesics are added to the treatment. The main drug of this group, used for deforming osteoarthritis, is Tramadol (Tramolin, Tramal). It is released strictly according to a doctor's prescription, as a psychotropic drug.
To eliminate inflammation, NSAIDs (Nimesulide, Diclofenac, Celecoxib, Meloxicam) are usually prescribed. During the acute period of the disease, glucocorticosteroids (Triamcinolone, Diprospan, Hydrocortisone) can be used. Their active substances are instantly hydrolyzed and almost immediately absorbed from the injection site, thereby causing a rapid onset of the therapeutic effect.
To restore the cartilage fibers of the joint, drug treatment of grade 2 arthrosis involves the use of chondroprotectors (Mukosat, Structum, Teraflex, Sustilak). Although these remedies are slow-acting (therapy is carried out for at least 6-12 months), with the help of them a person can completely avoid disability. Such drugs usually contain the structural elements of cartilage - glucosamine and chondroitin, which in the treatment of deformed knee joints help to stop the degeneration processes. Chondroprotectors are administered both intramuscularly and intraarticularly.
Conservative treatment of second-degree osteoarthritis of the knee joint can also be done using physiotherapy:
- SUV irradiation in erythemal doses - to reduce pain;
- infrared laser or low-intensity UHF therapy - as a treatment for inflammation in the knee;
- high-frequency magnetic therapy - to accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues;
- ultrasonic influence - to normalize metabolic processes.
To improve blood supply to the limb, doctors can prescribe a course of interference therapy, amplipulse therapy, peloid therapy, local darsonvalization, radon or hydrogen sulfide baths for osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
In the treatment of incompletely advanced knee pathology, a special role is given to gymnastics. Due to it, the elasticity of the joints increases, their natural mobility returns and is preserved. In addition, therapeutic exercises help strengthen muscles and overall immunity.
Sets of exercises that a person suffering from knee osteoarthritis should regularly perform are developed by specialists in a strictly individual form. To avoid stress on the affected joint, they often involve only a sitting/lying position. If pain occurs during physical therapy, further exercise should be abandoned. By the way, gymnastics should generally be prescribed during the period of remission of the disease, that is, when pain and other symptoms have subsided.
As for surgical intervention, for grade 1 and 2 osteoarthritis of the knee joint it is practically not used (only in case of ineffectiveness of medicinal and physiotherapeutic treatment in combination with gymnastics). However, in advanced situations, when the likelihood of disability due to neoarthrosis (formation of a false joint) or ankylosis (complete fusion of the ends of the bones) is as high as possible, surgery is the only way out. At the same time, treatment of deforming osteoarthritis surgically can be carried out in different ways: minimally invasive (arthroscopy) or large-scale with the implantation of an artificial prosthesis.
It is, of course, impossible to cure grade II knee arthrosis using folk remedies. However, alternative medicine methods make it possible to soften the symptoms, slow down the destructive effects of the disease and prevent exacerbation. The following folk recipes cope especially well with these tasks:
1. Rubbing celandine oil into the knee.
Celandine, famous for its powerful anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, is ideal for combating osteoarthritis of the knee joint, both 1st and 2nd degree. To prepare a homemade medicine from it, you will need to take 3 large spoons of its crushed leaves and stems, mix them with vegetable oil and let it brew for half a month.
Read also: Doa of the ankle joint
2. Clay compress.
To treat deforming osteoarthritis, it is better to make a compress from blue clay by heating it moderately and applying it to the affected knee, followed by fixing it with woolen cloth.
3. Rubbing with elecampane root.
This folk remedy treats grade II osteoarthritis of the knee joint by quickly relieving swelling and pain. Preparing the rub is not difficult: just pour 50 g of the dry root of the plant with 150 ml of high-quality vodka and leave it to steep for 2 weeks.
4. Yolk ointment.
Since the degree of joint disease and its treatment are interrelated, this recipe is recommended for use in the 2nd stage of the disease. To prepare the ointment, you will need 4 commonly available ingredients: chicken yolk (one), vinegar (2 tablespoons), any vegetable oil (1 tablespoon), purified turpentine, sold in every pharmacy (1 teaspoon). Having mixed the components until a homogeneous consistency, the medicine for deforming osteoarthritis is considered ready. It should be applied to the knee and covered with a bandage at night.
To avoid grade 2 osteoarthritis of the knee joint, and especially grade 3, the pathology should be treated at its initial stage, that is, when the first signs appear. But it’s even better if you can completely avoid the development of degenerative-dystrophic knee disease. For this purpose it is recommended:
1. regularly engage in general health exercises;
2. monitor body weight;
3. eat right;
4. adequately calculate and distribute physical activity;
5. postmenopausal women should undergo hormone replacement therapy;
6. visit specialists in a timely manner in case of inflammation or injury to the knee;
7. systematically use folk remedies to relieve tired legs and improve blood supply to them (for example, herbal baths, rubbing).
Let preventive measures seem banal to some, but it is better to adhere to them than to follow multiple doctor’s orders for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint for a long time.
What drugs are used to treat the disease?
For osteoarthritis of the knee joint, treatment begins with the development of comprehensive measures. An experienced doctor tactically builds each step, using several tools at once to combat the disease. In this regard, the stage of the disease, the well-being of the patient himself, and the individual characteristics of his body are taken into account.
Physiological effects
When deciding how to treat osteoarthritis of the knee joint, the doctor is guided by the degree of the disease. If the disease is diagnosed at the very beginning, an effective method of treatment is the use of physiotherapy and work to eliminate some of the causes that led to the disease. The specialist may ask the patient to reduce weight and avoid heavy loads on the knee. Local physiotherapy in the form of magnetic therapy, acupuncture, ultrasound can stop the progress of negative processes, remove inflammation and reduce pain.
Having determined osteoarthritis of the knee joint, the doctor can send the patient for sanatorium treatment. Mud baths, a calm environment, and clean air have a positive effect on a person’s psychological state. Such activities are very important for the successful fight against the disease. A beneficial environment combined with effective treatment procedures returns the patient to a fighting spirit and allows him to return to his usual way of life.
Physiotherapy can be supplemented with special massage and exercise therapy. With massage, blood circulation in the affected area is improved, tissues receive enough nutrition, and healthy cells are regenerated. All massage techniques are carried out in a slow, gentle rhythm, without amplification or deep pressure. Try to find an experienced massage therapist who is familiar with the method of performing procedures for knee osteoarthritis.
Physical therapy exercises are aimed at relieving muscle atrophy. With the help of special actions with the knee and leg, the blood accelerates, metabolism improves, and joint mobility improves. You can clearly see the exercise therapy complex for osteoarthritis of the knee joint in the video:
In order for exercise therapy to bring maximum benefit, it is necessary to exercise at least 2 times a day. After exercise, you should lie down quietly for 40 minutes. It should be noted that gymnastics for osteoarthritis of the knee joint is undesirable during the period of exacerbation of the disease. In addition, it must be performed under the close supervision of a specialist. The slightest inaccuracy in performing movements can lead to complications in the situation.
READ
Correction with orthopedic means
For patients with osteoarthritis, special shoes are produced that reduce the load on the knee and facilitate movement. In the store you can buy:
- Shoes that compensate for the difference in length when it is shortened in one of the limbs.
- Knee pads that allow you to properly fix the joint to reduce pain.
- Orthoses that stop the destruction of cartilage and joints. They are produced in various versions and are indicated for use in the postoperative period.
Tablets, ointments, injections
The use of non-steroidal drugs (Diclofenac, Meloxicam, Aspirin, Nimesulide) is included in the treatment regimen. However, these drugs for osteoarthritis of the knee do not treat the disease itself, they help relieve its symptoms. They are produced in different dosage forms: ointments, gels, creams, tablets, suppositories.
To restore cartilage tissue, chondroprotectors (Glucosamine, Chondroitin) are prescribed. The substances they contain stimulate cell regeneration, stabilize the formation of intercartilage lubrication, and maintain its normal properties.
Novocaine blockades in the form of injections are prescribed if a person experiences excruciating pain.
They are not resorted to if the changes have become serious and the patient is indicated for surgical intervention.
The use of products based on hyaluronic acid allows you to strengthen cartilage tissue, increase its endurance, and protect it from overload. 4-5 injections are enough to form reliable protection inside the knee and replenish the lubricating fluid, which prevents painful friction.
Folk remedies
In the folk treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint, the main remedies are decoctions, ointments and compresses prepared at home. They cannot be compared with medications, but they can relieve pain and swelling. For example, ginger tea reduces the level of prostaglandins, which helps reduce the severity of symptoms of the disease.
You can apply plantain leaves to your sore knee. Collect two or three leaves, wash, dry, and apply to the sore spot. Secure the leaves and leave overnight.
If you can collect fresh wormwood, you can make an ointment from it. You will need several leaves of the plant, which must be crushed and mixed with vegetable oil. The resulting mixture is placed in a water bath, simmered for an hour, then allowed to brew for 2 days. Strain and rub into affected areas.
With the help of black cumin oil, puffiness is effectively removed and the intensity of inflammatory processes is reduced. If you rub the oil in at night, you will get up in the morning without feeling stiffness in your limbs.
How to treat grade 2 osteoarthritis of the knee joint
Here you will learn:
The pronounced symptoms of this stage of the pathology most often force patients to seek medical help. In the treatment of grade 2 osteoarthritis of the knee joint, various methods are used. But which ones are more effective? How do the symptoms appear? What are the features of the development of the disease? And is it possible to somehow prevent the transition of knee arthrosis to the second stage?
Diagnosis, basic treatment
To identify the disease, a whole range of studies is used, which can be divided into two large groups: laboratory and differential. The first are necessary to clarify the cause of the development of osteoarthritis and determine the effectiveness of treatment.
Differential diagnosis is carried out by an orthopedist directly to make a diagnosis and establish the degree of severity.
Laboratory
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a chronic disease in which remissions alternate with exacerbations. During the latter period, symptoms of inflammatory-intoxication syndrome appear. It can be detected by doing the following laboratory tests:
- General blood analysis. It is carried out to assess the severity of inflammation.
- General urine analysis. It is performed to exclude damage to the urinary tract and kidneys, which can provoke an inflammatory process.
- Blood chemistry. A number of markers for osteoarthritis of the knee joint will be elevated.
Differential
To diagnose joint osteoarthritis, doctors perform the following tests:
Osteoarthritis of the knees requires a competent and professional approach. If you have any prolonged knee pain or other symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
There are also a number of assessment tests that will help the doctor accurately determine the stage of the disease. For example, a special diagnostic test, the Lequesne index, is widely used to assess the functional state of joints.
The main goals of treatment are pain relief, restoration of cartilage, other affected joint structures and motor function of the knee. Success can only be achieved with timely initiation of therapy.
If you start treating osteoarthritis at grade 1 or 2, it is possible not only to stop the development of the pathology, but even to partially restore the destroyed cartilage.
So, where to start, how to treat the disease correctly?
Features of grade 2 osteoarthritis of the knee joint
If a person does not pay attention to the first signs of the development of pathology - minor pain in the knees after exercise - osteoarthritis of the knee joint continues to develop and enters the second stage.
At this stage, all the negative processes occurring in the cartilage tissue begin to affect the joint. Insufficient synthesis of synovial fluid, which lubricates the joints, its thickening leads to the fact that the joint loses the ability to move properly. This occurs against the background of poor circulation and thinning of cartilage , which bone tissue tries to “grow” due to osteophytes.
Diagnosis of pathology
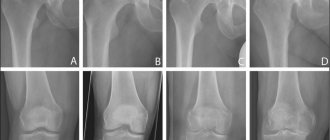
The diagnosis is made by a specialist based on examination, patient complaints and the results of an x-ray examination. Radiography is a technique that allows you to clarify the diagnosis, the severity of the pathology and monitor the process of changes. It is considered the most important method in making a diagnosis. This method eliminates the possibility of developing other diseases in this area.
Osteoarthritis of the knee at the initial stage is not visible on an x-ray. Then the narrowing of the joint space is determined. In modern medicine, the following methods for diagnosing gonarthrosis of the lower extremities are also used: computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging.
Symptoms of stage 2 osteoarthritis
Due to serious disturbances in the structure of cartilage and bone tissue, all initial symptoms intensify.
Painful sensations
If at the beginning of the disease pain occurs rarely, usually after significant stress (long periods of standing, kneeling work, etc.), now pain appears more and more often. They can occur in the morning, even before the process of flexion and extension of the knee, or at night, when the knee is motionless .
Rest alone is no longer enough for the pain to go away. You have to resort to taking painkillers.
Visual symptoms
In the first months, and sometimes years, gonarthrosis does not show itself outwardly, unlike grade 2 osteoarthritis, in which the knee is noticeably deformed, swells , redness appears, and the temperature of the skin rises.
Limited mobility
The gradual destruction of the joint leads to the fact that it becomes increasingly difficult for a person to bend and straighten the knee , and any movement is accompanied by pain. Over time, a person will no longer be able to move without a cane, crutch or wheelchair, as the joint will completely collapse.
Drug treatment of osteoarthritis
You can start with the restoration of synovial fluid, as the simplest tissues are the composition of the structure of the knee joint.
When damaged, the integrity of the synovial bursa is restored, the tissues heal, and the body’s immune forces normalize the composition of the synovial fluid. These processes are helped by drug treatment.
Treatment is considered by doctors in accordance with the symptoms, stage of the disease, and the strength of its manifestations.
Therapy involves removing symptoms while simultaneously restoring synovial tissue, cartilage, and returning functions to the joint.
Treatment is always carried out in a complex, including medications, physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy, wearing orthopedic products, following a diet, and folk remedies.
Only in difficult cases do doctors choose surgery, and after that, all of the above methods of treatment and rehabilitation.
Diagnostics
Medications
- non-steroidal painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs - Nimesil, Movalis. Taking them is important to reduce active inflammation and relieve pain. Such medications significantly improve the quality of life, but only remove symptoms and do not treat osteoarthritis, unlike synovitis, which is treatable at this stage and the knee can become healthy again;
- chondroprotectors – Artra, Teraflex nourish cartilage with hyaline and restore structures. These drugs are effective if the cartilage layer is not destroyed; having switched to treatment with chondroprotectors, you need to prepare yourself for long-term treatment;
- painkillers - Nise, Alflutop relieve the patient of pain; But at the last stage of the disease, painkillers and injections are not enough; the doctor prescribes intra-articular injections. They are especially effective in the treatment of grade 2 osteoarthritis;
- muscle relaxants and antispasmodics - Mydocalm, Sirdalud, improve blood circulation and tissue nutrition in the joint.
Mydocalm
Treatment methods for grade 2 osteoarthritis of the knee joint
It should be understood that when treating grade 2 deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint, you will have to use different approaches to influence the affected joint from different sides. Such an integrated approach becomes the key to successfully inhibiting negative processes and preserving the remains of a healthy joint. If you follow your doctor's recommendations and regular preventative measures, you can extend the life of your knee joint for a long time. What treatment methods are used?
Medicines
Since the pain at this stage of development of the pathology is already quite strong, the first priority will be to eliminate it. For this purpose , conventional analgesics are used, as well as non-steroidal drugs .
With the help of another group of drugs, it will be possible to stop degenerative disorders and stabilize the functioning of cells and tissues, as well as speed up the processes of synthesis of necessary substances. Chondroprotectors are capable of creating such “miracles” - special preparations that contain artificial substances (hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, glucosamine) necessary for the normal functioning of cartilage and joints.
Typically, chondroprotectors are injected into the joint or muscle tissue . They do not begin to act as quickly as painkillers and require long-term use, but have a long-lasting effect, helping joints function normally.
Therapeutic gymnastics, physiotherapy, massage
Both physiotherapy and massage can improve blood supply to tissues, but the procedures should only be carried out in specialized institutions.
Separately, it is necessary to say about therapeutic exercises, which are of great importance not only at the stage of treatment, but also after its successful completion . A complex is prescribed taking into account the patient’s condition, and each exercise is aimed at stabilizing the condition of the knee joints. Correct movements accelerate the beneficial processes that occur while taking medications. In addition, they mobilize the vital forces of the body, forcing it to find internal potential to fight the disease.
Read also: Osteoporosis of the ankle joint
Therapeutic exercise is also considered one of the most effective preventive means , because regular exercise sufficiently loads the joint, preventing it from “stagnating.”
ethnoscience
Home remedies can also be used in consultation with your doctor as additional measures to support a problematic joint . With osteoarthritis of the 2nd degree of the knee joint, they, of course, will not have the same effect as in the early stages, and yet if the recipes turn out to be effective (the pain stops, swelling and redness subsides), then using ointments, compresses and tinctures from natural ingredients is not prohibited.
How to prevent grade 2 knee osteoarthritis
It is possible to prevent the disease from progressing to the second stage, but only if you seek medical help in a timely manner . Often, patients self-medicate, make diagnoses with the help of “smart” neighbors or colleagues, and thus waste precious time or simply do not pay attention to the first bells, waiting until the body begins to “ring the alarm.”
At an early stage, it is possible to quickly stop degenerative processes in cartilage and joints, and to use more gentle methods that do not have side effects - traditional medicine, synthesized food additives and vitamins, a complex of therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy , etc.
Causes of the disease
The main reason for the occurrence of pathology is ignoring the first signs of dysfunction. Due to too late contact with a rheumatologist, a person does not have time to be cured before major damage occurs.
The causes of the disease can also be:
- injuries received;
- excess body weight;
- too heavy physical activity;
- arthritis;
- eating junk food;
- passive lifestyle.
With gonarthrosis of the 2nd degree, disability can be assigned if both lower limbs are affected - bilateral gonarthrosis.
Disease prevention
Those who never want to learn how to treat grade 2 osteoarthritis of the knee joint, as well as patients who have gone through the difficult path of restoring knee mobility and getting rid of excruciating pain, are advised to follow simple prevention.
Movement is life!
Since one of the main reasons for the development of knee osteoarthritis, like all chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system, is a sedentary lifestyle, the main preventive measure will be a change in lifestyle. Follow these simple guidelines:
- try to move more;
- once again refuse to travel by car;
- Take regular walks with your family, friends or your favorite dog (if you don’t have one, be sure to get one - it will make you leave the house);
- Be in the fresh air, go out of town, to picnics or to the country house.
When performing monotonous work in one position, be sure to warm up , paying special attention to your knees. Perform special exercises for your knees every half hour for 5-10 minutes. Sit correctly, placing your entire feet on the floor or a special stand, do not cross your legs.
Lack of minerals and vitamins is another reason for the development of gonarthrosis. That is why it is so important to pay attention to creating a menu, including a variety of foods high in calcium (low-fat fermented milk products, cheese), vitamin D, magnesium , etc.
Fatty and spicy foods, fast food and fried semi-finished products, white bread, sweets, pastries - all this is very tasty, but, unfortunately, very harmful, and not only for osteoarthritis. You will also have to give up alcohol, including beer.
Excessive loads are no less harmful to the knees than a lack of essential substances for the body. And in this case, it is important to control your weight , preventing you from gaining extra pounds. Proper nutrition will also help with this, unless, of course, you have serious diseases that affect weight gain.
Take care of yourself!
Listen more carefully to your body. Overwork and stress are malicious provocateurs of many diseases , including osteoarthritis. If possible, put things off until tomorrow if the day has been too busy. Try not to worry about little things and look more positively at what is happening around you.
At the first manifestation of symptoms of osteoarthritis, find time to visit the clinic and get an x-ray. This will help you avoid the development of the disease, “strangle” osteoarthritis in the bud at the very beginning and keep your knees in a form that will allow you to lead a normal lifestyle (not counting some restrictions).
Treatment
When choosing treatment for knee osteoarthritis, the doctor takes into account complaints, symptoms, examination and radiography data. Depending on these factors, treatment may include:
- drug therapy -
- orthopedic correction -
- massage-
- therapeutic exercises-
- physiotherapeutic procedures -
- diet-
- surgical methods.
Drug therapy
For knee osteoarthritis, non-steroidal analgesics are used. They are prescribed in courses to reduce pain and symptoms of synovitis. In case of severe inflammation of the synovial membrane of the knee joint or severe pain, corticosteroids can be used, which have more pronounced anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects than non-hormonal analgesics. Spasms of the periarticular muscles can be relieved with the help of antispasmodics and muscle relaxants.
To improve the nutrition of cartilage, vasodilators and antioxidants are used. The main role in the conservative treatment of arthrosis belongs to chondroprotectors containing natural components of cartilage - chondroitin and glucosamine sulfate. These include rumalon, chondrolone, structum and others. These drugs are considered basic in the treatment of arthrosis of any location.
Important: for successful treatment, basic pathogenetic drugs must be taken for a long time and regularly.
Orthopedic correction
For knee osteoarthritis, the patient is recommended to use a cane to reduce the load on the joint. You can choose orthopedic shoes that will evenly distribute the load across the foot. In this case, the limbs will be in a more physiological position.
Massage
With the help of massage, pain is reduced and range of motion is increased by relieving muscle spasms. Blood supply and nutrition to the joint also improves.
Physiotherapy
To reduce the load on the diseased joint, in case of gonarthrosis, exercises are prescribed to strengthen the muscles of the lower extremities. As a result, it takes on part of the load. At the same time, you should not perform exercises that load the joint. In this case, swimming and water gymnastics are ideal.
Description of some exercises:
- To improve mobility in the knees, you need to take a sheet, fold it into a strip 20 cm wide. Then lie on your back, hold the ends of the sheet with your hands, and rest your right foot in the center. The leg must be raised and straightened until you feel maximum tension, hold for 20 seconds. Do the same with the other leg.
- While standing, place your hands on a table or the back of a chair for better balance, bend one leg and at the same time lunge back with the other, already straightened, leg. In this form, squat down, simultaneously lowering the other leg down until the calf muscles reach maximum stretch. Remain in this state for half a minute. Change legs.
- Lie down, rest your elbows on the floor and slightly raise your body. Bend your knees. The right leg should be raised to approximately the height of the left knee, straightened, without extending the toe. Hold it for 3 seconds and slowly lower it. Do this ten times with each leg.
- Lean your palms against the wall, rise on tiptoes as high as possible, hold the position for 3 seconds. Gradually lower your heels. Do this 10-12 times.
Any gymnastics must begin with a warm-up. Before exercise, it is useful to walk for 5-10 minutes at a free pace. The number of repetitions of each technique should be increased gradually. Exercises should not be accompanied by pain. Therefore, if pain occurs, you should think about reducing repetitions or completely eliminating any technique. At the end of classes, you also need to walk around a little and relax, take a few deep breaths and exhalations. Other exercises can be selected by a physical therapy doctor.
Physiotherapy
To improve nutrition, blood circulation, relieve spasm and pain, the following physiotherapeutic methods are used:
- ultrasound,
- electrophoresis,
- magnetic therapy,
- mud and paraffin applications,
- hydrogen sulfide or carbon dioxide baths, etc.
Diet for gonarthrosis
Often knee arthrosis develops against the background of excess weight. Therefore, it is necessary to draw up an individual weight normalization plan, which can be done by a nutritionist.
Dietary recommendations
It is necessary to consume the following products more often:
- low-fat fish and meat
- dairy products-
- fruits and vegetables-
- greenery-
- almonds, pine nuts-
- jellies and jelly.
The following foods should be limited in your diet:
- fatty meat (pork, lamb) -
- citrus and sour fruits, juices from them -
- spices-
- whole milk-
- some vegetables (red peppers, white cabbage, tomatoes).
Animal fats (beef and pork fat, butter) should mostly be replaced with vegetable oils. For example, olive, sunflower, mustard. If possible, food should be varied as much as possible.
Surgical correction of knee osteoarthritis
Surgical treatment is necessary if there is a noticeable decrease in working capacity, especially in people under 45 years of age. It can be radical (joint replacement) or corrective (removal of osteophytes or contractures). The choice of method is determined by the stage of the disease and its symptoms, the age of the patient and concomitant diseases.
Treatment of grade 2 knee osteoarthritis: the power of nature for healthy legs
Deforming osteoarthritis of the knee (DOA) is a disease in which the functioning of the articular cartilage is impaired. At the same time, the amount of lubricating fluid decreases, shoots appear on the bones, which interfere with the normal functioning of the knees. As a result, the owner of such knees experiences pain, stiffness and tension.
This disease has three stages. The first stage can be identified by a person who carefully takes care of their health, but in most cases the problem is discovered during a medical examination.
Treatment of grade 2 osteoarthritis of the knee joint should be carried out urgently, immediately after its diagnosis. Otherwise, the disease develops into the third degree and then the patient becomes disabled, suffers from incessant pain and immobility.
Traditional treatment
Osteoarthritis can also be treated using traditional medicine methods, without abandoning the medications and procedures prescribed by the doctor. Using traditional methods as an additional method will help you get rid of the disease faster and improve your well-being. You should first select individually suitable methods with your doctor.
Clay compresses applied to the damaged area for 15–20 minutes help relieve pain and swelling. For internal use, you can use a decoction of pine buds: 10 g of buds are boiled in a glass of boiling water, then cooled to room temperature and drunk throughout the day. For external use, a mixture of 1 part hop cones with 4 parts Vaseline helps: the plant is crushed, the components are mixed until a homogeneous mass is obtained, the resulting ointment is applied to the affected joint 4 times a day for 30 days.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee joint 2 degrees DOA
How to identify this disease in yourself?
The second stage of development is expressed by noticeable symptoms that a person is no longer able to ignore. This is the height of the disease, accompanied by constant symptoms that do not leave the patient even during periods of rest. X-ray photographs clearly show deformation of the articular cartilage, affected areas of the bone, general deformation, noticeable narrowing of the joint space, and foci of inflammation.
In the second stage, the patient begins to complain of the following symptoms:
constant pain in the knee, regardless of physical activity;- pain in the calf muscle at night;
- noticeable joint deformity;
- inability to fully bend or straighten the leg at the knee;
- edema;
- crunching sound when moving.
If you notice similar symptoms that characterize the second degree, seek help from a rheumatologist. Timely detection of the disease will help avoid possible problems in the future.
This determines whether you will be able to walk and whether you will have to go under the surgeon’s knife to solve the problem surgically.
Read also: Grade 1 knee joint pain
Causes of development of grade 2 osteoarthritis of the knee joint
What are the causes of this disease?
There are several main causes of this disease. The risk group mainly includes older and overweight women, but cases of “young” osteoarthritis of the knee joint often occur.
Here are the main causes of DOA.
- Age. The older a person is, the more likely he is to have this problem. There is nothing strange about this. A joint, like any organ, has its own service life. When it wears out, it needs to be restored using various methods.
- Excess weight. The legs and knees in particular bear a lot of strain. The higher the body weight, the stronger it is. As a result, the joint begins to malfunction, its deformation and inflammation begin.
- Hormonal imbalance. Health largely depends on the proper production of hormones. If this balance is not maintained, the functioning of various systems begins to deregulate, metabolism is disrupted, and immunity decreases. Women most often fall under this reason. Childbirth and menopause often lead to disruption of the hormonal system.
- Injuries and heavy physical exertion. Passion for sports does not pass without a trace. Constant stress on the knee joints, for example, when riding a bicycle or lifting a barbell, takes its toll. The knee deteriorates, leading to osteoarthritis.
- Uncomfortable shoes. Heels or their complete absence also often cause the disease. This is especially true for overweight women who love stilettos.
The cause may also be occupational characteristics, heredity, or lack of vitamins. There are cases when doctors cannot say why deforming osteoarthritis DOA developed.
Treatment of stage 2 osteoarthritis of the knee joint using traditional methods
If you are interested in traditional medicine, then you definitely need to apply your knowledge and skills in this area to treatment. Just remember that such treatment is not always enough to completely cure DOA.
The best option would be the simultaneous use of various methods of therapy:
- medications, including painkillers, anti-inflammatory medications, chondroprotectors;
- therapeutic physical training complex consisting of rehabilitation exercises;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- maintaining a proper diet;
- taking essential vitamins.
Of course, traditional medicine can also be added here. Before starting such treatment, be sure to consult your doctor; some plants can cause resonance with the medications you are taking, and this is dangerous.
Here are some easy recipes.
Compresses
- For a compress, prepare cabbage leaves and pour boiling water over them. Apply them to the sore spot, secure on top with a bandage and a warm woolen scarf or scarf. Leave for two hours, after which remove the compress and wrap again in a warm thing for several hours.
- Compress made from lilac leaves. Apply slightly crumpled lilac leaves to the joint in the same way. Instead, they also use plantain.
- Dimexide compress. Dilute dimexide with clean, slightly warmed water one to one. Soak a piece of clean gauze in the resulting solution, apply it to your knee, wrap it with polyethylene, and secure it on top with a woolen scarf. Walk for two hours.
- Herbal compress. Chamomile, St. John's wort, celandine, calendula, lemon balm, and juniper are suitable for these purposes. Brew a decoction using one tablespoon of dry plants per glass of boiling water. Soak gauze in cooled, but not cold, product and apply to the joint. Secure the top with film and a warm scarf. Leave the compress overnight.
Ointments
- Birch bud ointment. Birch buds must be crushed in a coffee grinder and poured into a small saucepan. Turn on low heat, add beaver (preferably) or pork fat to the container in a one-to-one ratio. Heat for 10 minutes in a water bath, stirring thoroughly with a wooden spatula. Pour the finished mixture into a glass container and put it in the refrigerator. Use two to three times a day for a month.
- Ointment made from propolis and wormwood.
To prepare it you will need:
- two tablespoons of crushed dried wormwood;
- five drops of propolis tincture;
- three tablespoons of vegetable oil, preferably olive.
You should heat the wormwood and oil in a water bath for ten minutes, then add propolis tincture. Mix thoroughly and put in the refrigerator. Treatment: use as an ointment or under a compress.
Prepare the following for this:
- 1 tablespoon mustard powder;
- 1 tablespoon honey;
- 2 tablespoons butter.
All ingredients must be mixed and heated in a water bath for 10 minutes. Use at night as a compress or rubbing. During the procedure you will feel warm, this is what mustard does.
It is also recommended to drink tea made from medicinal herbs to treat osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
This drink helps relieve inflammation, reduce pain, increase immunity, and calm. Use hop cones, chamomile, mint, thyme.
How does the disease develop in stages?
Medicine describes three stages of osteoarthritis of the knee joint - 1, 2 and 3. Arrangement in order means that from a mild or initial stage a more severe degree is formed:
First stage
It is very difficult to understand that a problem has arisen in the form of grade 1 osteoarthritis of the knee joint. The onset of the disease is latent and does not manifest itself in anything bright. You should be wary if:
- After physical activity on the knee, some discomfort is felt and heaviness appears in the muscles.
- Your legs get tired quickly, even if you only walk a short distance.
- When the knee is sharply extended or bent, pain occurs.
Many of us do not react to such symptoms, attributing them to isolated cases, and the disease continues its dangerous movement and intensifies the damage. Please note that stage 1 osteoarthritis of the knee joint can be easily cured if you start fighting it in time; do not dismiss the signals that your knee gives you.
Second stage
The pathology of grade 2 osteoarthritis of the knee joint is marked by well-defined symptoms. As the disease develops, it “finishes off” the affected tissues, radically reducing their functionality. Here is what the signs of osteoarthritis of the knee joint look like at this stage:
- Permanent knee pain that worsens in the morning and evening.
- The intensity of gait decreases.
- Movement of the knee joint is reduced.
- The crunching sound is clearly audible when bending and straightening the knee.
- Deformation of the periarticular tissues becomes noticeable visually.
- Swelling of the knees.
- When you press your fingers on the knee joint area, a localized pain syndrome occurs.
What happens in the limb with stage 2 osteoarthritis of the knee joint? As pieces of cartilage and tissue become deformed and die, they fall out into the knee joint, causing painful friction and abrasion of the bone. The patient needs immediate therapeutic treatment, because at this stage it is still possible to cope with the disease without serious consequences.
Third stage
When grade 3 osteoarthritis of the knee joint is diagnosed, the patient is also diagnosed with disability. The changes that have occurred by this time are so destructive that they cannot be fully restored. In stage 3 of the disease, the patient feels:
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
Have you been struggling with JOINT PAIN for many years without success?
Read the article where I told HOW I HEALED JOINTS with the help of four plants and Soviet technology from 1983
READ
- Permanent pain in the knee is excruciating.
- A loud crunching sound is heard at the slightest activity of the knee joint.
- Muscle tissue atrophies greatly and is constantly in a state of spasm.
- The deformation of the joint becomes visually pronounced, its mobility is lost by almost 100 percent.
- Fluid accumulated in the knee visually increases its size.
- Curvature of the lower extremities occurs.
Conservative treatment for the diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the knee joint in stage 3 does not lead to positive results. The patient is indicated for a special operation to implant a knee joint prosthesis, which helps restore the mobility of the limb.
Treatment methods
Treatment of osteoarthritis requires effort and time. Prescribed by a doctor who specializes in orthopedics or rheumatology. The disease is irreversible, and it is important to begin a set of therapeutic measures as early as possible aimed at stopping the pathological process and eliminating the provoking factor. Treatment is complex, but can take place in a segmented direction.
After making an accurate diagnosis and assigning a grade to osteoarthritis, treatment begins, usually including:
- Medications – relieving pain and inflammation is a task of first importance. First of all, analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed and strictly dosed, and in the absence of results - hormonal ones. Then chondroprotectors, designed to have an anti-inflammatory effect, slow down destruction, and restore damaged structure and functionality. Calcium-containing preparations, vitamin complexes, mainly group B, warming ointments, vasodilators that increase blood flow are useful for the knee joint. If indicated, antispasmodics and muscle relaxants are used, whose action is aimed at relieving muscle spasms, skeletal muscle tone, and knee pain.
- Orthopedic correction - the use of special devices that reduce the load on the knee: an orthopedic knee brace (splint, orthosis, bandage), load-distributing shoes, instep supports, and, if necessary, a cane.
- Therapeutic physical education, massage - usually with a frequency of 4-6 months/year, they conduct massage courses for the lower leg, knee, thigh, 2-3 times a day - physical therapy classes, do not allow the development of contracture, increase blood flow.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures – UHF therapy (heat treatment, source – high-frequency electromagnetic field), laser (monochromatic light). Magnetotherapy (exposure to magnetic fields), electrophoresis (exposure to an external electric field), amplipulse therapy (sinusoidal alternating current).
- Diet – it is important to lose excess weight, move more, eat healthy foods.
- Surgical intervention - surgery is prescribed for patients under 45-47 years of age, if the knee joint is destroyed, there is nothing left to restore, conservative methods do not work. Knee arthroplasty is performed - partial or total, removal of osteophytes by laser or resorption by shock wave therapy.
- Folk remedies - for a positive result, use proven recipes after obtaining a doctor’s permission, in parallel with medications.
Emergency treatment involves the use of pain-relieving injections, corticosteroids, and the injection of synovial fluid into the joint cavity of the prosthetic joint - a drug of hyaluronic acid.
Spa treatment has a beneficial effect on joints; the most popular resorts are in Israel, where there are healing waters and salts of the Dead Sea, the Czech Republic, Bulgaria with its unique climate, and the Black Sea coast. Mud therapy, heating and saturation of tissues with minerals, application of clay, diadynamic therapy, various procedures to relieve swelling and improve blood supply are indicated. It is not recommended to rest in winter.