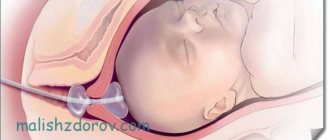
A follicle is a structural component of the female reproductive gland, consisting of an egg and surrounding tissue.
Its persistence appears when the rupture of the capsule is not detected and the egg is not able to enter the uterine cavity. The dominant follicle is the one that will very soon ensure the release of the egg into the uterine cavity.
Knowing information about what a follicle is helps to plan a pregnancy and detect problems associated with conception.
What are follicles
In the female body, unique processes of follicle maturation occur. They are laid during the period of embryonic development. Their approximate number in the womb is approximately 500 thousand.
By the beginning of puberty, their number decreases to 40 thousand, but not all of them fully mature. During the entire reproductive period, 500 unique sacs with eggs mature. The rest gradually become atretic, that is, they fade away.
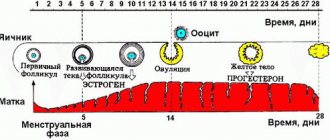
The process of their ripening is extremely complex from a biological point of view. It is influenced by a huge number of factors. It begins in the first phase of the female cycle. In order for this process to occur normally, the presence of follicle-stimulating hormone is required.
At one time, about 10 sacs with oocytes mature, but only one of them will be dominant. An egg will be released on the 14th day.
Approximately on the 7th day of the cycle, using ultrasound, it is possible to visualize the process of growth of the oocyte capsule. The size of each is several millimeters.
Daily ultrasound determines further growth. Reaching 2 cm in diameter, the follicle bursts, the germ cell is released and enters the fallopian tube. In a normal monthly cycle, this occurs on days 13–15. This may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- some pain in the lower abdomen,
- the amount of mucus from the female genital organs increases,
- basal temperature drops,
- an increase in the amount of luteinizing hormone in the blood.
In one monthly cycle, one follicle matures in the female body. Rarely there are 2 of them, which is not considered a pathology. Moreover, releasing multiple eggs significantly increases the chances of getting pregnant.
Fertilization
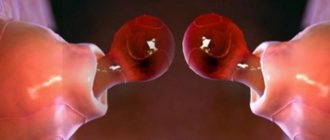
The maximum lifespan of an egg is 36 hours. When she leaves the follicle, sperm may already be waiting for her, remaining active for several days. Then fertilization can occur in a matter of hours.
This is how fertilization of the egg occurs
Conception is affected not only by this indicator, but also by the duration of sperm activity. They can retain their abilities for 2-4 days. Some sometimes remain in the uterine cavity for a week. In this regard, the favorable period for conception begins 6 days before the expected fertilization.
After the release of seminal fluid, the path is paved to meet the egg. Sperm reach their goal in a maximum of six hours.
By the way, only one sperm is involved in the birth of a fetus. It pierces the outer membrane of the egg. After this, the body is given a signal that pregnancy has occurred.
Kinds
The following types of follicles are distinguished:
- primordial,
- primary,
- secondary,
- tertiary
Primordial are otherwise called resting. They are localized in the subcapsular zone. They are the smallest. Cells have a flat structure.
The primary ones are otherwise awakened. They are slightly larger than the primordial ones. Around the egg there is a membrane formed by protein substances.
Secondary follicles are somewhat larger. They have stratified epithelium and several small chambers filled with fluid. Around it grows a membrane inside the ovary - the theca. It appears in the ovary earlier than the theca and it is by it that the secondary capsule is identified.
Finally, the tertiary follicle (or Graafian vesicle) is mature. He has reached his greatest development. It begins to put pressure on the surface of the ovary. Its predominant volume is occupied by a cavity (capsule) filled with fluid and containing an oocyte. Surrounded by theca.
What is a persistent follicle?
A persistent follicle develops when the capsule does not rupture. The egg then remains in her because it does not enter the uterine cavity.
This process is pathological, because in the presence of persistence, fertilization cannot occur. A woman experiences difficulties with the onset of gestation.
The capsule can exist in the ovary for about 10 days. After this period ends, a new menstruation begins. In some cases, a woman experiences a delay, and it can even last up to one and a half months.
Ovarian capsules dissolve on their own without taking additional medications. Sometimes an ovarian cyst develops and requires treatment.
Classification and features of treatment of glandular endometrial hyperplasia Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia - causes and signs of pathology Treatment of two-chamber ovarian cyst - symptoms of pathology Rabies of the uterus - what is it, signs and symptoms of pathology
In the blood of women with persistent ovarian capsules, the amount of estrogen increases and the level of progesterone decreases. Signs of ovulation disappear because the corpus luteum moves into the so-called posterior uterine space.
If the ovarian capsules exist for a long time, then delays in the monthly cycle occur. When menstruation occurs, a large amount of blood is released.
Note! Reproductive activity is related to the balance of hormones. Due to the fact that hormonal levels are disrupted, persistence develops.
If a persistent follicle is detected, pregnancy can be planned only under the supervision of a doctor. To do this, the gynecologist determines the dominant capsule. This is possible with the help of ultrasound examination.
It is done on the eighth day of the cycle. On day 12, the most suitable conditions for conception are created. For this, another ultrasound is prescribed.
The third examination is scheduled for the 18th day. The specialist checks for ovulation. A woman should carefully monitor the condition of her body. After 10 days, a pregnancy test is allowed.
What is a dominant follicle?
Every month, several capsules containing eggs increase in the ovary. Then their growth stops, only one or very rarely two continue to increase. He is dominant. The rest are gradually regressing.
Every day the size of the dominant follicle grows by several millimeters. On the eve of ovulation, it reaches a size of up to 18 - 20 mm. Under these conditions, an oocyte emerges, completely ready to receive a sperm and form a zygote.
On ultrasound, the dominant follicle can be seen already from the fifth day. It is less often seen on the eighth day. At this time, it is significantly superior to other bags.
This growth is due to the active influence of follyl-stimulating hormone. If there is not enough of it in the blood, then it does not reach the required values and even decreases. In this case, an ovarian cyst develops. After ovulation, the corpus luteum grows in the ovary.
Interesting! The dominant follicle is most often found in the right ovary. Today it is not known exactly what causes this phenomenon. Often the corpus luteum can be found just in the right ovary. It is assumed that the phenomenon in question occurs due to the activation of the nervous system.
Ovulation of the egg
The pattern is clear: ovulation on average occurs 14 days before menstruation and lasts 48 hours. And it is during these 48 hours that conception is most likely. But we know that “in general” and “on average” does not happen to everyone and not always. Sometimes the circuit gets blocked and stops working. Therefore, you should study not the general rules, but your own body.
The rhythm of ovulation can change due to endocrine diseases, after abortion, childbirth. There are menstruation without ovulation and ovulation without menstruation. Breastfeeding mothers and menopausal women are often confident that they are not at risk of pregnancy. Sometimes this leads to various incidents (“Darling, we are going to have a child. Again...”).
Young mothers should know that the process of egg maturation is inhibited only if the break between breastfeedings does not exceed three hours during the day and four at night. I decided to rest longer - and that’s it, you’re at risk. Even women over 50 cannot sleep peacefully. Reproductive function fades gradually - sometimes the maturation of a “late” egg is possible.
2-3 cycles a year without ovulation is the medical norm. Do the math. If your cycle is 21-23 days long and your menstruation is 6-7 days, then ovulation occurs immediately after your period. Strong love excitement and stress also lead to unexpected results. Additional ovulation may occur. Especially without a permanent partner.
Norms
How many follicles should there be in an ovary?
The number of all sleeping oocytes is laid down by nature at the stage of embryonic development. It is characteristic that before the onset of puberty it decreases significantly. One egg is released every month.
The number of capsules with oocytes is determined by the day of the cycle. There may be several of them just a few days after your period. On the fifth day there can be up to 10 of them, and this is also the norm. After all, only one follicle will be dominant.
Deviations
In the absence of a dominant follicle, the egg is not released. This happens as a result of hormonal imbalance and certain pathologies:
- decreased production of follicle-stimulating hormone and increased excretion of luteinizing hormone,
- regression due to hormonal disorders (including due to increased insulin levels),
- the presence of a persistent process,
- the presence of an overripe pouch,
- formation of a follicular cyst that grows in place of the dominant follicle (dimensions exceed 2.5 cm on ultrasound examination),
- polycystic ovary syndrome,
- pathological luteinization, when without ovulation the corpus luteum grows at the site of dominance.
Note! With persistence, the follicular membrane ruptures. The egg can be released into the abdominal cavity. Pregnancy does not occur in these cases.
All ovarian development disorders require a thorough instrumental examination. Doctors prescribe tests of a woman’s hormonal levels, since the cause of deviations may be pituitary gland dysfunction and endocrine diseases.
Increased quantity
If the ovaries have more than 10 follicles, they are called multifollicular. There is also polyfollicularity, that is, when an ultrasound reveals a significant number of vesicles. When their number increases several times, the diagnosis of “polycystic disease” is determined.
If the follicular elements are scattered throughout the periphery of the ovary, they become crowded. This interferes with dominance and all processes that promote conception.
This pathology develops due to stress and goes away after a short time. Treatment of the problem is carried out if:
- multifollicularity is caused by problems with the functioning of the endocrine glands,
- there is sudden weight loss or weight gain,
- there were failures in the choice of oral contraceptives.
An insufficient amount
Follicular insufficiency is caused by hormonal problems. You can find out the problem with an ultrasound on the seventh day. If there are less than 6, then the probability of conception is negligible. Finally, if there are less than 4 of them, then pregnancy practically does not occur.
In some cases, women have no follicles at all. The occurrence of problems with the female body is signaled by the complete absence of menstruation. If they are absent for more than 3 weeks, you need to urgently visit a gynecologist.
Why does the follicle not mature?
It may not ripen due to the following reasons:
- dysfunction of the female reproductive glands,
- dysfunction of the endocrine system,
- tumors of the pituitary gland, hypothalamus,
- inflammatory pathologies of the pelvis,
- stress, nervous instability or depression,
- early onset of menopause.
In these situations, there may be no follicles in the ovaries at all. It often happens that it does not reach sufficient size for an egg to be released.
Folliculometry: definition, possibilities
Folliculometry is an ultrasound diagnosis of the uterus, ovaries and follicles throughout the menstrual cycle.
The study is carried out using a special scanner and sensor , which are able to see the slightest changes in the reproductive system.
Generally speaking, this is a regular ultrasound, which is performed several times during one menstrual cycle.
For the first time, the doctor prescribes a study on days 5-10 of the menstrual cycle, and then individually sets the timing of subsequent diagnostics.
The intervals between procedures are 2-3 days. The final decision on this issue is made by the doctor. It happens that ultrasound is performed only before the period of ovulation or exclusively after it.
Folliculometry is a highly informative diagnostic that can answer many questions.
Carried out in order to:
- Analyze the size of the follicles.
- Record the presence or absence of ovulation.
- Assess the function of the reproductive system.
- Choose the right day to conceive.
- Monitor the condition of functional cysts, as well as other benign neoplasms (fibroids).
- Monitor treatment.
- Analyze the regularity of menstruation.
- Examine endometrial growth.
- Calculate the size of the corpus luteum, starting from the period of ovulation.
- Diagnose infertility.
The possibilities of folliculometry are quite extensive. It all depends on what goal the gynecologist sets for carrying it out. Most often, such a procedure is needed to understand whether ovulation occurred in a certain menstrual cycle and whether it needs to be stimulated with medication.
As a result, it turns out that the dimensions of the “Graafian bubble” are constantly changing. Its diameter directly depends on the day of the menstrual cycle. In the first phase it constantly increases by 1-2 mm, and in the second it stops its development and regresses. If the dimensions of the capsule do not fit into the standard values, then folliculogenesis is impaired . In this case, a thorough diagnosis is required to identify the cause of the pathology and prescribe treatment.
Women's health largely depends on the supply of follicles in the ovaries. This reserve is called ovarian reserve, and it is what limits the reproductive period of a woman’s life. As soon as there are no follicles left in the ovaries ready for maturation, menopause occurs.
Follicle growth chart - size by day
The pattern of its growth can be clearly presented in the form of a table.
| Cycle day | Quantity and characteristics |
| From 1 to 4 | Several follicles develop, each no larger than 4 mm in size. |
| 5 | Uniform development with atresia of several follicles. |
| 7 | The dominant follicle is determined. All others are completely reduced. |
| 8 | 12 mm |
| 9 | 14 mm |
| 10 | 16 mm |
| 11 | 18 mm |
| 12 | 20 mm |
| 13 | 22 mm |
| 14 | 24 mm. At this stage, ovulation occurs. |
Stages of development
During its development, the follicle goes through several stages (phases).
Early phase
Several follicles are growing. After one of them (dominant) reaches 24 mm in diameter, ovulation occurs.
Luteal phase
The period between ovulation and the start of a new cycle is called the luteal phase (or corpus luteum phase). After the graafian bubble bursts, it begins to accumulate fats and pigments. This is how the corpus luteum develops. It produces progesterone, androgens, esradiol.
These substances activate the maturation of the endometrium. The uterus is preparing for the implantation of a fertilized oocyte. If pregnancy occurs, the corpus luteum continues to secrete progesterone until the placenta reaches a certain size and begins to produce it itself.
If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum is destroyed. The levels of estrogen and progesterone gradually decrease, which contributes to the start of a new monthly cycle.
What does an ultrasound show?
Capsules with eggs can be easily detected on the screen during ultrasound diagnostics from the fifth day of the cycle. In the future, their dimensions increase. On the 7th day of the cycle, you can see which of them is dominant.
Upon examination, empty follicle syndrome can be detected. This means that the ovary is not able to provide the release of the sex gland. Such a woman needs to get rid of infertility.
Ultrasound is completely safe for the body.
FAQ
How many days does a follicle mature?
This process lasts only 9 days (plus or minus one). Provided that the woman’s hormonal levels are stable, ovulation occurs on the 14th day of the cycle.
What could go wrong
With a hormonal disorder, there may be too many follicles in the ovary or, conversely, too few. Sometimes there is no sex gland at all.
All these phenomena negatively affect a woman’s reproductive function.
If the size does not correspond to the standards
The shrinkage of the follicle on the day of ovulation leads to the fact that the egg cannot be released from it. The woman will not be able to get pregnant. An increase in the Graafian vesicle indicates a high probability of a cystic process. It also has a negative effect on conception.
If the follicle does not burst
In this case, they talk about its persistence. This phenomenon is considered pathological and requires correction.
Factors determining cell quality
Consistently and universally, what affects egg quality is related to age. Quality cannot be determined by examining the germ cells, measuring their susceptibility to fertilization by sperm.
Since they are with a woman from the moment of birth, they are exposed to various kinds of stress, this is inevitable. Diseases, anatomical and gynecological problems, stress, toxins, free radicals - these are the notable factors that affect the quality of eggs.
They can lead to small errors in DNA called chromosomal abnormalities.
Damaged DNA cannot be cured medically. If a cell is abnormal, then it can no longer be improved. The quality of the germ cell is genetically determined as euploid and aneuploid, and with age the percentage of aneuploid gametes increases more and more. The abnormal units usually do not fertilize or implant in the uterus, but in rare cases they can lead to miscarriage or genetic disorders such as Down syndrome.
Ovarian reserve gradually decreases with age. Decreased ovarian reserve is characterized by abnormally low androgen levels, resulting in the production of poor quality eggs. The sooner effective treatment begins, the greater the chances of increasing their quality and maintaining their quantity, which is associated with greater chances of pregnancy.
Important! Dehydroepiandrosterone has demonstrated remarkable results as an innovative infertility treatment for women with reduced ovarian reserve. Androgen, which is converted into testosterone and estradiol in the body, improving the environment for maturation.