admin Home page » Thyroid
Poor environmental conditions, iodine deficiency, and disruption of certain brain structures lead to an enlargement of the thyroid gland. This pathology has a negative impact on the functioning of the entire body and in some cases can be a symptom of dangerous diseases.
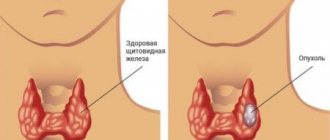
The increase manifests itself in different ways. Nodules may appear and their size may change. In some pathologies, the lobes, isthmus, and total volume increase.
Thyroid
The organ located in the front of the neck, on the sides of the trachea, is the thyroid gland. Its structure consists of two lobes and an isthmus. The main tissue that forms the tissue of the gland is connective.
It is pierced by vessels through which blood and lymph flow. Small bubbles are found in the thickness of the tissue. These are follicles. In their cavity on the inside there are thyrocytes, the functions of which include the production of thyroid hormones.
The thyroid cartilage protects the gland from external influences.
The functions of the thyroid gland are closely related to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. The first stimulates the synthesis of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the pituitary gland. This substance acts on the thyroid gland, causing it to increase the synthesis of thyroxine, triiodothyronine and tetraiodothyronine.
Causes of goiter
Among the reasons for an enlarged thyroid gland are the following:
- Constant stress. Unfortunately, they are widespread. Therefore, to treat the symptoms of an enlarged thyroid gland, many therapists recommend psychological relaxation sessions, yoga and meditation. These methods of relieving psychological stress are safe and can be recommended to almost all patients;
- Ecological poisoning. Toxins, which are abundant in the environment, destroy the system of endocrine glands. This also affects the functionality of the thyroid gland;
- Deficiency of food products and microelements. Common deficiencies include iodine deficiency in food and water. The culprit of the disease can also be called low content of selenium and fluorine in food;
- The appearance of thyroid synthesis inhibitors in the blood. These substances include sulfonamide drugs, para-aminosalicylic acid, resorcinol. Many doctors claim that substances that interfere with the synthesis of thyroid hormones are contained in turnips and soy;
- Damage to the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. These endocrine glands produce substances that significantly affect the functioning of the thyroid gland. This is how the pituitary gland secretes thyroid-stimulating hormone, which controls the subsequent functioning of the thyroid gland. And the increased function of the hypothalamus has the opposite effect on the thyroid gland;
- The presence of infection in the body. Some bacterial pathologies negatively affect the functioning of the thyroid gland;
- Hypovitaminosis. You need to know that vitamin deficiency impairs thyroid function;
- Insufficient physical activity;
- No insolation. If the body functions with a lack of sun, then the functions of the thyroid gland are significantly impaired.
With the combined influence of unfavorable factors, a person may notice many symptoms of an enlarged thyroid gland. However, only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
Reasons for the increase
Certain reasons lead to changes in the size of the thyroid gland. The most common include:
- iodine deficiency;
- vitamin D deficiency;
- hormonal disorders characterized by changes in the content of active thyroid hormones in the blood;
- hereditary factors;
- poor environmental conditions;
- neoplasms;
- frequent situations of high psycho-emotional stress;
- pathologies of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
Thyroid enlargement
Symptoms and diagnosis
An enlarged thyroid gland may have the following symptoms (in addition to physical growth):
- a sharp change in body weight - both increase and decrease;
- change in heart rate;
- violation of thermoregulation - sweating increases, chills or heat may be felt;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- increased fatigue, apathy;
- irritability, nervous breakdowns;
- squeezing the neck as if a tightly tied tie.
We also recommend viewing: “Women’s Problems.” How to detect thyroid disease
But here it is important not to confuse causes and consequences. For example, a person holding a leadership position may become very irritable over time, and this will be attributed to working conditions, and an enlarged thyroid gland will be attributed to the consequences of a nervous emotional state. But in fact, everything will be the other way around: the presence of an infection in the body leads to dysfunction of the thyroid gland, and a lack of iodine provokes a nervous condition.
Symptoms and treatment are, of course, related, but the causes are no less important. That is why you should not take the diagnosis into your own hands - it is better to contact a professional immediately when symptoms appear. The only thing you can do at home is to test the level of iodine in your body. To do this, before going to bed, apply an iodine mesh to your leg, arm or stomach with a cotton swab. If in the morning there is not a trace of the iodine network, it means that there is an iodine deficiency in the body. If the mesh does not turn pale or turns only a little pale within a day, there is an excess of iodine in the body.
If the thyroid gland is enlarged, you should consult an endocrinologist. In this case, diagnostics will take place in the following order:
- physical examination, patient interview;
- blood test to determine antibodies and hormone levels;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- scintigraphy (optional - injection of a radioactive isotope and scanning);
- histology (optional - laboratory examination of a tissue sample).
Symptoms
An important symptom of thyroid disease is a change in its size. The isthmus and lobes become visible. The organ becomes hard and loses mobility.
Additionally, the following groups of symptoms are noted:
- Psycho-emotional disorders . The person becomes hot-tempered, irritable, restless. He is tense and anxious.
- Physiological changes. Increased sweating, tachycardia, and edema are detected. Skin dries, hair falls out, sleep is disturbed.
- Weight gain. A person gains weight, even if he maintains his previous eating habits and physical activity.
- Changes in the organs of the neck. Due to compression of the larynx and trachea, an involuntary cough and tickling occurs. Impact on the vocal cords leads to a change in voice. The effect on the esophagus leads to a feeling of coma and discomfort when swallowing.
- Increased blood pressure. Occurs when passing blood vessels are compressed.
- Hormonal changes. Violation of potency, menstrual cycle.
Symptoms of thyroid disease
In the initial stages, inflammation of the thyroid gland can be confused with a mild cold or the consequences of a strained neck muscle.
The peculiarity of this disease is that it does not manifest itself immediately, but gradually. In the initial stages, inflammation of the thyroid gland can be confused with a mild cold or the consequences of a strained neck muscle.
In modern endocrinology, there is the following classification of this disease according to the stages of its progression:
- The organ is not deformed. Internal inflammatory processes occur.
- The thyroid gland is slightly enlarged in size. This is not visible externally, but can be determined by touch.
- The organ is significantly increased in volume. This is easy to detect with the naked eye.
- The goiter is clearly visible. When touching it, a person feels pain. An unpleasant sensation of throat squeezing and hoarseness appears. Difficulty swallowing food.
- There is a constant cough. The organ becomes so huge that its structure can be seen through the skin stretched by it.
The symptoms are as follows:
- an enlarged thyroid gland causes pain when swallowing food and liquids;
- increasing the density of the organ, up to a solid state;
- loss of mobility of the thyroid gland, which stops moving simultaneously with the cartilage when swallowing;
- constant pain in the neck, especially in the front part;
- fatigue, even during light work;
- constant nervous tension, short temper;
- worsening sleep, constant feeling of anxiety;
- uncontrolled weight gain, when extra pounds quickly add up with a normal diet;
- profuse sweating even at rest;
- rapid heartbeat regardless of the type of activity;
- persistent cough caused by deformation of the respiratory tract;
- the appearance of unexplained swelling, dry skin and hair loss.
The constantly enlarging gland compresses the trachea, esophagus and blood vessels. This leads to high blood pressure and severe headaches. Reduced oxygen supply to the brain leads to dizziness and lightheadedness.
Magnification levels
Characteristics of how enlarged the gland are are key to assessing the stage of the disease and subsequently determining treatment tactics.
There are several degrees of the disease:
- Zero . This degree characterizes a healthy gland. It is not enlarged. Inspection and testing are not painful.
- First . Upon palpation, a slight increase is detected, which creates some discomfort when swallowing. This is the first stage of the development of the disease. Starting treatment at this stage prevents the occurrence of goiter.
- Second . The isthmus is visually visible. Upon examination, the doctor also finds lobes and small nodules. The appearance of the latter is associated with the development of goiter and oncology.
- Third . Without any special knowledge or tools, you can see the lobes of the gland. On palpation, the thickness is felt.
- Fourth . A formation called a goiter appears. If you touch it, it hurts. Due to the size of the gland, it puts pressure on surrounding tissues, causing coughing and a sore throat.
- Fifth . The goiter is much larger than normal and hurts greatly when touched.
Why does diffuse nodular goiter develop and how does it manifest?
In endocrinological practice, a pathological condition such as diffuse nodular goiter occurs. This is an increase in the mass and volume of the thyroid gland.
Multiple nodes form in the organ. They can be detected by palpation.
Severe goiter can cause neck deformation, difficulty swallowing and breathing.
Hypertrophy of thyroid tissue
This organ is not considered vital. Despite this, it performs a number of valuable functions:
- regulates the process of bone growth and development;
- participates in metabolic processes;
- normalizes the functioning of the nervous system;
- regulates the state of the immune system;
- ensures proper energy metabolism.
A person with a goiter can live for decades. This endocrine pathology is mixed, since nodules are found against the background of diffuse enlargement of the organ.
In terms of prevalence, it is second only to diabetes mellitus. It combines the signs of diffuse toxic and nodular goiters.
In Russia, about 0.3% of the population suffers from this disease. Mostly adults are affected.
This form of goiter is diagnosed in less than 0.1% of people. In childhood, this pathology is detected very rarely.
There are 3 known degrees of severity of diffuse nodular goiter. At stage 0, the goiter is not detected during palpation. The neck is not changed.
At grade 1, the size of one or both lobes of the organ of the more distal phalanx of the first finger. On visual examination, hypertrophy is not detected.
In grade 2, goiter is detected by palpation and is visible to the naked eye. This is a classification developed by WHO.
Main etiological factors
Euthyroid or hypothyroid multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland develops for several reasons. The following etiological factors are known:
|
|
|
|
Diffuse nodular hyperplasia of the thyroid gland is most often detected in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, are exposed to constant stress and often suffer from infectious pathologies.
Predisposing factors are drinking water with a high content of chlorine and fluorine, exposure to chemicals (cyanides, heavy metal salts, sulfur, benzene), taking toxic medications, menopause and pregnancy.
Mixed diffuse endemic goiter is most often associated with poor nutrition.
Iodine is necessary for good functioning of the thyroid gland.
The consumption rate of this element is 150 - 200 mcg. For pregnant women, this figure is 250 mcg.
When there is a lack of iodine in the body, the gland tissue grows. This is an adaptive reaction aimed at capturing the compound.
Iodine is required for the formation of the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine. It is found in seaweed, iodized salt, seafood and bread.
In the formation of nodular goiter of the thyroid gland, an important role is played by such a factor as an excess of goitrogenic products in the diet.
These include spinach, Jerusalem artichoke, soybeans, carrots, radishes, turnips, cauliflower, peaches, peanuts and beans. They promote the growth of organ tissue.
Hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the gland are in most cases observed with colloid goiter. It is based on the accumulation of a special substance (colloid).
Diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland is often observed in people with congenital pathology (Klinefelter and Down syndrome) and exposed to radiation.
Manifestations during the hypothyroidism phase
The clinical picture is determined by the degree of organ dysfunction and the level of thyroid hormones. With diffuse nodular toxic goiter, 3 conditions are possible:
- euthyroidism;
- hypothyroidism;
- hyperthyroidism.
In the first case, the function of the organ is not impaired. In hypothyroidism it is reduced. Hyperthyroidism is characterized by increased production of thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
Thyrotoxicosis often develops. This is a condition in which organ dysfunction occurs due to excess hormones. In most cases, a euthyroid type of goiter is observed.
No complaints. Rarely, pain, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness and dysphagia are observed. With diffuse endemic goiter with nodes in the hypothyroidism phase, the following symptoms are possible:
- dry skin and mucous membranes;
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- swelling of the face and limbs;
- drop in blood pressure;
- pale skin;
- depression;
- weight gain;
- lethargy;
- memory loss;
- menstrual irregularities;
- constipation;
- brittle nails;
- deterioration of hair condition;
- tingling feeling;
- muscle pain.
In severe cases, signs such as hearing loss, voice changes and slow speech are detected. The person must be treated.
With diffuse endemic goiter with nodes, a decrease in sexual desire is possible. Signs of organ hypofunction are sleep disturbances, bad mood, bradycardia and headache.
Anemia often develops.
Symptoms in the stage of hyperthyroidism
It is necessary to know not only what toxic thyroid goiter with nodes is, but also how it manifests itself in the stage of hyperthyroidism.
The symptoms are the opposite of those with low hormone levels. The following changes are possible:
- bowel dysfunction such as diarrhea;
- increase in body temperature against the background of an increase in basal metabolism;
- extrasystole;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- cardiopalmus;
- weight loss;
- irritability;
- sweating;
- tremor of the limbs;
- exophthalmos;
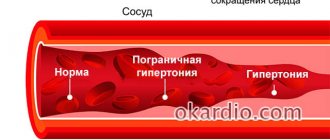
- hypertension.
Against the background of deficiency and excess of thyroxine with triiodothyronine, the functioning of the central nervous system is disrupted.
With hyperthyroidism in a child and an adult, symptoms such as emotional lability, rapid speech, anxiety, fear and sleep disturbances are possible.
Almost every 2 patients have impaired vision function.
This is manifested by an increase in the size of the palpebral fissure, bulging eyes, limited mobility of the eyeball, diplopia and rare blinking.
Against the background of hyperthyroidism, thyrotoxicosis is possible. When it occurs, the body is poisoned with hormones. This condition affects muscles and bones. This causes osteoporosis and myopathy.
Signs of diffuse toxic goiter
Many people have signs of diffuse toxic goiter (Graves' disease). With this disease, a thyretoxic crisis may develop. The nature of the manifestations depends on the level of hormones in the blood. The following organs and systems are affected:
- heart;
- vessels;
- nervous system;
- digestive organs;
- eyes.
The most common symptoms of diffuse toxic goiter are:
| feeling of heartbeat; | tachycardia; | swelling; | dyspnea; |
| cough; | increased appetite; | weight loss by 10 - 20 kg; | sweating; |
| weakness; | increased resistance to cold; | feeling of heat; | low-grade body temperature; |
| exophthalmos; | lacrimation; | feeling of sand in the eyes; | facial change; |
| decreased visual acuity; | pain in the right hypochondrium and abdomen; | skin hyperpigmentation; | pressure surges; |
| pain in bones and muscles; | mental instability; | decreased libido and potency. | |
This clinical picture is associated with an increase in all types of metabolism and poisoning of the body. With diffuse toxic goiter, hair changes are observed.
They become dull, fall out and split. Thyrotoxic goiter (Graves disease) is manifested by soft, moist and warm to the touch skin.
The severity of the patient's condition depends on the severity of hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the gland.
Manifestations of colloid goiter
Very often, adults are diagnosed with nodular colloid goiter associated with iodine deficiency. The main reason for its development is poor nutrition.
In the early stages, the goiter is invisible. No complaints. When the mass of the organ increases several times, symptoms appear.
With diffuse colloid goiter, the first complaint of patients is thickening of the neck on the front side.
With multiple nodes, a roller is formed. At the first stage, the nodes cannot be felt. They can be palpated when the diameter of the formations is more than 1 - 2 cm.
The knots are dense and elastic. They contain a colloid. It covers the struma of the organ.
Nodular goiter with diffuse changes in the gland of the 3rd degree is manifested by soreness, difficulty swallowing, cough, feeling of a lump in the throat and hoarseness.
Diseases
A certain set of signs and causes associated with changes in the size of the thyroid gland allows us to identify several syndromes.
Hypothyroidism
Due to iodine deficiency, insufficient production of thyroid hormones occurs. As a result, the thyroid gland works harder and increases in size.
The syndrome appears either due to gland dysfunction or due to disruption of the organs that regulate its functioning: the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
Hyperthyroidism
With this syndrome, on the contrary, the synthesis of thyroid hormones increases. It is characterized by an increasing metabolism. The disease is caused by tumors, inflammation of the gland, Graves' disease.
Euthyroidism
There is an increase in the organ, however, the level of hormones is normal. This condition is observed during pregnancy, during puberty, and characterizes PMS.
Thyroiditis
The size of the gland increases rapidly. The main reason is heredity. Increases sensitivity to low temperatures. Men turn gray early and have difficulty having children.
Causes
The proliferation of glandular tissue and an increase in the size of the gland is noted in connection with the influence of certain factors, both on the thyroid gland itself and on the body as a whole.
Hyperplasia of the gland tissue is most often observed with a lack of iodine in food or impaired absorption, and is compensatory
Other reasons for an enlarged thyroid gland:
- immunity disorders that provoke autoimmune thyroiditis;
- hormonal dysfunctions;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland with hypofunction (hypothyroidism) or excess production of hormones (thyrotoxicosis) and inflammation of the glandular tissue;
- unhealthy diet (lack of proteins and various microelements, abuse of products with dyes and preservatives);
- bad habits;
- poor environmental situation in the area of permanent residence;
- occupational hazards (inhalation of varnishes, paints, chemicals);
- exposure to radiation;
- constant use of certain medications;
- frequent stress, overwork;
- tumors of the gland itself or other organs of the endocrine system.
Factors provoking thyroid hyperplasia in children
Today, endocrine and metabolic disorders are increasingly common in children and adolescents.
In this regard, planned annual examinations of children of certain age groups by a pediatric endocrinologist have been introduced.
Mandatory additional examinations are also carried out:
- Ultrasound at 7 and 14 years old;
- determination of hormones at 14 years old.
In children, a condition when the thyroid gland is enlarged - the causes and symptoms of its hypo- or hyperfunction can be suspected during a period of active growth, hormonal changes in the body, in case of disturbances in appetite or absorption of beneficial nutrients, especially proteins and iodine, in cases of immunity disorders.
Also of particular importance is a family predisposition to an enlarged thyroid gland, frequent stress and overwork
Against the background of unstable thyroid function, severe weakness, increased nervousness and insomnia, headaches, areas of hair loss, weight loss or gain, swelling, discomfort in the neck, periodic hoarseness or shortness of breath without signs of a cold may occur.
In this situation, you should not postpone visiting a specialist - the price may be too high in the form of progression of the disease and hormonal dysfunctions with the formation of persistent symptoms of the disease and metabolic disorders.
Enlarged thyroid gland in women - causes and consequences
When determining an increase in the size of the thyroid gland in the early stages of the disease, they are treated with medications (taking iodine preparations, normalizing hormonal levels, treating concomitant pathologies). They have no consequences for the body and in most cases are completely cured.
Enlarged thyroid gland, causes and consequences are of particular importance for the female body and are diagnosed much more often than in male patients.
This is due to the high hormonal load on the body from the onset of puberty (the first menstruation and its formation), pregnancy, childbirth, menopause. Any hormonal imbalance causes multiple disruptions in hormone production and changes in the functioning of the endocrine system.
Malfunctions of the thyroid gland can be triggered by inflammation of the genital area, stress, overwork and occupational hazards
In the initial stages of thyroid hyperplasia, it is almost impossible to notice an increase in its size on your own, but it is necessary to pay attention to the appearance of certain signs:
- discomfort when swallowing saliva or food;
- hoarseness or occasional hoarseness of voice;
- irritating cough without signs of a viral infection or cold;
- weakness;
- dry skin, swelling;
- nervous excitability;
- insomnia;
- hair loss;
- increased sweating;
- weight gain with the same diet.
With timely diagnosis of pathological enlargement of the thyroid gland and determination of its causes, the health consequences are minimal.
In this case, the doctor’s instructions must be followed before conducting the examination, especially laboratory research methods (hormone analysis), ultrasound, tissue biopsy, as well as nutritional recommendations and treatment of the disease that provoked the increase in the size of the gland.
Article read: 234
Diagnostics
In order to accurately determine the causes and nature of the enlargement of the thyroid gland, a number of studies are carried out:
- Blood analysis . Allows you to detect the content of hormones T3, T4, TSH, cholesterol, bilirubin, creatinine and other indicators.
- Radiography . Its main difference is that before the procedure the patient takes a certain dose of iodine preparation. In some cases it is injected into the blood. It acts as a contrast agent and allows you to detect changes in the gland.
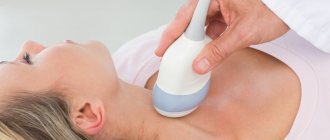
- Ultrasonography. When examined, organic changes can be seen.
- Biopsy . Using a thin needle, a tissue sample is taken from a separate node.
- CT scan . Provides layered snapshots so you can see all the changes.
Enlarged thyroid gland: what to do
If the thyroid gland is enlarged, then the first thing to do is to be examined by an endocrinologist. Without it, any treatment (even folk remedies) is extremely dangerous; it will not only not stop growth, but will also cause rapid progression of the disease.
Diagnostics
Without undergoing an ultrasound and a blood test for hormones (thyroxine, triiodothyronine and thyroid-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland), even the most experienced doctor will never correctly diagnose thyroid diseases. This is explained by the fact that all complaints can be caused by many other diseases, and their absence does not mean that the functioning of the organ is normal. In addition to these most important methods, the following are prescribed:
- determination of antibodies to hormones and cells;
- biopsy (cellular analysis) from a large node;
- iodine level in urine;
- radionuclide scanning (scintigraphy);
- tomography - MRI or.
MRI of the thyroid gland
To determine how much the large thyroid gland is compressing neighboring organs, a chest x-ray is recommended. In this case, the esophagus is filled with barium for contrast. Typically, such patients undergo an examination of the larynx, vocal cords, and bronchi (bronchoscopy).
Treatment
Therapy for an enlarged thyroid gland will depend on the disease, the degree of growth of the organ and deviations in hormonal status.
The following options may be recommended:
- diet and iodine tablets of 100-200 mcg with a slight increase (usually 1 degree) and normal hormone levels, prescribed on an ongoing basis in endemic areas;
- Levothyroxine at a dose of 2-4 mcg per 1 kg of body weight for 6 months with grade 2, elevated TSH levels and normal thyroxine levels (subclinical hypothyroidism) or reduced (overt hypothyroidism);
- a combination of levothyroxine and iodine 100 mcg long-term for grade 2-3, hypothyroidism against the background of endemic goiter under the control of blood tests;
- thyreostatics, most often Thiamazole 5-60 mg per day until hormone levels normalize in diffuse toxic goiter.
Levothyroxine
Thiamazole
How to stop growth using folk remedies
It is not possible to stop the growth of the thyroid gland using folk remedies alone, so herbs can be used in combination with iodine. This is only permissible for patients who do not require hormonal or thyrostatic therapy. The following plants are used:
- cherry leaves,
- Potentilla erecta,
- chokeberry,
- dyeing gorse.
They are taken in equal parts and brewed at the rate of 1 tablespoon per 300 ml of boiling water. Keep in a water bath for 15 minutes, filter. Take a third of a glass 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 1 month.
For diseases of the thyroid gland, herbs should be prescribed by a doctor. It is important to take into account that they contain biological stimulants, so they can themselves provoke the growth of a node, and in advanced cases, its degeneration into a tumor.
Nutrition
Choosing the right diet depends on the function of the thyroid gland. With increased production of hormones (thyrotoxicosis), it is necessary:
- daily intake of calcium, it inhibits the activity of thyroxine - cottage cheese, cheese, fermented milk drinks, soy milk, tofu;
- include in the menu foods that slow down the absorption of iodine - cabbage, radishes, beans, beans, lentils;
- limit cardiac stimulants that increase the load on the heart - coffee, cocoa, spicy, salty foods, infusions, alcohol, energy drinks.
For hypothyroidism and iodine deficiency, the diet should include:
- seafood, seaweed, fish, nori seaweed;
- fresh vegetables, berries, fruits;
- feijoa, apples with seeds;
- iodized salt (add only to ready-made dishes).
It is important to reduce the consumption of soy, legumes, cabbage, radishes, radishes.
Physiotherapy
If the thyroid gland is enlarged, physiotherapeutic treatment is prescribed with great caution. Until a complete examination, it is necessary to abandon electrical and thermal procedures, exclude massage of the cervical-collar area, and prolonged exposure to the sun. After diagnosis, water methods (pine, salt, sea baths, showers), magnetic therapy, and laser therapy are most often allowed.
Surgery
Indications for surgery for enlarged thyroid gland are:
- pressure of the goiter on neighboring organs;
- ineffectiveness of drug treatment;
- nodes, tumors.
The following operation options are possible:
- cutting off a share;
- almost complete excision of the gland, leaving small areas near the recurrent nerve and parathyroid glands;
- complete removal.
An alternative to surgery may be the use of radioactive iodine.
Radioactive iodine
In case of iodine deficiency, surgical intervention must be performed only in very advanced cases, and in case of diffuse toxic goiter, it may be recommended in case of intolerance to drugs or contraindications to them.
Treatment
Therapy is prescribed only on the basis of a carefully conducted diagnosis and determination of the diagnosis.
Drug treatment involves taking drugs that suppress the functioning of the gland. This is Thiamazoz, Propycil. In order to reduce the synthesis and release of T3 and T4 in the blood, iodine-containing medications are prescribed.
Surgery is indicated in the presence of tumor formations, substernal nodes, cysts and nodes measuring more than three centimeters.
Therapy is carried out using radioactive iodine. Its disadvantages are the impossibility of choosing the right dosage and making a prediction about how the disease will develop in the future.
Causes
Various factors influence the formation of goiter. An enlarged thyroid gland is often observed with iodine deficiency. Its limited amount in the body is explained by its complete absence in the climatic zone of human habitation. In addition, poor ecology has a negative impact on the functioning of the thyroid gland. Thus, substances of toxic origin found in the environment sooner or later accumulate in the human body, suppressing the functioning of the thyroid gland, slowing down the degree of its activity.
Endemic goiter is formed with low consumption of foods that contain iodine (fish, milk, fruits). When diagnosing Graves' disease, the endocrine gland is often under the influence of specific antibodies that are produced by the body and are part of the immune protection against its own tissues. With adenoma and oncology of the organ, there is a disruption in the process of cell division and cell differentiation. The cause of illnesses may lie in background radiation, in the constant presence of dangerous toxic substances, or be genetic.
Among women
The beautiful half of humanity has a predisposition to this disease. Goiter most often develops in middle-aged women. This is due to the following reasons:
- hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause;
- bad ecology;
- constant stress, psycho-emotional stress;
- lack of physical activity;
- diseases of the genital area;
- general hypovitaminosis.
In men
Anomalies of the endocrine organ occur in the stronger half of humanity less often than in women, in approximately 15% of cases. The main reasons for an enlarged thyroid gland in men:
- the presence of inhibitors of thyroid hormone synthesis in the blood;
- poor nutrition;
- high background radiation;
- bad habits;
- chronic diseases;
- iodine deficiency;
- difficult working conditions.
The child has
According to medical research, the incidence of goiter in childhood has increased by 6% over the past 10 years. High rates are mainly associated with unfavorable environmental conditions and poor nutrition. In the vast majority of children, diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland develops. Reasons influencing the occurrence of childhood pathology:
- puberty;
- hereditary predisposition;
- weakened immune system;
- the presence of bacterial infections in the body;
- pathologies of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
Share the article on social media. networks:
Prevention
The main way to prevent changes in the size of the thyroid gland is considered to be proper nutrition. The daily menu should include foods with iodine. These are the germs of grains, fish.
To improve the absorption of this element by the body, it is recommended to eat radishes and turnips.
Normal sleep, quality rest, and physical activity are important. At the first stage, it is impossible to detect changes in the thyroid gland on your own, so doctors advise regularly visiting an endocrinologist and doing an ultrasound.
How to identify the disease
The patient undergoes an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland to identify the dynamics of the growth of the endocrine organ.
Diagnosis of a disease such as diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland is carried out by an endocrinologist based on an analysis of the following clinical indicators:
- increased levels of hormones T3 and T4 in a general blood test;
- an increase in the degree of absorption of radioactive iodine by the thyroid gland;
- TSH levels in the blood serum are significantly underestimated;
- The patient undergoes an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland to identify the dynamics of the growth of the endocrine organ.
Complications
An enlarged thyroid gland should never be ignored. Some of the complications are life-threatening.
Hypothyroidism under the influence of infections, cold, and certain medications leads to the development of hypothyroid coma.
A dangerous consequence of malignant tumors is hemorrhage into neighboring organs and disruption of their functioning. Respiratory, cardiovascular diseases, and pathologies associated with digestion occur.
Changes in the size of the thyroid gland are provoked by various reasons: intoxication, disturbances in the functioning of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, poor environmental conditions, iodine deficiency.
Detection of pathology in the early stages of the disease helps prevent the occurrence of dangerous diseases. Treatment uses medications and surgical methods.
Preventive measures
To avoid an enlarged thyroid gland, you must adhere to the following recommendations from endocrinologists:
- Find out what level of iodine is entering the body at the place of residence - it also depends on how clean the ecology of the region is and what the composition of the water is. You can obtain such information either from the department of the sanitary-epidemiological service or from an endocrinologist.
- Replace regular table salt with sea or iodized salt. Please note: this salt has a very peculiar taste, which discourages many people from consuming it. You can combine both types of salt - for example, use iodized salt only in spicy dishes and broths.
- There should be seafood on the table at least 2 times a week. Let it be a simple kelp salad (seaweed) or fried squid in batter - the necessary dose of iodine will be delivered to the body.
- You can prevent enlargement of the thyroid gland by regularly eating nuts. You can use any type of nuts, but it is better to focus on walnuts.
- At least once a year you need to visit an endocrinologist for a preventive examination - the doctor will be able to detect an enlarged thyroid gland at an early stage and, by prescribing iodine-containing drugs and diet, adjust the functionality of the organ.
An enlarged thyroid gland is a rather unpleasant pathology that can lead to serious disruptions in health and the usual rhythm of life. But at the same time, endocrinologists assure that by adhering to a certain diet and constantly taking hormonal or iodine-containing medications, you can live a long life even with this disease.
It is important to detect the problem at the very beginning of its development, so you can periodically diagnose it yourself. You just need to feel your own thyroid gland and make sure that it is mobile, painless, the lobes are well palpated and soft/elastic. If any of these “points” confuse you, or if you feel, in addition to discomfort, there are pronounced painful sensations, then a visit to the doctor should not be put off for long. You can get more information about inflammation of the thyroid gland by watching this video:
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category.
34, total, today
( 64 votes, average: 4.61 out of 5)
High blood sugar in a child: is it dangerous?
Gestational diabetes during pregnancy: symptoms, causes and treatment
Related Posts
Consequences
People often have a natural question about how dangerous an enlarged thyroid gland is. Any disease, if left untreated, can lead to negative consequences. This also applies to the thyroid gland. For example:
- For the most part, changes in the size of the thyroid gland are the result of hormonal imbalances. And this is fraught with the development of many other diseases, impaired attention, memory, fatigue, and an increase in the amount of cholesterol in the body.
- If you do not pay attention to the development of the disease in time, it will only progress. And as a result it will reach an irreversible level. As a result, the person will have to take hormonal medications for the rest of his life.
- If the disease is caused by a high content of hormones, then this also poses a great danger to humans. The fact is that with this development of the disease, first of all, the human heart and blood vessels suffer.
- In addition, an enlarged gland has a negative effect on neighboring organs. The person may lose their voice and may have problems with their voice and eating.
Why does my throat feel sore when I have thyroid disease?
Often, with pathologies and ailments of the thyroid gland, patients complain of discomfort in the throat - soreness, lump, pain, etc.
Of course, such symptoms may be completely unrelated to the thyroid gland, and the discomfort may go away without treatment and not affect a person’s health in any way. However, unpleasant symptoms can also be signs of various pathological processes, so if they continue for a long time or are repeated quite often, it is recommended to consult an endocrinologist.
The essence of the problem
Why can a sore throat occur with thyroid diseases? The fact is that pathological processes in the thyroid gland provoke an increase in the size of the gland, as a result of which neighboring organs are compressed (in particular the trachea) and unpleasant sensations arise - this can be soreness, pain, a lump in the throat, etc.
Most often, an enlargement of the thyroid gland occurs with cystic formations in the organ, with thyrotoxicosis and hypothyroidism. The causes of these ailments are different - lack of iodine in the body, poor environmental conditions in the place of residence, genetic factor, chronic infections, and so on.
Gland work
The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland that is located in the front of the neck, covering part of the larynx and the upper part of the trachea. The organ consists of two lobes and an isthmus. Normally, in a healthy adult, the thyroid gland weighs about 30 grams.
The function of the gland is to produce hormones that are very important for the human body, which regulate metabolic processes in the body, influence the functioning of the cardiovascular system, nervous system, and also directly affect mental development.
Gland diseases:
- Hyperthyroidism. This is excessive activity of the thyroid gland, which provokes the synthesis of excess amounts of hormones, and, consequently, too fast a metabolic process in the body, which naturally affects the functionality of other organs and systems. With hyperthyroidism, a person complains of insomnia, severe nervous excitability, sudden weight loss in the absence of changes in diet, but in this case there are no painful sensations in the throat area.
- Hypothyroidism. This disease is the opposite of the previous one. In this case, the function of the gland is suppressed and hormone deficiency develops. At the same time, metabolism slows down, the body consumes less oxygen, and accordingly, less energy is released than normal. Patients complain of dry skin, excessive drowsiness, and chills. As for unpleasant symptoms in the pharynx area, for example, a sore throat, with this disease of the thyroid gland there are no such symptoms. It can only occur if side effects develop - disturbances in the functioning of other organs.
- Endemic goiter is a disease that directly depends on the lack of iodine in the body. At the same time, the gland increases in size, and a goiter (tumor) grows. Symptoms of this disease are rapid heartbeat, thinness, sweating, and bulging eyes.
- Thyroiditis is an inflammatory process in the thyroid gland, which can have various causes - from infectious to hereditary. In this case, there may be pain, a lump in the throat - and the thyroid gland increases in size, in addition, the lymph nodes become enlarged, and the temperature may rise.
Thyroid norms in a healthy person
The thyroid gland has two lobes and an isthmus; normally, the right lobe may be slightly larger than the left; the structure of the gland is granular, since it contains a large number of follicles. In rare cases, the thyroid gland may have three lobes, then it does not have an isthmus. The organ is permeated with vessels, the blood circulation in which depends on how the gland works.
A person's gender and age affect the size of the gland. In newborn children it should not exceed 1 ml, in adult women it should not exceed 18 ml, and in adult men it should not exceed 25 ml.
Why does the thyroid gland enlarge?
An enlarged thyroid gland is not a bad thing, a third of the population of our planet suffers from this pathology, about 5% of the population has such an enlarged organ that it significantly worsens their quality of life. In women, an enlarged thyroid gland is more common, since in the fair sex the hormonal levels can undergo changes several times a month. And in adolescents, pregnant women and women in the premenopausal period, hormone imbalance can generally occur several times a day.
When the thyroid gland is enlarged, unpleasant symptoms often occur - squeezing of the throat, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and sometimes breathing. Due to a thyroid gland that does not function properly, obesity or pathological thinness may develop, hair may fall out, the skin may dry out, nervous disorders may develop, and so on.
For what reason the thyroid gland may increase in size, doctors have not yet been able to determine exactly; however, it is known that iodine deficiency in the body and hormonal fluctuations play a large role in this pathological process. In addition, the following factors can provoke an enlargement of the gland:
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the food consumed;
- work in hazardous production;
- drinking strong black coffee;
- smoking;
- drinking alcohol;
- chronic inflammatory processes;
- abnormalities in the gland itself;
- development of tumors in the brain;
- improper treatment with medications that lead to suppression of thyroid hormones;
- stress and various disorders in the psycho-emotional state.
Of course, this is not a complete list of provoking factors that can lead to the thyroid gland enlarging.
It is believed that some gland diseases can be inherited genetically, this is not entirely true, since thyroid diseases cannot be inherited; only a feature in the structure of the gland can be inherited, which can cause an enlargement of the gland.
Diagnosis of the thyroid gland
If you have a pressing sensation in the thyroid gland, cough, tickling or other discomfort, you should consult an endocrinologist. The doctor will palpate and refer the patient for tests. Required:
- blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound of the gland;
- blood test for thyroid hormones;
- if necessary, an MRI, CT scan, or biopsy may be required - these studies can provide more detailed information that is necessary if the results of the above studies are low.
Treatment of thyroid diseases
Thyroid diseases can be treated only after a specialist has identified the cause of the disease. If it lies in a lack of iodine, then the patient is prescribed medications containing this element. If the cause of an enlarged gland is a hormone imbalance, then hormonal medications are prescribed to help establish proper synthesis. Most often, such therapy can be carried out for quite a long time or even for life.
If the case is severe and there is a tumor in the gland, then a decision is made on surgical treatment. As you can see, treatment options for the thyroid gland are different, and only a doctor should decide which treatment regimen to choose, based on test results.
As for alternative treatment methods, they can be used by the patient only after a thorough diagnosis and with the permission of the doctor. Milk and figs relieve a sore throat. Several figs are boiled in milk for a minute, and then left to infuse for about 30 minutes. This remedy is then drunk warm before bed.
If a lack of iodine in the body has been diagnosed, it is recommended to apply a pharmaceutical alcohol solution of iodine to the heel area, or apply a salt compress to the thyroid area. Salt for the compress should be iodized. Such a compress will not only replenish iodine deficiency in the body, but will also relieve unpleasant symptoms. If you don’t have time for a compress, or you generally don’t tolerate any compresses well, then you can simply gargle with a saline solution. The effect, of course, will be somewhat weaker than from a compress, but still the unpleasant symptoms will decrease.
A way to treat unpleasant symptoms in the throat with hypothyroidism is walnuts, and it is not the kernels themselves that are used, but the partitions. 100 grams of nut partitions should be poured with half a liter of vodka, left for a month, and then drunk a teaspoon before meals.
White cinquefoil root is often used to treat thyrotoxicosis. For 50 grams of root you will need half a liter of vodka. The product is infused for a month, then drunk 30 drops, diluted with water.
Uncomfortable sensations in the thyroid gland in themselves are not dangerous, but any pathological process in the gland can lead to serious illnesses. Therefore, it is very important to undergo a thorough examination if such symptoms occur. We must also not forget that an enlarged thyroid gland may be associated with a malignant process, which must be diagnosed as early as possible.
Consequences of an enlarged thyroid gland
The consequences of an increase in the size of the gland can be in the form of digestive disorders, a sharp change in body weight towards decrease or increase, sleep disturbances, increased or decreased body temperature.
These consequences are associated with the development of a disease accompanied by either excessive or decreased synthesis of iodine-containing hormones, accelerated or slow metabolism.
Serious complications in the development of an enlarged thyroid gland can be:
Hypothyroid coma , which develops with insufficient synthesis of hormones. It is characterized by a decrease in body temperature below 35 degrees, which leads to oxygen starvation of the brain. If the patient does not receive timely medical care, coma can result in death.
Thyrotoxic crisis manifests itself in a sharp increase in body temperature to 40-41 degrees, a drop in blood pressure, and impaired cardiac activity. The patient loses consciousness, which can also lead to death.
Prevention of goiter formation
In order to prevent enlargement of the thyroid gland, it is recommended to carry out comprehensive prevention:
- adhere to proper nutrition, lead a healthy and active lifestyle;
- strengthen the immune system, prevent long-term infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- undergo regular medical examinations;
- get enough iodine, zinc, calcium, other minerals and vitamins;
- spend a holiday by the sea, sanatorium treatment.