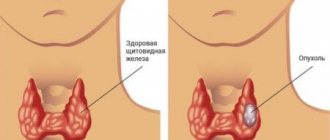
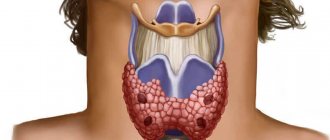
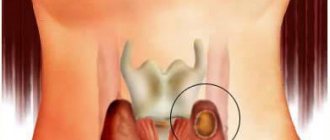
What is a nodular goiter?
In order to understand what it is - nodular goiter, it is necessary to understand what diseases are included in the structure of this concept.
ICD 10 revision proposes the following classification:
- nodular colloid goiter;
- follicular adenoma;
- hypertrophic handicap of AIT with the formation of false nodes (pseudo thyroid nodes);
- solitary cyst;
- thyroid cancer.
Thus, we can say that the term nodular goiter includes all local formations of the thyroid gland that have a capsule. If more than 1 node is detected on the surface of the gland, one should speak of a multinodular form of the disease.
Endemic inflammation
Symptoms of endemic goiter indicate the need to urgently treat the regional infectious pathology. It is observed in a number of biogeochemical zones with a predominance of primary or secondary exogenous neoplasm.
Manifestations of the disease:
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland, systematically destroying the normal vital signs of the population of a given zone.
- Nodular forms of goiter appear in people of different sexes and ages.
- Stable insufficiency of the functioning of the thyroid gland causes the risk of extreme severe forms of hypothyroidism (myxedema), cretinism.
Causes of nodular goiter
The etiology of the disease certainly depends on its morphological form. So colloid goiter is a non-toxic, euthyroid form (nodular non-toxic goiter of the thyroid gland), the only cause of which is a lack of iodine in the food consumed, as well as water and air. This form often occurs against the background of diffuse lesions and is called diffuse nodular goiter of the thyroid gland.
Follicular adenoma and cancer are tumor diseases, with the difference that adenoma is benign and responds well to treatment. The unambiguous cause for the occurrence of the tumor has not yet been clarified, but a number of factors have been established that create the prerequisites for its development:
- hereditary predisposition;
- low standard of living in areas with poor ecology in the area of hazardous industries and work in them;
- neck injuries;
- hormonal and metabolic disorders;
- iodine deficiency.
Cysts are formed as a result of organic damage to organ tissue. Hemorrhage from a small vessel leads to tissue saturation with blood. A capsule is formed on top of it as a protective mechanism to delimit healthy areas, thereby forming a false cyst. A false cyst is also called an empty capsule formed as a result of degeneration of the colloid node.
A pseudonodule develops as a result of an autoimmune lesion when the body produces antibodies against its own cells. In this case, certain areas are more susceptible to the action of immunoglobulins and cause hypertrophy of individual follicles. The cause of autoimmune diseases in most cases is a genetic defect of the immune system and hereditary predisposition.
Goiter with reduced hormonal activity of the gland
As mentioned above, with a persistent lack of hormones, hypothyroidism develops. It is accompanied by diseases such as myxedema or “mucoedema”, autoimmune thyroiditis or chronic inflammation of the thyroid gland.
Exophthalmos is caused by ophthalmopathy; the release of inflammatory cytokines increases, aggravating the course of the disease. Ophthalmopathy appears before hyperthyroidism, hyperfunction intensifies, and the disease enters the stage of active development. The course of the complication does not depend on the clinical development of hyperthyroidism.
The appearance of pathology does not depend on belonging to a particular gender. The disease affects men and women equally. There are several more reasons for its manifestation in women.
These may be the following violations:
- Changes during the menstrual-ovarian cycle.
- Infertility.
- Spontaneous termination of the pregnancy period.
- Premature birth (miscarriage).
Theoretical approaches
Medical sources offer several theories about the causes of hyperthyroidism:
- The reason is the patient’s condition under conditions of fear or stress. Frequently changing working conditions and increased stress on the body (mental and physical) can lead to stress in the body. The chronic course of undiagnosed and therefore untreated diseases leads the body to stress.
- The second theory is based on the impact of infectious and chronic processes on the functional state of the thyroid gland. Hyperfunction is susceptible to the external influence of the virus.
- Theoretical provisions are based on the appearance of inflammation of the gland itself. The causes of inflammatory processes can be injuries, hypothermia, and radioactive radiation. Complications from other pathologies lead to inflammation.
- The fourth theory. Autoimmune process, disruption of its normal functions.
The disease can be determined by knowing the symptoms and other accompanying signs and pathologies:
- diabetes;
- vitiligo;
- early gray hair;
- anemia.
Types of disease
Doctors divide hyperthyroidism into several groups.
Only such a decoction will trigger REGENERATION of the thyroid gland. The goiter will disappear in 3 days! This remedy has become a sensation in the treatment of the thyroid gland!
Drug-induced.
This type is a consequence of taking medications or chemicals containing elements harmful to the body:
- amiodarone;
- interferon-alpha;
- lithium.
Before starting treatment, patients should be tested for compatibility with drugs; treatment must be carried out under the strict supervision of a physician.
Artificial. This type is a consequence of taking large doses of hormones (thyroiditis). The reception can be either conscious or accidental; the result does not depend on the form of reception.
Iodine.
The type develops when there is an excess intake of iodine in the body, accompanying such pathologies or procedures:
- non-toxic nodular goiter;
- X-ray examination with iodine-containing medications.
True. The appearance manifests itself when the ovarian teratomas contain an increased number of thyroid tissue cells. Accompanying the process of struma of the ovary, iodine accumulates in the pelvic organs.
Symptoms of pathology
The clinical course of the disease may vary. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the patient, development conditions, stage and cause of gland damage. The disease can occur openly, then it has bright and clear symptoms characteristic of a specific form. There may also be an erased (hidden) current. It is more difficult to diagnose and causes difficulties in the treatment system.
Vivid and visible symptoms:
- excitability of the patient;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased sweat production by the body;
- heavy heat transfer;
- fast fatiguability;
- increased appetite;
- weight loss;
- lack of sleep;
- frequent diarrhea;
- unexplained, quickly manifesting weakness.
Side effects
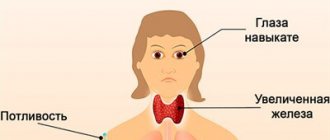
Pathology affects the condition of the eyes.
The symptoms are complex and difficult for patients.
- fixity of look;
- not closing the eyelids;
- lacrimation;
- fear of bright light.
Hyperthyroidism is accompanied by conjunctivae, diplopia, and infiltration of the eye muscles.
The acute form of the disease has a medical name - crisis.
Causes of the crisis:
- improper treatment;
- incompleteness of the treatment system;
- infections during therapy;
- injuries;
- surgical operations.
A crisis exacerbates the symptoms of the disease, increases the severity of their manifestation, and delays a person’s recovery. The specialist will conduct a special diagnosis and make an accurate diagnosis. An indicator of hyperthyroidism is the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the serum. The indicator for the presence of T4 and T3 in the blood is studied. In some cases, it is recommended to capture the thyroid gland or study the content of thyroglobulin in the serum.
Therapeutic effect on the disease
The patient’s lack of desire to begin treating pathological disorders of the body leads to serious consequences. Most often, a thyrotoxic crisis develops. The disease is accompanied by unpleasant phenomena: diarrhea, vomiting, decreased blood pressure, increased temperature to critical. The patient may fall into a coma, which is life-threatening for anyone.
Incorrect treatment or choice of remedies without consulting a specialist also leads to negative phenomena for human health. Heart attack, stroke, and kidney failure develop. The patients' eyes are affected.
Only proper treatment leads to positive results and recovery. The main goal in the system of therapeutic actions is to reduce the amount of hormones in the affected organ and maintain them at the required level.
Treatment is carried out by a specialist – an endocrinologist. The system of medical intervention is built in stages: examination, diagnosis, drug correction. If hormone levels do not return to normal, resort to the following methods.
The system of therapeutic actions most often involves the use of the following methods:
- Conservative.
- Medication.
- Surgical.
Medications
Any method involves the use of drugs. The recommended drugs have a specific purpose and focus, but the endocrinologist decides how to treat the patient with them.
- Thyrostatics. The drugs block the increased formation of thyroxine in the gland. They suppress autoimmune processes. Drugs with this effect: mercazolil, methizol, thiamazole, propylthiouracil. Propylthiouracil is prescribed to patients who have suffered complications from the listed drugs, and to pregnant women. Taking medications from this group is quite long. Treatment lasts approximately 4-6 weeks. Then it does not stop, but the dose is reduced. Therapy, aimed at maintaining the achieved level, lasts about a year. Doctors state that 30% of patients experience a return of the pathology. The best results are obtained by combinatorial treatment, when other drugs, for example, levothyroxine, are combined with these drugs. Taking thyreostatics is accompanied by changes in skin condition: itching, urticaria, dermatitis.
- Beta blockers. Drugs of this type normalize cardiac arrhythmia and reduce the formation of thyroxine.
- Sedatives. The drugs are aimed at calming, normalizing the nervous system, and reducing the patient’s excitability. Often they become accompanying in the treatment system, accelerating the patient’s recovery process.
- Radioactive iodine. The drugs are used as directed. They are available in the form of capsules and liquid tinctures. The method is recognized by experts as an alternative to surgical intervention. Treatment with it leads to the accumulation of iodine in the gland. The method is quite lengthy, requires repetition, and must be carried out under the supervision of specialists.
- Modern drugs. The constant development of the chemical industry allows the creation of new products. One of them is Carbimazole. It takes a long time to take. Doctors from clinics around the world are confident in its effectiveness, which has been proven repeatedly. The medicine blocks the release of hormones into the blood, restraining crises.
Surgical treatment is based on surgical intervention. The surgeon removes the node; in severe forms, the entire thyroid gland is removed. Indications for surgery are large nodes, tumors, and enlargement of the thyroid gland. Symptoms are eliminated.
Symptoms of nodular goiter
As a rule, patients do not experience significant symptoms of nodular goiter. This is due to the fact that the area of overgrown tissue does not exhibit excessive hormonal activity, so the level of hormones in the peripheral blood does not change and the function of the gland does not suffer.
Mechanical and cosmetic symptoms of nodular goiter depend on its degree:
- 0 degree – the node is not palpable;
- 1st degree - upon palpation a formation is detected, but it is not visually visible;
- 2nd degree - a serious deformation in the neck area is visible to the naked eye.
Nodular goiter of the 1st degree rarely gives mechanical complications, since its size is insufficient to deform neighboring organs, however, hemorrhage into the tissue of the node is quite possible, which can cause pain.
Nodular goiter of the 2nd degree is, firstly, a visible cosmetic defect, which is one of the main problems of this pathology, and secondly, it is a real threat of compression of surrounding tissues, which in exceptional cases can lead to death.
Compression of the esophagus and pharynx leads to disruption of the swallowing process and the sensation of a lump in the throat. Subsequently, this can lead to significant exhaustion, since it becomes physically impossible to eat enough food.
Pressure on the trachea causes significant difficulty breathing. First, shortness of breath of a mixed nature develops (both inhalation and exhalation are difficult), and then periodic attacks of suffocation develop, which without specialized help can have negative consequences.
Most often, the cause of pain is compression of the nerve trunks by an overgrown node. In the area of the thyroid gland there are branches of the vagus nerve, which innervates many internal organs and areas of the body, so the localization of pain can be very diverse, including pain in the oral cavity.
In rare cases, nodular lesions lead to an increase or decrease in the hormonal activity of the gland. Symptoms in this case may not be very specific, but appear with grade 0 nodes and be the only sign of the disease.
A decrease in thyroid hormones manifests itself as follows:
- weakness, fatigue, decreased performance and resistance to stress, depression, apathy, loss of appetite;
- decreased body temperature, chills, increased sensitivity to acute respiratory diseases;
- menstrual dysfunction, decreased libido and potency.
Elevated hormone levels manifest themselves exactly the opposite:
- irritability, aggressiveness, insomnia;
- increased body temperature, increased appetite, weight loss;
- tachycardia.
What signs characterize the development of the disease?
Characteristic signs of an enlarged thyroid gland are a forward displacement of the eyeball and an increase in heart rate. Characterized by involuntary trembling of the limbs or the whole body, increased sweating or hyperhidrosis, unintentional weight loss. Detachment from the entire white world: irritable, conflict-ridden, do not want to get along with everyone. Sleep disturbance is typical during the development of the disease. Patients often do not see significant changes in themselves. They tend to think that the world around them is changing and hectic.
Patients may experience the following symptoms:
- Fatigue during physical and mental stress.
- Women have swelling of the face.
- Heart rhythm disturbances act as a serious complication of too high levels of hormones.
- Menstrual irregularities, premature amenorrhea, which affects reproductive function and the general condition as a whole.
Such signs are more common during the period of decline of sexual functions. Goiter with hyperthyroidism can lead to another more dangerous pathology, such as the formation of benign tumors, when nodes form in one of the lobes.
Diagnostics
To diagnose this disease, taking an anamnesis is of great importance. It is necessary to provide the doctor with information about living or long-term stay in an area endemic for iodine deficiency in the air and water. In addition, it is advisable for the patient to be informed about any thyroid diseases, autoimmune and hormonal disorders in relatives.
It is important to indicate as accurately as possible the moment the goiter appears and the intensity of its development (after what time it increased, by how much). Complaints of coughing, choking, changes in voice and difficulty breathing are not insignificant; you must inform your doctor about any discomfort, even if it seems that they do not relate to the underlying disease.
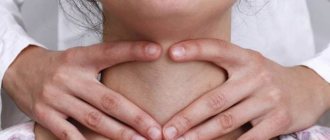
During external examination, grade 0 and 1 nodes are not visible in the normal position of the neck, so it is necessary to examine the area when tilting the head back. Palpation allows you to evaluate the consistency of the gland, as well as palpate single or multiple nodes.
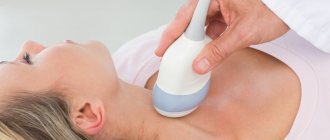
In the initial stage of the disease, in the presence of a multinodular goiter, by palpation it can be determined as a variant of the anatomical structure of the gland, therefore ultrasound is always used to make the correct diagnosis.
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland can detect even the smallest lumps less than 1 cm in diameter. Nodes larger than 1 cm are an absolute indication for a biopsy with sampling of material for histological examination. This procedure is necessary to exclude a malignant neoplasm, as well as for a morphological assessment of the formed node.
The thyroid gland is not always located in the usual place for everyone; sometimes it has a retrosternal localization. In this case, the ultrasound will be uninformative, since the bone interferes with the transmission of waves. The use of radiography, as well as CT and MRI will allow us to visualize the gland even in such a hard-to-reach place.
Computer and magnetic resonance imaging are additionally used for symptoms of mechanical compression of nearby organs and allow visualization of compression of the trachea, esophagus and nerve trunks.
The most modern and sensitive diagnostic method is scintigraphy , which, using intravenous administration of labeled iodine isotopes, allows one to visualize the functional activity of the thyroid gland in general and the node in particular. When the iron captures the isotope, it begins to “glow,” as it were, which indicates its normal functioning. “Cold” areas indicate a focus of hormonally inactive tissue, and “hot” areas indicate excessive production of hormones.
From laboratory tests, it is most advisable to determine the level of T3, T4 and TSH in venous blood. Their change is not a pathognomonic sign of nodular goiter, but confirms the presence of pathology in the thyroid gland, and in some cases makes it possible to differentiate nodular goiter from a number of other endocrine diseases.
Treatment of thyroid nodules
Only a competent endocrinologist can identify nodes in the thyroid gland and prescribe treatment. Neoplasms are detected during the examination, and large lumps can be determined by palpation. Smaller nodes are clearly visible during ultrasound examination. Most thyroid tumors are benign and do not require special treatment.
Symptoms of thyroid nodules
The nodules themselves are not a disease, but only a symptom. For proper treatment, it is important to determine the nature of the compaction and the features of its localization. Unfortunately, not the entire population undergoes regular medical examinations, so people often turn to a doctor for help with an already advanced disease. Small and harmless nodules of the thyroid gland have the ability to grow and degenerate without showing themselves in any way. Clear signs are noticeable when the tumor is malignant and progresses rapidly.
Nodules in the thyroid gland can be suspected based on several signs:
- Discomfort in the neck area.
- Feeling of pain and burning.
- Compression of the larynx and esophagus by too large tumors.
- Difficulty breathing, swallowing, voice disturbances not associated with a cold.
Regular examination by an endocrinologist is necessary for persons who have undergone radiation exposure, work in harmful and dangerous conditions, and have a genetic predisposition to pathologies of the endocrine system. You need to contact a specialist as soon as the first symptoms of a thyroid gland malfunction appear.
How and with what to treat thyroid nodules
The treatment method depends on the nature of the detected nodes, and not on their size and number. Even the level of specific hormones does not always make it possible to determine whether a neoplasm is malignant. To do this, a biopsy is necessary.
Colloidal nodes are considered the most harmless. These are benign neoplasms that are not capable of degeneration and therefore are not dangerous to humans. If the thyroid gland is affected by lumps with a diameter of less than 1 cm, then treatment is not prescribed. It is enough for the patient to undergo a control ultrasound once a year.
Surgical treatment of colloid nodules of the thyroid gland is carried out in the presence of the following indications:
- Difficulty swallowing and breathing.
- Excessive synthesis of hormones in the nodes (toxic adenoma).
- External manifestations of the disease (ugly bulges on the neck).
For nodes of a different nature, the doctor prescribes conservative, minimally invasive or surgical treatment.
Conservative treatment of thyroid nodules
The first condition for effective treatment is the identification and elimination of factors that provoked pathological processes in the body of the gland. There are many reasons why the thyroid gland becomes enlarged, so the doctor carefully interviews each patient.
The goal of conservative treatment is to reduce the load on the thyroid gland. For this purpose they can assign:
- injections of artificial hormones;
- taking iodine-containing medications
Drug therapy can only alleviate the symptoms of the disease and stop the growth of the node, but it is impossible to cure the patient only with conservative methods.
Minimally invasive treatment of thyroid nodules
Minimally invasive treatment has a number of advantages over surgical treatment. Firstly, it is possible to avoid hormonal deficiency during the recovery period. Secondly, hospitalization of the patient is not required. All procedures are performed on an outpatient basis and do not affect a person’s performance. Thirdly, there are a number of concomitant diseases for which surgical intervention is contraindicated. Minimally invasive methods can be used to treat young children and people of retirement age.
- Ethanol sclerotherapy. Ethyl alcohol is injected into the nodes using a special syringe.
- Ultrasound treatment.
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy.
- Radiofrequency thermal destruction. The node is exposed to radio waves of a certain frequency. They cause local heating in the tissues and subsequent destruction of the tumor.
- Laser-induced thermotherapy, or laser treatment of thyroid nodules. The procedure is carried out under ultrasound control, so the impact of the beam is targeted and does not affect surrounding tissues.
In cases where such hardware treatment is ineffective, neoplasms from the gland body are surgically removed.
Surgical treatment of thyroid nodules
Surgery is absolutely indicated if:
- nodes degenerate into malignant tumors;
- Diagnosed with breast cancer;
- the nodes grow very quickly;
- in the body of the gland there are seals more than 3 cm in diameter;
- toxic adenoma develops.
The doctor removes part of the nodule (hemithyroidectomy) or all of the lumps from the body of the gland (thyroidectomy). Lymph nodes in which pathological cells will be found are also removed.
Before the operation, the surgeon consults the patient, explains how to prepare for an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and what restrictions to observe in the postoperative period.
Folk remedies for thyroid nodes
Folk remedies help relieve the symptoms of the disease and serve as a complement to traditional treatment. It is better to use any prescription after consultation with your doctor.
- A tincture of fern roots in 6% vinegar will help get rid of the feeling of a lump in the throat. External rubbing agent, course of treatment 10 days.
- There is evidence that nodules can be cured with urine therapy. But the effectiveness of urine lotions has not been scientifically proven.
- For thyrotoxic adenoma, you can take decoctions of fucus vesicularis, blackcap, trifoliate, motherwort, mint, and skullcap Baikal. These herbs will lower thyroid function, calm the patient and help normalize blood pressure.
- Fresh woodlice juice helps stabilize the psycho-emotional background in patients with thyroid nodules. Take freshly squeezed juice in courses of three weeks. At the end of the course, after a break of 30 days, take a decoction of wood lice and rose hips. Treatment is carried out in spring and autumn.
The thyroid gland is one of the most important human organs. Any deviations in its functioning cannot be ignored. Any disease, even cancerous nodes, can be treated well at an early stage.
Treatment
How to treat nodular goiter depends on its origin.
Treatment of colloid goiter
This type of nodule is not an absolute indication for surgical treatment, therefore the main principles of treatment are dynamic observation and drug therapy with iodine preparations.
Iodine-containing preparations are consumed in a daily dose of 100 to 200 mcg for a maximum course of 6 months, during which the node develops back by 30 percent or more. The undoubted advantage of these drugs is the absence of side effects and the need to calculate an individual dose for each patient.
The indication for surgical treatment is the lack of effect of drug therapy, as well as the volume of the node, which creates discomfort and a pronounced cosmetic defect. Removing a colloidal node is a fairly simple operation, but only if all existing nodes have reached a certain size. Otherwise, removal may not be complete and the disease will soon recur.
If after a long postoperative remission the disease begins to progress again, a second operation is no longer performed. The use of radiation therapy with radioactive iodine isotopes is highly effective, but is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation. The essence of the procedure is the complete destruction of thyroid cells and is used in exceptional cases.
Autoimmune pseudonodes require treatment without surgery. The doctor monitors hormone levels over time and, if necessary, prescribes replacement therapy, since the risk of developing hypothyroidism is high.
Treatment of nodular goiter of the thyroid gland associated with a tumor is exclusively surgical. During the operation, the obtained material is subjected to urgent histological examination. If the tumor is benign, then its complete removal and further observation by an endocrinologist is quite sufficient in order to prevent the development of a relapse. Radiation therapy with radioactive iodine is always added to the treatment of malignant neoplasms. At the request of the doctor, additional use of suppressive therapy with Levothyroxine sodium is possible.
Traditional methods of treatment
Treatment of nodular goiter at home is not a replacement for the main treatment, but its continuation and intensification.
Half of the existing problem can be solved on your own by adjusting your diet. You need to add iodine-rich foods to your diet:
- iodized salt;
- seafood (fish, etc.);
- seaweed;
- spinach;
- fruits, vegetables, herbs;
- dairy products.
You should monitor the amount of calories you consume, trying not to go beyond your age and gender norms, and also adhere to the general principles of proper nutrition.
Treatment of nodular goiter with folk remedies opens up an unlimited number of methods, among which you can always find the right one. The most widespread are various tinctures, decoctions and juices, for example:
- tincture of white cinquefoil root;
- potato juice;
- walnuts with honey;
- horse sorrel tincture;
- infusion of hawthorn flowers.
All these products are quite easy to prepare, they do not require strict concentration and lend themselves well to combination with each other.
Classification of goiter by degree
There are two such classifications. Since 1955, O. V. Nikolaev’s gradation has been used and was practiced before the advent of ultrasound. The WHO classification has been used abroad since 1992.
Nikolaev’s gradation is still used today due to its practicality, detail and correct choice of treatment tactics. It examines 6 degrees of goiter:
- 0 degree – there is no clinic, there are only changes in the tests;
- 1st degree – there are no visual or clinical changes, the node is detected only by palpation;
- 2nd degree thyroid goiter – the entire thyroid gland is palpated and the isthmus is noticeable when swallowing;
- 3rd degree – the anterior surface of the neck is visually changed;
- 4th degree - thick neck and drooping goiter;
- Grade 5 – a goiter of gigantic size, there is a compartment syndrome, which is very rare.
In the WHO systematization, there are 3 stages of thyroid enlargement. Therefore, all degrees after 2 are classified as 2, which makes diagnosis and choice of treatment difficult. There is no clear differentiation.
In this classification there are the following 3 degrees:
- Grade 0 – there are no visual changes, but the gland is palpable. Its lobes do not exceed the size of the distal phalanx of the patient's thumb. Areas of hypertrophy are detected on biopsy.
- 1st degree – the size of the thyroid lobes is larger than the distal phalanges. They are determined only by palpation, not visually.
- 2nd degree goiter - the neck is deformed, and the patient can feel changes in the gland on his own.
Prevention
In most cases, it is impossible to purposefully protect against the disease, so prevention includes general measures to improve health, normalize nutrition and timely treatment of diseases, especially the endocrine system.
People at risk require special attention - these are people living in areas endemic for iodine deficiency, with a family history (relatives with a similar pathology), as well as pregnant and lactating mothers. Such people need a preventive examination by an endocrinologist and an ultrasound of the thyroid gland at least once a year, as well as the use of iodized salt and food rich in iodine.
It should be remembered that a thyroid examination is not included in the mandatory list of preventive medical examinations, so you must consult a doctor yourself.
Symptoms of thyroid goiter
Unfortunately, it is impossible to immediately recognize the presence of this disease externally; only when the size of one to two centimeters is reached, the nodule can be recognized and the symptoms of thyroid goiter in women may begin to show a little ailment. Such small-caliber neoplasms can be accidentally discovered when visiting a doctor or during an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland.
At the first “bell” you need to contact an endocrinologist
If a person wants to independently accurately recognize the thyroid node, then this procedure is easy and simple to carry out due to the fact that the thyroid gland is located on the surface. The endocrine gland is located in the anterior part of the cervical region below the Adam's apple. In a normal condition, palpation does not reveal any compactions on it; these dense areas are nodular formations.
Nodes in the third stage of development are large and therefore easy to detect even without palpation. They are clearly visible under the skin, while the cervical spine becomes asymmetrical and swelling occurs.
Common signs of thyroid nodular dysfunction are associated with the degree of production of thyroid hormones:
- With reduced hormone production, the following occurs:
- Body temperature and blood pressure decrease.
- The heart rate goes down.
- Insomnia and lethargy during the day.
- Weight gain.
- Depressive states.
- Decreased memory and concentration.
- Decreased appetite, problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- With high levels of hormone production:
- Body temperature increases, heart rate reaches a maximum.
- Hot temper, nervous imbalance.
- With a good sense of appetite, weight decreases.
- Hot skin and increased sweating.
- Trembling in the hands for no apparent reason.
- With normal hormone production, the following occurs:
- In the case when the diameter of the node is three or more centimeters, pressure appears in the cervical region.
- Difficult and uncomfortable swallowing.
- Frequent cough and bronchitis.
- Shortness of breath when turning the head.
Forecast
Of the entire series of diseases united by the term “nodular goiter,” thyroid cancer has the most unfavorable prognosis. Although removal of the gland is an effective treatment method, it cannot provide a 100% guarantee that the disease is cured. In addition, removal of the organ leads to lifelong replacement therapy with synthetic thyroid hormones, which to a certain extent reduces the quality of life.
Autoimmune pseudonodes are a lifelong disease that requires constant monitoring and subsequent use of corrective medications, so we cannot say about a favorable prognosis, but there is no acute risk with this variant of the disease.
Follicular adenoma also requires constant monitoring, since there is a fairly high risk of malignancy, but at the same time it does not require treatment other than surgery.
Colloid goiter is the most favorable pathology, since the risk of complications or malignancy is extremely low, and treatment has no side effects. However, iodine deficiency diseases significantly change lifestyle, as they require constant dieting and giving up bad habits.
The more accurately the doctor’s recommendations are followed, the lower the risk of recurrence of the disease.
Treatment measures
Symptoms and treatment of grade 2 thyroid goiter are always interrelated, i.e. treatment tactics depend on the original cause, degree of goiter, age, etc.
For grade 2 goiter, antihypertensive drugs and sedatives are prescribed. In order to normalize the production of thyroid hormones, thyreostatics are used. There are a lot of them - “Mitezol”, “Tyrozol”, “Carbimazol”, “Tiamazol”, “Propicil”, etc. “Mercazolil” is used more often than others, because it gives results for any degree of hyperthyroidism. The dosage is individual. The course of treatment ranges from 3 months to six months.