Colitis is a multifactorial disease of the large intestine, manifested by an inflammatory reaction of its tissues and the appearance of various symptoms of digestive disorders. It occurs in all age groups (from newborns to the elderly), regardless of gender.
The incidence rate of this pathology is high, so the question: what is intestinal colitis, symptoms and treatment in adults at home, worries many.
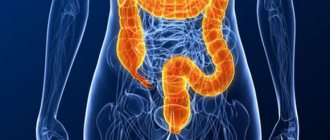
The large intestine is part of the digestive tract. It begins at the point of transition from the small intestine to the large intestine in the area of the ileocecal angle.
The following sections are distinguished: transverse colon, cecum, sigmoid and rectum, which ends in the anus. The glands of the mucous membrane (inner) produce very few digestive juices, but a lot of mucus. Water is absorbed in this section of the gastrointestinal tract. Under the influence of beneficial bacteria, fiber is broken down and vitamins are produced (K, group B, D, E, PP). The special structure (extensions - haustra), active peristalsis and mucus contribute to the formation of feces from undigested food debris and bacteria.
What drugs to use for colitis
Medicines are selected by a doctor; self-medication is not recommended, as this can lead to serious complications. The choice of drug is determined by certain factors:
- To eliminate abdominal distension and flatulence, medications that contain activated carbon, for example, Polysorb, as well as fennel extract, are used.
- Restoring microflora in the intestines is the task of biologically active additives.
- If there is difficulty in emptying, a laxative is used.
- When a person has an intestinal disorder, he is recommended to take antidiarrheal drugs.
- To reduce the lesion and relieve the inflammatory process, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs.
Complex therapy helps eliminate problems and return to your previous lifestyle.
What kind of colitis can be treated at home?
Acute colitis is dangerous due to its complications. In the absence of timely assistance, the patient may develop heart pathologies, blood poisoning, and anemia. With frequent and prolonged diarrhea, the human body loses a lot of fluid, so dehydration quickly develops. All these conditions can lead to irreversible changes, so severe forms of colitis are treated in a hospital setting.
Important! Therapy with traditional methods, as well as home treatment, are allowed only for chronic intestinal colitis. During periods of exacerbation, the patient requires drug treatment to relieve inflammatory processes and destroy bacterial flora (in the case of infectious colitis caused by pathogenic bacteria).
To choose the right treatment, it is important to determine the type of disease. To do this, you need to know how the types of colitis differ and how they manifest themselves.
Severity of colitis
Eliminating the cause of the disease
The initial and one of the main stages of diagnosis is the collection of anamnesis. The resulting data helps the doctor determine the likely cause of colitis. Naturally, without eliminating this factor, further treatment of colon colitis simply does not make sense.
If the cause is helminthic infestations, then appropriate medications are prescribed. Usually prescribed are albendazole or vormil, azinox, decaris. These drugs have the widest possible spectrum of action against protozoan parasites.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of colitis involves the following manipulations:
- Anamnesis collection, analysis of complaints;
- General examination, palpation of the abdomen (areas of spasmodic intestines, dense and rumbling loops, pain are determined);
- Laboratory examination of stool (mucus, fiber, leukocytes are determined);
- Analysis of stool for dysbacteriosis (predominance of pathogenic flora);
- Detection of the causative agent of acute colitis in feces;
- Irrigoscopy - radiography of the intestines, with a contrast agent;
- Colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy (insertion of an endoscope to examine the mucous membrane);
- Digital examination of the rectum.
Article for you:
What is schizophrenia and how does it manifest in women?
If there is a concomitant pathology, consultation with related specialists (neurologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist) is required.
Antimicrobials
The prescription of antibiotics for intestinal colitis is very controversial; most doctors have their own opinion on this matter. Sometimes such components eliminate beneficial microorganisms, causing dysbacteriosis and aggravating the course of colitis. The intestinal microflora is affected, and treatment is delayed. But it happens that without the prescription of antibacterial agents, recovery does not occur.
If spastic colitis is diagnosed, then it is better to treat it without antimicrobial drugs. In rare situations, antibiotics may be prescribed by a medical professional.
When a harmful environment spreads quickly, you have to resort to antibacterial drugs. They are used strictly according to the scheme prescribed by the gastroenterologist. Depending on the patient’s condition and the stage of the disease, the medical specialist selects the appropriate treatment.
These may be drugs from the sulfonamide group, for example, Fthalazol or Sulgin. Their use is carried out strictly as prescribed by a gastroenterologist according to the following scheme:
- For intensive treatment of the inflammatory process, the medicine is used six times a day. The duration of therapy is determined by the severity of the disease.
- The second stage is the suppression of residual pathogens. It lasts two days, application is carried out four times a day.
- The third stage is consolidation of positive action. Two days are allotted for it, with the use of medications three times a day.
Based on the results of a study of the patient’s microflora, a medical specialist can recommend an antimicrobial drug, the action of which is aimed at eliminating a specific type of pathogen.
Antibacterial drugs with hydroxyquinoline (Intestopan and Enteroseptol) are also used to eliminate colitis. These are more severe drugs, their use is justified when pathogens have developed resistance to many antibiotics. The treatment regimen depends on the stage and severity of the disease. The duration of treatment with medications that contain hydroxyquinoline is approximately ten days.
Colitis - what is it?
Intestinal colitis is an inflammatory lesion of the colon mucosa. Colitis is often combined with enteritis, gastritis, damage to the bile ducts or pancreas.
The disease occurs acutely (from one to several weeks) with severe symptoms or chronically (develops over months, years) with periodic exacerbations. In this case, inflammation is combined with impaired blood circulation in the walls of the colon and its irreversible changes at the microscopic level (atrophy) with a long chronic course.
The causes of colitis are very diverse:
- infectious factor - dysentery, salmonellosis, viral infections, fungus;
- poor nutrition, alcohol abuse;
- circulatory disorders (a common cause of colitis in the elderly);
- taking antibiotics and dysbacteriosis;
- long-term use of laxatives, regular cleansing enemas;
- inflammatory pathology of the upper gastrointestinal tract;
- food allergies and helminthic infestation;
- burdened heredity;
- various poisonings;
- stress, insufficient rest and excessive physical activity.
Intestinal colitis in adults is often triggered by the negative impact of several factors. Sometimes, for example, with nonspecific ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, the cause of the disease cannot be determined at all.
Antibacterial therapy
Some doctors are ambivalent about prescribing antibiotics during anti-inflammatory therapy for intestinal colitis. The fact is that this disease is almost always accompanied by dysbacteriosis, and antibacterial drugs only worsen it. But in many cases you simply cannot do without them.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Q1pPfkczKQ
The course of drug treatment for colitis includes the administration of sulfonamides, such as sulgin and phthalazole. They need to be used according to a special scheme: in the first days, 1g six times a day, then in the same dosage four times for two days, and in the last days - three times. Narrow-spectrum antibacterial drugs are very effective, which selectively affect pathogenic intestinal microflora. These are chloramphenicol, terramycin, polymyxin, etc.
Treatment of intestinal colitis with medications: tablets, drugs
UC medicines tablets treatment
Colitis treatment. How to treat intestinal colitis with folk remedies.
Treatment of the intestines with tablets: anti-inflammatory drugs, suppositories
Antibacterial drugs that contain hydroxyquinoline deserve special attention. These are enteroseptol, intestopan, mexaza. They act on bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics and sulfonamides. They are usually prescribed in a course of 10–12 days, 2 g per day. The dosage may vary depending on the patient's condition and his or her tolerance to the medication.
Intestinal colitis: symptoms, treatment, complications
Intestinal colitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the colon, which occurs chronically or acutely. It often occurs in women 20-60 years old and men 40-60 years old. Symptoms of intestinal colitis in children are less common and occur due to an unformed protective barrier of the organ mucosa.
There is an opinion that colitis occurs in every 2nd patient with a disease of the digestive system. Its appearance is promoted by inflammatory diseases of the anorectal area, consumption of foods low in fiber and a decrease in overall resistance.
Chronic intestinal colitis often develops against the background of other diseases - enteritis and gastritis.
Every year the incidence rate of the colon mucosa is growing. This is due to the appearance on store shelves of a large amount of food “garbage” - products containing dyes, flavor enhancers, stabilizers and preservatives. The intestines do not know how to cope with such food, as a result of which all kinds of diseases of the digestive system appear.
This is an inflammation of the colon due to damage to the intestine by protozoan bacteria that enter its mucosa. There are many reasons that lead to such a situation. As a result, the walls of the colon swell and it begins to contract incorrectly, which leads to the appearance of symptoms. Most often, a chronic form of the disease develops.
In medicine, nonspecific ulcerative colitis of the intestine is distinguished, the etiology of which remains unclear to this day. This is a very serious disease that affects every 35-100 people per 100,000 inhabitants. One of its varieties is considered focal intestinal colitis. What kind of disease is this? It is characterized by well-defined areas of the inflammatory process, which are localized in one place in the colon.
Despite the fact that the etiology of nonspecific ulcerative colitis of the intestine remains a mystery, three reasons for the development of the disease are being considered today:
- The entry of viruses and bacteria into the intestinal mucosa.
- Genetic predisposition. Scientists have been unable to prove the role of genetic factors alone in the development of ulcerative colitis. There are other reasons for its appearance.
- Environmental factors - strict diets, smoking, taking oral contraceptives.
The disease can be diagnosed fairly quickly. Clinically, it is manifested by severe abdominal pain, frequent visits to the toilet, and the presence of mucus and blood in the stool.
There is such a thing as psychosomatics of intestinal colitis. Over the course of two years, four studies were conducted (Wirsching, Stierlin, Wirsching, Uexkull), which proved that patients with colitis have high family cohesion. They leave their parents' house late and maintain mutually beneficial, useful connections with them. In patients with ulcerative colitis of the intestine, classic personality traits are revealed, which, according to psychologists, are the basis for the development of the disease. These patients experience:
- Strong desire for care and dependence.
- High sensitivity to personal failures.
- Low self-esteem.
Therefore, if proper nutrition does not help with intestinal colitis, it may be worth seeking the help of a psychotherapist who will help you understand yourself.
There are two forms of the disease: acute and chronic. Acute intestinal colitis is characterized by pronounced symptoms that occur in parallel with gastritis of the stomach and inflammation of the small intestine. With this disease, the mucous membrane of the digestive organ becomes inflamed, after which it ceases to function. Acute colitis occurs in adolescents and people aged 55-70 years. Elderly people have a weakened digestive system, and young people are more likely to come into contact with a variety of infections. All this leads to the development of the disease.
The chronic form is manifested by the fading of signs of acute colitis, which are activated from time to time and remind of themselves. Occurs in patients of any age. The main importance is a timely analysis of symptoms, in rare cases, colonoscopy with a biopsy of the mucous membrane and sigmoidoscopy. It is difficult to say how chronic intestinal colitis manifests itself in different patients. In some cases, the course of the disease is asymptomatic and long-lasting, while in others it is rapidly progressive with remissions and exacerbations. If chronic intestinal colitis is not treated in a timely manner, atrophic changes begin to develop in the intestinal wall. Possible complications such as:
- Adhesive process.
- Narrowing of the intestinal lumen.
- Intestinal bleeding.
- Formation of ulcers.
The main risk factors for the development of chronic colitis include chronic gastrointestinal diseases, damage to the intestinal tract by protozoan bacteria and previous intestinal infections.
Depending on the etiology of the disease, the following types of colitis are distinguished:
- Ulcerative is a chronic, long-term disease that leads to inflammation of the rectum and colon. Symptoms periodically subside or, on the contrary, worsen. Among the striking signs it is worth highlighting: bleeding from the rectum, diarrhea, severe pain in the lower abdomen and passage of mucus. Currently, when asked whether ulcerative colitis of the intestine can be cured forever, doctors give a disappointing answer. It is impossible to completely get rid of the disease. All that remains is to follow the doctor’s recommendations and proper nutrition.
- Infectious - appears due to pathogenic microflora, which is of three types: opportunistic, banal and specific. The first includes E. coli, the second staphylococci and streptococci, the third dysenteric colitis. In some cases, infectious intestinal colitis is a complication of syphilis and tuberculosis. In patients with weak immune systems, the disease can be caused by fungi.
- Ischemic - appears due to a transient decrease in blood flow in the colon. Most often found in older people (60+). Doctors call atherosclerosis of small vessels one of the reasons for the development of ischemic intestinal colitis. In addition, the disease can develop as a result of surgical treatment of an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
- Toxic – the cause of the disease is poisoning with drugs and poisons. If treatment is untimely, dystrophy and inflammation of the colon, small intestine, and stomach tissues are observed. Often, toxic colitis develops acutely within 2 days from the moment the patient comes into contact with a toxic substance.
- Radiation disease is a disease caused by exposure of the patient’s body to ionizing radiation.
Depending on where exactly the colitis is located, it comes in several types:
- Typhlitis - indicates inflammatory processes occurring in the mucous membrane of the cecum. The disease appears due to disturbances in its emptying, atypical fermentation or rotting, as well as prolonged retention of feces.
- Pancolitis is inflammation of the colon along its entire length. Characteristic symptoms: bloating, diarrhea, rumbling in the intestines, severe abdominal pain, frequent bowel movements.
- Transversitis - the transverse colon is involved in inflammation. The disease is indicated by dyspepsia, constipation, diarrhea, pain in the upper abdomen and near the navel. For the purpose of diagnosis, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, colonoscopy, stool analysis, bacterial culture of stool and other methods are used.
- Sigmoiditis is an inflammatory process in the sigmoid colon. The disease is not accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the intestinal epithelium and occurs in parallel with the pathological process of its surface layers.
- Proctitis is a colitis in which the sigmoid colon or mucous membranes of the rectum become inflamed. Appears due to an advanced acute disease or the presence of other diseases - gonorrhea, syphilis, tuberculosis.
Gastroenterologists and coloproctologists deal with the symptoms and treatment of intestinal colitis in adults. If the first signs of the disease appear, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor, because untimely treatment is fraught with serious consequences.
The main cause of colitis is the penetration of infection into the intestinal mucosa. Among other factors contributing to the onset of the disease, doctors include:
- Improper eating behavior.
- Starvation.
- Self-medication, use of antibiotics and other medications that disrupt the acid-base balance of the intestinal environment.
- Drinking alcohol in large quantities.
- Stress.
- Overeating.
- Overwork.
- Consumption of low-quality products that contain stabilizers, preservatives and other chemicals.
- Inflammatory and infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Also, one of the reasons for the development of colitis is a person’s genetic predisposition to the disease. In some cases, congenital pathologies are recorded. Symptoms of intestinal colitis in men who do not maintain personal hygiene are more common. This is due to the fact that the infectious agent can enter the intestinal mucosa from the environment.
Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves depending on the location and degree of damage. With chronic colitis the following appear:
- nagging, constant, cutting, severe pain in the rectal area;
- defecation disorder;
- abdominal pain;
- feeling of heaviness;
- flatulence;
- bloating.
Symptoms of intestinal colitis in women often appear after eating. Pain can be provoked by an enema, running, walking, or playing sports.
Catarrhal colitis of the intestine indicates the initial stage of colon disease. It often appears as a result of eating seasonal vegetables and fruits. It is often confused with a classic bowel disorder and does not seek medical attention. In the future, this may lead to chronic disease. Catarrhal colitis of the intestine is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain in the abdominal area;
- general weakness;
- constipation;
- irritability;
- fast fatiguability;
- diarrhea.
In the development of this type of colitis, immunity disorders, intestinal infections, constipation, dysbacteriosis and a lack of essential vitamins and microelements are of primary importance.
Spastic intestinal colitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- alternating spastic diarrhea and constipation;
- a motility disorder of the large intestine, with which patients complain of painful cramps in the lower abdomen;
- blood and mucus in the stool.
Timely diagnosis (coprogram, ultrasound, stool and blood tests) allows you to identify other symptoms of the disease. Among them are swelling and hyperemia of the walls of the colon.
Erosive intestinal colitis is characterized by:
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- severe and sharp pain in the abdomen;
- bleeding.
At this stage of the disease, blood from damaged vessels is found in the stool. Due to damage to the mucosa, any infection can easily enter the circulatory system.
As a result of prolonged inflammation of the colon and lack of treatment, atrophic intestinal colitis appears, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- thinning and stretching of the intestinal walls;
- frequent constipation;
- the appearance of fistulas and ulcers.
Superficial intestinal colitis indicates the presence of a pathological process in the upper layer of the intestinal mucosa. Often it is asymptomatic and does not make itself felt for a long time. Therein lies the danger, since the disease worsens and can lead to consequences.
With intestinal colitis, symptoms in the left side indicate microscopic ischemic inflammation of the colon. Among the signs are discomfort in the abdomen, pain in the abdominal region and in the left hypochondrium, which appear after holding stool and eating food. Pain in the left side may indicate irritable bowel syndrome, in which constipation or diarrhea, a feeling of pressure in the organ, abdominal pain, and bloating are observed.
With intestinal colitis, symptoms in the right side may indicate ulcerative colitis, IBS and Crohn's disease. Most often, patients complain of swelling in the abdomen, cramps, and pain in the navel. Less common are symptoms such as general weakness, weight loss and bloody discharge in the stool.
During diagnosis, the gastroenterologist must exclude the presence of other diseases, including hemorrhoids, atypical appendicitis, enteritis, and cancer. All these diseases have similar symptoms. To determine the signs of intestinal colitis and its treatment, modern diagnostic methods and effective drug therapy are used.
Diagnosis of colitis involves:
- Examination by a doctor, analysis of typical patient complaints.
- Anamnesis collection.
- Physical examination.
- Instrumental diagnostic methods.
- Laboratory research.
- Analysis of feces for helminth eggs.
- Intravenous angiography if ischemic colitis is suspected. Used to visualize the patency of blood vessels that deliver nutrients to the intestines.
Among the instrumental diagnostic methods, irrigoscopy, sigmoidoscopy and endoscopy are most often used. Thanks to them, it is possible to visually monitor the condition of the mucous membrane and determine the type of colitis.
Additional diagnostic methods:
- Urine and blood analysis.
- X-ray and computed tomography.
- Biopsy.
Timely diagnosis of the disease can prevent chronicity of colitis, prevent serious consequences and complications.
Treatment of colitis is most often carried out in the proctology department, less often in special infectious diseases departments of hospitals (if the disease is infectious in nature). Proper nutrition plays an important role in recovery. The doctor prescribes a diet for intestinal colitis with constipation, diarrhea, frequent bowel movements, pain and other symptoms. Drug treatment is also recommended, which involves the use of a number of drugs:
- Painkillers to relieve spasms and pain.
- Antibacterial agents. Used in cases where intestinal inflammation is caused by pathogenic flora.
- Probiotics for the treatment of dysbiosis.
- Saline laxative.
- Intravenous saline infusion.
- Sulfate preparations with antibiotics.
- Alkaline mineral waters.
In case of chronic colitis, constant monitoring by your doctor is mandatory. Such patients need to know what they should not eat if they have intestinal colitis, what diet they should follow, and what tests they should take. They are advised to avoid heavy loads, stress, and take medications to improve immunity and reduce inflammatory processes in the intestines. It is forbidden to consume raw tomatoes for intestinal colitis during an exacerbation, like many other unprocessed vegetables. Taking vitamins and microelements is mandatory. To avoid getting bored with the same dishes, it is recommended to change the menu for ulcerative colitis for a week each time.
Physiotherapy
It is aimed at improving the secretory and motor-evacuation function of the intestine. In the treatment of colitis, physiotherapy methods such as:
- UHF.
- Electrophoresis.
- Ultraviolet irradiation.
- Magnetic therapy.
- Mud applications.
A course of treatment in a sanatorium that specializes in the rehabilitation of patients with gastrointestinal diseases has a good effect.
Operation
Surgery is indicated if drug treatment does not produce a positive result. The operation is performed in only 10% of patients. The surgical method for ischemic colitis is used if blood clots were found in the abdominal aorta or its branches.
If the disease is left to take its course or treatment is not fully completed, this is fraught with the following complications:
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Anemia.
- Dehydration.
- Intoxication.
- Cancer.
- Disorders of intestinal motor function.
- Peritonitis.
- Migraine.
The greatest danger is the chronic form of colitis, which can develop into cancer of the gastrointestinal tract, lead to a septic process and peritonitis in the circulatory system, which can lead to serious complications and even death of the patient. All this can be avoided if you seek medical help in a timely manner, lead a correct lifestyle and do not ignore the symptoms of the disease.
It is better to prevent a disease than to treat it. In the case of intestinal colitis, this is not difficult to do. Basic preventive measures for the disease include:
- Maintain proper nutrition and avoid unhealthy foods.
- Timely treatment of constipation, diarrhea and other diseases indicating intestinal irritation.
- Quitting bad habits, especially alcohol, which increases the permeability of the intestinal wall, promotes the absorption of toxins.
- Avoiding stressful situations and intense physical activity.
- Passing an annual medical examination.
- Compliance with safety rules when working with poisonous and toxic substances.
- Taking medications only as prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication can lead to worsening of the disease and serious complications.
The prognosis for this disease is quite favorable if an accurate diagnosis is established and treatment for colitis is started. In the absence of timely medical treatment, the disease will progress and have more serious consequences. For example, erosive colitis, if treatment is ignored, becomes one of the varieties of ulcerative colitis. If the disease becomes chronic, no one will be able to help the patient. He will have to live with the symptoms of colitis, which will make themselves felt from time to time. In addition, you will have to adhere to a diet for life to avoid exacerbation of the disease.
Rate the material:
- 100
Classification
When eliminating the disease, medical specialists use various medications for intestinal colitis. All of them can be divided into the following types:
- Sulfonamides (“Sulfasalazine”, “Mesacol”). Their influence is aimed at eliminating pests.
- Complex drugs (“Intestopan”, “Mexaza”). They inhibit pathogenic microflora and also contain enzymes.
- Biological medicines with beneficial microorganisms and medicines of the eubiotic class (Bifidumbacterin, Bifiform, Linex). As a rule, they are localized in the intestines, in the form of lacto- and bifidobacteria.
- Medicines that contain enzymes (Pancreatin, Mezim, Festal).
- Medicines from the category of antispasmodics (“No-shpa”, as well as “Papazol” and “Bellasthesin”). These medications effectively neutralize pain.
- Monoclonal antibodies help the body cope with the inflammatory process on its own, giving immune cells the ability to recognize the problem and eliminate it.
Antispasmodic drugs
Medicines for any colitis included in this group relieve muscle spasms of internal organs. Basically, patients are prescribed myolytics, which reduce tone and slow down the contractions of the affected organ. The doctor decides how to treat colitis independently.
"No-Shpa"
A highly active myotropic agent, characterized by safety and excellent tolerability. It has good bioavailability (up to 65%), the maximum amount in the blood is determined an hour after use. This ensures effective elimination of muscle spasm of the intestine and relief of pain. In the remission stage, 2 pills are allowed to be taken in the morning and in the evening. During an exacerbation, the frequency of use can be increased up to 3 times with the same single dosage. The maximum course is three days, however, in rare situations it can be extended to five days.
When used, symptoms such as sweating, rapid heartbeat, and rarely dizziness are possible.
"Papaverine"
The myotropic drug is an opium alkaloid, however, it does not affect the central nervous system. Effectively relieves abdominal muscle spasms. It has the maximum therapeutic effect on the large intestine, then on the duodenum and antrum, promoting rapid healing. The drug is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and has the ability to increase in lipid tissues and the liver. In some cases, it causes nausea, stool disorders, headaches, and allergic rashes. The medication is convenient to use because it can be prescribed for oral administration, rectally in the form of suppositories, in the form of injections under the skin, into a muscle or vein.
Treatment of dysbiosis and enzymatic disorders
In the process of drug treatment of colitis, it is advisable to treat dysbiosis after completing a course of antibacterial drugs. But sometimes they are also prescribed in parallel. These medications not only form normal intestinal microflora, but also help eliminate toxins. As a result, stool normalization, appetite increase, and symptoms of increased gas formation are reduced.
There are many probiotic preparations available today. All of them, by and large, act the same, so you need to rely on your doctor’s recommendations or choose a product that is suitable for the price. This:
- bifidumbacterin,
- lactofiltrum,
- lactobacterin, Narine powder,
- bifiliz,
- probifor, etc.
Various enzyme disorders are also closely related to dysbiosis. For this purpose, special medications that contain pancreatin are prescribed. The most common medications in this group are Festal, Mezim and Panzinorm.
Prevention
In order to reduce the risk of developing inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract, you need to:
- Eat only fresh and high-quality products;
- Conduct general strengthening activities (hardening, gymnastics);
- Normalize your daily routine, ensure proper sleep and sufficient physical activity;
- Organize rational, fortified, nutritious nutrition;
- Monitor regular bowel movements;
- Timely identify and treat chronic diseases;
- Limit (in consultation with your doctor) the intake of drugs that affect the gastrointestinal tract.
Colitis of various origins is a common problem in gastroenterology. The clinical course of the disease is varied. Diagnosis at the present stage is not difficult. Treatment of colitis should be comprehensive and begin only after consulting a doctor.
Normalization of intestinal motility
During colitis, spasm of the intestinal muscles is observed. To eliminate it, antispasmodic drugs such as no-spa or papaverine are prescribed. Their combination with platyphylline is very effective.
To restore motor skills, Motilium and Cerucal are indicated. For diarrhea, astringents are prescribed; the most harmless and popular is regular calcium carbonate. It is completely non-toxic and can be used for a long time.
To reduce flatulence, which causes quite inconvenience to the patient, use the already mentioned calcium carbonate, a decoction of fennel or dill seeds, carbolene, and chamomile infusion.
With colitis, the intestinal walls begin to intensively produce mucus, which further slows down peristalsis. In addition, it has a strong irritating effect on the epithelial membrane and aggravates the course of the disease. To neutralize its action, various enveloping agents are prescribed.
"Sulfasalazine"
Has a strong anti-inflammatory effect. It is based on the rapid suppression of the source of pathogens by disrupting the metabolism in their cells. The active component does not allow the deoxyribonucleic acid chain to multiply.
According to reviews, “Sulfasalazine” for intestinal colitis is prescribed to people over sixteen years old, one or two grams three times a day. Next - 500 milligrams of the active substance until the end of the maintenance stage. The drug has a number of negative reactions, so it is prescribed only by a doctor.
Vitamin therapy and emotional stress relief
Symptoms of colitis are very exhausting for a person. He becomes restless and irritable. Headache, insomnia, and a feeling of constant fatigue appear. Therefore, the course of treatment for this disease must necessarily include mild sedatives and sedatives, such as glycine or persen.
Their combination with B vitamins, especially B6 and B12, is very effective. Their injections are quite painful, so they are best taken either in the form of tablets or ampoules for oral use. These are drugs such as Magne-B6, Neurovitan, Magnicum.
Types and symptoms
The most important classification is the division of colitis into acute and chronic. The acute course of the disease determines the rapid course of colitis and pronounced symptoms. The duration of such colitis reaches up to 3 months. Pathology of the large intestine that lasts beyond this period is defined as chronic. This type of colitis progresses “sluggishly”, the symptoms are not very acute, but constantly interfere with the patient’s normal life. The main symptoms of colitis are:
- constant (often false) urge to defecate;
- bloating;
- rumbling along the large intestine;
- profuse diarrhea;
- constipation;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- there is mucus and blood in the stool;
- foul-smelling stool;
- sharp cramping pain in the abdomen.
Acute colitis is usually accompanied by an increase in body temperature, and its chronic subtype is characterized by loss of body weight, loss of ability to work, and vitamin deficiencies, which are manifested by brittle nails and hair, and loss of skin elasticity.
Diet for colitis
Even the most effective treatment will not bring any results if the appropriate diet is not followed. On the first day, complete fasting is generally indicated; you can only drink. Doctors recommend hot unsweetened tea.
Fatty, fried foods, various smoked meats and sausages, flour products, coffee, cocoa and sweets, cold and carbonated drinks are strictly prohibited. Meat must be present in the diet, but only in the form of steamed cutlets or soufflés. Recommended are chicken, turkey, veal or beef, and rabbit.
Meals should be fractional - 5 - 6 times a day. The diet should fully provide the patient with the necessary vitamins and minerals. When introducing any new product, it is better to consult your doctor first.
What does Phthalazol help with?
Experience with the use of the medication shows that it should not be prescribed to children under twelve years of age. But if necessary, the doctor can prescribe this medication to the child, individually calculating the dosage depending on the weight.
What does Phthalazol help with? According to the instructions for this medication, the drug eliminates:
- acute intestinal infections;
- enterocolitis;
- colitis;
- diarrhea.
The medicine can be prescribed in combination with sulfonamide medications and antibacterial agents. The tablets should not be used together with antacid drugs or adsorbents, since in this situation the pharmacological effect of the drug will be reduced. The medication does not affect the functioning of the central nervous system and the speed of psychomotor reactions.
Recovery period
After the main drug treatment for intestinal colitis is completed, a fairly long rehabilitation period is necessary. At this time, vitamin preparations, medications and measures aimed at strengthening the immune system, weakened by a long course of antibiotics, are indicated.
In parallel with the main treatment of intestinal colitis, you can also use remedies from the arsenal of traditional medicine, but this must be agreed upon with your doctor. In addition, decoctions and tinctures from medicinal plants alone are not able to fully relieve inflammation.
After the end of drug therapy, it is recommended to continue treatment in a specialized sanatorium, where the patient will be offered an optimal diet and the necessary physical procedures.
Treatment
Which doctor treats colitis? Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are dealt with by a gastroenterologist, or, in his absence, a therapist or pediatrician. A coloproctologist treats diseases of the colon and, in particular, the rectum.
Even if catarrhal colitis of the intestine occurs, treatment must be carried out in full to avoid deeper damage and transition to a chronic form. The regime should be gentle, excluding physical fatigue and emotional stress during the period of acuteness of the process.
"Bifidumbacterin"
The medication is considered a probiotic that stabilizes the intestinal microflora. Due to the huge number of active ingredients and bifidobacteria, the medicine can stimulate the functioning of the stomach and intestines, the digestion process, as well as the body’s nonspecific resistance to various factors, metabolic processes, and the synthesis of vitamins.
According to reviews, “Bifidumbacterin” for intestinal colitis helps to effectively eliminate most pathogenic organisms, including enteropathogenic E. coli, Proteus, as well as staphylococci and some types of yeast-like fungi. The drug is produced in the form of a solution, powder, capsules and suppositories.
"Enterofuril"
The active substance is enterofuryl nifuroxazide, which belongs to the chemical derivatives of 5-nitrofuran. The drug has an antimicrobial effect, which is carried out by disrupting the connection of proteins in the cells of microorganisms. The drug has a wide spectrum of activity. “Enterofuril” is prescribed by specialists for intestinal colitis.
It leads to the elimination of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Despite the increased antimicrobial activity, the drug has virtually no detrimental effect on the state of normal intestinal microflora.
"No-shpa"
Antispasmodic tablets for intestinal colitis, which relax the smooth muscles of the intestine, neutralizing pain. For chronic illness, take two tablets twice a day.
Before starting therapy with No-Spa, you must read the instructions. After all, the medication has its own contraindications and side effects. In pharmacies the medicine is dispensed without a doctor's prescription. If you have any doubts or questions, you should consult a medical specialist.
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome is a spastic form of colitis. A common problem is spastic colitis of the intestine, the symptoms of treatment, nutrition, in which they differ from colitis caused by an organic lesion. This pathology refers to functional disorders.
The causes of spastic colitis can be:
- Psychosomatic disorders;
- Increased bowel irritability;
- Changes in the composition of the intestinal contents;
- Violation of the quantitative and qualitative ratio of microflora.
Clinically, the following signs are distinguished:
- Pain and discomfort associated with bowel movements;
- Flatulence, gas movement disturbance;
- Spastic pains arising from nervous overstrain.
The diagnosis of spastic colitis is made after excluding all possible organic causes of inflammation.
Nutritional Features
Not all tablet medications are approved for use by young patients, so a pediatrician should be involved in the child’s therapy. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease.
The main treatment measure for the restoration of the mucous membrane is considered to be specialized nutrition. In addition to diet, medications with enzymes, as well as prebiotics and adsorbents are recommended for use. The difference between pediatric therapy and adult therapy is the prescription of antimicrobial drugs only for strict medical indications.
When treating colitis, following a diet is almost the most important component of recovery. If you have an intestinal disease, you can eat the following foods:
- Yesterday's coarse wheat bread, crackers. Fresh white bread and baked goods increase the production of gases, peristalsis accelerates - this will negatively affect the patient’s condition.
- Soup, porridge with water, vegetable broth. Soup and not only animal fats burden the work of the stomach, intestines, and liver.
- Meat, fish in the form of steamed cutlets.
- Consume low-fat dairy products.
- Confectionery in moderation.
- Tea, cocoa, soft coffee.
- No more than two spoons of sugar per day, a few sweets.
It is worth giving up:
- legumes, pasta - cause excessive gas formation;
- raw fruits and vegetables – fiber enhances peristalsis;
- canned food, pickles, smoked, pickled - these products irritate the intestinal lining and cause inflammation;
- fast food;
- spices, seasonings.
Causes and provoking factors
Colitis can be caused by various damaging agents that enter the mucosa through hematogenous (through the blood), lymphogenous (through lymphatic vessels) routes, or from the lumen of the small intestine.
The immediate causes of inflammation are:
- Bacteria (Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, streptococci, salmonella, shigella);
- Viruses (adeno-, entero-, rotaviruses);
- Fungi (candida, aspergillus);
- Parasites (trematodes, amoebas, lamblia, pinworms);
- Allergic antigens (food, household, medicinal).
When pathogens enter the mucous membrane, they provoke the development of an inflammatory reaction. Redness (hyperemia), swelling of the wall appears, its functioning is disrupted (peristalsis decreases or increases, mucus secretion). The biocenosis (the balance of intestinal microflora) is upset, fermentation and rotting occur.
Such provoking factors as:
- Poor quality food and drinking water, irregular meals, lack of dietary fiber.
- Abuse of fried, fatty foods, fast food.
- Bad habits (alcohol, smoking).
- Decreased immune defense.
- Taking medications (NSAIDs, antibiotics, laxatives).
- Irregular bowel movements.
- Congenital diseases (elongated and/or dilated intestine, Hirsprung's disease).
- Diseases of the digestive system (gastroduodenitis, cholecystitis, enteritis, pancreatitis).
- Endocrinological diseases (thyroid diseases, obesity, diabetes mellitus).
- Neurological and mental disorders (vascular dystonia, neuroses, psychoses);
- Mesenteric circulation disorders (heart failure, vascular atherosclerosis).
- Tumor processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Radiation damage (radiation sickness, radiation in oncology).
- Exposure to toxic substances.
Provoking factors contribute to disruption of work, nutrition of the walls, motor activity, stagnation of feces in the lumen of the organ. Therefore, in the presence of a predisposition and the appearance of a causative pathogen, the inflammatory process quickly develops.