This, at first glance, absolutely simple and not severe viral disease can lead to serious health problems. Adenoviral conjunctivitis is a “disease of dirty hands” that occurs in both children and adults of all ages. A person came home, did not wash his hands, rubbed his eye (or did it on the street, in a public place) - and now the organ of vision is already infected with one of the types of adenovirus, of which there are many. If timely treatment is not started, one of the likely outcomes of the disease will be loss of vision.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis - symptoms and treatment
About the virus
Adenovirus is more virulent (infectious) than other viruses, for example, herpes or human immunodeficiency. It can remain infectious when dried at room temperature for many weeks. Adenovirus is a DNA-containing type and does not have a lipoprotein coating bilayer. The pathogen can be destroyed only by prolonged exposure to high temperature or antiseptics such as chloramine and phenol.
The virus is transmitted by airborne droplets or by direct contact of biological fluids with mucous membranes. The most unsafe in this sense are secretions from the respiratory tract and tears. The virus also survives in swabs, towels, door handles, soap, everyday items, glasses, and on hands.
The structure of the adenovirus
Symptoms
Symptoms of adenoviral conjunctivitis usually last for 7-28 days. If the disease lasts more than four weeks, then they speak of chronic conjunctivitis. In a third of patients, symptoms manifest as subepithelial infiltration of the cornea, which can progress to complete loss of vision. How long it takes to heal, the severity of symptoms and complications depend on the type of serotype of the virus (of which there are more than 20). However, it is known that serotypes 8, 19, 37 and 53 have the greatest epidemic potential.
Before the appearance of symptoms of the disease, the so-called incubation period occurs - the time from infection to the onset of clinical manifestations. In the case of adenoviral eye infection, this period is about a week, then the development of the disease begins. It manifests itself as inflammation of the nose and pharynx (pharyngitis) and fever. Against this background, inflammation begins in one eye, and two to three days later the infection covers both organs of vision (acute adenoviral conjunctivitis). This is manifested by swelling of the eyelids, uniform redness of the mucous membrane (picture of “pink eye”). There is a noticeably small amount of transparent mucous discharge, the cornea is not sensitive. The general condition worsens, the lymph nodes increase in size while fighting the infection.
Consequences
The occurrence of consequences of adenoviral conjunctivitis is associated with late treatment or an incorrectly selected therapy regimen. Inflammation can spread to the cornea. Pinpoint opacities appear on it, which reduces visual acuity. In the future, this threatens the development of eyesores and irreversible loss of vision.
Depending on the severity of the adenovirus, complications may develop within 1–12 months after illness. Among the most severe complications of this disease are:
- iridocyclitis, affecting the iris of the eye;
- keratoconjunctivitis;
- chronic recurrent conjunctivitis;
- development of secondary bacterial infection;
- dry eye syndrome.
What are AFKL and EKK
The symptoms mentioned above are inherent in the so-called adenopharyngoconjunctival fever. It is characterized by the fact that pharyngitis and conjunctivitis occur in people who have had acute respiratory diseases. Adenoviral conjunctivitis in children occurs in the form of an epidemic, since it is transmitted by airborne droplets, less often by contact. The onset is usually acute and most often occurs in young children.
Usually the prognosis is favorable, the disease can last no more than four weeks, pinpoint infiltrates in the subepithelial area and keratitis disappear on their own without affecting visual acuity.
Another possible course of adenoviral infection is called epidemic keratoconjunctivitis and has more pronounced symptoms, accompanied by the formation of follicles and soreness of the pre-auricular lymph nodes.
Typically, epidemic keratoconjunctivitis occurs against the background of general unwellness of the body - fever, damage to the respiratory tract and dyspepsia. Damage to the cornea has the form of pinpoint superficial subepithelial keratitis and coin-shaped infiltrates, often accompanied by hemorrhages and corneal edema.
Consequences of EKC – filamentous keratitis
In the adult population, symptoms are much less severe, often without fever. Infection occurs through contact from a patient with keratoconjunctivitis through infected devices, the hands of medical staff, instruments, and eye droppers.
Forms
Adenoviral eye infection produces various symptoms that determine the form of the disease.
Catarrhal
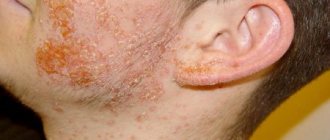
Mild form of the disease. Conjunctivitis occurs after ARVI, and the symptoms are mild. The redness of the conjunctiva is slight, there is little mucous discharge. This condition lasts about a week.
Conjunctivitis often accompanies respiratory viral infections
Membranous adenoviral keratoconjunctivitis
This form is characterized by the appearance of thin white-gray films on the membranes of the eye. Usually they are easily separated with a sterile swab, but sometimes the films are firmly “soldered” to the conjunctiva and, after removal, expose the wound surface. With this course, it is necessary to identify the film form of adenoviral keratoconjunctivitis from diphtheria, which is caused by Corynebocterium diphtheria and is the cause of conjunctivitis in children who did not receive vaccinations or became infected from the mother during childbirth.
Removing the film from the conjunctiva
Due to the fact that there may be bleeding surfaces under the films, scars or seals can often form during their healing. They usually resolve on their own after the disease goes away.
Follicular adenoviral keratoconjunctivitis
The main symptom of this form is the appearance of small bubbles on the conjunctiva of the eyes.
Follicles are clusters of lymphocytes under the epithelial layer of the conjunctiva
Often, in the absence of other symptoms of adenoviral keratoconjunctivitis, follicles from the papillae, which are an enlarged system of capillaries growing into the epithelium in the form of bundles, can be mistaken for the follicular form. This happens under the influence of drugs (Pilocarpine, Physostigmine) or toxic substances. But still, more often, follicles are formed during viral infections - herpes or caused by adenoviruses.
The follicular form is typical for children over two years of age and adults, the film form is more common in infants, and the catarrhal form can occur at any age.
Diagnostics
If a viral eye infection is suspected, it is necessary to establish the nature of the disease in order to correctly determine how to treat it. The consequences of improper therapy are usually chronic disease, progression and recurrent rashes of corneal infiltrates, and decreased visual acuity.
It is impossible to reliably establish a diagnosis of adenoviral eye infection based on examination and visible symptoms alone.
This is done using laboratory diagnostics:
- immunofluorescence method or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of material taken from the conjunctiva;
- the cytological method determines the presence of the virus by its characteristic cytopathic effect;
- indirectly confirm the presence of adenovirus by serological studies of antibody titer and bacteriological method for determining the accompanying microflora.
How to diagnose adenoviral conjunctivitis?
Diagnosis of such an eye disease can only be carried out if the patient has the above-mentioned characteristic symptoms.
In order to confirm the initial diagnosis, additional clinical tests may be prescribed for the patient. Currently, laboratory serological or virological methods are used to isolate adenovirus.
Perhaps the most common is PCR, through which adenovirus DNA can be detected in conjunctival scrapings.
Treatment
Due to the viral nature of the disease, treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis in adults, and especially in pediatrics, should be carried out as prescribed and under the supervision of the attending physician.
Eye drops with antiviral activity
First of all, drugs with antiviral effects, interferon inducers or recombinant interferons are prescribed.
Interferons (Okoferon, Ophthalmoferon drops) help in the treatment of adenovirus infection by influencing the metabolism of host cells. As a result, virus replication becomes impossible in such a cell.
Interferon inducers (Aktipol, Poludan drops) stimulate the production of internal interferons by the body itself. As a result, treatment with these drugs is much more effective than narrowly targeted antiviral drugs.
Antiviral agents can be used not only topically, but also in the form of systemic drugs (Amiksin, Likopid, Amizon, Larifan tablets). The positive effect of the drugs helps to reduce the number of subepithelial infiltrates, reduce the severity of corneal opacification and corneal syndrome.
Immunostimulants of various origins are also used systemically: levamisole, pyrogenal, thymogen, timolin, polyvinylpyrrolidone.
In order to prevent toxic-allergic reactions, the glucocorticosteroid dexamethasone is prescribed in the form of instillation. It reduces the manifestation of signs of inflammation, but its use must be strictly justified (for example, the presence of hemorrhages), since drugs in this group reduce the body’s immune response and can provoke the development of a concomitant bacterial or fungal infection.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are considered a safer group of drugs. In ophthalmology, there are eye drops containing indomethacin, ketorolac, diclofenac sodium. They are designed to eliminate inflammation of the anterior segment of the eye.
Prevention
To avoid primary adenoviral conjunctivitis or its relapse, you must adhere to the following rules:
- complete recovery after an initial adenoviral disease to prevent the development of a chronic inflammatory condition of any part of the eye;
- avoiding visiting crowded places during an epidemic of viruses or infections, especially in the autumn-winter period;
- proper nutrition with a sufficient amount of nutrients entering the body; if this is not enough, multivitamin complexes are used, this improves the functioning of the immune system, it can fight invading viruses or infections;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases, especially viral ones;
- no contact with infected people; if one of your close relatives is sick, he must be isolated from the child.
Prevention methods will not completely eliminate the possibility of the virus entering the child’s body. But their use significantly reduces the risk of developing viral and bacterial diseases during their exacerbation among people.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis can occur in a child in several forms. The condition may be complicated by elevated body temperature, as well as the formation of bubbles and films in the eyes. To avoid this, it is recommended to contact an ophthalmologist in a timely manner. The prescribed drug treatment is strictly adhered to; you cannot independently replace medications with analogues.