Keratitis refers to inflammation of the cornea of the eye . It can occur as a primary disease or develop as a consequence of any pathology in the body.
Endogenous keratitis can occur in the presence of various infections that are chronic, such as herpes, tuberculosis and a number of other conditions. However, it can be considered as a complication of the underlying disease.
In terms of symptoms, it may be similar to conjunctivitis, but, as an independent nosological form, it has more extensive and severe complications.
Eye keratitis - photo in a person
After such a condition, with a favorable prognosis, recovery occurs. If only the superficial layers of the cornea are involved in the process, then the disease, as a rule, does not leave scars. The outcome of deep keratitis is always associated with the formation of scars, which, naturally, can affect visual acuity.
Eye keratitis - photo
Causes
There are many reasons for the development, the most common is the entry of viruses and bacteria into the organ of vision, which cause inflammation of the cornea. Other reasons are as follows:
- Injuries to the eye or the presence of foreign bodies in it.
- Violation of the rules for caring for contact lenses.
- Burns of various origins.
- Presence of immunodeficiency states.
- The eye disease keratitis develops due to vitamin A deficiency.
- Increased dryness of the eye.
- Problems with nerve conduction in this area. For example, with neuritis of the facial nerve, lagophthalmos develops, as a result of which the eyelids do not close completely, which facilitates the penetration of pathogens into this area.
- Keratitis is often a consequence of allergies.
- Concomitant endocrinological and autoimmune diseases.
- Pathology can also develop as a result of long-term use of hormonal and psychotropic drugs.
In case of chronic diseases of the organ of vision, there is a risk of the inflammatory process spreading to the cornea. In some cases, the cause of the pathology is parasitic infestations.
Top 4 most effective drops prescribed for inflammation of the cornea
I bring to your attention the top 4 eye drops that have proven themselves in the fight against various types of keratitis in adults:
- Aktipol. This drug has antiviral, antioxidant and regenerative effects. The main advantage of this medication is that they are quickly absorbed into the eye tissue, accelerating the process of restoration of the cornea.
Thanks to the use of this drug, small ulcers on the surface of the cornea heal and swelling caused by infection disappears.
- Oftalmoferon. These drops have anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects. They not only enhance and accelerate the regeneration process in eye tissues, but also help strengthen the immune system.
- Poludan. An antiviral agent based on a biosynthetic polyribonucleotide complex. Poludan is prescribed mainly for herpetic and adenoviral types of disease.
- Opatanol. This antihistamine reduces the permeability of blood vessels in the mucous membrane of the eye, helping to eliminate the possibility of contact of the allergen with mast cells of the conjunctiva.
Symptoms and types
Symptoms of keratitis in humans are lacrimation, fear of light and blepharospasm. The latter term refers to the reflex closure of the eyelids; often patients cannot open their eyes at all during the acute period of the disease.
There are also complaints of pain of varying intensity, there is clouding of the cornea, and hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the organ of vision. Patients may describe the sensation as a feeling of a foreign body in the eye. During the period of illness there is a decrease in visual acuity.
Other symptoms of eye keratitis depend on the type of pathology. The variants of the disease are as follows:
- Allergic is characterized, in addition to the above symptoms, by the presence of a runny nose, swelling of the face, cough, itching and burning in the eyes.
- Bacterial keratitis often occurs due to injury or when wearing contact lenses, as this makes it easier for pathogens to enter the organ of vision. Patients have complaints of severe throbbing pain in the eye, swelling in this area, and the appearance of purulent discharge. Complications include ulcers and opacities.
- Viral keratitis has a corresponding etiology, spotty opacities on the membrane. With this type, more often than with others, a cataract forms. In most cases, herpetic (or dendritic) and adenoviral keratitis are diagnosed.
- Acanthamoeba . A simple organism, an amoeba, can get into the eye. This happens when rinsing lenses under running water. In such cases, acanthamoeba keratitis is formed. Its symptoms are severe pain, clouding of the cornea and ring-shaped ulcers on it.
- Fungal keratitis is characterized by the presence of diffuse pain in the eye, severe hyperemia, and when the cornea is irritated, the eyelids close. Complications include decreased visual acuity, formation of a cataract, and ulceration.
- Parenchymal keratitis is caused by Treponema pallidum, the causative agent of syphilis. Its signs are that the cornea gradually becomes matte, the sclera grows with vessels that give it an orange tint. In the case of this type of pathology, great importance is attached to the accompanying symptoms of syphilis.
- filamentous develops . The amount of tear fluid is significantly reduced, and the pathology often becomes chronic.
- If a foreign object gets in, the risk of ulceration is much higher. The ulcerative type of the disease is severe, often with breakthrough of pus into other structures of the eye, perforation of the membranes of the organ of vision.
- A separate group includes the tuberculosis type of disease, in which white nodules accumulate in the cornea and infiltrates form on the surface.
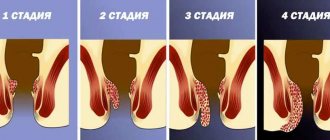
The classification of keratitis according to localization is as follows: superficial, involving the upper layer of the membrane, and deep, which affects the underlying structures. With the latter type of disease, scars form.
Acute keratitis of the eye is more often diagnosed, which usually ends without any consequences for the organ of vision. But the process can become chronic, occurring with exacerbations and remissions.
Also, according to localization, marginal keratitis is distinguished, which is a type of viral or bacterial. The pathological process is localized on the peripheral part of the cornea and is easily detected by visual examination.
Diagnostic features
Diagnostics plays an important role in the treatment process, since if it was carried out incorrectly and the doctor made an incorrect diagnosis, the patient will be prescribed medications for the wrong disease. This will slow down the therapy process. Therefore, diagnostics should be carried out by a qualified specialist. The most common and effective research methods include eye biomicroscopy - a diagnostic procedure that can be used to determine the degree of damage to the cornea of the eye. Biomicroscopy allows you to identify symptoms of eye keratitis at an early stage of development of the pathology.
Diagnostic features
The doctor may also prescribe other diagnostic procedures for the patient, including:
- specular microscopy method;
- laboratory blood test;
- immunological research methods (conducted to identify pathogens of infectious pathologies);
- cytological examination of epithelial tissue of the cornea.
Diagnosis of keratitis
Based on the data obtained, the doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe a course of therapy. Only after this can you begin the next stage on the path to recovery - treatment.
How to treat keratitis
It is important to note that keratitis in children and adults occurs in the same way, and treatment methods are no different from each other. It is important to start treatment for the disease as early as possible. Treatment is complex, includes various areas, depending on the etiology of the disease.
Some patients have a question about how to treat eye keratitis at home. Hospitalization to an ophthalmology department is usually required; only the superficial, uncomplicated form can be treated on an outpatient basis.
Anti-infective therapy
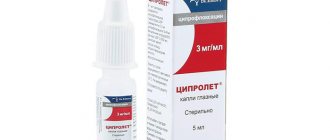
This type of therapy depends on the pathogen. For bacterial etiology, Ofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Sulfacyl drops are used. If necessary, apply antibacterial ointment to the organ of vision (for example, Tetracycline). In case of severe intoxication, antibiotics are taken in the form of injections or tablets.
Treatment of herpetic keratitis of the eye includes the mandatory use of Acyclovir in the form of tablets and eye drops. Ganciclovir can be used and is more effective in severe cases. Arborescent keratitis often requires surgical correction, including corneal transplantation.
Also, for viral etiology, drugs containing interferon are used, and special ointments are placed in the organ of vision (for example, Florenal ointment).
To eliminate allergic reactions, special eye drops are used for keratitis of a similar etiology - Allergodil, Opatanol.
If a patient has syphilis or tuberculosis, drugs specifically directed against these pathogens are used for treatment.
Symptomatic treatment
The symptoms and treatment of keratitis are inextricably linked. To improve the patient's condition, mydriatics are prescribed that stimulate the outflow of tear fluid (Atropine, Cyclomed), artificial tears, and antiseptics (Albucid, Vitabact).
Agents are used that promote epithelization of the organ of vision - Solcoseryl, Cytochrome, Retinol. Vitamin eye drops - Taufon, Quinax, Katachrom - are also prescribed as symptomatic remedies.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of eye keratitis is required for the formation of scars, ulcerative lesions, deeper penetration of the pathological process, and severe herpetic lesions. Laser or thermal coagulation and keratoplasty are used (if this layer is destroyed). In some cases, treatment for keratitis in people may require a cornea transplant or laser vision correction. In very advanced cases, the question of complete removal of the affected eye may arise.
Is it appropriate to use folk remedies?
According to ophthalmologists, treating keratitis with folk remedies is inappropriate and even dangerous. The use of these techniques can worsen the course of the disease and increase the risk of complications, including the most serious ones (more on them below).
Therefore, you should abandon traditional medicine and, at the first signs of illness, consult an ophthalmologist.
Allergic form
Allergies can also cause serious pathological processes, one of which is allergic keratitis. A similar acute reaction to exposure to an allergen is typical for adolescents and children. It appears on medicines, animal hair, dust, etc.
With high sensitization of the body, allergic keratitis is often provoked by endoallergens, i.e. toxins. They are produced during tuberculosis intoxication and helminthiasis. Moreover, there may not be Mycobacterium tuberculosis, it’s just a reaction of a weakened body.
Allergic keratitis occurs with the corneal syndrome inherent in any type of such disease (blepharospasm, excessive tear secretion, photophobia). Additionally, pain, redness in the eyes, and low-grade fever appear.
Successful treatment is possible with immediate cessation of contact with the allergen. You need to put corticosteroid-based ointments behind the eyelid and drip dexamethasone. The doctor selects antihistamines and supplements the therapy with vitamin supplements. If allergic keratitis constantly recurs, steroids are used. Decreased vision is treated with physiotherapeutic methods (electrophoresis, phonophoresis).
Complications and consequences
One of the complications is ulceration of the cornea, which can lead to the penetration of pathogens deeper into the underlying and nearby structures of the organ of vision. In severe cases, this process can cause significant reduction or complete loss of vision.
Complications also include scars on the cornea, which remain after recovery from the inflammatory process. The consequence of the disease can be glaucoma, cataracts, and cataracts. In some cases, inflammation (neuritis) of the optic nerve develops.
Classification
The division of the disease into varieties is based on many criteria - the depth of the lesion, the cause, the location of the infiltrate, the nature of the course.
According to the depth of the lesion there are:
- superficial keratitis – affects the epithelium and upper stromal layer, total depth up to a third of the cornea;
- deep type - the entire stroma is inflamed;
Depending on the location of the infiltrate, 3 types of keratitis are distinguished:
- central - in the area of the pupil, so vision deteriorates as much as possible;
- paracentral – in the projection of the iris belt;
- peripheral - in the limbus area.
One of the classification criteria is origin, or etiology. According to him, there are the following types of keratitis:
- exogenous forms;
- endogenous forms.
In turn, exogenous forms are divided into:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- fungal;
- amoebic;
- traumatic types;
- meibomian;
- keratitis caused by damage to the conjunctiva and eyelids;
- corneal erosion.
Exogenous forms include varieties provoked by infections and other factors:
- allergic;
- tuberculosis;
- syphilitic;
- brucellosis;
- hypo- and vitamin deficient;
- malarial;
- neurogenic;
- dystrophic;
- keratouveitis;
- traumatic;
- photokeratitis;
- of unknown origin (rosacea keratitis, filamentous keratitis, corneal ulcer), etc.
The filamentous type is provoked by insufficient production of tear fluid and drying of the epithelium.
The disease is divided into acute, subacute, recurrent and chronic stages.
Is it possible to wear lenses after keratitis?
This issue is always resolved by the doctor individually. If the process is complete, then wearing lenses is allowed after some time from the moment of recovery. The type of lenses must be selected by a doctor, the duration of use is gradually increased. The rules of care must be strictly followed, otherwise re-infection cannot be avoided.
If complications in the outcome of keratitis could not be avoided or the disease has become chronic, then wearing lenses is contraindicated. They can further injure the eye, which will only worsen the patient’s condition.
ethnoscience
To treat different types of keratitis, medicinal plants with antiseptic properties are used. One of them is aloe.
Several lower leaves of a three-year-old plant or older are cut off, wrapped in paper and sent to the freezer for a week . After this, the juice is squeezed out from the leaves, filtered and a grain of mumiyo is added. Use the product 1 drop 1 time per day for a month. From the second month, pure aloe juice is used.
Honey has absorbent, antiseptic and healing properties . The solution requires a liquid product. At first, in order to accustom the eyes (since real honey in its pure form causes a burning sensation), it must be diluted with boiled, non-hot water in a ratio of 1:2. Use up to 4 times a day for 1 week ; from the second week, honey and water are diluted 1:1. From the third week, pure honey is used.
Prevention
Complications of keratitis can be easily prevented by timely consultation with a doctor at the first symptoms and full treatment of the disease. As for other methods, doctors do not recommend prolonged exposure to the sun in cloudless weather. It is important to follow all rules for hygienic care of contact lenses.
For any disease of the organ of vision, it is important to start treating it on time to prevent the process from becoming chronic and the inflammation spreading further. Any concomitant pathologies should be transferred to the stage of decompensation; it is important to sanitize all sources of chronic infections in the body.
Traumatic keratitis is easily avoided if all necessary requirements in the workplace are met - wearing masks and other protective items, following safety regulations.
Definition of disease
The following layers of the cornea are distinguished:
- The epithelium is the uppermost one, its main role is a protective function. The epithelium also delivers nutrients and oxygen to the corneal tissue, supplied to it from the tear film. The epithelium has high restorative abilities;
- Bowman's membrane is a thin layer of cells that separates the stroma from the epithelium and cannot be repaired. Its meaning is not fully understood;
- Stroma is the most voluminous layer, consisting of collagen fibers and cells responsible for restoration;
- Descemet's membrane - its function is to separate the stroma and endothelium. Has high elasticity and resistance to damage;
- Endothelium – is responsible for maintaining the cornea’s transparency and is involved in nutrition. It is a kind of “pump” that removes excess moisture from the cornea. It recovers very poorly.
The place where the cornea meets the sclera (the opaque part of the cornea) is called the limbus.
The severity of inflammation depends on the location and depth of penetration of the damage.