Fractures, sprains, bruises – such troubles can affect anyone. Timely and competent actions during the provision of first aid significantly affect the outcome of treatment and restoration of the functionality of the damaged part of the body. Therefore, it is extremely important to have information on how to provide first aid to a victim with a dislocation.
Joints in the human body are under constant stress and are therefore prone to injury. Among all other joint injuries, dislocations lead.
Symptoms of dislocation
A dislocation is an injury to a joint with a violation of its structure, accompanied by damage to the ligamentous-capsular apparatus and displacement of all bones.
A dislocation will be signaled by acute severe pain, partial or complete loss of function of an arm or leg, an unnatural position of the damaged part of the body, a peculiar crunch at the time of injury, rapidly developing swelling near the damaged joint, the inability to move an arm or leg (an attempt to move will cause severe pain), bruise.
A distinctive feature of a dislocation from other types of injuries is that the above symptoms appear a few seconds after the incident, and do not occur over time.
When is help needed?
A dislocation is a displacement of the bone of a joint, resulting from injury, a strong blow, etc. Sometimes certain pathologies - arthritis, arthrosis - can cause the bone part to leave the joint cavity.
Pre-medical measures must be carried out competently! It is important to be able to distinguish a dislocation from a fracture so as not to harm the victim!
When joints are dislocated, patients experience the following clinical signs:
- Limitation of physical activity;
- Pain syndrome;
- Joint deformity;
- Swelling.
In addition, this traumatic injury may be accompanied by swelling, redness of the skin, hematomas, and sensory disturbances.
The main difference between this injury and bruises and sprains is that the symptoms listed above appear immediately after the injury. Unlike fractures, dislocations are not accompanied by mobility of bone fragments or a change in the length of the damaged limb. Motor activity, as a rule, is preserved, although any attempts to move bring the patient severe pain.
First aid for sprains
First aid for dislocation of closed joints is as follows:
- It is necessary to immobilize the joint in the position in which it is after the incident. Under no circumstances should you attempt to correct the misalignment yourself.
- To prevent the development of severe swelling, apply any cold object to the affected joint (ice bag, package of frozen vegetables). Such a simple manipulation will also reduce the risk of bleeding into the joint cavity.
- Give the victim any painkiller (if he is not allergic to this drug).
- The limb is immobilized using a splint. If a medical splint is not available, then use available materials. If the upper limb is damaged, a scarf or bandages should be used for immobilization, while the arm is suspended and secured in a comfortable, pain-free position. If the lower part of the body is damaged, a splint made of hard material (board, plywood) is used. It is important to know that in addition to fixing the injured joint, you should also fix the neighboring ones - 1 upper and 2 lower. This will provide the damaged joint with complete rest.
- After carrying out the above measures, it is necessary to urgently transport the victim to the emergency room.
All of the above actions are general and are suitable for joint displacements of different locations. It is also important to know the distinctive features of providing first aid for dislocations of the joints of the upper and lower parts of the body.
Dislocations of the upper limbs
- Collarbone. To provide first aid, all the steps described above are used; a special Deso bandage is used for immobilization; a bandage roller should be placed under the armpit. The victim is transported in a sitting position or even on foot.
- Shoulder. This type of physical injury most often occurs as a result of falling on an outstretched arm. First aid methods for closed or open dislocation of this area, according to the standard, involve the use of a scarf to fix the arm. Transport the victim to a medical facility in a sitting position, but without putting any weight on the injured shoulder.
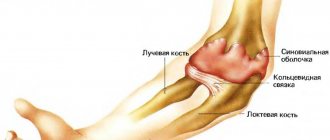
- Forearm. In such a situation, immobilization is carried out using a headscarf; the patient can be transported to a medical facility in a sitting or standing position. It is imperative to check for damage to blood vessels and nerve endings. To do this, try to feel the pulse on the radial artery (in the area of the cubital fossa). If the pulse cannot be felt, it means that the vessels of the forearm are affected and the blood supply to the tissues is disrupted. In this case, you should hurry to deliver the victim to a medical facility. Next, evaluate the integrity of the nerve fibers. To do this, touch different areas of the skin of the sore limb. If the touches are indistinguishable, numbness is felt, then the nerve fibers are also damaged.
- Fingers. First aid for dislocations in this area involves the following actions: secure the injured finger to a healthy one, after removing all jewelry, cool the damaged area. Give the victim an analgesic.
Dislocations of the lower extremities
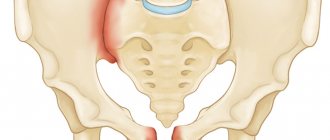
- Hip. This is a severe injury, accompanied by severe pain, and there is a danger of developing traumatic shock. The patient needs to be given a painkiller, immobilize the leg with a splint, apply ice to the damaged area, and call an ambulance.
- Shin. This type of injury is rare in domestic injuries. Basically, the risk group consists of athletes. The injured leg should be kept immobilized in an elevated position and the injured area should be cooled. If necessary, give the patient an analgesic. The victim should be transported to the hospital in a supine position.
- Ankle. The principles of first aid are identical to measures for a sprained leg: ensure an elevated position and rest for the injured leg, apply local cold, transport the victim to a medical facility in a lying position.
More information about what first aid should be for dislocations and fractures.
Anatomical features and classification
A joint is a strong and elastic connection of bones that is covered with cartilage tissue. It works as a kind of shock absorber that prevents bones from rubbing against each other, protecting them from premature abrasion. The elements of the articular bone are located in a special bag, which is called the articular. The entire bursa is filled with synovial fluid, a kind of “lubricant” for the joints.
Thanks to the joint, the limbs produce flexion and extension movements. It is durable and can withstand heavy loads. However, a blow or an accidental coincidence, when a limb acquires an unusual position, causes damage to the joint. Such injuries may be complicated by rupture of the joint capsule or ligaments, which will require a long treatment and recovery period.
Doctors carry out a conditional classification of dislocations in several directions.
Origin of injuries:
- Traumatic. Caused by mechanical stress;
- Pathological. They are classified as diseases that weaken joint and ligament tissue;
- Congenital. Their appearance is due to developmental disorders of the baby in the womb.
Degree of displacement of articular bones:
- Full. Complete divergence of the ends of the joints;
- Incomplete. The joint ends remain partially connected.
Presence or absence of skin damage:
- Closed. The integrity of the skin is not compromised;
- Open. A wound is fixed in the area of the damaged joint.
Time period after injury:
- Fresh. Recorded injury no more than 3 days;
- Stale. 2 weeks have passed since the injury;
- Old. The joint remains in a damaged state for more than 2 weeks.
The following classification is based on the specifics of dislocations. Their characteristic features are presented in the table.
Regardless of the type of injury, first aid for joint dislocations is carried out according to the general scheme. The characteristics of the injury are determined by the doctor after examination. After diagnosis and identification of the specifics of the damage, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
The following actions in case of dislocation are strictly prohibited:
- Attempts to make adjustments on your own. A doctor can carry out such manipulation only in a medical facility, and inept actions will lead to disastrous results.
- Use warm compresses.
- Delay in transporting the victim to a medical facility. Effective reduction is possible within the first three days after its occurrence. Failure to correct the displacement in a timely manner and give the arm or leg a natural position may result in further surgical intervention.
How to apply a bandage correctly?
First aid for sprains and other injuries mainly involves applying a bandage to the injured area correctly.
Of course, depending on the type of injury (simple bruise, dislocation, joint sprain, fractures, and so on), dressings may differ from each other. But the principle of their application remains the same:
- The person providing first aid must have clean hands. Ideally, they should be washed with soap; if this is not possible or you need to act immediately, then it is enough to treat them with some kind of antiseptic agent (sprays, wipes).
- If the injured area has an abrasion or an open fracture, then the area around the bruise (fracture) should be treated with hydrogen peroxide, iodine or brilliant green. As a last resort - alcohol.
- The victim is placed in a comfortable position with a convenient approach to the injured area.
- Bandage in a spiral from bottom to top. For example, if an arm or leg is injured, then the bandage is directed from the fingers to the torso.
- The first few turns of the bandage are fastening, that is, it is tightly wrapped around the limb or body, and placed at some distance from the injury.
- Each new layer of bandage should cover the previous one by one third.
- The last turns of the bandage are the same as the first ones - securing and located over the injured area.
For greater reliability, you can cut the end of the bandage into two parts, wrap them around the damaged area and tie them.
Causes of damage to the ligamentous apparatus
Common causes of sprains:
- careless movements, twisting of the foot, dislocations or twisting of joints;
- sports injuries or falls;
- overweight;
- joint diseases (arthritis, arthrosis);
- incorrectly selected shoes;
- developmental anomalies of the musculoskeletal system.
Damage to the ligaments of the acromioclavicular joint often occurs with a blow to the shoulder or during a fall, the sternoclavicular joint - with a fall, the wrist - with a sharp extension of the hand, the knee - with a blow or twisting, the anterior cruciate ligament - with twisting of the hip during the period of fixation of the lower leg , ankle - when turning the legs, landing incorrectly.
What is a joint
A joint is a connection of bones that allows movement in a limb. The joint is formed by the articular ends of two bones, covered with cartilage tissue, which absorbs and softens friction during movement. Sometimes there is additional cartilage in the joint as a kind of cushion, for example the meniscus in the knee joint. The joint parts of the bones are enclosed in the so-called articular capsule, inside which there is synovial fluid. The joint also includes ligaments that firmly connect its components to each other. Thus, the joint is a very durable structure that can withstand heavy loads.
Signs
How to recognize a dislocation? Let's get acquainted with the main signs of this pathological condition.
- A characteristic click (pop) at the moment of injury.
- Sharp pain in the part of the body where the dislocation occurred. The joint is completely or partially immobilized.
- Quite often there is a change in the shape of the joint, which is easy to determine upon examination. For example, the leg will be moved to the side and bent at the joint.
- The most common sign of a sprain is swelling and swelling of the injured area.
- Nerve damage during injury also occurs, which is accompanied by loss of sensation in the lower or upper extremities.
Physiotherapy
The most important stage in the treatment of all musculoskeletal injuries is rehabilitation. After swelling and pain are relieved, the patient is prescribed therapeutic exercises with a gradual increase in load. It consists of a program of rehabilitation exercises, which the attending physician selects individually, taking into account the nature of the injury. The patient can perform the complex at home, and after 2-3 weeks he will be able to completely forget about the sprain (if it is mild or moderate in severity).
Performing daily stretching exercises increases the length and flexibility of muscles and ligaments. This strengthens the entire musculo-ligamentous system, allowing joints to move with a wider range and maintain greater activity. Therapeutic exercise is the best prevention of ligament sprains and other joint damage.
First Aid Notes
First aid for sprains and other injuries will not be given correctly if the person providing it does not follow the existing notes.
We suggest you read: Arthritis of the wrist, treatment for relieving severe pain at home
Their list includes the following:
- Do not try to put a fracture or dislocation back into place yourself - this may cause further injury.
- It can be difficult for people without medical education to determine what nature of the injury is - a fracture, dislocation or sprain. When in doubt, always treat injuries as fractures.
- If the collarbone is broken, support the arm slightly away from the victim by making a sling.
- If you suspect a joint dislocation, rest the injured area and apply an ice pack.
After injuries, the victim may occasionally experience minor discomfort in the injured area (for example, nagging pain that appears when the weather changes from sunny to rainy). But such a result is possible with almost one hundred percent probability if first aid for sprains, dislocations, bruises and fractures was not provided correctly. Therefore, this is another encouragement to comply with all the points in the above notes.
The most important thing is that first aid for sprains, dislocations, bruises and other injuries should be provided by a person who does not panic and thinks sensibly. In most cases, the success of healing of damaged areas depends on this.
Tags: dislocation, which, provide, first, help, sprain, ligament
About the author: admin4ik
« Previous entry
How does a dislocation form, its diagnostic signs
Dislocation occurs when a joint is subjected to a sudden and excessive force, usually in a direction that is unusual for movement in that joint. In this case, the articular part of the bone comes out of its anatomically correct position, and the joint capsule may be damaged, ligaments and blood vessels may be torn, and nerve endings may be compressed and damaged.
The most common dislocations occur (in descending order): finger, shoulder, foot, elbow, temporomandibular joint, knee, hip joint.
Before you begin to provide first aid for a dislocation, you need to make sure that there are symptoms.
Signs that a dislocation has occurred are:
- Sharp pain in the joint;
- Unnatural position of the limb;
- Impossibility of movement in the joint or a sharp limitation of its mobility, increased pain when trying to move.
As a rule, when a joint is dislocated, it changes shape, which is especially noticeable in people of thin build. Also, traumatic edema often occurs due to damage to blood vessels, and sometimes the release of synovial fluid from the joint capsule.
A dislocation differs from less dangerous injuries, such as a sprain or bruise, in that the symptoms described above do not increase gradually, but appear immediately after the injury. If you are not sure what kind of injury occurred, it is better to assume a more severe version and provide the first aid required for a dislocation. If it later turns out that the diagnosis was wrong and a sprain actually occurred, this will not have any negative consequences. It is much more dangerous to underestimate an injury.
What are dislocations, sprains, contusions and fractures?
A sprain is an injury to the soft tissue of the ligaments or those around the joint. As a rule, the blood vessels adjacent to the rupture site are also affected. To get a sprain, you just need to trip, slip, or exaggerate physical activity.
Dislocation is the result of a bone falling out of its place (“socket”). In other words, the joint bones are displaced. For example, as a result of heavy physical activity or some kind of body movements. The most commonly affected parts of the body are the leg, arm, finger and shoulder.
A bruise is damage to tissues (sometimes organs) without disturbing their structure. With minor bruises, the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles and periosteum are injured. During severe bruises, internal organs can be damaged and even tissue necrosis can occur.
A fracture is a disruption of the integrity of a bone as a result of severe damage. There are open fractures, when adjacent tissues and skin are injured and a wound is formed, and closed ones.
Inexperienced people may confuse a dislocation with a closed fracture. The main distinguishing feature of the latter is that the pain does not go away even after time, and the injured area begins to swell and change color to dark blue.