With an inflammatory process in the synovial bursa of the elbow, the patient is diagnosed with bursitis. This is a pathology that is accompanied by a number of unpleasant symptoms (pain, poor joint mobility, etc.). The cause may be a simple household injury, or prolonged stress on the joint. The disease requires timely treatment, otherwise the risk of developing associated complications increases. Often the acute stage of bursitis becomes chronic, which requires further surgical intervention. From the article you will learn why elbow bursitis is dangerous and how to treat it.
What is olecranon bursitis?
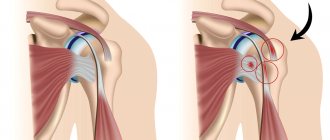
First, you need to consider the anatomy of the elbow joint. It consists of several types of bones: the humerus, radius and ulna, all of which, when connected to each other, form a joint. Each connection occurs due to the bursa (synovial bursa), inside it is filled with fluid. It is thanks to this fluid that the joints have their mobility. When there is a large accumulation of it in the joint capsule, an inflammatory process called bursitis begins.
Elbow bursitis is considered an occupational disease of students and athletes. It is in this category of patients that an increased load is placed on the elbow, and it is often susceptible to injury.
Doctors recommend not to let the disease progress and to begin treating it when the first unpleasant symptoms appear.
Classifications
The classification of bursitis depends on the nature of the fluid produced (excreted), the form of the disease and the type of pathogenic microorganisms.
The following types of liquid are characteristic:
- serous (excessive, uninfected);
- fibrinous (over time, the fluid develops into dense connective tissue);
- purulent (contains cells destroyed by bacteria).
Any of these types of fluid may contain blood cells when the walls of the bursa are damaged. Exudate mixed with blood is called hemorrhagic.
Based on the form of its occurrence, bursitis is divided into two main types:
- Acute course. It is characterized by the immediate manifestation of pathological symptoms and lasts from several hours to several days. The acute course may disappear or turn into a chronic form of the disease.
- Chronic course. It is characterized by a slow and gradual onset of symptoms. Often the patient may not feel symptoms.
Often there is a case of repeated violation of the integrity of the walls of the articular bursa. This causes symptoms similar to the acute course of the disease and is called the relapsing form. Each form of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of purulent or serous exudate, therefore laboratory and instrumental detection methods are used for diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Depending on the type of disease, the patient experiences various symptoms; let’s look at the main ones.
Serous - hemorrhagic
With acute bursitis of the serous or serous-hemorrhagic type, slight swelling and redness occurs on the elbow. When touched, there is a slight pain and a strong warmth is felt (due to the acute process of inflammation). Movement of the arm is limited, swelling is visible to the naked eye on the elbow. If the pathology is not treated on time, it will go from acute to chronic.
Chronic
Chronic bursitis is characterized by a long course of symptoms . In this case, the patient has limited movement in the elbow, slight discomfort is felt when flexing and extending, and the bursa becomes significantly thicker.
Purulent
In the purulent form of the disease, the symptoms occur in an acute form . The patient feels aching and tugging pain in the elbow, the joint is very painful, and the swelling increases. The painful sensations intensify when touched; in addition, the area has a characteristic redness and is hot to the touch. The patient's body temperature rises, inflammation of the lymph nodes is observed, and sweating increases. The person becomes irritable, and the condition worsens greatly.
It is important to note that purulent bursitis is a very dangerous disease; if it is not treated in time, the patient may develop sepsis, and cases of death have been recorded.
The signs of bursitis are similar to many other diseases of the musculoskeletal system (arthritis, gout, etc.), so you should not self-medicate, it is best to immediately consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis.
Types of bursitis
Depending on the nature of the disease, four stages are distinguished:
- subacute;
- acute;
- remission;
- chronic.
At the initial stage, the patient is bothered by minor itching and burning in the elbow area, which can worsen if treatment is not started in a timely manner. Bursitis of the elbow joint in the acute stage causes the patient a lot of suffering. When bending the arm, a sharp stabbing pain occurs, the elbow swells and turns red. The patient may experience a rise in body temperature, general weakness and loss of strength.
During the remission stage, it is important to make every effort to avoid relapse. The chronic stage of the disease develops in case of untimely or incorrectly selected therapy. At this stage, the patient is bothered by constant aching pain, and a lump is felt under the skin.
Based on the nature of the exudate, the following types of bursitis are also distinguished:
- serous;
- hemorrhagic;
- purulent.
The serous type is considered the most common and least complex. With hemorrhagic bursitis, additional bleeding occurs into the cavity of the elbow joint. If a purulent type of lesion occurs, surgery is usually required. Depending on the severity of the situation, the synovial bursa may be opened to flush out pus, or it may be partially or completely removed.
There are several types of elbow bursitis.
Purulent
With constant irritation of the synovial bursa in the elbow area, mucous-serous exudate begins to accumulate in it, and the penetration of infection leads to the transformation of serous exudate into purulent. The patient observes redness of the skin in the elbow area, increased temperature, and limited mobility of the limb.
Purulent bursitis
Acute bursitis
It manifests itself as severe pain, aggravated by movement. A painful point is felt in the inflamed area, touching which leads to pain spreading to the entire surface of the arm.
In acute inflammation, the elbow becomes very swollen and painful. When palpating the joint, fluctuation is determined, that is, fluctuation of the fluid when pressing on the skin of the elbow.
We suggest you read: Pain in the elbow joint on the inside of the arm, why does the elbow hurt?
Recurrent
Chronic (recurrent) bursitis is manifested by mild pain in the joint, which lasts for a long time. The joint is not limited in movement, the tumor is not visible or felt, but when palpated, some dense formation can be detected.
Where is the bursa located in the elbow?
Recurrent bursitis occurs due to reinfection of damaged areas. Any damage provokes an exacerbation of the pathology.
The disease develops with occupational stress on the elbow joint. After injury, the bursa usually becomes infected with streptococcus, staphylococcus and other pathogenic organisms.
Based on the nature of the fluid accumulating in the bursa, they are distinguished:
- Serous bursitis, which is considered quite mild and harmless. The liquid has a whey consistency.
- Hemorrhagic, when fluid along with blood accumulates in the cavity of the synovial bursa.
- Purulent, in which, as a result of the neglect of the case, pus forms in the bursa. This species is considered dangerous as it can lead to sepsis and limb amputation.
(if the table is not completely visible, scroll to the right)
- The subcutaneous bursa is most often affected with the development of the serous type of the disease.
- Nonspecific infected bursitis of the elbow is also common, and rarely - brucellosis, syphilitic or another specific type.
- Of all types of pathology, the purulent one is the most dangerous, since it gives severe complications: sepsis, osteomyelitis, the appearance of an abscess, phlegmon, fistulas, inflammation of the ulnar lymph nodes.
- The most “harmless” is serous bursitis of the elbow joint, since the joint fluid is not infected.
The primary purulent process develops when the elbow is injured, the secondary one - against the background of an existing acute or chronic process after infection of the bursa secretion.
Post-traumatic serous bursitis can eventually become purulent due to the high risk of infection through existing wounds, scratches or other violations of the integrity of the skin.
Purulent bursitis
Elbow bursitis has several forms and types, each of which has its own symptoms, manifestations and possible complications. Bursitis is classified into the following forms:
- Chronic. This form is characterized by pain of low intensity that lasts for a long time. There is no visually noticeable tumor, the elbow joint is not constrained in movement, but upon palpation a small compaction is noticeable.
- Recurrent. Appears due to infection or repeated violation of the integrity of a previously injured area. Even after healing, exudate with pathogenic microorganisms is present in the synovial bursa. The symptoms are similar to the acute form.
- Spicy. Characterized by the appearance of severe pain when moving. Accompanied by fever and symptoms of general intoxication. Affects the normal functioning of internal organs.
In addition, it is customary to divide bursitis into specific and nonspecific. Specific is typical for those who are constantly engaged in heavy physical labor or as a result of injury. Nonspecific common among people with tuberculosis or syphilis.
Diagnostic methods
Making a diagnosis of bursitis is not difficult. First of all, the doctor conducts an external examination and interviews the patient for the presence of the main symptoms. Let's consider the main methods for diagnosing elbow bursitis.
Radiography
Using an x-ray, you can determine the localization of inflammation and the degree of damage to the joint . This is the most informative and accessible method of hardware diagnostics. It can be performed in almost any hospital. Not suitable for pregnant women, patients with contraindications.
Ultrasound examination of the elbow joint
Helps to establish the focus, area and localization of the source of inflammation. In addition, ultrasound can identify concomitant pathologies. An advantage of the procedure is the ability to carry out diagnostics even at home, which is sometimes important in advanced cases of bursitis.
CT and MRI
These techniques are used in severe cases when bursitis develops in deep joint capsules. It is the most accurate way to diagnose internal pathologies, allowing you to determine the location, extent and severity of the disease with 100% accuracy.
Analyzes
Among the main types of analyzes are:
- puncture of the joint fluid helps to establish the specific or nonspecific form of the disease;
- in the presence of a purulent process, it is necessary to test for the resistance of pathogenic microorganisms to various groups of antibiotics;
- in the case of specific bursitis, the patient is prescribed bacteriological and serological tests ;
- A general blood test helps determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- vascular angiography , which helps to study the boundaries of the inflammation.
An additional consultation with a phthisiatrician, rheumatologist and venereologist is also prescribed. They help exclude the presence of concomitant diseases .
Treatment of acute and chronic bursitis
After receiving the results of a comprehensive examination, the doctor determines the form of the disease and prescribes an individual treatment regimen for the patient. In case of acute bursitis, the patient is treated by a rheumatologist or orthopedist, in case of chronic bursitis - by a trauma surgeon. There are several types of therapy: conservative, medicinal and surgical . Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Drug treatment of traumatic disease
As a rule, effective anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are selected for the patient. They help reduce discomfort and prevent further progression of bursitis. In most cases, treatment occurs on an outpatient basis; the patient must be periodically seen by the attending physician.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
The most common method of drug treatment. Allows you to relieve inflammation, reduce swelling and pain. The following means are most often used:
- Diclofenac;
- Ibuprofen;
- Movalis.
They are prescribed exclusively in the form of tablets or powder for the preparation of a suspension for oral use. Diclofenac can be used to create compresses and blockades.
In the initial stages of the disease, the use of drug therapy is usually sufficient for complete recovery of the patient.
Antibacterial drugs
Prescribed after preliminary bacterial seeding of the contents of the joint capsule. Until the laboratory test results are obtained, the patient is prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics. In serous and hemorrhagic forms of the pathology, these drugs help prevent the development of the infectious process . Most often, the cephalosporin, macrolide or penicillin group is used (Cefazolin, Cefix, Ampicillin, etc.). They are prescribed in the form of tablets or injections (intramuscular or intravenous). The duration of treatment is from 7 to 14 days, depending on the severity of the disease.
Ointments and gels
They have local anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. They usually contain Diclofenac and an anesthetic (lidocaine, etc.). They are applied to the affected area several times a day, the duration of use is selected by the doctor individually for each patient. The most popular remedies are Traumeel S, Vishnevsky ointment, Diclofenac . Doctors often prescribe warming ointments (in the absence of acute symptoms) Fastum gel, etc. To reduce swelling and pain after the procedure, it is recommended to apply a tight sterile bandage to the inflamed elbow. Sometimes the patient requires complete immobilization of the elbow joint.
Antiseptics
These drugs are used as a treatment for inflamed bursa. These include Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Zerkalin and others. The procedure for treating the internal cavity of the joint is carried out in a hospital setting; subsequently, antiseptics are used to prevent infection of external tissue damage.
Injections
Typically these are corticosteroid injections that are injected directly into the joint capsule. They help relieve pain, swelling and stop the inflammation process. The procedure can be quite painful as the steroids take effect very quickly. This method has many contraindications, so such drugs should only be prescribed by a doctor based on the diagnosis.
Compresses
Therapeutic compresses are used for acute bursitis after eliminating the inflammatory process. For this procedure, use a solution of Dimexide with water. It is applied directly to the elbow. The concentrate is diluted according to the instructions for the drug; the duration and frequency depend on the form of the disease.
The advantage of this method is the ability to carry out the procedure at home. The course of treatment and dosage depend on the severity of the case.
Helper Methods
In addition to medications, it is advisable for patients with this diagnosis to undergo various physiotherapeutic procedures. They help improve the effect of taking medications and speed up the healing process. It is important to note that such procedures are performed only during periods of stable remission. Conservative methods of treating elbow bursitis include:
- acupuncture;
- mud baths;
- applications with paraffin and ozokerite.
It is advisable to combine physiotherapy with drug treatment, which significantly increases the effectiveness. The course of treatment is usually long - 7-15 sessions, depending on the severity of the disease. A special role in conservative therapy is played by therapeutic exercises, which are aimed at strengthening muscle mass. Classes are conducted under the strict supervision of a doctor. The load on the joint is increased gradually. Along with this, a massage is prescribed, it is performed by a chiropractor. He works on the painful area with massage movements. This helps eliminate excess fluid, relieve pain and swelling. Self-massage is prohibited, as it can cause complications.
Therapeutic massage technique for bursitis of the elbow joint.
Physiotherapy
For the treatment of acute bursitis, microwave and UHF therapy sessions are prescribed in combination with medications. Electrophoresis with Prednisolone or Dexamethasone has a good therapeutic effect.
Such treatment methods are not used for purulent or hemorrhagic forms of pathology.
Among the most effective physiotherapeutic procedures, doctors identify:
- Electrophoresis . Under the influence of a certain current strength, the drug is absorbed. There are no unpleasant sensations or side effects when using this method. Electrophoresis helps to establish metabolic processes in a sore joint, relieves inflammation and pain, removes excess fluid, dilates the walls of blood vessels;
- Laser therapy . In this case, laser radiation is used. To obtain results, the patient needs to undergo an average of 10 to 15 sessions. This therapy helps relieve swelling and inflammation, starts the process of regeneration in tissues, improves blood circulation;
- Shock wave therapy . The affected areas are exposed to infrasound. It has an anti-inflammatory effect, reduces the amount of accumulated fluid, and increases the mobility of the diseased joint. The most important advantage of this method is complete safety and quick results;
- UHF therapy . The inflamed bursa is affected by electromagnetic radiation. The advantage of this procedure is that it can be used at the stage of exacerbation of symptoms.
The duration and type of a specific physiotherapeutic procedure is prescribed by the attending physician.
Surgery as a treatment option
If drug and conservative therapy do not bring results, then the patient undergoes surgery. Most often, indications for surgical intervention are frequent relapses of the disease, purulent, hemorrhagic or persistent serous form.
How is the disease treated by draining the ulnar bursa?
This operation is usually performed for purulent bursitis. Local anesthesia is applied, the joint capsule is opened and drainage is placed in it. It stays there until all symptoms of the pathology subside. The patient remains in the hospital all this time; the accumulated fluid in the drainage is periodically pumped out.
Does bursal puncture help get rid of bursitis?
Prescribed to patients with acute bursitis. The operation includes removing the purulent contents of the bursa and thoroughly washing it. It is important to note that this procedure must be performed several times in order to completely flush out the pus from the cavity. The puncture is performed while taking antibacterial drugs and corticosteroids. Surgery is performed using local anesthesia; the patient does not need to stay in the hospital.
Antibiotics help prevent the development of an infectious process, and corticosteroids relieve inflammation. In addition, local antispasmodics may be prescribed.
Bursectomy and recovery period
The operation is performed under local anesthesia and is prescribed for patients with a chronic form of the disease. In this case, with constant exacerbations, the walls of the joint capsule become denser, it greatly increases in size and becomes dense. All these processes severely restrict hand movements, so the patient is prescribed radical surgery.
During a bunionectomy, the joint capsule is completely removed, a splint is placed on the elbow and complete rest is provided for several days .
During the recovery period, a new bursa is formed in place of the old one, thus the patient’s joint mobility is restored. The sutures are removed on days 5-7, after the operation antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are taken.
Causes and provoking factors
The synovial bursa (bursa) is a small slit-like cavity, which is lined with a membrane and delimited from the surrounding tissues by a capsule. Inside it is synovial fluid that nourishes hyaline cartilage and prevents damage to bone structures when they are displaced relative to each other. If the elbow joint is exposed to loads that exceed its strength limits, then an inflammatory process begins to develop in the synovial membrane. This also happens when performing monotonous hand movements for a long time, for example, when carrying out painting work. As a result of microtrauma of tissue in the synovial bursa, more fluid is produced than is required to protect the tissue from rapid wear. The bursa stretches and increases in size, causing a decrease in the functional activity of the elbow joint. In the chronic course of bursitis, destructive processes occur:
- adhesions are formed;
- fibrous foci form in place of the tissues of the synovial bursa;
- areas with calcifications (accumulations of calcium crystals) appear.
The cause of purulent pathology is the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms, most often bacteria, into the joint cavity. These are the causative agents of gonorrhea, syphilis, brucellosis, and tuberculosis. The development of nonspecific bursitis is provoked by streptococci and enterococci. In case of injuries accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the skin (cuts, punctures), Staphylococcus aureus and epidermal staphylococci penetrate into the synovial bursa. Immediately after infection, bacteria begin to multiply, releasing toxic products of their vital activity into the surrounding space. The result is inflammation of the bursa and the accumulation of purulent exudate in it. Microbes can be transported by the blood stream from primary foci formed by them in other organs. Therefore, bursitis is often diagnosed with the following diseases:
- furunculosis;
- osteomyelitis;
- carbuncles;
- bedsores;
- trophic ulcers.
Factors predisposing to inflammation of the bursa are arthrosis,
arthritis, rheumatoid, reactive, infectious, gouty. The development of pathology is provoked by metabolic and endocrine diseases (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus), hematopoietic disorders, a sharp decrease in immunity, and long-term use of glucocorticosteroids.
In what cases is it possible to treat an elbow at home if there is an injury?
Patients often resort to treating bursitis at home. Traditional medicine can be used for uncomplicated forms of the disease (if a purulent or hemorrhagic form is not diagnosed).
The following tools are popular:
- infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants (linden, plantain, calendula, burdock, etc.). They help relieve inflammation and swelling. Drink 0.5 glasses at least 3 times a day;
- drink celery tea 2 times a day for 2 weeks;
- compresses from beets, potatoes or cabbage;
- baths with pine needles;
- massage using essential oils of eucalyptus or lavender.
It is important to note that compresses must be applied correctly. Warm types are used for mild pain. It is strictly forbidden to place them at the acute stage of bursitis, this will lead to even greater inflammation and can provoke the development of infection.
To relieve acute symptoms, it is allowed to apply cold compresses. Traditional methods of treatment are best used in combination with taking medications. Otherwise, the risk of complications increases.
Treatment
Treatment should always begin with immobilization of the joint. Of course, a plaster cast is not always necessary, but for sprains and various diseases, a scarf bandage is used. The fact is that if you do not immobilize the limb, recovery or subsidence of the disease will take an extremely long time, and it is not a fact that everything will be completely restored.
The affected exudate, if present, is removed by puncture, after which special non-steroidal drugs, antibiotics or anything else are injected there.
Be sure to use vitamin complexes, attend effective physiotherapy, engage in physical therapy and many other things that can help restore joints, muscles or bone tissue.
Prevention
In general, if treatment is started on time, doctors give a favorable prognosis. After just a few weeks, the elbow joint is restored and the patient can return to normal life. At the same time, it is very important to take preventive measures that will help prevent a relapse:
- avoid heavy loads on the elbow;
- minimize the risk of joint injury;
- Athletes must warm up well before starting training.
By fulfilling all these simple conditions, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing this unpleasant disease. At the first alarming symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor ; delaying the process can lead to bursitis becoming chronic.
conclusions
- Bursitis of the elbow joint is an inflammatory process in the joint capsule . Characteristic symptoms include redness, swelling and pain in the elbow.
- With timely diagnosis, it can be easily treated with medication .
- Purulent-hemorrhagic or persistent serous bursitis can only be treated surgically.
- In combination with the main therapy, it is necessary to undergo physical procedures , this helps speed up the healing process.
Reasons for development
Viruses are a common cause of bursitis.
Elbow bursitis involves inflammation of the joint structures, as well as nearby tendons and muscles. The causes of this pathological condition are as follows:
- Severe intoxication of the body.
- Strong physical activity, during which the hands constantly experience a state of overload.
- Keeping hands in one position for a long time.
- Any injuries to the bones or joints in the elbows.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Gonorrhea, syphilis, tuberculosis.
- Inflammatory processes such as arthritis or gout.
- Presence of pyogenic viruses in the body. For this reason, the development of purulent bursitis is possible.
- Frequent pressure on the elbow area.
In some cases, a complex of causes leads to the disease. For example, as a result of injury, an infectious infection of the joint capsule occurs. Elbow bursitis is most common among athletes, office workers, and people with autoimmune diseases.