Retinal pigmentary abiotrophy is a rare ophthalmological abnormality that affects one in five thousand people. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in male patients. The deviation develops regardless of age. Dystrophy is characterized by individual symptoms for each form of the disease. Sometimes at an early stage the disease does not manifest itself in any way and a person learns about the anomaly when a “veil” covers the eyes.
Description
Retinal pigment abiotrophy refers to pathologies that are characterized by the presence of a genetic predisposition. In most cases, at the initial stage, the disease occurs without pronounced symptoms. A distinctive feature of the disease is that it can progress over several years and ultimately lead to complete loss of vision.
Retinal abiotrophy can be diagnosed at an early age. In adults, the pathology in the future leads to the appearance of cataracts or glaucoma. The maximum effect of therapy is achieved in children.
Diagnosis of the disease
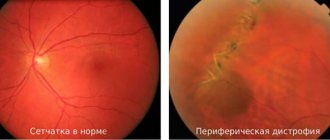
In most cases, the disease is detected during a routine examination by an ophthalmologist, when checking the quality of vision and the width of its fields. A specialist examines the bottom of the eyeball to identify pathologies associated with retinal diseases.
One of these pathologies may be the formation of bone bodies of receptor sites that are subject to dystrophic destruction. In addition, the disease can be diagnosed based on the size of the retinal arteries and the transparency of the vitreous. In most cases, after finding the first symptoms, a competent specialist sends the patient for additional research. EPI of the eyeball helps to most reliably assess the functioning of the retina.
Usually the lesion affects both eyes at once, and the first symptoms of the disease can be detected already in childhood
There are also special tests that can be used to evaluate the performance of individual photoreceptors. Thus, to evaluate the performance of rods, a technique is used to identify the adaptation of the organs of vision to darkness.
When a patient is diagnosed with retinal pigmentary abiotrophy, the doctor requires an examination of the next of kin. Since the disease is hereditary, this measure can help diagnose the disease at the earliest stages of development in family members.
Reasons for development
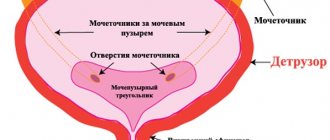
The mechanism of development of retinal degeneration has been thoroughly studied. To understand it, you will have to delve a little into the anatomy of the visual apparatus. The retina contains photoreceptors: cones and rods. Their name is determined by the corresponding form.
| The bulbs are located in the central zone of the shell and are responsible for clarity of vision and processing of light fluxes. The rods occupy the entire surface of the retina and control twilight and peripheral perception. |
When the integrity of the genes responsible for the proper functioning of the shell is violated, degeneration of the outer surface begins. This is where the photoreceptors are concentrated. Damage to the rods and cones can take fifteen to twenty years.
Total destruction of receptors is the main cause of the development of a pathology called retinal pigmentary degeneration.
Symptoms of retinal abiotrophy
In a disease such as retinal abiotrophy, the symptoms are quite variable due to the large number of different mutations that lead to the development of this pathology. But at the same time, between the different variants of dystrophy within the same group (peripheral, central or generalized abiotrophies) there are a number of similar manifestations.
- Central retinal abiotrophies are characterized by predominant damage to cones, the concentration of which is highest in the area of the macula - therefore they are also called macular degenerations. A sharp decrease in visual acuity comes to the fore, color perception is impaired, and with the complete destruction of photoreceptors in the center of the fundus, a central scotoma develops. If the pathological process does not spread to the peripheral areas of the retina, then peripheral and twilight vision are slightly affected. In forms of abiotrophy, characterized by focal damage to photoreceptors, blind spots develop in the visual field. In particularly severe forms, atrophy of the optic nerve fibers and complete blindness may occur.
- Peripheral abiotrophies of the retina (pigmentary dystrophy, white spot abiotrophy) begin with a predominant lesion of rods, so one of the first symptoms of the disease will be hemeralopia. With the progression of the pathology, with further destruction of the rods, a decrease in night vision can develop into its complete loss - nyctalopia. Peripheral vision is impaired, a concentric scotoma occurs, after which the field of vision narrows so much that it becomes “tubular”. With white spot abiotrophy of the retina, more severe disorders most often do not develop, daytime vision and color perception remain unchanged. In some cases of pigmentary dystrophy, cones are also involved in the pathological process, which leads to a decrease in daytime vision, a decrease in its acuity and sometimes complete blindness. The course of the disease can take decades, although transient and juvenile forms also occur.
The complete form of congenital stationary night blindness is characterized by severe nyctalopia with preservation of daytime vision and color perception. In this case, the disease does not progress. Symptoms of an incomplete form of VSNS are moderate hemeralopia, decreased visual acuity, impaired color perception, and difficulty adapting to low light levels.
Symptoms
The main danger of the disease is that for a long time it does not manifest itself in any way. However, as the disease progresses, patients begin to complain of a sharp decrease in visual acuity at dusk (“night blindness”). There are some difficulties with orientation in space.
The majority of patients suffering from retinal dystrophy are children. This leads to difficulties in diagnosing the deviation. Because parents may not pay attention to some oddities in the behavior of a junior student. The baby himself, in turn, does not complain about the discomfort. This leads to the fact that the child does not receive competent and timely treatment. As a result, the pathology continues to progress.
At later stages, approximately three years after the onset of the destructive process, the patient experiences peripheral retinal degeneration. The deviation is accompanied by a narrowing of the optical fields and a decrease in lateral vision. This causes clouding of the vitreous and can lead to the development of glaucoma.
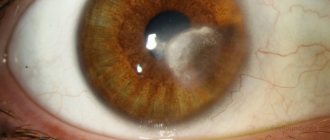
Later, characteristic pigmentation appears around the fundus. It can be seen during ophthalmoscopy. At first, bone bodies are concentrated on the surface in small quantities, but over time their concentration increases. The rings increase in size, and foci of pigmentation move from the periphery to the center. There is a narrowing of the blood vessels, as a result, the damaged areas of the membrane become white.
| The anomaly is also characterized by impaired color perception and a decrease in visual acuity. Similar symptoms occur in the last stage due to the complete degradation of rods and cones. Further progression leads to blindness. |
Abiotrophy of the retina of the eyeball
The first mention of this disease was published in 1857 by the Dutch scientist Francis Donders. He described the symptoms of the disease and also gave the disease a name - retinitis pigmentosa. Subsequently, the disease changed its name several times as researchers found more suitable terms.
The photoreceptors of the eyeball contain two types of cells: cones and rods. These cells got their name due to their appearance. Cones are responsible for the quality of the central area of vision and the perception of the entire color spectrum. They are localized in the central region of the retina of the eyeball. In contrast, rods are located over the entire surface of the retina, but their main clusters are located away from the center. They are responsible for the expansion of visual fields, as well as for high-quality vision in the twilight hours.
Abiotrophy of the retina is a degeneration of a pigmentary nature, which is inherited and is a dystrophic disease
Pathology or mutation of certain genes in the body that are responsible for the circulation of nutrients and the functionality of the retina causes the onset of deformation of the outer part of the retina. The disease spreads at a slow pace, and its growth from the outskirts to the central region of the retina can take decades.
In ninety percent of cases, the disease affects two organs of vision at once. The main symptoms of the disease may appear immediately after birth. The gradual development of the disease leads to the fact that by the end of adolescence the quality of vision begins to gradually deteriorate. There are other, more rare subtypes of the disease, when the disease begins to develop in adulthood, affecting a certain part of the retina or only one eye. Tapetoretinal abiotrophy of the retina can cause the development of the following diseases:
- glaucoma;
- swelling of the central part of the retina;
- cataract;
- vitreous opacification.
Retinal abiotrophy is a disease that is extremely rare and in most cases is caused by a genetic predisposition.
The main damage occurs to the rods located in the retina
Diagnostics
It is extremely difficult to recognize the disease in children under six years of age. Only when they experience disorientation in space can doctors judge that tapetoretinal retinal abiotrophy is developing. Unfortunately, at this point the disease causes a serious blow to the health of the visual system.
To make a final diagnosis, establish peripheral vision and determine visual acuity, a number of procedures are prescribed. The doctor examines the fundus of the eye to detect bone bodies and determine their number.
If doubt remains about the diagnosis, an electrophysiological study is prescribed. With its help, doctors assess the patient’s ability to navigate space in low light conditions. Return to contents
Diagnostic technique
Diagnosis in the early stages can be quite difficult. The presence of abiotrophy can be determined only after 6 years. It is during this period that the symptom of “night blindness” may occur. During the examination, specialists will check your peripheral vision. Doctors will also check the fundus of the eye, since this is where changes in the retina will be noticeable. The bone bodies that affect the areas of dystrophic lesions will undergo the most changes.
In order for the diagnosis to be correct, it is also necessary to conduct an electrophysiological examination, which can provide completely objective data. The patient's ability to remain in complete darkness will then be checked. Only after collecting all the necessary data will a diagnosis be made.
Treatment of pigmentary dystrophy
Treatment of the disease begins with the selection of medications. Their main purpose is to normalize blood circulation and metabolism of nutrients in the retina and blood vessels.
Most often, doctors prescribe the following medications:
- "Emoxipin". The medicine is aimed at correcting microcirculation in the body.
- "Taufon". Eye drops that stimulate restoration processes in the tissues of the visual apparatus.
- "Retinalamine." The medication is prescribed for retinal degeneration. Has regenerative properties.
- A nicotinic acid. The vitamin stimulates metabolism and normalizes blood circulation.
- No-shpa with papaverine. An antispasmodic agent aimed at reducing pressure in blood vessels.
The drugs are prescribed in the form of eye drops, tablets or injections. In addition to medications, doctors often resort to physical therapy. The procedures stimulate regenerative processes in the retina and are able to activate the functionality of the receptors.
Some of the most popular methods are: exposure to electrical impulses, magnetic resonance and ozone therapy. If, as a result of pathological processes, the integrity of the choroid has been compromised, it is worth considering surgical intervention.
| With the help of surgery, doctors normalize blood circulation in the retina. Sometimes an eyeball tissue transplant is required to achieve a positive result. |
Some doctors recommend fighting the disease with the help of photostimulation devices. Their work is based on causing excitation in certain areas of the eyeball and slowing down the progression of the disease.
The radiation that the device emits stimulates blood circulation and normalizes metabolism. The procedure will help get rid of retinal swelling and strengthen it.
In addition, the course of therapy includes:
- Taking medications aimed at increasing blood circulation (Nigexin, Mildronate, Undevit).
- The use of eye drops that improve the nutrition of the retina.
- Carrying out electrophoresis to eliminate inflammation and block pathological processes in the retina.
- A course of injections that are administered under the conjunctiva (Thrombolitin, liquid aloe). Helps control blood clotting.
- Taking biogenic stimulants that enhance the therapeutic effect of medications.
Sidorenko glasses have a preventive effect. Surgeons can implant special lenses into the patient that help them navigate in the dark. Return to contents
Treatment of pathology
There are no specific methods of treating pigmentary abiotrophy; patients are prescribed supportive treatment that reduces the progression of the pathology. For this purpose, drugs are used that improve nutrition and blood circulation in tissues, vitamins A and E, peptide bioregulators, and vasodilators. Medicines slow down the destruction of the retina and the development of visual impairments, increase the regenerative properties of the eyes, and prevent serious complications.
Physiotherapeutic methods, laser treatment, and microsurgery are used in combination with conservative treatment. In some countries, special retinal prostheses are used to treat pathology, which are implanted into the eyes, improve vision and prevent the development of complete blindness. The success of treatment largely depends on timely diagnosis of the disease. Since many forms of pathology are inherited with a 100% probability, children with a family history should be monitored by an ophthalmologist from the moment of birth.
REFERENCE! Most innovative treatments for retinal pigmentary abiotrophy are at the development and testing stage. The most promising direction is genetic engineering, which allows you to restore damaged genes and eliminate the cause of the disease.
Prevention
If retinal dystrophy is detected in the later stages, it cannot be completely cured. In most cases, the outcome of therapy is disappointing. Unfortunately, in medicine there are still no means and techniques that can overcome the disease at any stage.
To minimize the risk of developing an anomaly, it is worth reviewing your own diet. Doctors are confident that eating a healthy and balanced diet is the best prevention. The body receives the necessary substances and vitamins, which guarantees the proper functioning of the visual apparatus.
| Patients sometimes pay attention to the disease too late, since it progresses sluggishly. Typically, a visit to the ophthalmologist occurs after loss of peripheral vision. For this reason, it is extremely important to undergo a preventive examination once a year. After all, only a doctor can notice the deviation and prevent the progression of the pathology. |
Treatment
If you have retinal pigmentary degeneration, treatment will not be possible in this case. Today there is no method that would help get rid of this disease. Today, medicine can only slow down development through the use of special vitamins and medications.
In addition to tablets, drops can also be used, which include Taufon and other regulators that will have a peptide base. Today, to combat such diseases, physiotherapeutic methods can also be used, which can dramatically increase blood flow to the eyeball. If you want to carry out prevention at home, then you can also use Sidorenko glasses. You can see these glasses in the photo below.
Sidorenko glasses for the prevention of abiotrophy at home
Medicine does not stand still and therefore there is no need to be upset. Doctors are constantly studying and applying new methods and therefore we hope that significant results will be seen in the near future. The methods that were used previously were considered bad, since they could only delay development for a certain time. Now, thanks to the use of modern methods, it is possible not only to stop the disease, but also to achieve a significant improvement in vision.
During the procedure, remember that such a process is considered quite lengthy and labor-intensive. The entire treatment process must be carried out only under the attention of specialists. Doctors must have significant experience in carrying out such treatment.
Treatment of the disease
Pigmentary dystrophy should be treated comprehensively. To get rid of age spots, the doctor prescribes the patient a complex of various vitamins and medications to nourish the retinal pigment epithelium. In addition to tablets and injections, drops are also used. Treatment is aimed at restoring the natural functionality of the retina. Additionally, therapeutic methods are used that are aimed at improving the blood supply to the eye. This can really slow down the pathological process, and even start remission.
For home use, “Sidorenko glasses” were developed - a simulator for the eye muscles, which combines several methods of influence and is especially effective in the initial stages.
Features in children
In the early stages, retinal pigmentary abiotrophy in children is especially difficult to diagnose, and before the age of 6 it is almost impossible. Later, the presence of visual dystrophy can be detected by noticing the child’s difficulties with orientation in space at night. Children do not do their usual activities at such times and stop playing. Without seeing the periphery of the visual field, the child can bump into surrounding objects, since only the center of the eye works efficiently. If a child is diagnosed with a pigment spot on the eye, experts recommend direct relatives to be examined by a doctor in order to identify eye dystrophy at an early stage and prescribe treatment.
Pediatric retinal pigmentary dystrophy requires the selection of implants.
It is necessary to recall radically new experimental techniques for influencing the pigment layer of the retina, in particular, gene therapy. With its help, you can restore damaged genes, which means you can gain hope for improved vision. Specific eye implants have also been developed. Their task is to work similarly to the natural retina. And indeed, people with such implants are gradually beginning to navigate more freely not only within the walls of a room, but also on the street.
Folk remedies
As an addition to complex treatment, you can also use traditional methods of restoring health:
- Goat milk. Drops made from milk will help restore the normal functionality of the eye lens. It is mixed with water in a 1:1 ratio. For 1-2 weeks, you need to instill the liquid into both eyes, then apply a dark bandage to your eyelids for 30 minutes and lie quietly. This will help relax your eyes.
- Cumin decoction. To prepare and use this folk medicine, you will need one spoon of cumin seeds and 200 g of hot water. Warm the seeds over low heat for 5 minutes, then add a pinch of cornflower flowers and leave for another 5 minutes. The finished decoction is filtered and a couple of drops are instilled into both eyes twice a day.
- A decoction can be prepared using pine needles, onion peels and rose hips (ratio 5:2:2). Dry substances should be crushed and filled with clean filtered water (1 l). After boiling the broth for 10 minutes, it is cooled and it is already possible to consume it. It is recommended to drink half a liter per day for a month.
Important: under no circumstances should you self-treat ophthalmic pathologies. This may result in aggravation of the disease process. You should always seek advice from a suitably qualified professional.
Folk remedies for retinal pigmentary dystrophy are not effective, but serve as a good addition to the main therapy.
Retinal pigmentary dystrophy is one of the most complex eye pathologies. It progresses over many years. The difficulty is that at the initial stage this disease is difficult to recognize, especially if there is a genetic predisposition to such a pathology. Therefore, at the first signs of vision abnormalities, it is important to consult a doctor in order to begin effective treatment as early as possible.
Symptoms
The disease is characterized by a whole complex of symptoms. Many of them do not appear in childhood, since in some forms of abiotrophy the pathology progresses very slowly.
IMPORTANT! If there is a sharp deterioration in vision at any age, it is necessary to immediately undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist in order to prevent further development of disorders.
With abiotrophy, patients experience:
- night blindness (hemeralopia) - develops due to damage to the rods. Patients in poor lighting lose the ability to orient themselves in space and cannot move safely in the evenings and at night due to their poor vision. The first deterioration in vision at night can be noticed even before pigmentary abiotrophy gives full symptoms of the disease;
- rapid progression of the disease - develops due to rapid damage to the retinal rods from the periphery to the center. Due to the reduced field of vision, patients may eventually develop near-total blindness. Only a small space remains, like a tube through which a limited space is visible;
- decreased visual acuity, both color and black and white - usually this symptom manifests itself against the background of significant pathological changes, which indicate a late stage of development of the pathology. The symptom occurs due to damage not only to the rods, but also to the cones located in the central zone. Usually, in the presence of this symptom, subsequent rapid progression of the pathology occurs;
- fatigue – patients cannot read or watch TV for a long time, because their eyes get tired quickly.
- Most of the above signs of pathology occur in a person over the age of twenty. The development of individual symptoms is possible in childhood. If the first signs of deterioration in a child’s vision occur, do not hesitate; it is better to consult a doctor promptly for advice.
Prevention and prognosis
Since the development of pigmentary dystrophy is caused by genetic disorders, it is impossible to prevent the disease. To detect pathology, in the first stages of development it is recommended to undergo regular medical examinations, especially if there are people in the family with such a disease. To strengthen the retina and provide the eyeballs with the necessary substances, the patient must eat a balanced diet and give up bad habits. When diagnosing an advanced form of dystrophy, the prognosis is unfavorable, and there is a high probability of blindness.
Causes and course of retinal pigmentary degeneration
Why retinal dystrophy occurs has not yet been fully studied. Ophthalmologists are considering several versions. Retinal pigmentary degeneration was named so because of changes that occur in the fundus of the eye, causing pigment spots to appear on the eyes. They are formed along the vessels located on the retina of the eye and come in different sizes and shapes. Gradually, the pigment epithelium of the retina becomes discolored, as a result of which the fundus of the eye becomes visible like a web of orange-red vessels.
Over time, the disease only progresses, and age spots in the eye spread more and more. Densely dotting the retina, they move into the central part of the eye and appear in the iris. The vessels become very narrow and practically invisible, and the nerve disc turns pale, later atrophying. Retinal pigmentary degeneration usually affects both eyes at the same time.
Many people are discussing that the pigment epithelium is formed against the background of diseases such as endocrine pathologies and vitamin deficiency, in particular, with a significant lack of vitamin A. Some experts are inclined to believe that infections and toxins have a negative impact. It is believed that retinal dystrophy can be inherited from relatives.
Retinal pigmentary dystrophy is dangerous for the patient's vision loss.
If the disease manifests itself at an early age, then by the age of 25 the patient may lose his ability to work. But there are exceptions here too. Sometimes dystrophy is observed only in one eye, or only a separate fragment of the retina is damaged. People who have pigment spots in their eyes are at risk for other ophthalmological diseases: cataracts, glaucoma, lens opacification.