In women, starting from adolescence, discharge appears. And they are not always dangerous. But in any case, you need to constantly monitor your body. Visit the doctor on time and do not panic if a deviation from the usual norm is detected. When a woman is expecting a child, monitoring changes in the body should be even more careful.
Discharge in a woman during pregnancy in the very early stages can mean either a normal restructuring of the body or the presence of abnormalities. But before making a stressful situation out of this, it is worth studying the types of discharge and their specifics.
Discharge during pregnancy at very different stages may differ in color and characteristics. It is worth remembering that expecting a child has a huge impact on the female body; it is literally rebuilt. Ladies who are unaware of this fall into a terrible panic and do not know what to do if something happens to them that has not happened before. First of all, you need to warn your doctor. Surely you are in touch, the specialist will explain what needs to be done next, and this is definitely not related to panic. However, let’s try to understand the discharge during pregnancy.
Discharge during early pregnancy: normal options
During pregnancy, the female body undergoes restructuring under the influence of physiological processes and the hormone progesterone. The appearance of light-colored discharge at the beginning of pregnancy is considered normal. In some cases, the discharge may be bloody, especially in the first weeks of pregnancy. This can happen on days when menstruation occurred before pregnancy. Normal secretions during pregnancy may be completely absent.
The main reason for the occurrence of discharge in the first trimester is hormonal changes in the female body:
- Transparent discharge is considered the safest.
- Slightly brownish discharge in a small volume (daub) may occur on the expected days of menstruation in the first month of pregnancy. If you experience aching pain in the lower back or lower abdomen, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
- If a woman notices brown discharge, this may indicate a threat of miscarriage. In some situations, it is accompanied by aching or severe pain in the lower abdomen.
- Bloody discharge, similar to that during menstruation, is considered dangerous: its causes may be an ectopic pregnancy or placental abruption.
Effects of Progesterone
Opaque creamy discharge in the second week is considered the result of active production of progesterone, the key hormone of pregnancy. Directly under its influence, a change in vaginal discharge occurs. The increased concentration of progesterone creates positive conditions for good implantation of the embryo in the uterine endometrium. Attachment occurs approximately 8-10 days after conception. For this reason, white and thick discharge in women can be an indicator of pregnancy.
Implantation of fertilized egg
In the first weeks of expecting a baby, vaginal secretion may come out with a small amount of bloody streaks, and may also have a pinkish or brownish color. They arise immediately at the moment when the embryo is attached to the endometrium of the uterus. In this case, damage to the upper blood vessels can often occur, which provokes a slight release of blood. The volume of discharge is very small, and the manifestation itself is short-lived. Such discharge in the first days of pregnancy is completely safe. If in doubt, it would be better to consult a doctor.
Mucus plug formation
Excessive discharge in the first weeks of pregnancy, similar to raw egg white, is not uncommon. Their reason is quite simple. At approximately the 3rd week of pregnancy, the development and formation of a mucous plug occurs, which reliably protects the internal cavity of the uterus, and, consequently, the child itself, from the penetration of various pathogenic substances and infectious agents throughout pregnancy. For this reason, pregnant women at this stage increase the volume of clear mucus secreted. Such discharge in the first 4 weeks of pregnancy is completely natural.
Fluctuations in hormonal levels
During the period of bearing a child, significant transformations occur in a woman’s body. Initially, a change in female hormonal levels occurs. In certain situations, such hormonal changes occur with a certain delay, since each organism is individual. There may be options when a woman during pregnancy, during the period of potential menstruation, experiences bloody discharge on her underwear. If such secretion is not accompanied by painful spasms and deterioration of health, goes away on its own and again changes to normal leucorrhoea, then there is no reason to worry. As a rule, during pregnancy there is an increase in the amount of leucorrhoea from the usual state and this is the norm.
Allergic reaction
During the period of bearing a child, the susceptibility of pregnant women increases significantly. That is why allergies in the form of irritation and itching can be caused even by familiar remedies that have not previously caused a negative response from the body. Intimate hygiene gel, powder, synthetic materials - all this can cause profuse liquid leucorrhoea, which is accompanied by itching and irritation. Such discharge at the 11th week of pregnancy can most likely be caused directly by this cause. Initially, you need to try to eliminate the influence of the allergen. Sometimes this is enough for such discharge to stop.
Transparent shade, small volume, lack of aroma are the normal state of genital secretion during pregnancy. Mucus discharge creates a mucus plug, which means that the fertilized egg has successfully implanted in the uterus. The process is slow, so white, thick or clear discharge will accompany the expectant mother throughout the entire pregnancy.
Discharge in the form of white clots: causes
Quite often, by the color of his waste, a person can suspect that something is not going quite smoothly in the functioning of his body or that he is sick. People pay attention to the color of urine and feces every day. Women can determine that there are any abnormalities in their reproductive system by the color, intensity and consistency of their discharge from the genital tract.
Female vaginal discharge
Changes occur in a woman's body throughout the menstrual cycle. Hormones play a major role in this. The sensitivity of the mammary glands and nipples, sexual desire and attraction, as well as the color of the cervical mucus that is secreted change.
Immediately after the end of menstruation, a woman may feel a dry vagina. Closer to the time the egg is released from the ovary, the lady notes that the discharge has become more mucous and abundant. After ovulation, hormones begin to actively work, under the influence of which cervical mucus resembles a thick cream. If pregnancy occurs, a representative of the fairer sex observes copious watery discharge.
Discharge in the form of white clots
Some women may be bothered by cervical mucus. Its production can be very abundant and cause discomfort or itching for the fairer sex. Also, discharge in the form of white clots can be large in volume and constantly stain your underwear.
Some women in this case go to the doctor. Others prefer to self-medicate or let things take their course. It is worth figuring out where the discharge in the form of white clots comes from. Is this the norm? And what can cause them to appear?
Thrush
One of the most common reasons for the appearance of such cervical mucus is the appearance of a fungus. In this case, the representative of the fairer sex has discharge in the form of white gus
Source
Abnormal discharge in early pregnancy with photo
Knowing which discharge in the early stages of pregnancy is considered a deviation from normal will help a pregnant woman, if she needs to, find her bearings in time and consult a doctor, which will help save her pregnancy and her life.
What should alert a pregnant woman if discharge occurs:
- Presence of pain and deterioration of well-being;
- Prolonged discharge;
- Consistency of the secretion;
- Quantity;
- Discharge shade.
To determine what shade of discharge occurred during the 10th week of pregnancy (or any other week), you need to use panty liners.
Red bloody discharge
Such discharge is a dangerous sign of a disorder. Often the causes of such discharge are considered to be such dangerous conditions as:
- Threat of interruption . Bloody scarlet discharge, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, pain in the lower back or sacrum. A positive outcome in such a situation mainly depends on timely access to a medical facility. It is better to call emergency services and wait in a lying position.
- Erosion, polyps, oncology of the uterine cervix . Bleeding is possible after sexual contact or examination by a specialist.
- Hydatidiform mole is a violation of the formation of the fertilized egg. The danger of this condition is heavy bleeding and the likelihood of cancer formation.
Only a specialist can determine the real cause of such discharge using an ultrasound, gynecological examination, and a blood test to determine whether the hCG hormone corresponds to the obstetric stage of pregnancy.
Spotting brown discharge
Such discharge can become signs of dangerous disorders:
- Ectopic pregnancy . With this violation, the fertilized egg attaches and develops in the wrong place (tube - 97%, ovary - 1%, peritoneum - 1%). The danger of an ectopic pregnancy is that the more a woman does not seek medical help, the more dangerous the consequences will be for her. In especially advanced cases, such a pregnancy ends in the death of the woman. For this reason, timely assistance is extremely important. Thanks to the operation, the embryo is removed and bleeding is stopped.
- Chorionic detachment. This condition is considered an immediate threat of miscarriage. Signs: brown discharge, sharp pain in the lower abdomen, weakness. Timely visit to the hospital increases the possibility of maintaining pregnancy and reduces the risk of complications.
- Frozen pregnancy. A condition when the fetus has died, but it is still in the uterus. Separation from the walls of the uterus and provokes bleeding. In addition to these, signs of a non-developing pregnancy include the disappearance of pregnancy symptoms (swelling and pain in the breasts, nausea, low levels of hCG for the current period). Therapy for this condition is carried out by removing the fetus from the uterine cavity.
Yellow discharge
The reasons for the appearance of yellowish vaginal discharge are:
- Inflammation of the genital organs . It can cause miscarriage or infection of the fetus. To stop this process, proper treatment is prescribed.
- Sexual infections (often chlamydia, ureaplasma). These infections can cause miscarriage. For this reason, it is important to determine effective and timely therapy. However, self-medication is prohibited, since treatment must be selected by a doctor, taking into account the ongoing pregnancy. Such discharge always has an unpleasant aroma.
Green discharge
The cause of greenish, often even foamy discharge in early pregnancy is considered to be Trichomonas. The disease they cause is called trichomoniasis. In addition to discharge, signs of this condition include itching, burning, and pain in the genitals. Trichomoniasis is quite dangerous during pregnancy as it can cause miscarriage. And only a specialist can determine further therapy, since with independent therapy there is a high probability of using drugs that are toxic to the child.
White discharge
Often at the beginning of pregnancy, many may experience candidiasis. Its expressions: copious curdled discharge, sour aroma, itching, irritation. Physiological immunodeficiency is often considered the cause of thrush. There is no need to self-medicate, since the use of basic remedies for candidiasis during pregnancy is prohibited due to their negative effect on the fetus.
If any of the above pathological types of discharge occur, you must immediately contact a specialist. If the creamy discharge is irregular, before contacting a gynecologist, take a photo of the pad so that the doctor understands what exactly is going on.
Pathological discharge
Gynecologists classify as pathological discharges in pregnant women in the early stages, caused by bacteria or fungi that can harm the child. These pathogens include candidiasis, which is caused by the proliferation of the Candida fungus. This disease cannot be treated, since the necessary medications are contraindicated for pregnant women. If there is itching, burning, color other than transparent or white, which are accompanied by unpleasant odors (strong or weak), you should consult a doctor to maintain pregnancy.
White
White discharge in small quantities in the early stages of pregnancy does not indicate problems. However, if you notice unpleasant symptoms (bad odor, the consistency of the secretion has changed (becomes like cottage cheese), the genitals are red, you regularly feel a burning sensation), consult your doctor. Candidiasis can become a threat of deep rupture of the genital tract during childbirth. The tissues near the vaginal walls will become loose and lose elasticity, which leads to difficult labor.
Reds
The appearance of scarlet secretion during pregnancy is the most dangerous for a woman. They can be abundant, scanty and brownish in color. In case of heavy bleeding with severe pain in the lower abdomen, it is recommended to consult a doctor immediately. Such a secretion signals a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy. Slight light brown or brown discharge in the early stages is considered not fatal to the fetus.
The cause of scarlet secretion may be:
- cervical erosion;
- inaccurate douching;
- inaccurate contact gynecological examination;
- hydatidiform mole;
- myomatous nodes;
- abdominal trauma;
- polyp of the cervical canal;
- diseases that affect the blood coagulation system.
Brown
A small, light brown secretion may occur during the attachment of the fertilized egg to the uterus. If this is a one-time, short-term and scanty brown discharge at the beginning of pregnancy, then it does not pose a threat. During this period, a woman may be bothered by nagging discomfort in the lower abdomen. Dark brown discharge may be a sign of chorionic detachment or future placenta.
The periodic or one-time appearance of brown secretion in the first trimester of pregnancy may be a sign of an ectopic, frozen or non-developing pregnancy, when the embryo dies and the fertilized egg remains in the uterine cavity. Over time, the placenta separates from the walls of the uterus, which is the reason for the appearance of dark secretions in women. If it occurs, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Gray
A gray secretion is released in the first stages, has a characteristic odor and is accompanied by a burning sensation in the genitals. This is a signal of the presence of sexually transmitted infections (vaginitis, trichomoniasis or other diseases). Trichomoniasis is very dangerous for pregnant women, who in this case are subject to urgent hospitalization. Bacterial vaginitis has a different character. Pregnant girls with this disease have difficulty bearing a child.
Cream
Slight beige or creamy discharge during early pregnancy may indicate an inflammatory disease. During the exacerbation of the inflammatory disease, a girl may feel discomfort near the external genitalia, accompanied by the release of milk secretions. The reasons for the appearance may be:
- coli;
- staphylococci or proteus;
- gonorrhea;
- gardenellosis or trichomoniasis.
Another cause of beige discharge is an insufficient amount of female sex hormones in the blood. The hormone progesterone supports the body during pregnancy, promotes the growth and tone of the uterus, reduces the activity of the immune system in the first stages of embryo development, which is necessary for the body to accept a fertilized egg. If you have bloody discharge, you should consult a doctor.
Vaginal secretion is yellow
There are two possible options for the appearance of deep yellow discharge during early pregnancy:
- Inflammatory process in the genitals;
- Reproduction of infection (ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, gardenellosis).
In parallel with this, a woman may experience pain in the abdomen and sacrum.
Itching and irritation may also be present in some variants. Such discharge in the first trimester of pregnancy can be dangerous, since it can cause spontaneous abortion, slow down the development of the child and its infection in utero, which subsequently leads to premature birth. In addition to a change in the color of the discharge, a woman may notice an increase in temperature and pain in the lower abdomen. Such changes are caused by diseases that are sexually transmitted. However, this does not mean at all that the pregnant woman became infected during the period of bearing the child. Most likely, the infection was caught earlier, but since the immune forces are weakened, it intensified and made itself felt. This also poses a threat to pregnancy, so you need to consult a doctor.
White discharge in lumps of pregnancy
What can cause white discharge in lumps?
Probably every woman sooner or later faces a problem when not everything is in order in the most intimate place. Discharge of varying strength and consistency begins. Knowing exactly what kind of discharge can appear in certain diseases is very important, because just such manifestations can tell a woman whether everything is okay with her health.
As such, vaginal discharge is normal for any healthy woman. But changes in their color, smell and consistency may indicate the presence of various kinds of problems or simply changes in the body itself.
For example, when hormonal status changes, the intensity of discharge may change. This often happens during pregnancy and shortly before the start of menstruation. But a decrease in the intensity of discharge is a harbinger of menopause.
If the mucus of the discharge increases, this may indicate problems in the cervix. And if there is a sour smell and white lumps, most likely the body has been affected by a fungal infection. Symptoms of a bacterial infection will include greenish or yellowish discharge.
White discharge in the form of lumps often appears during pregnancy. As practice shows, 95 percent of pregnant women suffer from heavy discharge. Although the discharge may sometimes be thin and sparse, it is often thick, white, and copious. And if lumps appear, there is a possibility that the disease has some advanced form.
That is why many pregnant women are forced to undergo treatment in order not to harm their child during childbirth, since, passing through the birth canal, the child can become infected. Therefore, during such an important event as pregnancy, it is impossible to ignore the doctor’s advice regarding treatment.
Source
Brown discharge in the early stages
- Frozen pregnancy
In certain situations, brown discharge may indicate a missed pregnancy. If a woman initially had all the signs of a pregnant state, and then they all suddenly stopped, plus brown discharge appeared on her underwear, then it is likely that the fetus died inside the womb. Gradual peeling from the uterine walls of the fetus causes the appearance of brown discharge. In order to dispel your worries and doubts, it is worth undergoing an examination. The most reliable will be an ultrasound examination, which will show that the embryo does not have a heartbeat.
- Cervical erosion
Indeed, erosion can cause brown discharge, which is explained by mechanical damage to the surface affected by the disease. Such discharge can be observed, for example, after examination in a gynecological chair. Erosion therapy is not considered during pregnancy and will have to be postponed until after delivery. Detailed details about the treatment of erosion after childbirth should be discussed with your doctor.
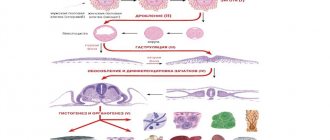
Normal and pathological discharge by week of pregnancy
The obstetric period of pregnancy is counted from the first day of the last menstruation, since while the endometrium is being rejected in the uterus, the same follicle with the egg that will give rise to our pregnancy is already maturing in the ovary.
1 – 4 weeks
The first weeks of pregnancy are a particularly crucial period, since many influences (an infectious disease with high fever and intoxication, the toxic effects of alcohol and drugs, taking medications, etc.) can lead to undesirable consequences (termination of pregnancy, bleeding). Therefore, we will provide the most detailed schedule of possible discharges by week so that you can figure out where the norm is and where the pathology is. But, of course, you cannot do without consulting a doctor.
1 Week
In the first week there is menstrual bleeding. In one of the ovaries (and occasionally in two at once), the follicle matures and prepares for release.
2 week
Ovulation is a physiological phenomenon that represents the release of a mature egg from the ovary into the abdominal cavity, where it is captured by the fimbriae of the fallopian tubes and carried into the tube.
Ovulation occurs approximately on the 14th day of the cycle, and this event can manifest itself as spotting, scanty bloody or brown discharge and moderate nagging pain in the lower abdomen and above the womb for 1-2 days (ovulatory syndrome). During this period, mucous discharge may appear more abundant than usual.
During ovulation, the egg is fertilized by a sperm.
3 week
On days 5–7 after fertilization, the egg is implanted into the prepared endometrium, and “implantation bleeding,” scanty spotting, lasting up to about 40 hours, can be observed. They are not accompanied by pain and go away on their own.
4 week
At the 4th week of pregnancy, the discharge is clear or whitish, not abundant, thick, odorless and not accompanied by additional sensations. Such discharge is caused by hormonal changes in the body (an increase in the concentration of progesterone) and increased blood circulation in the pelvic organs.
5 – 8 weeks of pregnancy
The discharge has a thick, but “slippery” consistency, and can be transparent or slightly whitish. Gynecologists call such discharge “milky.” The discharge has virtually no odor, or you may notice a subtle sour odor. The entire picture described above is a reflection of the normal secretory function of the female organs and is regulated by the “pregnancy hormone” - progesterone. Discharges at this stage of gestation perform a protective function, as they prevent the penetration of infectious agents to the fetus.
However, any discharge different from those described above should be cause for concern. Brown or dark, spotting discharge may indicate an incipient miscarriage and requires immediate clarification of the diagnosis. A miscarriage that begins does not always lead to complete rejection of the fertilized egg; timely treatment often helps to maintain the desired pregnancy.
Bright spotting is a threatening sign, and the more profuse the bleeding, the more unfavorable the prognosis for the fetus.
The appearance of fresh bloody discharge is a reason to immediately contact the gynecological department or call an ambulance.
There is such a phenomenon as “color pregnancy” or “fetal washing”, which consists in the fact that a woman regularly begins menstruation on time against the background of a progressive pregnancy. The pregnancy test is positive. But in order to calm down and be sure that the pregnancy continues to develop, a consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist is necessary.
Abundant, yellowish/greenish/gray, foamy discharge, liquid or, conversely, thick and “cheesy” with an unusual or pungent odor, accompanied by itching in the perineum, redness of the mucous membranes and skin of the external genitalia (labia) is a sign of an infectious process. Infections require timely diagnosis (specific smears and cultures for infections) and treatment. Therefore, if disturbing discharge appears, contact your doctor at the antenatal clinic.
Very often, candidiasis (thrush) develops in the early stages, which is associated with a change in immune status due to hormonal changes in the body. Candidiasis is not a “true” infection, but rather a manifestation of an imbalance in the vaginal flora. When registering, you will be examined in a chair and a smear taken for flora. But even if signs of thrush are detected, treatment will have to be delayed for up to 12 weeks. The maximum that can be used is external washing of the genitals with a soft gel for intimate hygiene (without applying to the mucous membranes!).
9 – 12 weeks
From 9 weeks, the discharge becomes more liquid, watery and transparent and can resemble egg white in appearance and consistency, has no noticeable odor (or has a barely noticeable sourish odor) and does not bring any unpleasant sensations.
Up to 12 weeks, a woman can normally experience a low-grade fever (up to 37.2°C). If the increase in temperature is not accompanied by other pathological symptoms (cough, runny nose, lower back pain, dysuria, bowel movements, and in our case, pathological discharge different from the above picture of the norm), then there is no need to worry.
However, an increase in body temperature in combination with the appearance of copious yellowish/greenish/gray discharge, which can be thick or, on the contrary, watery and foamy (you notice air bubbles in the copious secretion), indicates the development of a urogenital infection and requires diagnosis and treatment.
If you were diagnosed with cervical erosion before pregnancy, then during pregnancy a gynecological examination or sexual intercourse may cause slight spotting. Such discharge is observed for several hours and is not accompanied by any subjective complaints (no nagging pain in the lower abdomen). This happens because during gestation, all tissues of the body are under the influence of progesterone, which loosens all tissues. The mucous membrane of the cervix becomes looser, “juicier” and bleeds more easily upon contact.
13 – 16 weeks
During this period, the discharge becomes more liquid, has a transparent or slightly whitish color, and may become a little more abundant. This is due to an increase in estrogen levels in the blood. The smell still shouldn't bother you. The discharge is homogeneous and does not have inclusions (lumps of mucus, thick accumulations of white/yellowish color)
If there are pathological discharges, it is necessary to undergo additional tests (smear for flora, culture for infections and, possibly, a blood test from a vein for sexually transmitted infections). After 12 weeks, the use of some drugs for the treatment of candidiasis and STIs is already permitted.
17 – 21 weeks
The discharge remains neutral in color and odor, but may become more abundant and thin. The discharge is more liquid, but homogeneous and quite viscous, does not have foreign inclusions and is not accompanied by complaints (itching and burning in the perineum, swelling and redness of the external genitalia).
The appearance of brown discharge or bright bloody discharge should alert you, as it indicates a threat of late miscarriage. With timely treatment, pregnancy can be maintained.
22 – 24 weeks
Normal discharge at this stage is also transparent/whitish, homogeneous, liquid, without foreign odor and without complaints of discomfort in the intimate area and pain in the lower abdomen.
From 22 weeks we are no longer talking about the threat of miscarriage (or the threat of miscarriage, which means the same thing), but about the threat of premature birth.
Bloody discharge may indicate the onset of premature labor or placental abruption (premature abruption of a normally located placenta). This situation is urgent and you should contact the maternity hospital.
You should also be wary of excessively abundant transparent liquid discharge (resembling water, may be light or have a yellowish color), which appeared suddenly (possibly after sudden or heavy physical activity, sexual intercourse or severe stress), the discharge does not stop or comes in portions, wetting the underwear ( mucous secretions are usually viscous enough to saturate laundry).
Perhaps we are talking about leakage of amniotic fluid (PIV or PIOV - premature rupture of amniotic fluid).
This situation is emergency and is subject to urgent diagnosis and, if leakage of amniotic fluid is confirmed, development of management tactics depending on the obstetric situation.
The period from 22 weeks is already “maternity hospital” and in case of premature birth the child is subject to resuscitation and nursing (On approval of the Procedure for the provision of medical care in the field of “obstetrics and gynecology (except for the use of assisted reproductive technologies)” (as amended on January 12, 2020) ).
24 – 28 weeks
Discharge at this stage of pregnancy is whitish (milky) or transparent, quite liquid, homogeneous, has no distinct odor and is not accompanied by any complaints.
Bloody discharge (brown spotting or the appearance of scarlet drops of blood) indicates a threat of premature birth, and you should consult a doctor about this.
If spotting appears suddenly, is profuse (you need more than a daily pad) and/or is accompanied by nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, changes in fetal movements, then you should immediately contact the emergency room of the maternity hospital (on your own or by calling an ambulance team help").
If you notice the appearance of spotting brown discharge, your stomach does not hurt, and you do not notice increased tone of the uterus (the stomach is soft and does not “turn to stone” when touched, walked, or on its own), you feel the fetal movements well (they are the same as always, not violent and not sluggish, barely noticeable), then you should approach your obstetrician-gynecologist in the antenatal clinic during office hours without an appointment.
After the examination, the doctor will choose further management tactics. You should be prepared to be sent to a day or 24-hour hospital.
If thin, watery discharge appears (suspicion of premature rupture of amniotic fluid), you should contact the maternity hospital to clarify the diagnosis and be prepared to be offered hospitalization.
Premature birth before 28 weeks is characterized by deep prematurity and extremely low fetal weight (up to 1000 grams), so you must be very attentive to yourself and not neglect medical care and supervision.
29 – 31 weeks
The discharge retains a milky color, a thin, but viscous consistency, and may acquire a more pronounced sourish odor. If there are no other signs of infection (itching, burning, yellow/greenish/gray discharge, flakes), then there is no need to worry.
At 30 weeks, during a planned consultation, you will be examined on a chair and a smear will be taken for flora. If inflammation is present, you will be prescribed treatment and a control smear.
Everything that was said above about bloody discharge and suspicion of PIOV is also true at this time. It is unacceptable to delay consulting a doctor in these cases.
Preterm birth between 28 weeks and 1 day and 30 weeks and 6 days is characterized by severe prematurity and very low fetal weight (up to 1500 grams).
32 – 36 weeks
The discharge retains a neutral color, the same consistency and may have a sour odor.
At 36 weeks, you will have a flora smear taken for the third time (even if there were no pathological changes in the previous smears), this is necessary to prevent premature rupture of water (the infection “corrodes” the membranes and provokes PIV), timely sanitization of the genital tract prevents many problems. If you notice a change in the nature of your discharge, tell your doctor about it at your next visit.
Also, if inflammation is detected, it is necessary to have time to sanitize the vagina before childbirth. Childbirth against the background of an inflammatory process can be complicated by infection of the fetus.
The inflamed tissues of the birth canal are loose and vulnerable; they cannot stretch to the required amount during the birth of the fetus and ruptures occur. Ruptures can occur even with normal vaginal microflora, but in the presence of colpitis this is almost inevitable, and then healing of the sutures is more difficult.
37 – 41 weeks and 3 days
The pregnancy is full-term and labor can begin at any time.
The discharge gradually becomes more viscous, transparent and viscous, this is due to the increase in estrogen in the mother’s blood.
Estrogens prepare the cervix for childbirth, soften it and promote shortening.
The mucus plug, which worries expectant mothers so much, is a clot of clear or whitish mucus, possibly streaked with blood, which separates without any warning, and may be accompanied by nagging pain in the lower back or lower abdomen. The passage of the mucus plug is not the beginning of labor; on average, the plug comes off 2 weeks before birth. Sometimes a woman does not notice this moment if everything happened in the toilet or while swimming.
After the plug has come out, you should not swim in open bodies of water (rivers, lakes, etc.), since previously thick mucus closed the entrance to the cervical canal and thereby protected the fetus.
The breaking of water is a signal for the start of labor. If you notice the appearance of copious watery discharge that has soaked your underwear, and possibly your clothes, then you should go to the maternity hospital.
Pay attention to the color of the watery discharge. Normally, they are colorless, light, and have a weak specific odor (some compare it with the smell of mother's milk). If you notice greenish or dense green/brown water, then we are talking about fetal hypoxia. Yellow/brown appear with hemolytic disease (increased bilirubin levels). Cloudy water with flakes and an unpleasant odor is a sign of infection.
Be sure to tell the doctor at the maternity hospital about the nature of the discharge at home, since tactics in different cases can vary dramatically.
After a gynecological examination, mucous discharge streaked with blood and brown spotting may appear for several hours; this is normal and indicates the gradual preparation of the cervix for childbirth. Such discharge is not accompanied by a change in the nature of fetal movements.
Abundant scarlet discharge or brown discharge with clots may indicate the onset of premature abruption of a normally located placenta. This is an emergency that requires immediate medical attention and intervention. You should contact the nearest maternity hospital.
Dark discharge during pregnancy
Discharge at the 6th week of pregnancy (as well as any other week of gestation), accompanied by a dark shade and complemented by acute pain and general weakness, is not a normal and natural phenomenon. Similar symptoms are characteristic of an ectopic pregnancy, when the embryo is implanted not in the uterine cavity, but, for example, in a tube, abdominal cavity or ovary. Such a violation can be quite dangerous for a woman’s well-being and life, since as the embryo grows, the possibility of organ rupture and heavy bleeding increases.
Green color
The appearance of green discharge (pus) can be a symptom of diseases such as gonorrhea or trichomoniasis. These sexual diseases can provoke spontaneous abortion. Signs of this condition:
- Itching;
- Burning;
- Swelling of the labia;
- Pus spots;
- Unpleasant smell.
If such signs appear during pregnancy, it is necessary to consult a specialist as soon as possible and carry out appropriate examination and therapy.
White flakes in vaginal secretion
Such discharge at the 11th week of pregnancy appears with the same frequency as, for example, at the fifth week of pregnancy or at the thirtieth. Thrush can appear at any week of pregnancy. This stage is characterized by a certain decrease in the body’s defenses, which is why such an unpleasant disease as thrush often develops.
At first, the discharge looks like white flakes or grains of curd, which are easily separated from each other. As the disease progresses, the flakes turn into gray films, which, when separated from the mucosa, leave insignificant wounds. This increases discomfort significantly. The disease is accompanied by irritation, itching, swelling, hyperemia of the external genitalia, and a characteristic sour aroma appears.
Such white discharge during early pregnancy does not pose a danger to the fetus, but brings discomfort to the expectant mother. For this reason, it is important to carry out antifungal therapy, which must be prescribed by a doctor. Often during pregnancy, topical agents are used.
How to adapt to new changes in the body?
Simply following simple rules can be your assistant. Try using unscented pads for everyday use, changing them 2-3 times a day. To be on the safe side, you can temporarily exclude scented soaps, fragrances and deodorants from use. It is also advisable to refrain from using bubble bath. All of the above products may contain a fairly strong irritant. The use of tampons is strongly discouraged, as they significantly increase the possibility of infections entering the birth canal.
As for the external genitalia, they need to be washed with warm water at least twice a day. Before washing, you need to wash your hands with soap. During the procedure, hand movements are made in the direction from front to back, towards the anus. In no case should you do the opposite, as this can result in an infection in the vagina, and this is fraught with inflammatory diseases. For everyday care, using ordinary soap is not at all suitable; you need to use products special for intimate hygiene, the warehouse of which is compiled taking into account its effect on the microecology of the vagina. It is not at all recommended to direct a strong stream into the vagina, and it is also not recommended to use any sponges, as they can damage the sensitive skin on the genitals. During pregnancy, you should never douche, as this can disrupt the vaginal microflora. This increases the likelihood of contracting some kind of infection. Also, douching irritates the uterus and, as a result, can lead to abortion. After completing the procedure, you need to thoroughly dry the genitals with your towel. It must be remembered that a humid environment is conducive to the rapid development of fungal infections.
During pregnancy, it is recommended to frequently consume fermented milk products, which are rich in live bacteria cultures. In addition to all this, it is recommended to consume foods that contain coarse dietary fiber. Every day it is advisable to drink one cup of yogurt and this is the minimum. As for sweets, their consumption, on the contrary, should be limited, since their excess provides a favorable environment for the proliferation of harmful microflora.
White flakes in vaginal secretion from Utrozhestan suppositories
Utrozhestan is a synthetic analogue of the pregnancy hormone progesterone. This hormone is a gestagen, which is formed in the corpus luteum after ovulation and is responsible for the development of the secretory endometrium.
The appearance of white discharge from Utrozhestan suppositories must be divided. Thus, when using the drug intravaginally, the white discharge may simply be the contents of the capsule. If the woman correctly administered the drug and it managed to dissolve (after inserting the capsule you need to be in a horizontal position for about an hour), then there is nothing to worry about.
There is no need to try to wash the remnants of the drug from the vagina; it is forbidden to douche to clean off the remnants. Excessive hygiene in this case can be harmful - it can wash away the active component of the drug and prevent it from showing the desired effect. This can also provoke the formation of vaginal dysbiosis.
If Utrozhestan is taken orally, the occurrence of leucorrhoea may indicate the formation of a fungal infection. You need to carefully monitor your own well-being and if itching, burning, or redness of the labia occurs, you need to consult a specialist to exclude or treat an infectious disease.
When using Utrozhestan, white discharge may indicate that the woman is not lying down enough to absorb the drug. Let us remind you that you need to lie down preferably for about an hour.
Lots of discharge in white lumps
Is it possible to apply baby cream to the stomach during pregnancy Good afternoon! ICA stenosis more than 90% on the left. MS CT of the BCA: atherosclerotic changes in the CCA with stenoses below the bifucation level. Pronounced extended stenosis of the ICA on the left without signs of atherosclerosis. They suggest urgently
Good afternoon Please help me understand the problem. The break from sex was 9 months. Then a permanent partner appeared. From the first days of intimate life, the following began - it was DURING and AFTER sexual intercourse that white lumps remained on the partner’s penis, and at first this did not cause much discomfort because there weren't many of them. (I note that sexual intercourse without a condom is interrupted). I didn’t pay much attention to this problem, because... in everyday life there was no discharge that particularly bothered me and there was no itching. After about six months, the number of white lumps increased. Eventually the moment came when there were a lot of them. This is already starting to bother me! Again, there was no itching, the discharge was small and whitish. On the advice of a friend (thinking it was thrush), I used neo-penotran suppositories for 7 days. — they helped right away! after the first days of use (course of 7 suppositories). Nothing bothered me for exactly 2 months! And then at one moment it’s on you! — during sexual intercourse, so much came out like never before! The next day I went to the gynecologist. She took a smear, and while still in the chair said that it was probably thrush, because... He can already see by the discharge (I note that the lumps appear only during sexual intercourse! - it feels like the partner is “scraping out” them from there, or something...). Gynecologist She said the tests will come later, but in the meantime, buy lomixin - 2 capsules, and lomixin cream. I inserted the capsules on the first day and three days later. I started using the cream only probably on the 5th day - and I used it according to the instructions, i.e. I inserted a piston with cream deep into the vagina. I used it for 6 days, and this is what alerted me! For the first 4 days, the cream I introduced at night and the next day came out of the vagina, also white. But on the 5th and 6th day - for some reason it was pinkish! Why?? Is this normal?? It is clearly visible that this is a cream, but for some reason it
Source
Treatment of discharge during early pregnancy
Taking into account certain conditions that caused the occurrence of specific discharge in the early stages, various therapeutic measures are used. Below we present them in a small diagram:
| Diagnosis | Measures used |
| Placental abruption | Hospitalization in a medical institution, implementation of conservation and hormonal treatment. |
| Threat of spontaneous abortion | Hospitalization in an educational institution, implementation of preservative and hormonal treatment (use of hormonal drugs, adherence to semi-bed rest). Taking hemostatic drugs (if necessary). |
| Cervical erosion | Implementation of drug therapy, excluding the cauterization procedure. |
| Frozen pregnancy | Hospitalization in a medical institution, use of medical abortion, mini-abortion, vacuum, artificial birth or curettage. |
| Ectopic pregnancy | Hospitalization, surgical treatment. |
In addition to a quick visit to the doctor, a woman who has detected uncharacteristic discharge is advised to adhere to complete control.